Abstract
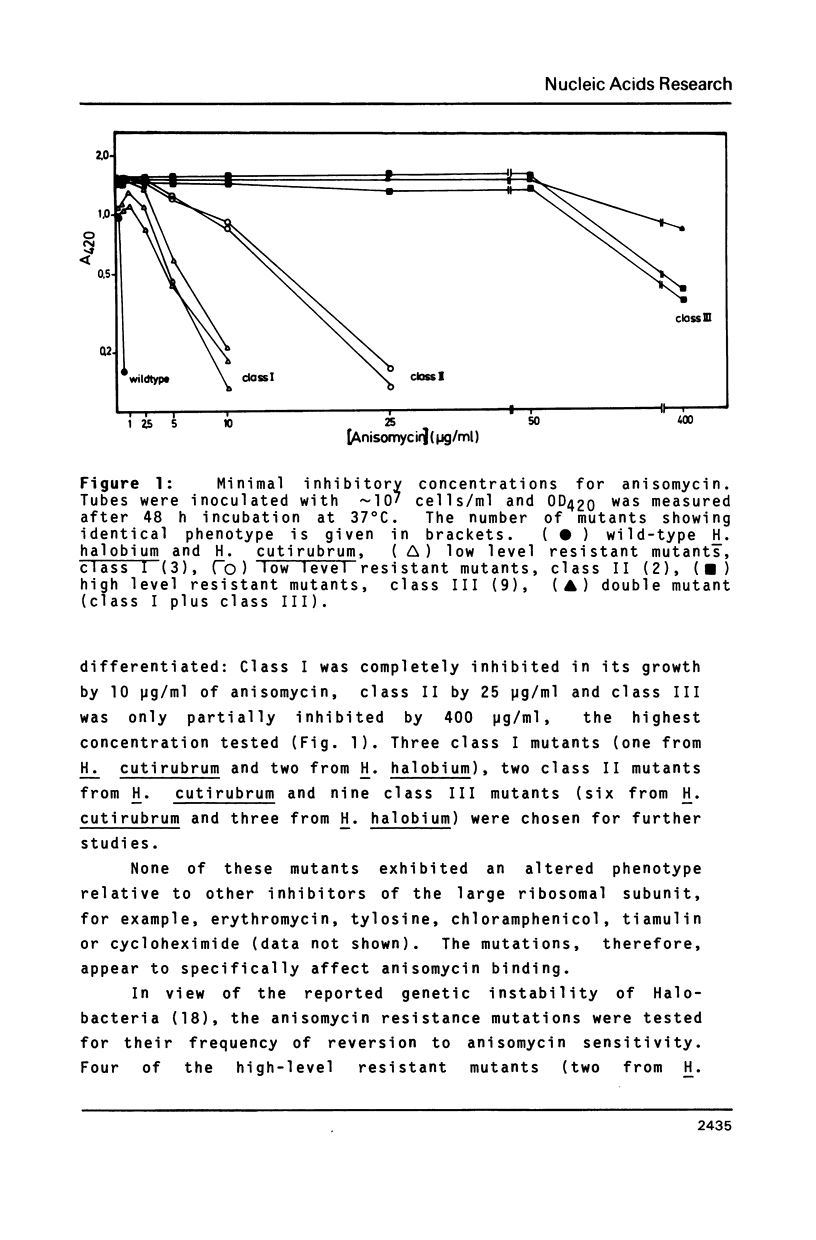
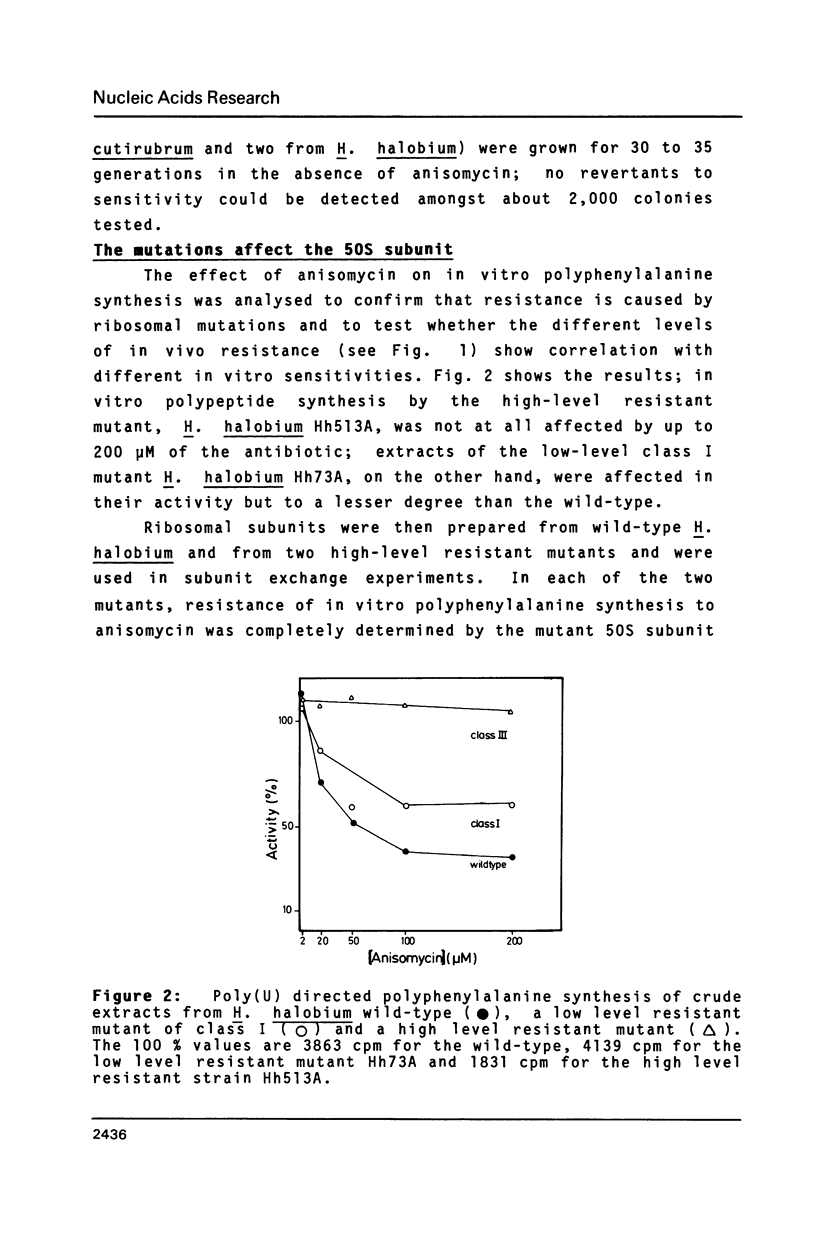
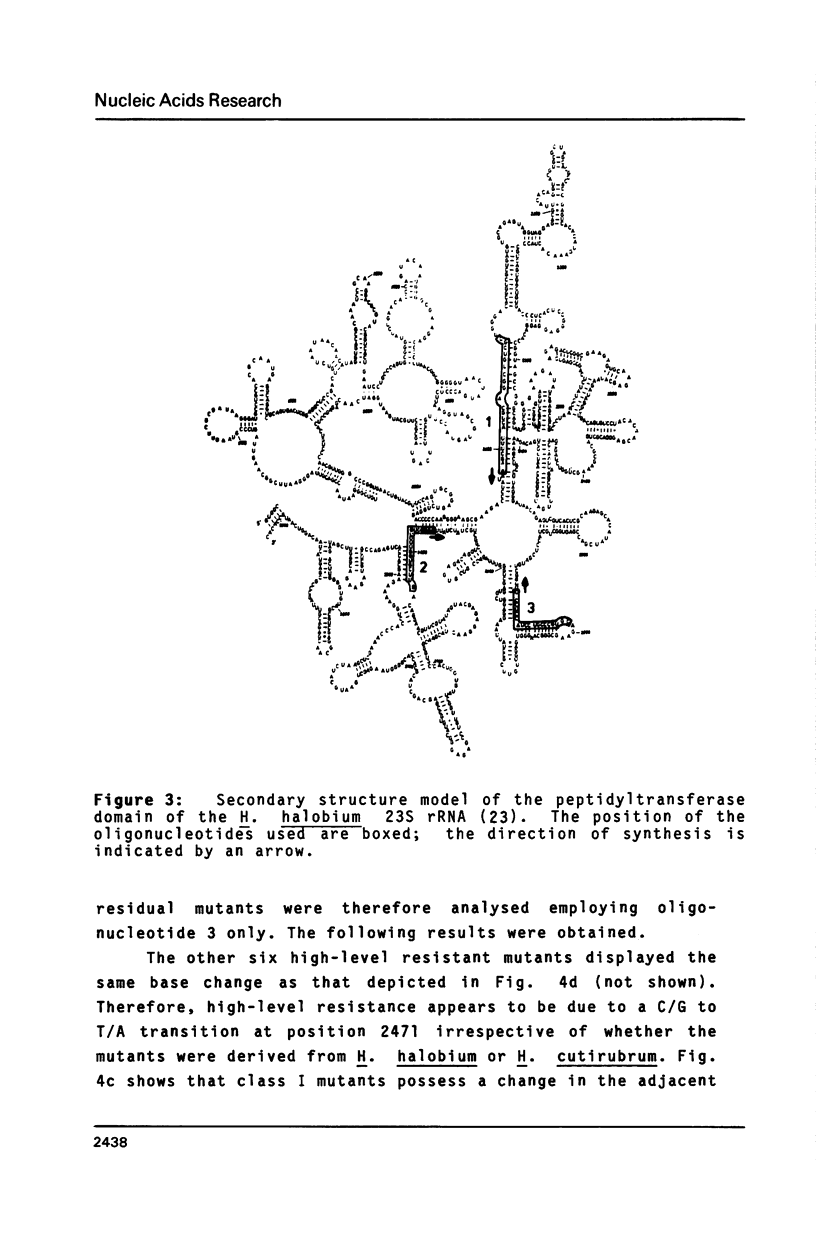
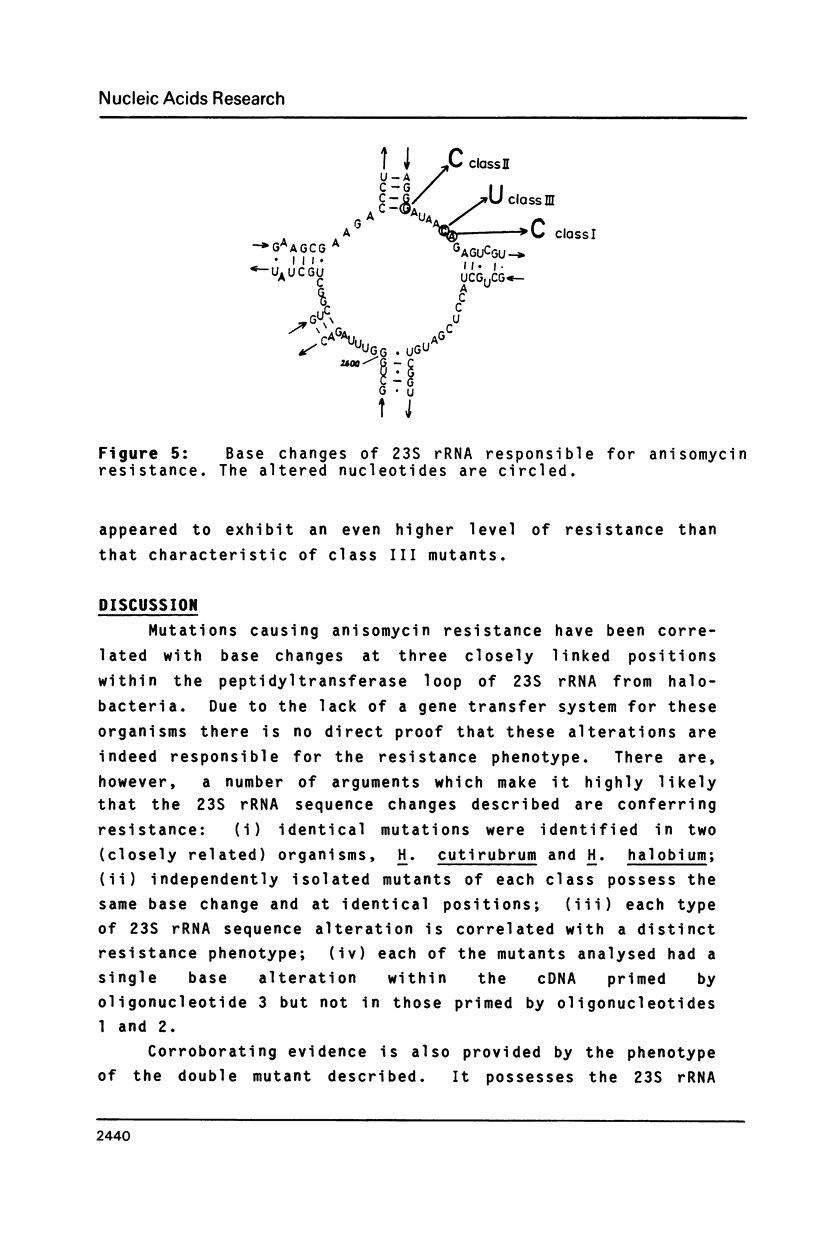
Halobacterium (H.) halobium and H. cutirubrum mutants resistant to the anti-80S ribosome targeted inhibitor anisomycin were isolated. Three classes of mutants were obtained: Class I displayed a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) to anisomycin of 10 micrograms/ml, class II of 25 micrograms/ml and class III of at least 400 micrograms/ml. In vitro polyphenylalanine synthesis assays demonstrated that in those cases tested resistance was a property of the large ribosomal subunit. By primer extension analysis, each mutation class could be correlated with a distinct base change within the peptidyltransferase loop of 235 rRNA. In class I A2472 was changed to C, in class II G2466 was changed to C and in the high-level resistant class III C2471 was replaced by U. A. double mutant - obtained by