Abstract
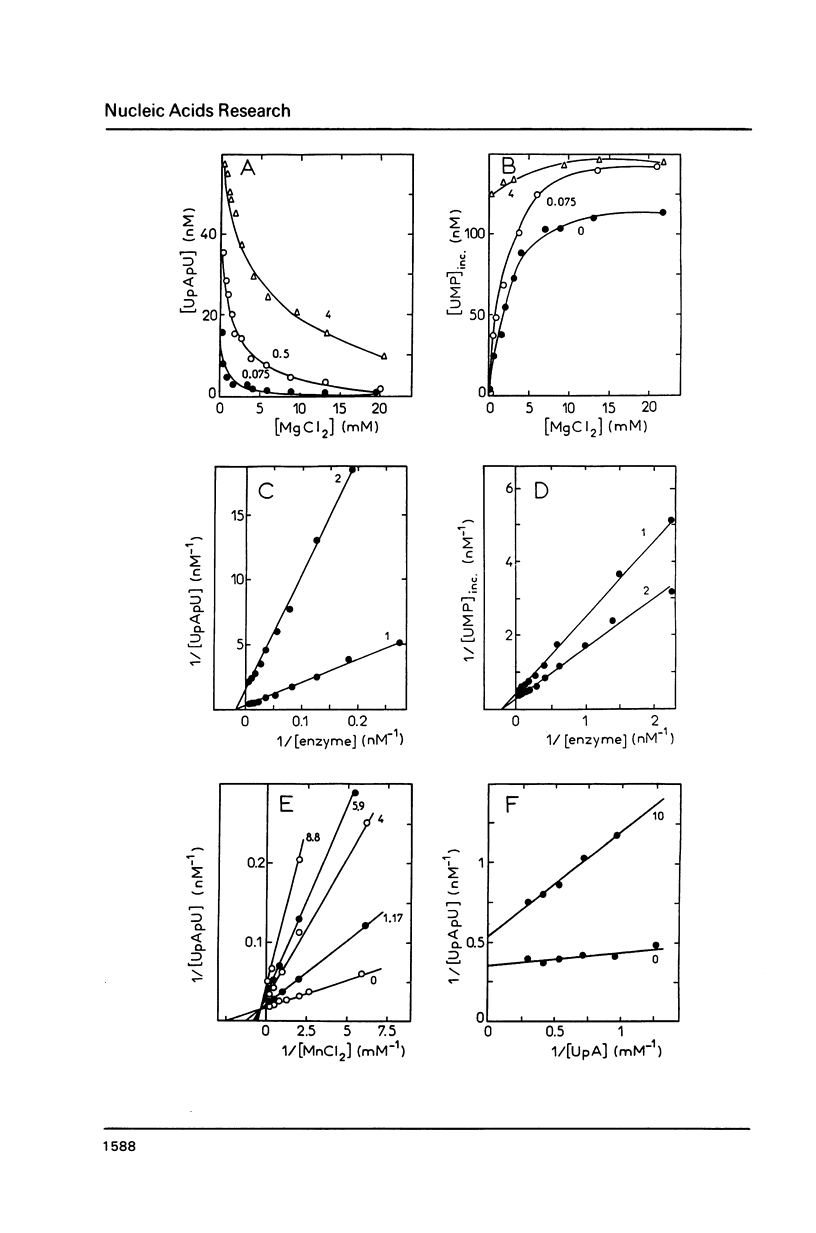
Modification of the ionic conditions in reaction assays containing wheat germ RNA polymerase II and poly(dAT) as template markedly alters the catalytic properties of the transcription complexes. These effects have been studied by measuring the rate of abortive initiation and the extent of productive RNA synthesis. Using combinations of metal ions or various salts, a marked inhibition of abortive initiation was always associated with an increased length of RNA chains. These results are discussed in terms of modulation of the stability of transcription complexes induced by salts or divalent cations. The behavior exhibited by wheat germ RNA polymerase II is also discussed in comparison with previously reported results for procaryotic and eucaryotic RNA polymerases.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S., Bunick D., Zandomeni R., Weinmann R. RNA polymerase II ternary transcription complexes generated in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):6041–6064. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanc M., Briat J. F., Laulhere J. P. Influence of the ionic environment on the in vitro transcription of the spinach plastid DNA by a selectively bound RNA-polymerase DNA complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 27;655(3):374–382. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpousis A. J., Gralla J. D. Cycling of ribonucleic acid polymerase to produce oligonucleotides during initiation in vitro at the lac UV5 promoter. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3245–3253. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech C. L., Lichy J., McClure W. R. Characterization of promoter containing DNA fragments based on the abortive initiation reaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1763–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. E., Greenleaf A. L. A mutation in