Abstract
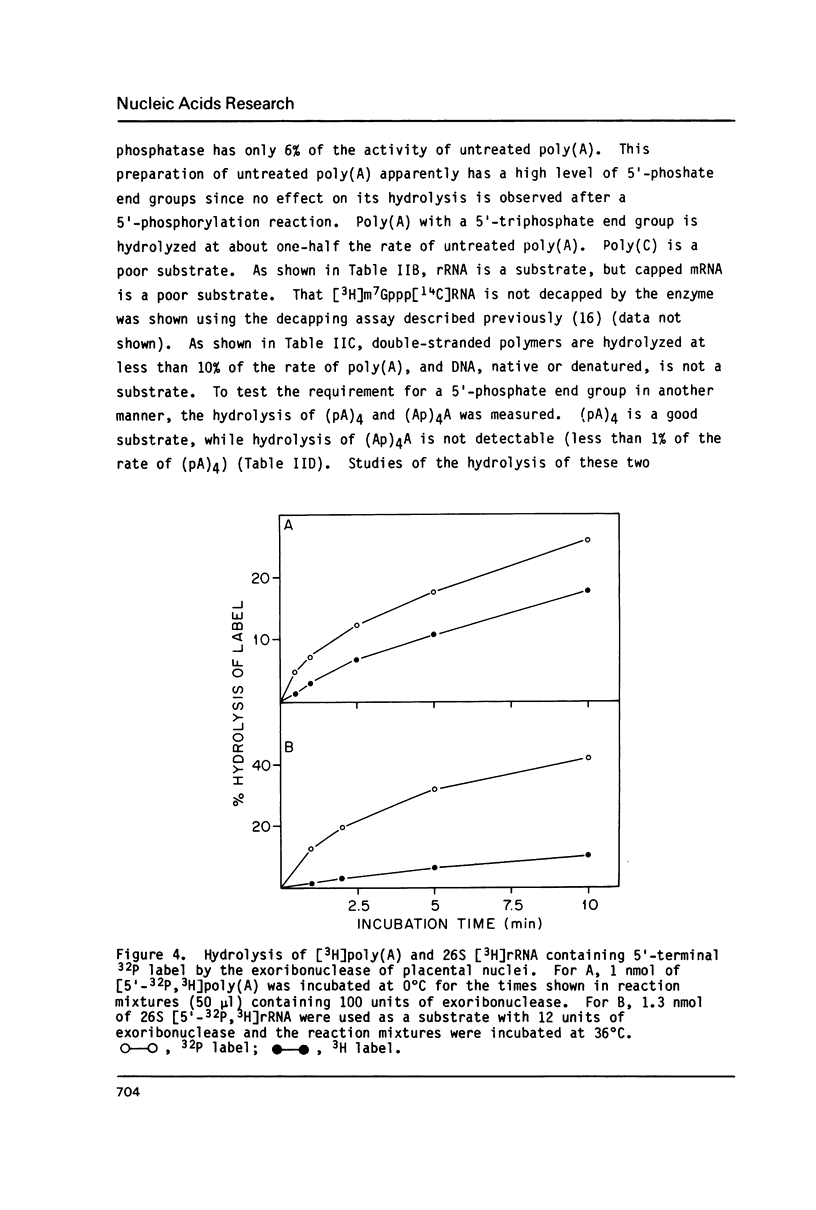
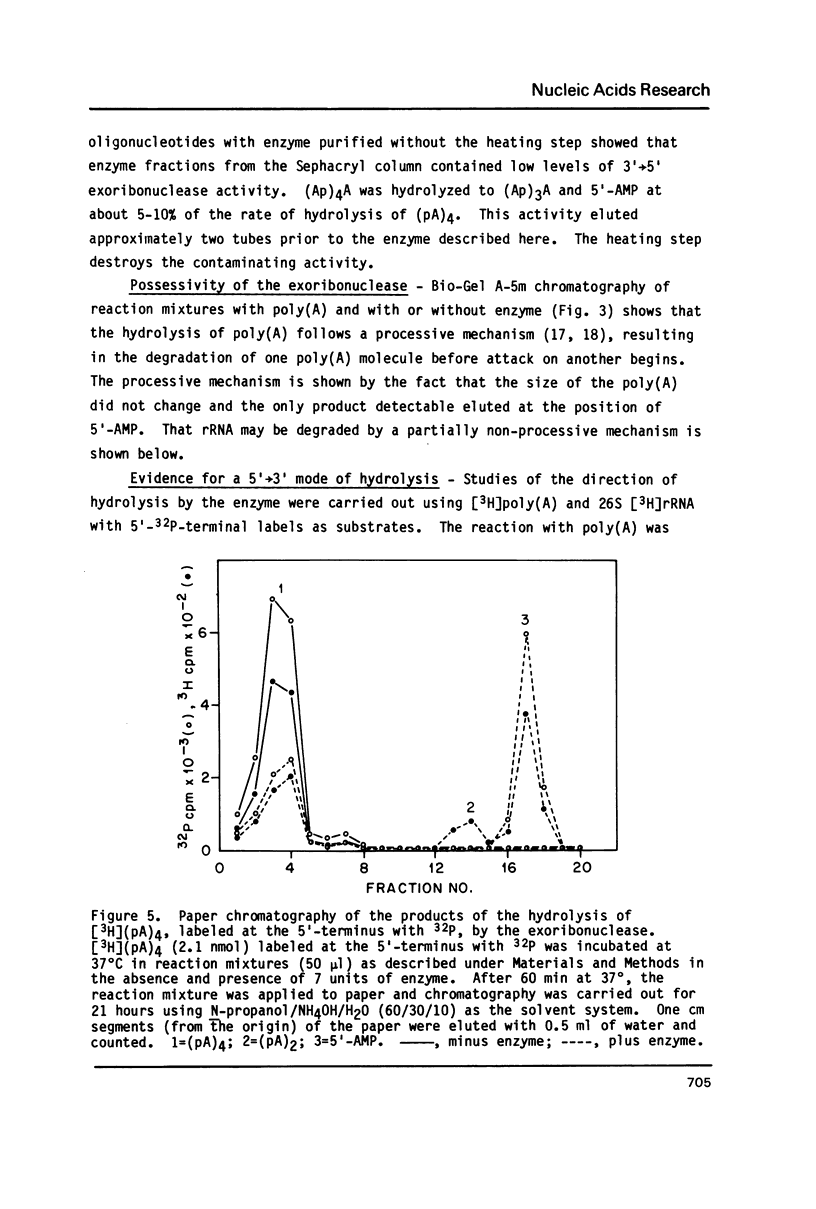
An exoribonuclease that hydrolyzes single-stranded RNA by a 5'----3' mode yielding 5'-mononucleotides has been purified from human placental nuclei. Chromatographic studies of crude placental nuclear extracts suggest that the enzyme is a relatively abundant nuclear RNase. Poly(A) is degraded by a processive mechanism while rRNA is degraded in a partially non-processive manner, possibly because of its secondary structure. The enzyme has an apparent molecular weight of 113,000, derived from determinations of the Stokes radius (43 A) and sedimentation coefficient (6.3 S). Substrates with 5'-phosphomonoester end groups are 10-20 times better than 5'-dephosphorylated substrates. The locale of the enzyme in nuclei of normal human cells as well as its mode of action suggest a role in nuclear RNA processing or turnover.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., LaFiandra A., Shatkin A. J. 5'-Terminal structure and mRNA stability. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):235–239. doi: 10.1038/266235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasater L. S., Eichler D. C. Isolation and properties of a single-strand 5'----3' exoribonuclease from Ehrlich ascites tumor cell nucleoli. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 11;23(19):4367–4373. doi: 10.1021/bi00314a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J. C., Prives C., Manley J. L. In vitro splicing of simian virus 40 early pre mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1219–1235. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal N. G., Singer M. F. The processive degradation of individual polyribonucleotide chains. I. Escherichia coli ribonuclease II. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):913–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Kodama Y., Hashimoto J., Miura K. I. Importance of 5'-terminal blocking structure to stabilize mRNA in eukaryotic protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2734–2738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Vaughan M. H., Warner J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr The turnover of nuclear DNA-like RNA in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Oct;39(1):112–118. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. An exoribonuclease from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effect of modifications of 5' end groups on the hydrolysis of substrates to 5' mononucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 30;81(2):656–661. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91586-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. An mRNA decapping enzyme from ribosomes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 16;96(3):1150–1155. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Deoxyribonucleic acid dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases from two T4 phage-infected systems. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):493–503. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Evidence for a 5' leads to 3' direction of hydrolysis by a 5' mononucleotide-producing exoribonuclease from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1126–1132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Purification and characterization of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae exoribonuclease which yields 5'-mononucleotides by a 5' leads to 3' mode of hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3080–3085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Pyrimidine-specific cleavage by an endoribonuclease of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):57–62. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.57-62.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Olivera B. M. Processivity of DNA exonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):424–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