selection of a class I mutant for high-level anisomycin resistance - acquired the C2471 to U replacement of class III in addition to the class I mutation. The results provide information on the action of a eukaryotic protein synthesis inhibitor on archaebacterial ribosomes and demonstrate the suitability of organisms with a single rRNA transcriptional unit on the chromosome for direct selection of mutations in ribosomal RNA.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M., Vazquez D. (3H)anisomycin binding to eukaryotic ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 25;84(4):603–623. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauclerk A. A., Hummel H., Holmes D. J., Böck A., Cundliffe E. Studies of the GTPase domain of archaebacterial ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):245–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanc H., Adams C. W., Wallace D. C. Different nucleotide changes in the large rRNA gene of the mitochondrial DNA confer chloramphenicol resistance on two human cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5785–5795. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano P., Teichner A., Londei P., Acca M., Nicolaus B., Sanz J. L., Amils R. Insensitivity of archaebacterial ribosomes to protein synthesis inhibitors. Evolutionary implications. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):811–816. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Fresno M., Vazquez D. Narciclasine: an antitumour alkaloid which blocks peptide bond formation by eukaryotic ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 1;52(2):236–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80813-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman J. D., Lau R. H., Doolittle W. F. The number, physical organization and transcription of ribosomal RNA cistrons in an archaebacterium: Halobacterium halobium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1321–1333. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui I., Dennis P. P. Characterization of the ribosomal RNA gene clusters in Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):899–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez A., Sanchez L., Vazquez D. Simultaneous ribosomal resistance to trichodermin and anisomycin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 2;383(4):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90312-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Weidinger G., Goebel W. Characterization of plasmids in halobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):369–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.369-374.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slott E. F., Jr, Shade R. O., Lansman R. A. Sequence analysis of mitochondrial DNA in a mouse cell line resistant to chloramphenicol and oligomycin. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1694–1702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