the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II alters RNA chain elongation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13190–13198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douzou P., Maurel P. Ionic regulation in genetic translation systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1013–1015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
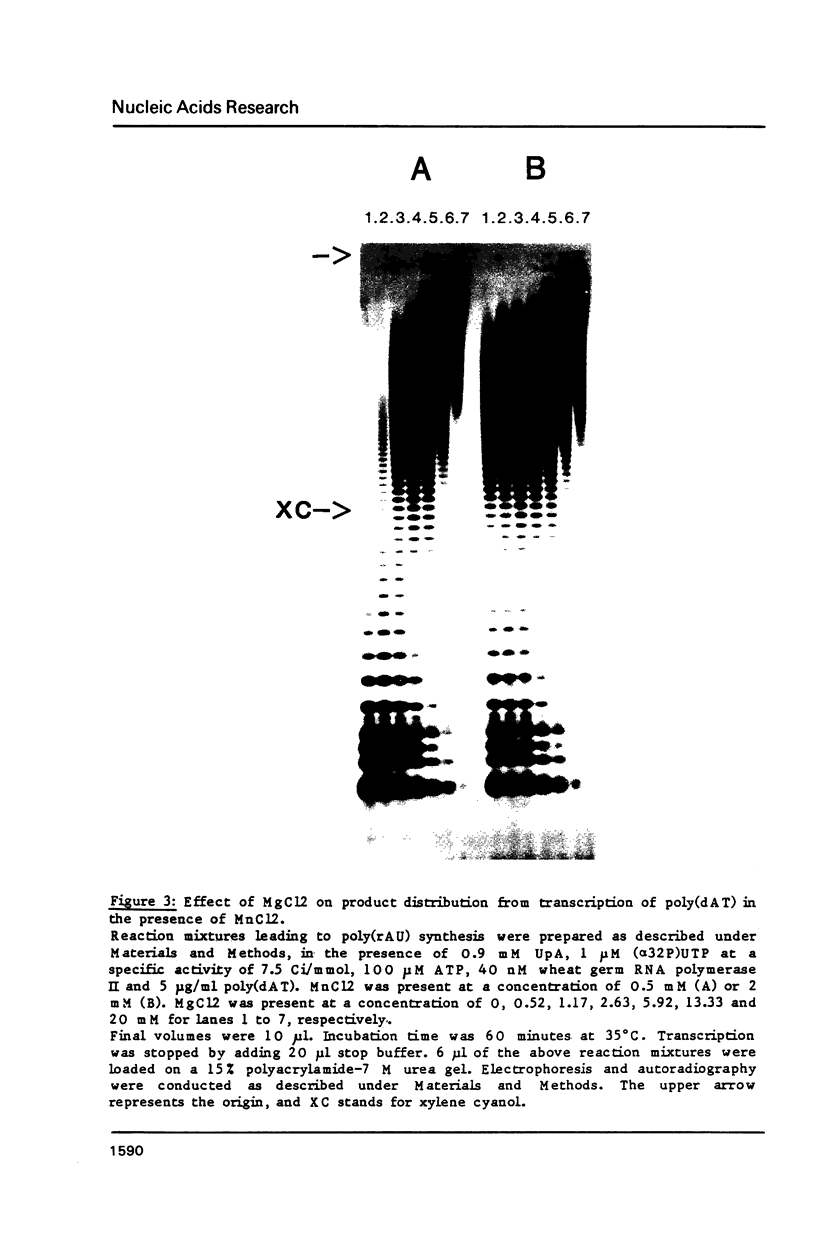
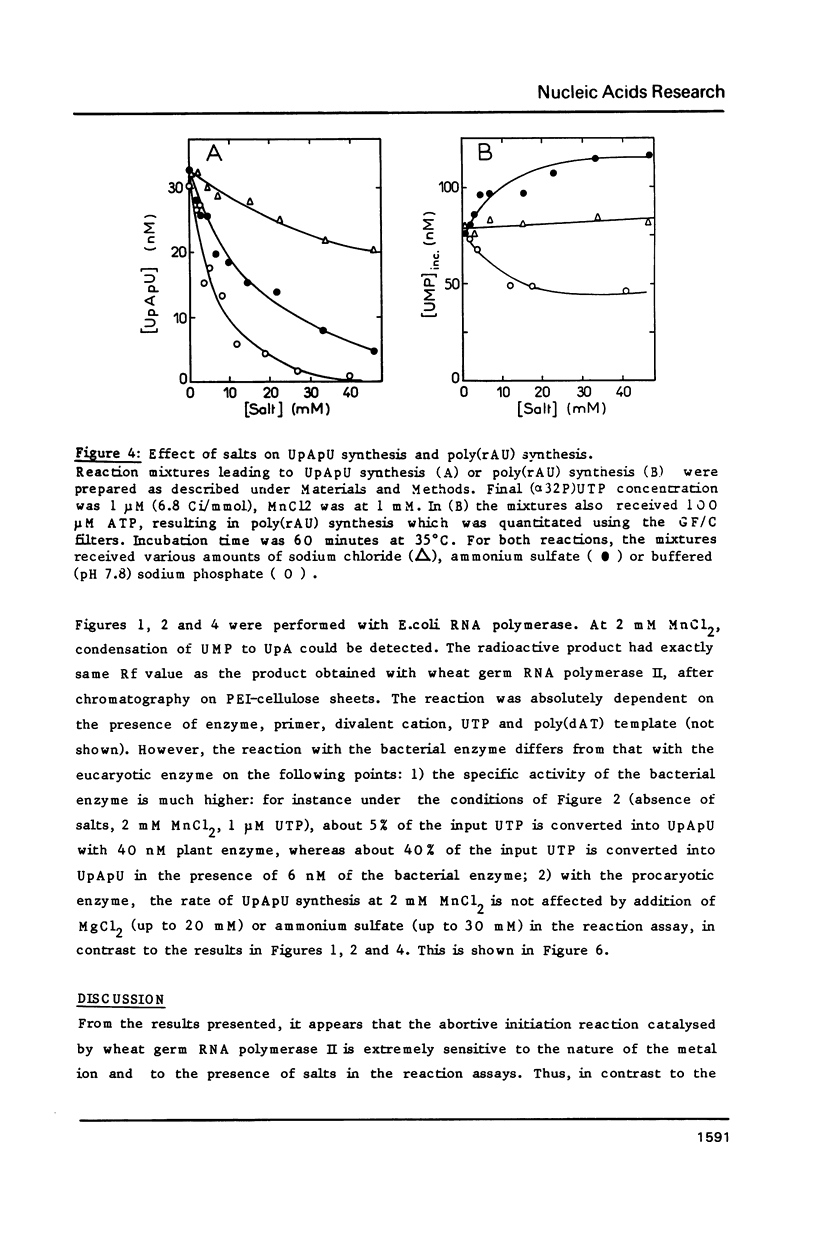
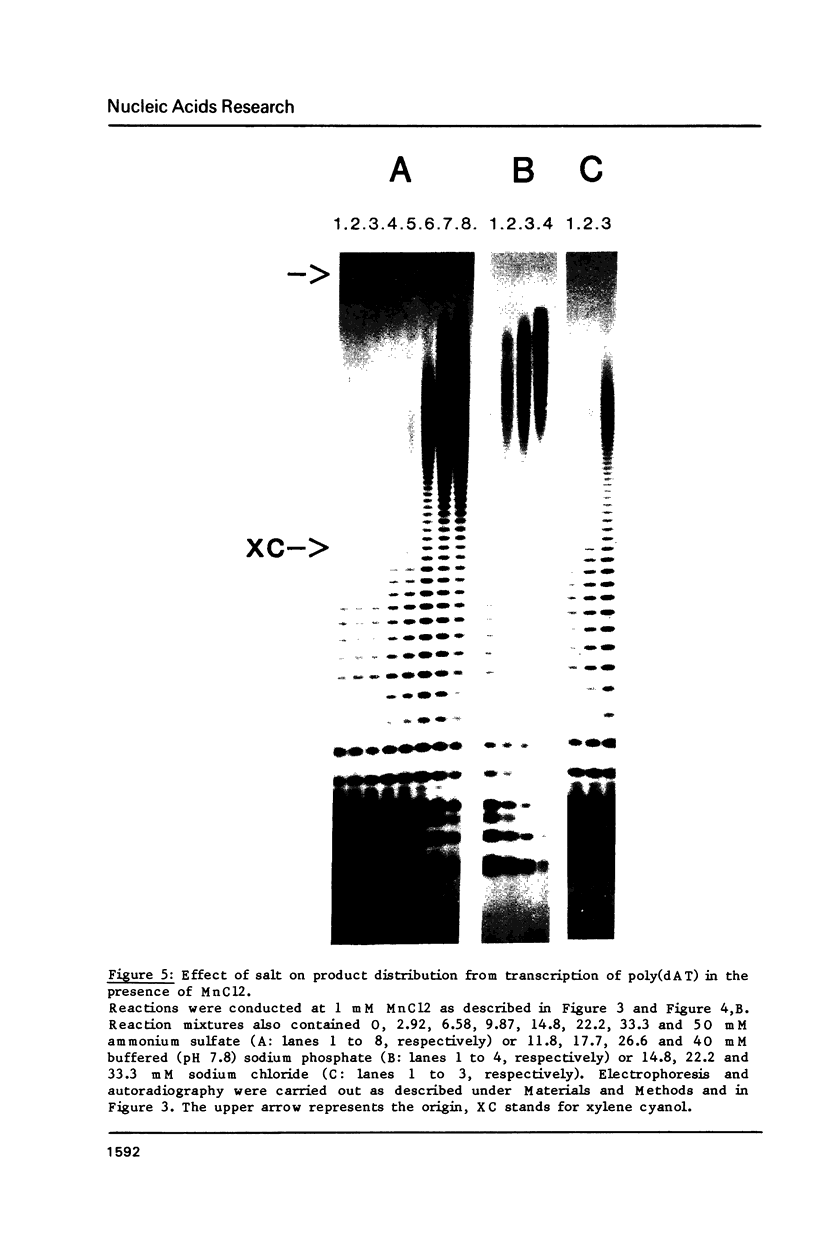
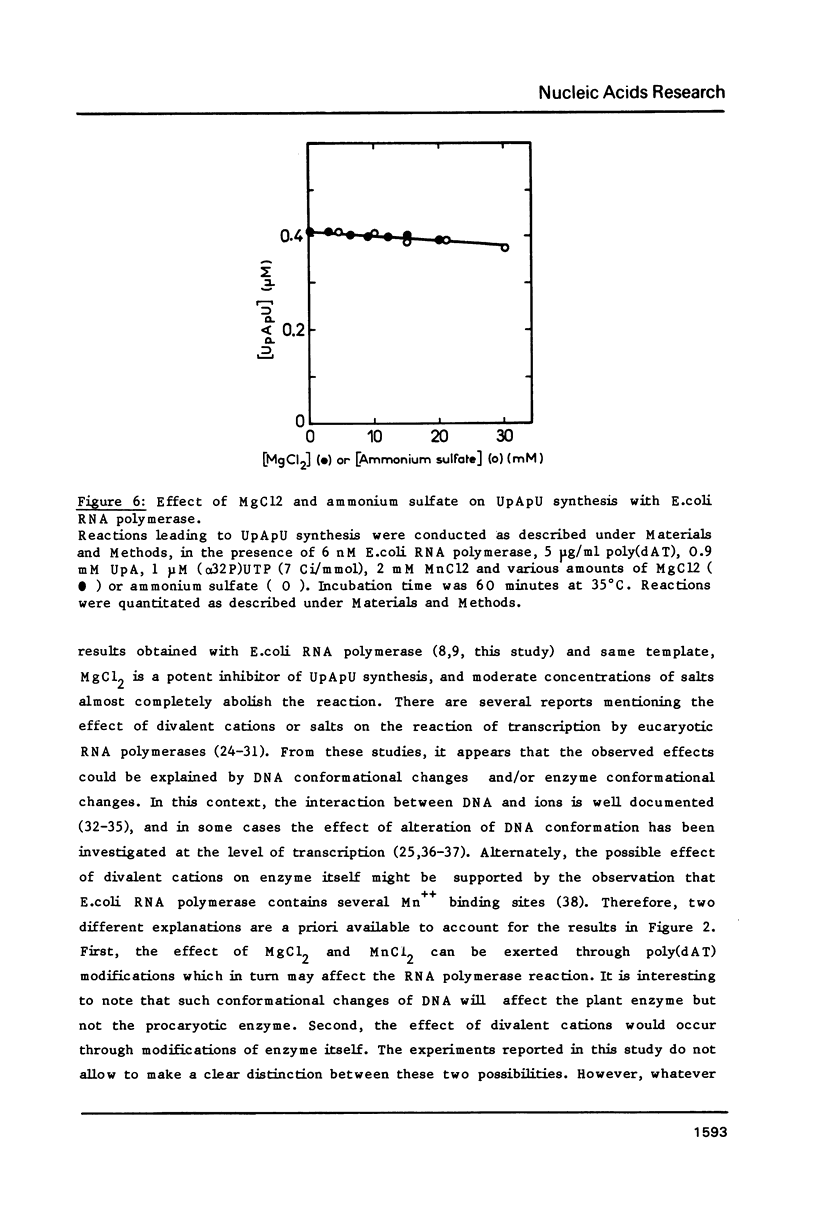
- Durand R., Job C., Teissère M., Job D. Non-processive transcription of poly[d(A-T)] by wheat germ RNA polymerase II. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):477–481. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80793-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand R., Job C., Zarling D. A., Teissère M., Jovin T. M., Job D. Comparative transcription of right- and left-handed poly[d(G-C)] by wheat germ RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1707–1714. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonds-Alt X., Houssier C., Fredericq E. Electric birefringence of DNA and chromatin. Influence of divalent cations. Biophys Chem. 1979 Jul;10(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(79)80003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between RNA polymerase II, factors, and template leading to accurate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2509–2516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla J. D., Carpousis A. J., Stefano J. E. Productive and abortive initiation of transcription in vitro at the lac UV5 promoter. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5864–5869. