Abstract
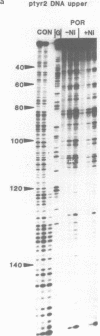
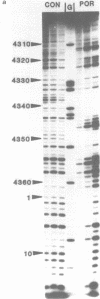
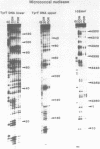
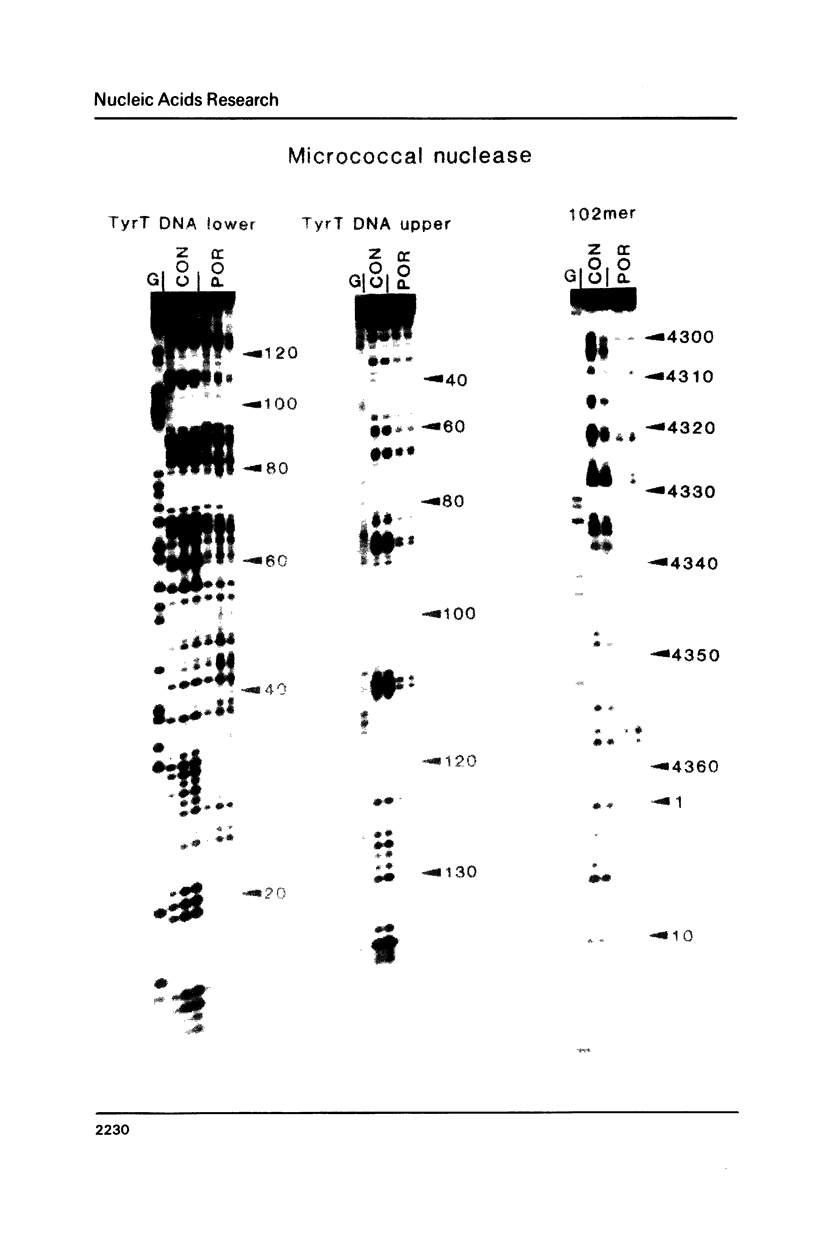
The DNA sequence preferences of the compound meso-tetra-(4-N-methyl(pyridyl) porphyrin and its nickel complex have been investigated by means of footprinting experiments on several DNA fragments, using DNAase I and micrococcal nuclease as footprinting agents. A complex pattern of both AT and GC-protected sites was found. Ligand-induced long-range conformational changes were inferred in several instances to be related to the observed large-scale blockages of enzymatic cutting.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banville D. L., Marzilli L. G., Strickland J. A., Wilson W. D. Comparison of the effects of cationic porphyrins on DNA properties: influence of GC content of native and synthetic polymers. Biopolymers. 1986 Oct;25(10):1837–1858. doi: 10.1002/bip.360251003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banville D. L., Marzilli L. G., Wilson W. D. 31P NMR and viscometric studies of the interaction of meso-tetra(4-N-methylpyridyl) porphine and its Ni(II) and Zn(II) derivatives with DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 31;113(1):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90444-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvlin M. J., Mark E., Fiel R., Howard J. C. Intercalative and nonintercalative binding of large cationic porphyrin ligands to polynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):6141–6154. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.6141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier D. A., Neidle S., Brown J. R. Molecular models for the interaction of the anti-tumour drug nogalamycin with DNA. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 15;33(18):2877–2880. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Lomonossoff G. P., Laskey R. A. High sequence specificity of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2659–2673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiel R. J., Howard J. C., Mark E. H., Datta Gupta N. Interaction of DNA with a porphyrin ligand: evidence for intercalation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3093–3118. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiel R. J., Munson B. R. Binding of meso-tetra (4-N-methylpyridyl) porphine to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2835–2842. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. DNA structural variations produced by actinomycin and distamycin as revealed by DNAase I footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9271–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. Nucleotide sequence binding preferences of nogalamycin investigated by DNase I footprinting. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4349–4356. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2643–2658. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Murphy M. J., McConnell D. J., OhUigin C. A comparative study of the interaction of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis (N-methylpyridinium-4-yl)porphyrin and its zinc complex with DNA using fluorescence spectroscopy and topoisomerisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):167–184. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low C. M., Drew H. R., Waring M. J. Sequence-specific binding of echinomycin to DNA: evidence for conformational changes affecting flanking sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4865–4879. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack R. F., Garrity P., Ehrlich B., Davis C. B., Gibbs E. J., Orloff G., Giartosio A., Turano C. The influence of ionic strength on the binding of a water soluble porphyrin to nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5919–5931. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack R. F., Gibbs E. J., Villafranca J. J. Interactions of porphyrins with nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2406–2414. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack R. F., Gibbs E. J., Villafranca J. J. Interactions of porphyrins with nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1983 Nov 8;22(23):5409–5417. doi: 10.1021/bi00292a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack R. F., Sidney D., Hunt P. A., Snowden E. A., Gibbs E. J. Interactions of water soluble porphyrins with Z-poly(dG-dC). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3927–3943. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B., Skorobogaty A., Dabrowiak J. C. DNA cleavage specificity of a group of cationic metalloporphyrins. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6875–6883. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]