Abstract
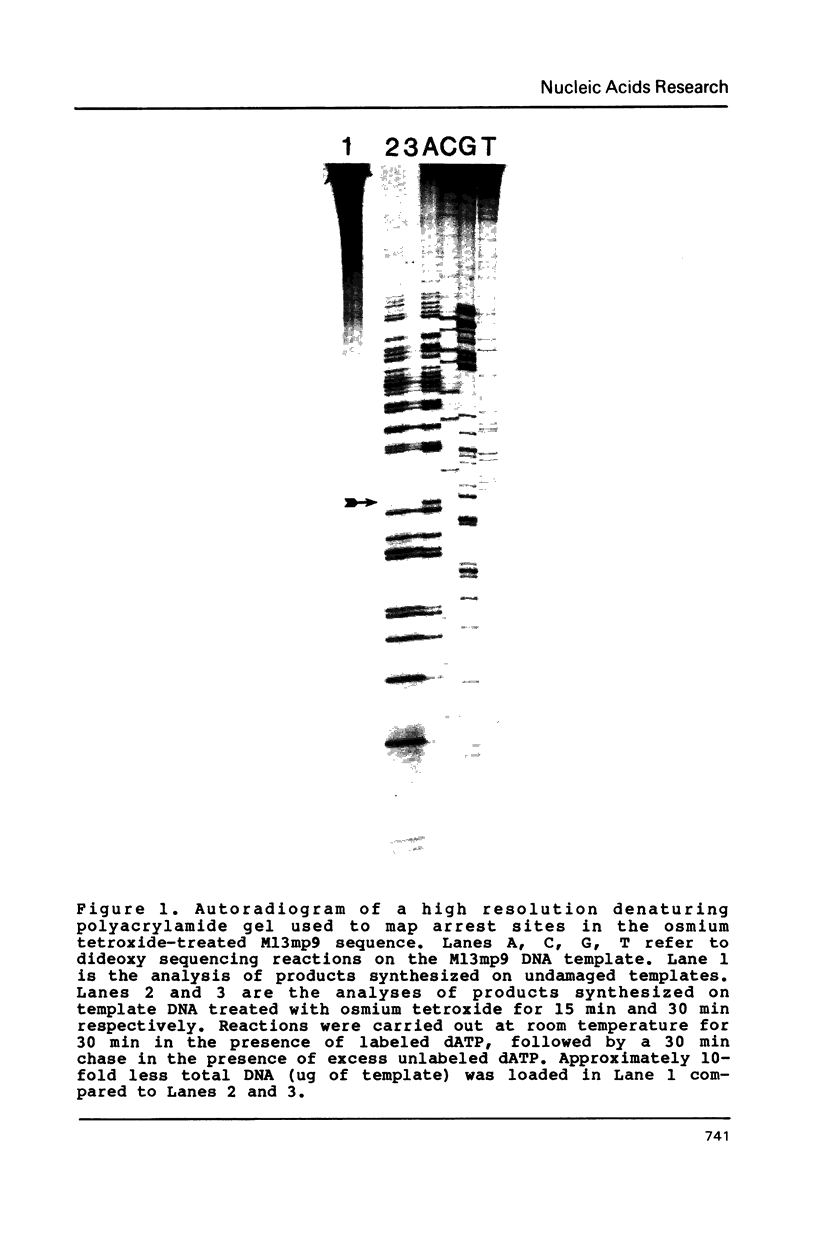
Single-strand circular DNA from bacteriophage M13mp9 was chemically modified with osmium tetroxide to introduce specifically cis-thymine glycol lesions, a major type of DNA damage produced by ionizing radiation. An oligonucleotide primer was extended on damaged and undamaged templates using either the large fragment of E. coli pol I or T4 DNA polymerase. The reaction products were analysed by electrophoresis alongside a DNA sequence ladder. Synthesis on the damaged templates terminated at positions opposite thymine bases in the template. These results indicate that cis-thymine glycol lesions in single-strand DNA constitute blocks to synthesis by DNA polymerases in vitro. Surprisingly, replication halts after the correct nucleotide, dAMP, is inserted opposite the lesion. These results imply that the primary effect of the thymine glycol lesion is suppression of DNA synthesis and that the lesion is not a potent mutagen.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beer M., Stern S., Carmalt D., Mohlhenrich K. H. Determination of base sequence in nucleic acids with the electron microscope. V. The thymine-specific reactions of osmium tetroxide with deoxyribonucleic acid and its components. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2283–2288. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breimer L. H., Lindahl T. DNA glycosylase activities for thymine residues damaged by ring saturation, fragmentation, or ring contraction are functions of endonuclease III in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5543–5548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Weiss B. Endonuclease III (nth) mutants of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):474–478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan P. V., Cerutti P. A. Excision of damaged thymine residues from gamma-irradiated poly(dA-dT) by crude extracts of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3532–3536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan P. V., Cerutti P. A. Formation and repair of gamma-ray induced thymine damage in Micrococcus radiodurans. J Mol Biol. 1972 Apr 28;66(1):65–81. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. C., Hearst J. E., Alberts B. M. Two types of replication proteins increase the rate at which T4 DNA polymerase traverses the helical regions in a single-stranded DNA template. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4087–4094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Hayatsu H. The permanganate oxidation of thymine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 16;213(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leadon S. A., Hanawalt P. C. Monoclonal antibody to DNA containing thymine glycol. Mutat Res. 1983 Aug;112(4):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(83)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:61–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern M. R., Hariharan P. V., Cerutti P. A. Selective excision of gamma ray damaged thymine from the DNA of cultured mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 2;395(1):48–55. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90232-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. D., Bose K. K., Rabkin S. D., Strauss B. S. Sites of termination of in vitro DNA synthesis on ultraviolet- and N-acetylaminofluorene-treated phi X174 templates by prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):110–114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. D., Rabkin S. D., Osborn A. L., King C. M., Strauss B. S. Effect of acetylated and deacetylated 2-aminofluorene adducts on in vitro DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7166–7170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P., Strauss B. S. Sites of inhibition of in vitro DNA synthesis in carcinogen- and UV-treated phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):664–666. doi: 10.1038/278664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollis D. L., Brick P., Hamlin R., Xuong N. G., Steitz T. A. Structure of large fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I complexed with dTMP. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):762–766. doi: 10.1038/313762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J. G., Hearst J. E. Termination sites of the in vitro nick-translation reaction on DNA that had photoreacted with psoralen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5540–5544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto A. L., Lippard S. J. Sequence-dependent termination of in vitro DNA synthesis by cis- and trans-diamminedichloroplatinum (II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4616–4619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagher D., Strauss B. Insertion of nucleotides opposite apurinic/apyrimidinic sites in deoxyribonucleic acid during in vitro synthesis: uniqueness of adenine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4518–4526. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teoule R., Cadet J. Radiation-induced degradation of the base component in DNA and related substances--final products. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1978;27:171–203. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81196-8_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]