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U. M., McClure W. R. A noncycling activity assay for the omega subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5713–5717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U. M., McClure W. R. Role of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in initiation. I. Characterization of core enzyme open complexes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9556–9563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U. M., McClure W. R. Role of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in initiation. II. Release of sigma from ternary complexes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9564–9570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendrisak J. J., Burgess R. R. A new method for the large-scale purification of wheat germ DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4639–4645. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job D., Durand R., Teissere M. Enzymatic properties and cooperative effects in the kinetics of wheat-germ RNA polymerases. A comparative study of the three nuclear enzyme classes. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov;128(1):35–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M. Recognition mechanisms of DNA-specific enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:889–920. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.004325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of in vitro transcription by calf thymus RNA polymerase II using a novel duplex DNA template. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5286–5295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescure B. Pure yeast RNA polymerase B (II) initiates transcription at specific points on supercoiled yeast DNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):946–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. K., Burgess R. R. Transcription of simian virus 40 DNA by wheat germ RNA polymerase II. Priming of RNA synthesis by the 3'-hydroxyl of DNA at single strand nicks. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4928–4936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., DeHaseth P. L., Record M. T., Jr Analysis of ion concentration effects of the kinetics of protein-nucleic acid interactions. Application to lac repressor-operator interactions. Biophys Chem. 1978 Sep;8(4):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(78)80011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Studies on the reaction parameters of transcription in vitro of Simian virus 40 DNA by mammalian RNA polymerases AI and B. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 16;41(2):367–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. Theory of the delocalized binding of Mg(II) to DNA: preliminary analysis for low binding levels. Biophys Chem. 1977 Sep;7(2):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(77)80006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurel P., Douzou P. Catalytic implications of electrostatic potentials: the lytic activity of lysozymes as a model. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 5;102(2):253–264. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Cech C. L., Johnston D. E. A steady state assay for the RNA polymerase initiation reaction. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8941–8948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Cech C. L. On the mechanism of rifampicin inhibition of RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8949–8956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mildvan A. S., Loeb L. A. The role of metal ions in the mechanisms of DNA and RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1979;6(3):219–244. doi: 10.3109/10409237909102564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosig H., Schäffner A. R., Sieber H., Hartmann G. R. Primer-independent abortive initiation by wheat-germ RNA polymerase B (II). Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):337–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson L. M., Reznikoff W. S. Abortive initiation and long ribonucleic acid synthesis. