Abstract
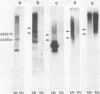
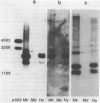
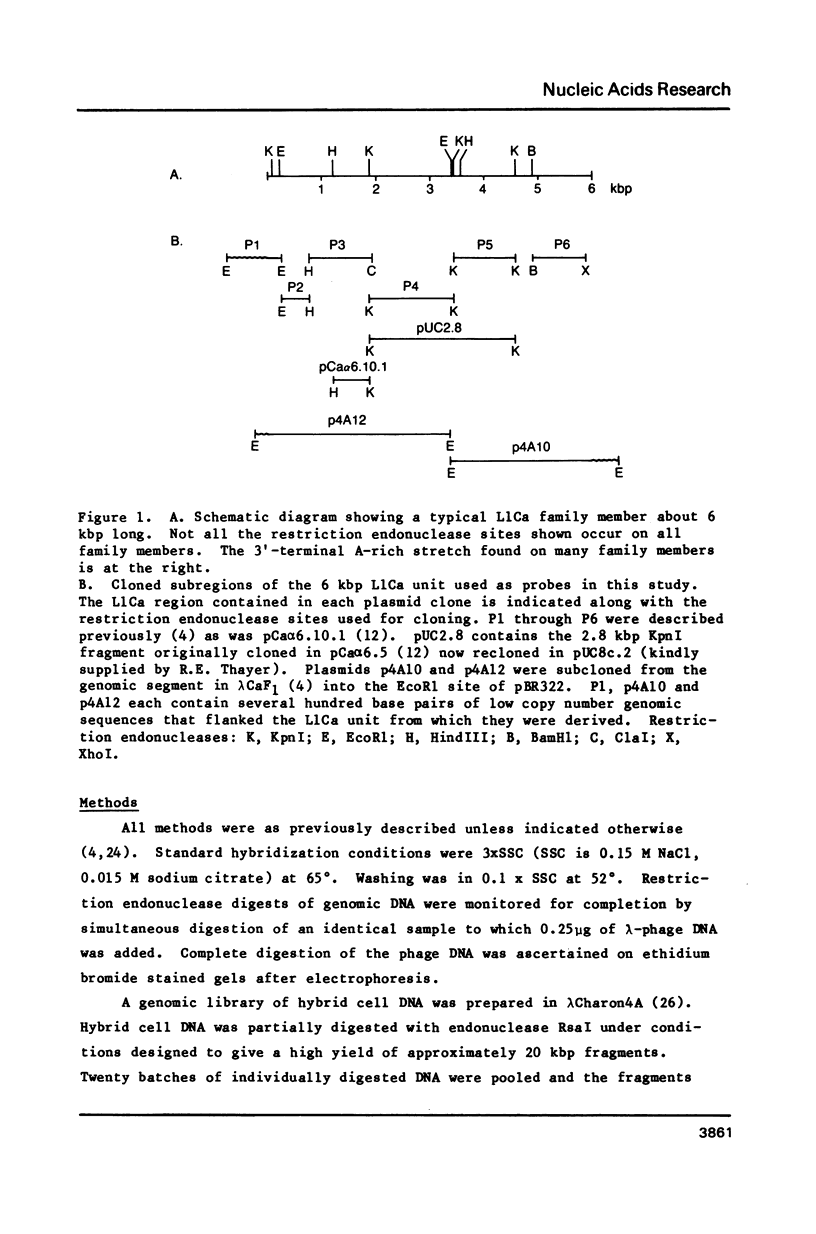
The structure of LINE-1 (L1Ca) family members present on African green monkey chromosome CAE-19 is compared with that of the entire set of L1Ca sequences present in the monkey genome. The analysis involved annealing of cloned subsegments of monkey L1 family members to DNA-blots containing restriction endonuclease digests of either total monkey liver DNA or DNA isolated from a monkey/mouse somatic cell hybrid carrying the single monkey chromosome. In addition, L1Ca segments cloned from hybrid cell DNA were characterized by restriction endonuclease mapping and hybridization. The data indicate that, taken as a whole, the set of L1Ca sequences on CAE-19 tends to differ in characteristic ways from the set present in the total monkey genome.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. W., Kaufman R. E., Kretschmer P. J., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. A family of long reiterated DNA sequences, one copy of which is next to the human beta globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6113–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett K. L., Hastie N. D. Looking for relationships between the most repeated dispersed DNA sequences in the mouse: small R elements are found associated consistently with long MIF repeats. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):467–472. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Dover G. Organization and evolutionary progress of a dispersed repetitive family of sequences in widely separated rodent genomes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 25;150(4):441–466. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Créau-Goldberg N., Turleau C., Cochet C., Huerre C., Junien C., de Grouchy J. Conservation of the human COL1A1-TK-GAA synteny and homoeologous assignment in the African green monkey and the baboon (Cercopithecoidae). Hum Genet. 1984;68(4):333–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00292595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Size and structure of the highly repetitive BAM HI element in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5073–5091. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard W., Zachau H. G. Organization of the R family and other interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the mouse genome. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Singer M. F. Members of the KpnI family of long interspersed repeated sequences join and interrupt alpha-satellite in the monkey genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):321–338. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Skowronski J., Singer M. F. Defining the beginning and end of KpnI family segments. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1753–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Rowe L., Rogers D. T. Transposition of yeast mating type genes from two translocations of the left arm of chromosome III. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1106–1119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Hidaka S., Sakaki Y. Sequence analysis of a KpnI family member near the 3' end of human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7813–7827. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinks-Robertson S., Petes T. D. High-frequency meiotic gene conversion between repeated genes on nonhomologous chromosomes in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3350–3354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzir N., Rechavi G., Cohen J. B., Unger T., Simoni F., Segal S., Cohen D., Givol D. "Retroposon" insertion into the cellular oncogene c-myc in canine transmissible venereal tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1054–1058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. N., Singer M. F. Structural organization of alpha-satellite DNA in a single monkey chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):323–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman M. I., Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Kpn I family of long interspersed repeated DNA sequences in primates: polymorphism of family members and evidence for transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Padgett R. W., Hardies S. C., Shehee W. R., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5' end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):168–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Biro P. A. Genomic representation of the Hind II 1.9 kb repeated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3221–3239. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Nucleotide sequence definition of a major human repeated DNA, the Hind III 1.9 kb family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3211–3219. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L., Voliva C. F., Burton F. H., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd A large interspersed repeat found in mouse DNA contains a long open reading frame that evolves as if it encodes a protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2308–2312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L., Voliva C. F., Hardies S. C., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Tempo and mode of concerted evolution in the L1 repeat family of mice. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Mar;2(2):127–140. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake T., Migita K., Sakaki Y. Some KpnI family members are associated with the Alu family in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6837–6846. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. Rearranged sequences of a human Kpn I element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1012–1016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Smith M., Lambie E. J. Intrachromosomal movement of genetically marked Saccharomyces cerevisiae transposons by gene conversion. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):703–711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Willard H. F., Smith K. D. Isolation and characterization of cloned human DNA fragments carrying reiterated sequences common to both autosomes and the X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1853–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F., Thayer R. E., Grimaldi G., Lerman M. I., Fanning T. G. Homology between the KpnI primate and BamH1 (M1F-1) rodent families of long interspersed repeated sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5739–5745. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. B., Schon E., Efstratiadis A. Rat LINE1: the origin and evolution of a family of long interspersed middle repetitive DNA elements. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(2):117–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02101690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Interruption of an alpha-satellite array by a short member of the KpnI family of interspersed, highly repeated monkey DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):967–973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voliva C. F., Jahn C. L., Comer M. B., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. The L1Md long interspersed repeat family in the mouse: almost all examples are truncated at one end. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8847–8859. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witney F. R., Furano A. V. Highly repeated DNA families in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10481–10492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]