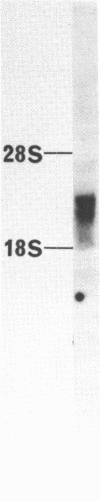
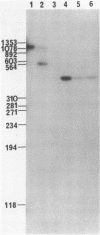
Abstract
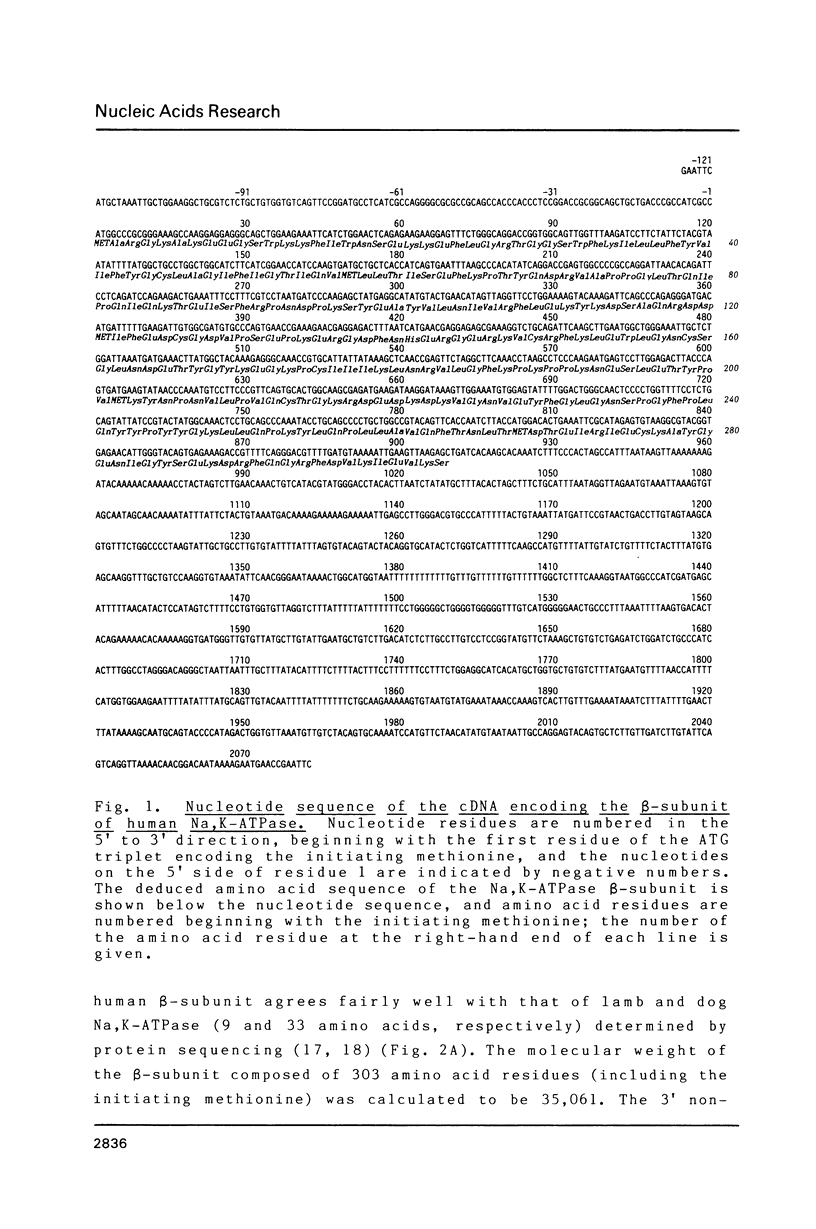
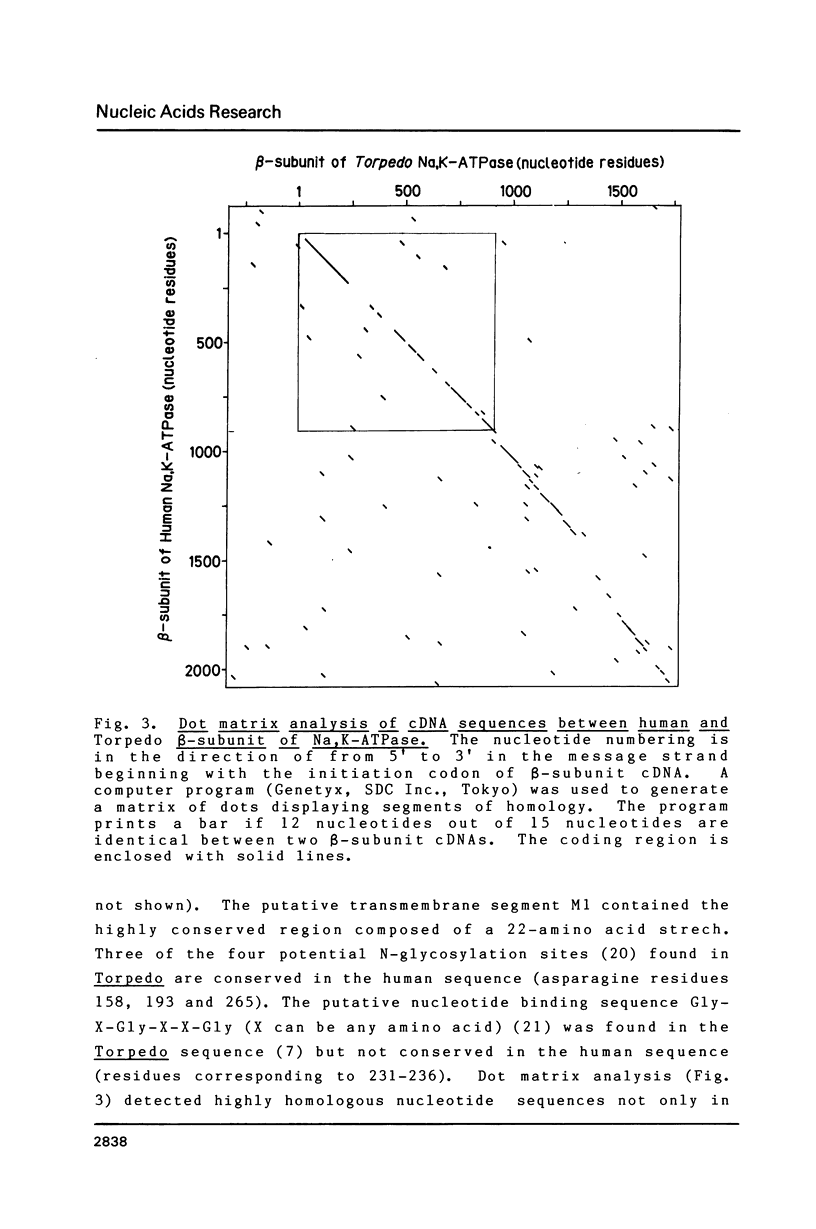
We have isolated a cDNA clone for the beta-subunit of HeLa cell Na,K-ATPase, containing a 2208-base-pair cDNA insert covering the whole coding region of the beta-subunit. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed that the amino acid sequence of human Na,K-ATPase exhibited 61% homology with that of Torpedo counterpart (Noguchi et al. (1986) FEBS Lett. in press). A remarkable conservation in the nucleotide sequence of the 3' non-coding region was detected between the human and Torpedo cDNAs. RNA blot hybridization analysis revealed the presence of two mRNA species in HeLa cells. S1 nuclease mapping indicated that they were derived from utilization of two distinct polyadenylation signals in vivo. Total genomic Southern hybridization indicated the existence of only a few, possibly one set of gene encoding the Na,K-ATPase beta-subunit in the human genome.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. II. Reconstitution of functional rough microsomes from heterologous components. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):852–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin G. J. Papain fragmentation of the (Na+,K+)-ATPase beta subunit reveals multiple membrane-bound domains. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 8;24(21):5943–5947. doi: 10.1021/bi00342a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag J. W. The (Na+, K+)ATPase exhibits enzymic activity in the absence of the glycoprotein subunit. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 8;159(1-2):280–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80464-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L. Mechanism of the Na+, K+ pump. Protein structure and conformations of the pure (Na+ +K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 11;694(1):27–68. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Noguchi S., Noda M., Takahashi H., Ohta T., Kawamura M., Nojima H., Nagano K., Hirose T., Inayama S. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of Torpedo californica (Na+ + K+)ATPase deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):733–736. doi: 10.1038/316733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D. The nature and metabolism of the carbohydrate-peptide linkages of glycoproteins. Biochem Soc Symp. 1974;(40):17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller W., Amons R. Phosphate-binding sequences in nucleotide-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 1;186(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack L. R., Tate E. H., Cook J. S. Turnover and regulation of Na-K-ATPase in HeLa cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Nov;241(5):C173–C183. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.241.5.C173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Cantley L. C. Increasing the intracellular Na+ concentration induces differentiation in a pre-B lymphocyte cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7547–7550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Schwartz A., Lingrel J. B. Amino-acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of the (Na+ + K+)ATPase deduced from a complementary DNA. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):691–695. doi: 10.1038/316691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Macara I. G., Levenson R., Housman D., Cantley L. Evidence that a Na+/Ca2+ antiport system regulates murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):773–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock R., Sweet R., Weiss M., Cedar H., Axel R. Intragenic DNA spacers interrupt the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]