Abstract
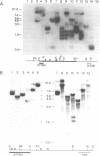
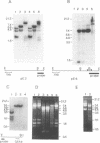
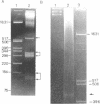
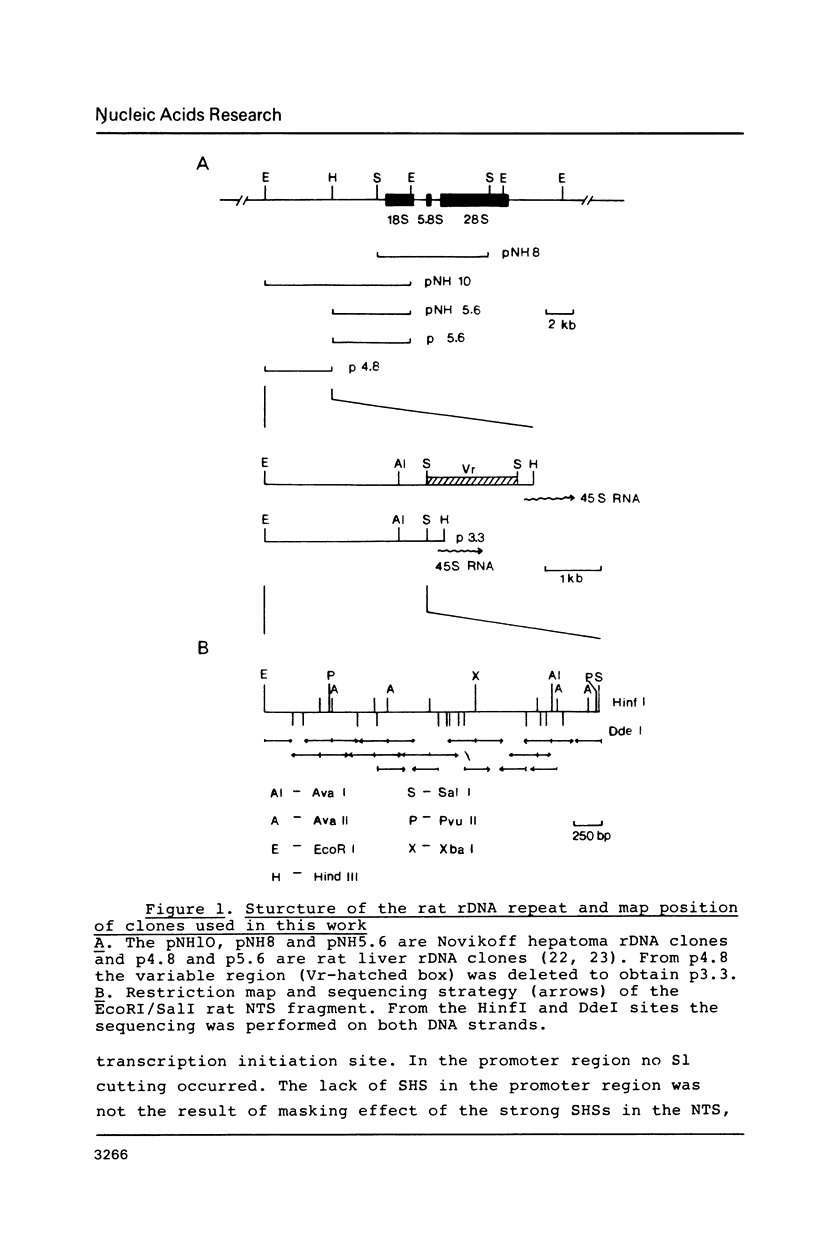
Rat and human ribosomal RNA gene fragments in supercoiled plasmids were examined for S1 nuclease hypersensitivity. In the transcribed portion of genes the number and distribution of S1 sites were found to be species specific. No S1 sites were detected in the promoter regions. In the nontranscribed spacer (NTS), downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA gene, S1 sites appear to be conserved in rat and human rDNAs. A rat NTS fragment (2987 nucleotides long), containing three S1 sites was sequenced and the S1 sites in this region were localized in polypyrimidine . polypurine simple repeat sequences. Other types of simple sequences, two type 2 Alu repeats and an ID sequence were also found in the sequenced region. The possible role of simple sequences and S1 sites in transcription and in recombination events of rDNA is discussed.
