Abstract
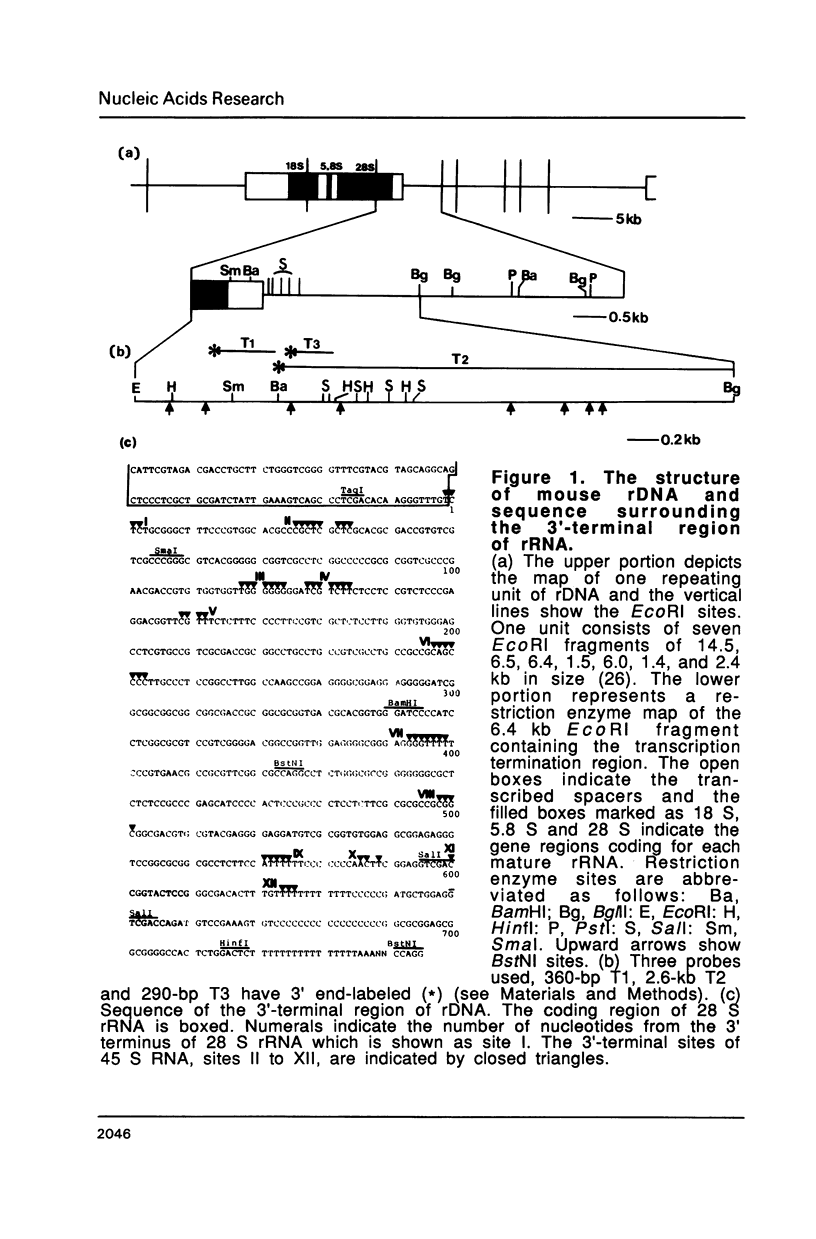
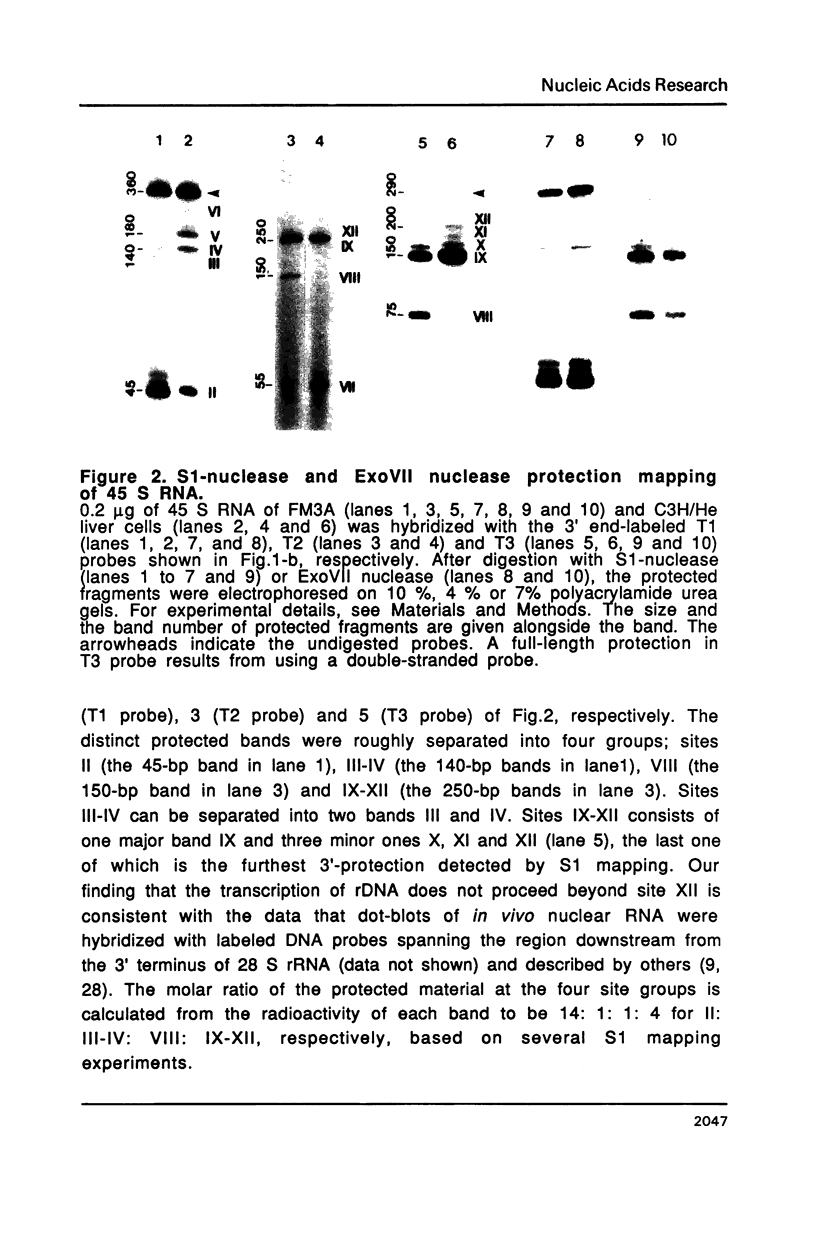
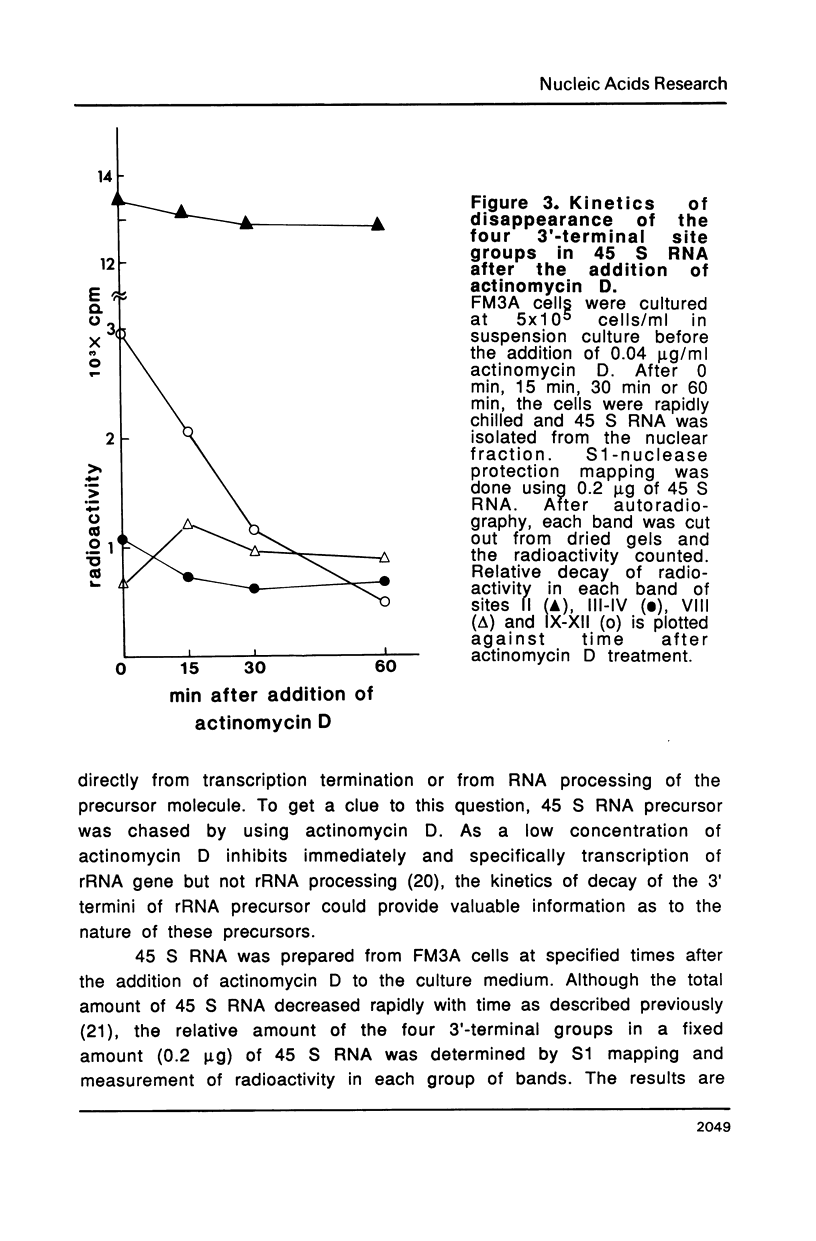
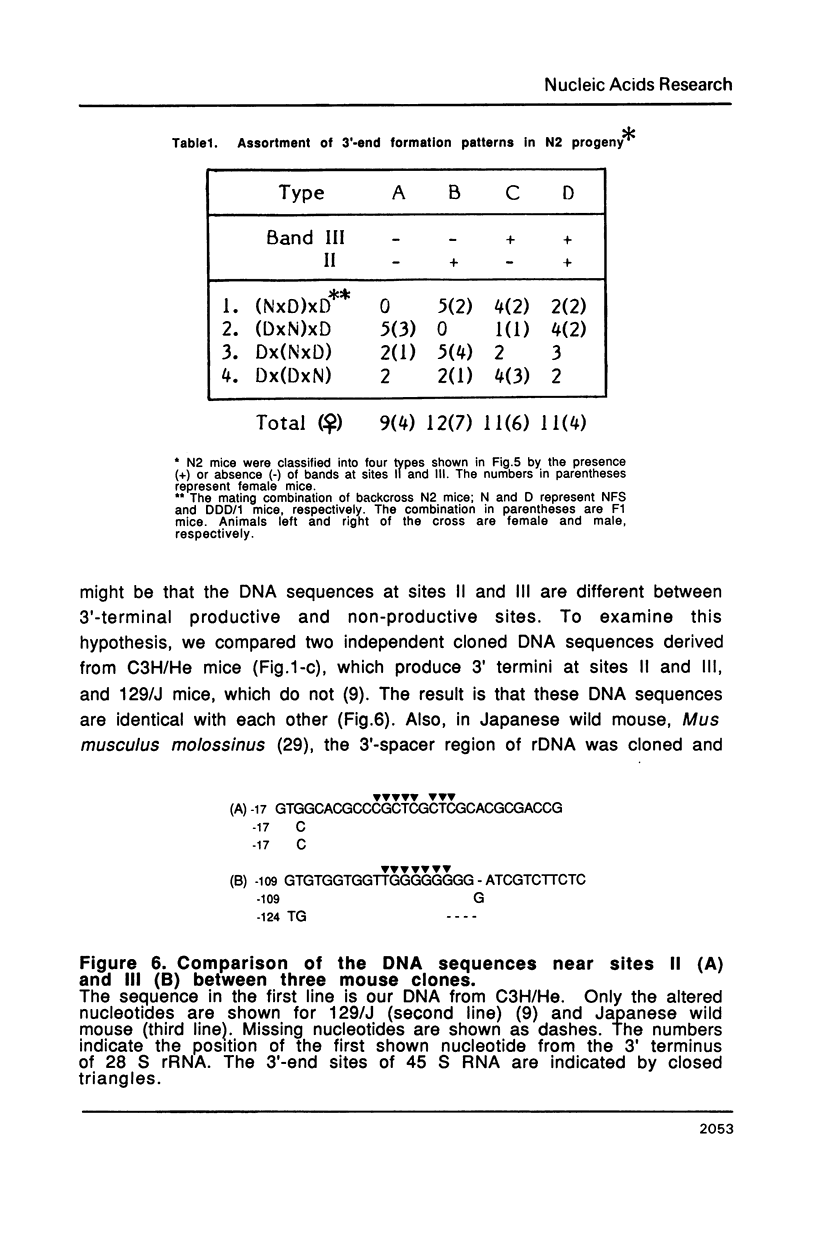
The 3' termini of ribosomal RNA precursors from mouse FM3A cultured cells are mapped to eight sites within 625 bp downstream from the 3' terminus of 28 S rRNA. Three additional sites are mapped in liver RNA from C3H/He strain mice. Two of them, the sites at 570 bp and 625 bp are assumed to be termination sites in vivo, because they correspond to in vitro termination sites of RNA polymerase I, and 45 S RNAs having these 3' termini decay with kinetics distinct from others. The amount of 45 S RNA having the 3' terminus at other sites is variable among several mouse strains, despite their having the same DNA sequence in these regions. The ability to produce 3' termini in these sites seems to follow Mendel's law of inheritance. Therefore, we postulate that these nine sites are RNA processing sites which are controlled genetically.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. M., Platt T. Pol I transcription: which comes first, the end or the beginning? Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):839–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman L. H., Goldman W. E., Goldberg G. I., Hebert M. B., Schlessinger D. Location of the initial cleavage sites in mouse pre-rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1501–1510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUVEAU J., MOULE Y., ROUILLER C. Isolation of pure and unaltered liver nuclei morphology and biochemical composition. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Aug;11(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Maier U., Ohrlein A., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Transcription of mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3' spacer. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Rosenbauer H., Niedermeyer I., Maier U., Ohrlein A. A repeated 18 bp sequence motif in the mouse rDNA spacer mediates binding of a nuclear factor and transcription termination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):837–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Specific transcription of mouse ribosomal DNA in a cell-free system that mimics control in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney T., Jr Characterization of mouse 45S ribosomal RNA subspecies suggests that the first processing cleavage occurs 600 +/- 100 nucleotides from the 5' end and the second 500 +/- 100 nucleotides from the 3' end of a 13.9 kb precursor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4905–4919. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. 3'-terminal processing of ribosomal RNA precursors in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 25;8(4):889–903. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Aloni Y. Attenuation in SV40 as a mechanism of transcription-termination by RNA polymerase B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1401–1414. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Sollner-Webb B. A transcriptional terminator is a novel element of the promoter of the mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90804-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Mishima Y., Urano Y., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Cloning and determination of the transcription termination site of ribosomal RNA gene of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1963–1979. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Heterogeneity of 5' -termini of nucleolar 45S, 32S and 28S RNA in mouse hepatoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jan;4(1):229–240. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Sudo K., Yoshikura H., Suzuki H., Moriwaki K., Hilgers J., Muramatsu M. A polymorphic repetitive-sequence PR1 family. Evidence for meiotic instability. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rands E., Scolnick E. M. Helper-independent transformation by unintegrated Harvey sarcoma virus DNA. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.291-298.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Mitsuma T., Ogata K. Coupled transcription and processing of mouse ribosomal RNA in a cell-free system. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3879–3886. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Hodnett J. L., Steele W. J., Busch H. Synthesis of 28-S RNA in the nucleolus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 20;123(1):116–125. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M. Preparation of RNA from animal cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;7:23–51. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61770-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano N. Establishment of cell lines in vitro from a mammary ascites tumor of mouse and biological properties of the established lines in a serum containing medium. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 25;88(1):69–84. doi: 10.1620/tjem.88.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. Processing of RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:605–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. THE CELLULAR SITES OF SYNTHESIS OF RIBOSOMAL AND 4S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec;48(12):2179–2186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Miyashita N., Moriwaki K., Kominami R., Muramatsu M., Kanehisa T., Bonhomme F., Petras M. L., Yu Z. C., Lu D. Y. Evolutionary implication of heterogeneity of the nontranscribed spacer region of ribosomal DNA repeating units in various subspecies of Mus musculus. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Mar;3(2):126–137. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano Y., Kominami R., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. The nucleotide sequence of the putative transcription initiation site of a cloned ribosomal RNA gene of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6043–6058. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota J., Iwamoto A., Suzuki A., Yamaguchi-Tejima S., Kitamura Y., Yoshikura H. Friend erythroleukaemia cell mutants defective in viral gene expression. J Gen Virol. 1984 Feb;65(Pt 2):429–435. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-2-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikura H., Tejima S., Kuchino T., Segawa K., Odaka T. Characterization of N-type and dually permissive cells segregated from mouse fibroblasts whose Fv-1 phenotype could be modified by another independently segregating gene(s). J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.145-152.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikura H. Ultraviolet sensitivity of helper function of murine leukemia virus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):76–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]