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2081–2085. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Bennetzen J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Single-stranded DNA transcription by yeast RNA polymerase B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 28;656(2):220–227. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Mizuno D., Natori S. Differences in the effects of manganese and magnesium on initiation and elongation in the RNA polymerase I reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 24;519(2):440–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oen H., Wu C. W. DNA-dependent single-step addition reactions catalyzed by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1778–1782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oen H., Wu C. W., Haas R., Cole P. E. T7 deoxyribonucleic acid directed, rapid-turnover, single-step addition reactions catalyzed by Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4148–4155. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Mazur S. J., Melançon P., Roe J. H., Shaner S. L., Unger L. Double helical DNA: conformations, physical properties, and interactions with ligands. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:997–1024. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.005025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricard J., Noat G., Crasnier M., Job D. Ionic control of immobilized enzymes. Kinetics of acid phosphatase bound to plant cell walls. Biochem J. 1981 May 1;195(2):357–367. doi: 10.1042/bj1950357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruet A., Sentenac A., Fromageot P., Winsor B., Lacroute F. A mutation of the B220 subunit gene affects the structural and functional properties of yeast RNA polymerase B in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6450–6455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Dinucleotide priming of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2517–2525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Croissant O., Yaniv M. Localization of the binding sites of prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases on simian virus 40 DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb05993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaner S. L., Melançon P., Lee K. S., Burgess R. R., Record M. T., Jr Ion effects on the aggregation and DNA-binding reactions of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):463–472. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Novello F. Factors affecting the activity of ribonucleic acid polymerase solubilized from rat liver nuclei. Effect on ionic strength, spermine and divalent ions with native and denatured deoxyribonucleic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;15(3):505–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester J. E., Cashel M. Stable RNA-DNA-RNA polymerase complexes can accompany formation of a single phosphodiester bond. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1069–1074. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarbrough L. R. Utilization of primers and primer-templates by wheat germ RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6171–6177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Roode J. H., Orgel L. E. Template-directed synthesis of oligoguanylates in the presence of metal ions. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 25;144(4):579–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90338-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Sande J. H., Jovin T. M. Z* DNA, the left-handed helical form of poly[d(G-C)] in MgCl2-ethanol, is biologically active. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):115–120. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]