Full text
PDF



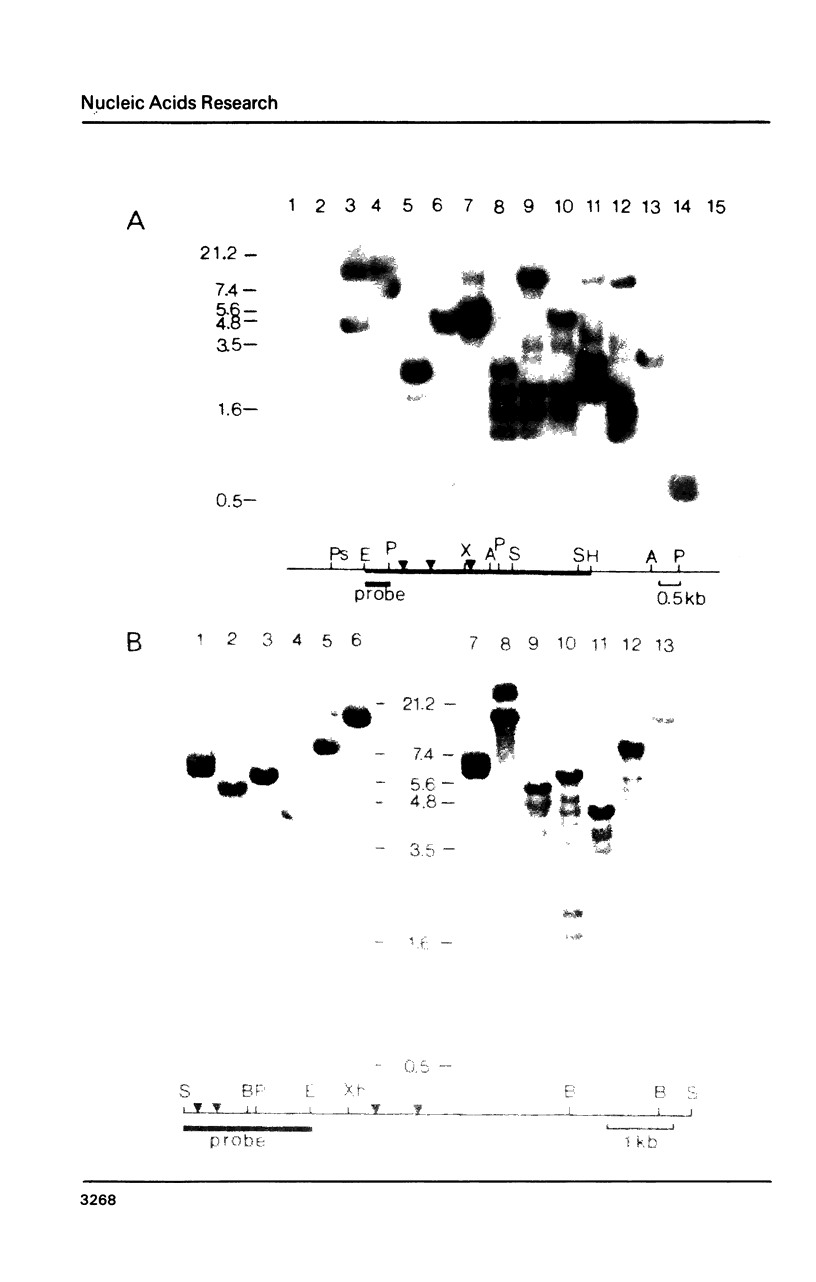

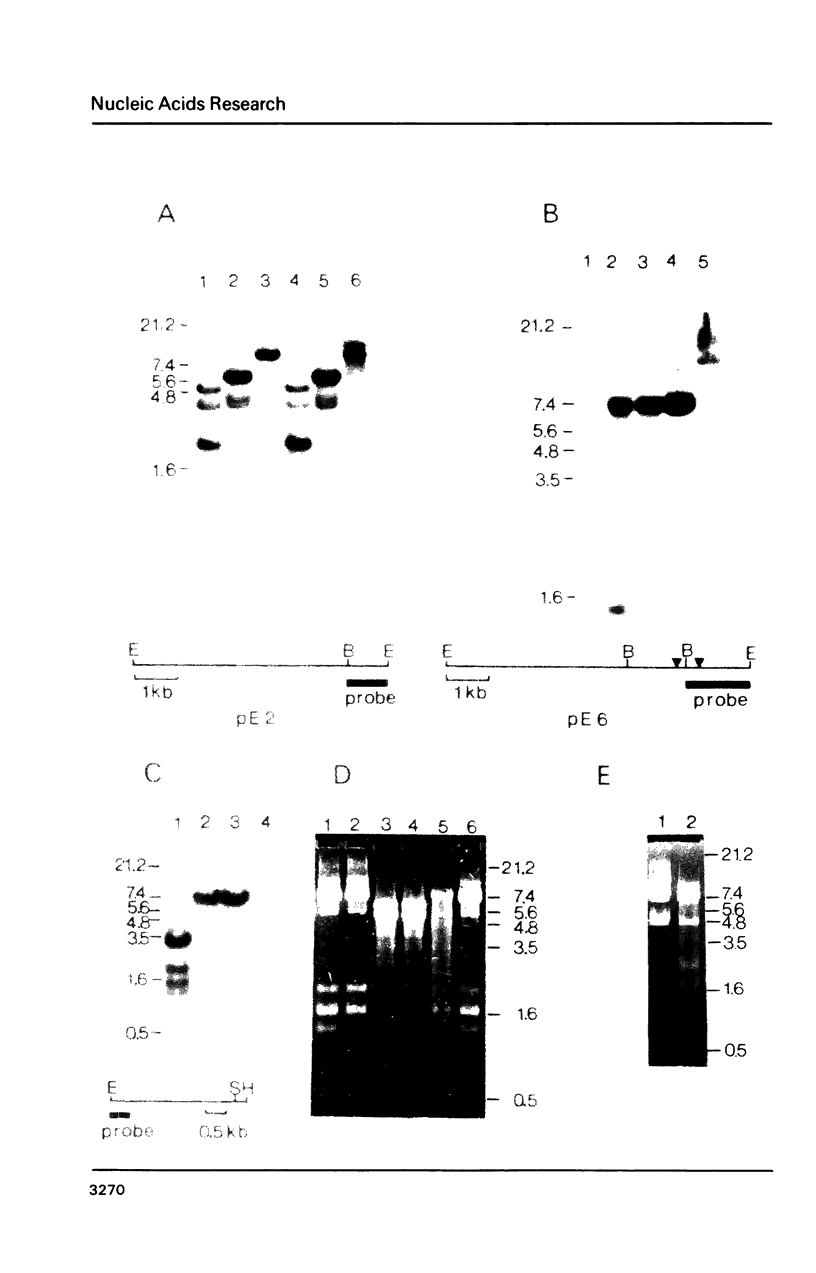


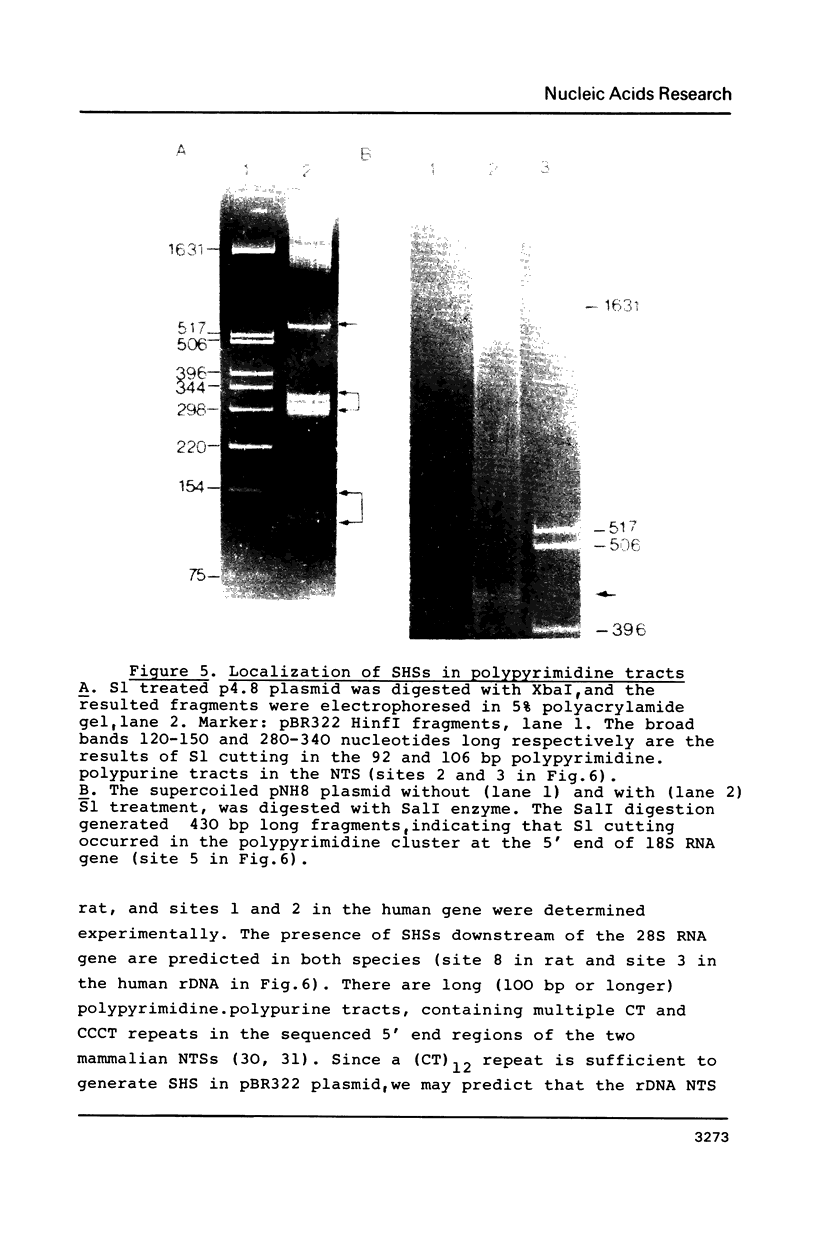




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Sederoff R. R., Paterson M. C. Distribution of polypyrimidine . polypurine segments in DNA from diverse organisms. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):301–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonven B. J., Gocke E., Westergaard O. A high affinity topoisomerase I binding sequence is clustered at DNAase I hypersensitive sites in Tetrahymena R-chromatin. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):541–551. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonven B., Westergaard O. DNase I hypersensitive regions correlate with a site-specific endogenous nuclease activity on the r-chromatin of Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7593–7608. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braga E. A., Avdonina T. A., Zhurkin V. B., Nosikov V. V. Structural organization of rat ribosomal RNA genes: interspersed sequences and their putative role in the alignment of nucleosomes. Gene. 1985;36(3):249–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Efstratiadis A. Possible structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine S1-hypersensitive sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8059–8072. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Subrahmanyan C. S., Rothblum L. I. The nucleotide sequence of the 5' region of rat 18S rDNA and adjoining spacer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug 31;107(4):1571–1576. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikaraishi D. M., Buchanan L., Danna K. J., Harrington C. A. Genomic organization of rat rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6437–6452. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Effron K., Rechavi G., Ben-Neriah Y., Zakut R., Givol D. Simple DNA sequences in homologous flanking regions near immunoglobulin VH genes: a role in gene interaction? Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3353–3370. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dybvig K., Clark C. D., Aliperti G., Schlesinger M. J. A chicken repetitive DNA sequence that is highly sensitive to single-strand specific endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8495–8508. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Interaction of specific nuclear factors with the nuclease-hypersensitive region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene: nature of the binding domain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Hidvégi E. J. Cloning and characterization of a Novikoff hepatoma ribosomal DNA-fragment containing the initiation site of transcription. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1984;19(3-4):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Muramatsu M. Nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region of a rat ribosomal RNA gene. Gene. 1982 May;18(2):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz G., Tautz D., Dover G. A. Conservation of major nuclease S1-sensitive sites in the non-conserved spacer region of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila species. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 25;183(4):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard W., Zachau H. G. Simple DNA sequences and dispersed repetitive elements in the vicinity of mouse immunoglobulin K light chain genes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):567–573. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S., Udvardy A., Schedl P. Transcriptionally active chromatin is sensitive to Neurospora crassa and S1 nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 5;179(3):469–496. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C. Homocopolymer sequences in the spacer of a sea urchin histone gene repeat are sensitive to S1 nuclease. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):714–716. doi: 10.1038/295714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick M. W., Klysik J., Singleton C. K., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M., Hanau L. H., Erlanger B. F., Wells R. D. Intervening sequences in human fetal globin genes adopt left-handed Z helices. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7268–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Volpe A., Simeone A., D'Esposito M., Scotto L., Fidanza V., de Falco A., Boncinelli E. Molecular analysis of the heterogeneity region of the human ribosomal spacer. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Volpe A., Taggart M., McStay B., Bird A. DNaseI-hypersensitive sites at promoter-like sequences in the spacer of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus borealis ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5361–5380. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Kemper B. Cruciform-resolvase interactions in supercoiled DNA. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchnik A. N., Bakayev V. V., Yugai A. A., Zbarsky I. B., Georgiev G. P. DNAaseI-hypersensitive minichromosomes of SV40 possess an elastic torsional strain in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1135–1149. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margot J. B., Hardison R. C. DNase I and nuclease S1 sensitivity of the rabbit beta 1 globin gene in nuclei and in supercoiled plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 20;184(2):195–210. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90373-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palen T. E., Cech T. R. Chromatin structure at the replication origins and transcription-initiation regions of the ribosomal RNA genes of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):933–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson D. S., Shupe K., Gorovsky M. A. Changes in chromatin structure accompany modulation of the rate of transcription of 5S ribosomal genes in Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8489–8507. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. E., Gilliam A. C., Shen A., Tucker P. W., Blattner F. R. Unusual sequences in the murine immunoglobulin mu-delta heavy-chain region. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):483–487. doi: 10.1038/306483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Kunz G., Daetwyler H., Telford J., Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. Genes and spacers of cloned sea urchin histone DNA analyzed by sequencing. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffery M., Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Gene expression in murine erythroleukemia cells. Transcriptional control and chromatin structure of the alpha 1-globin gene. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):417–436. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Klysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA is induced by supercoiling in physiological ionic conditions. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):312–316. doi: 10.1038/299312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam C. S., Cassidy B., Busch H., Rothblum L. I. Nucleotide sequence of the region between the 18S rRNA sequence and the 28S rRNA sequence of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3667–3680. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Z., Wu Z. H. [Recent progress in studies of adrenergic receptors (author's transl)]. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 1980 Apr;11(4):289–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Lowry J., Kedes L. H. The DNA sequence of sea urchin (S. purpuratus) H2A, H2B and H3 histone coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Gottesfeld J. M., Lerner R. A. Identifier sequences are transcribed specifically in brain. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):237–241. doi: 10.1038/308237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Renz M. Simple sequences are ubiquitous repetitive components of eukaryotic genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4127–4138. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. N., Hollar B. A., Waterson J. R., Schmickel R. D. Molecular analysis of cloned human 18S ribosomal DNA segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5367–5371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Subrahmanyam C. S., Cassidy B., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of rat ribosomal DNA II. identification of the highly repetitive DNA in the 3' non-transcribed spacer. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90289-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]