Abstract
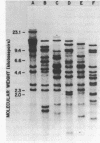
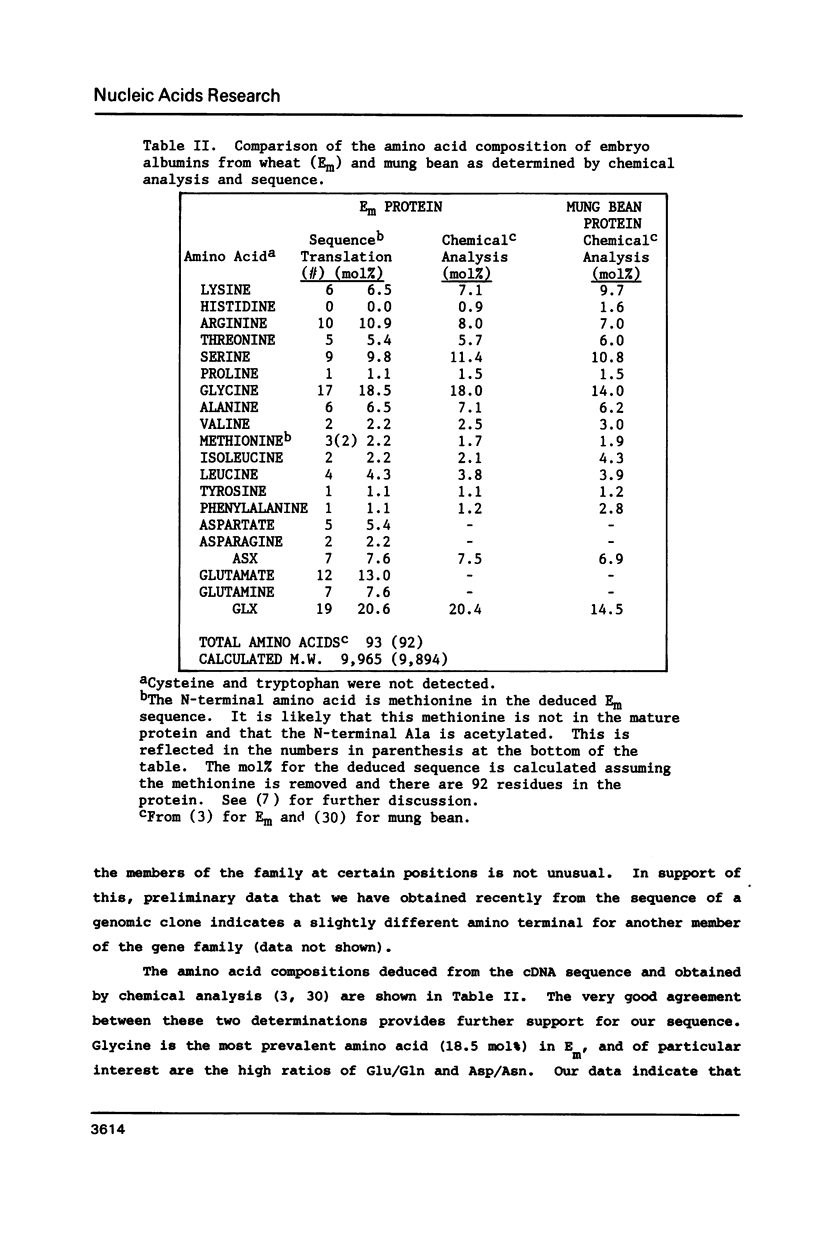
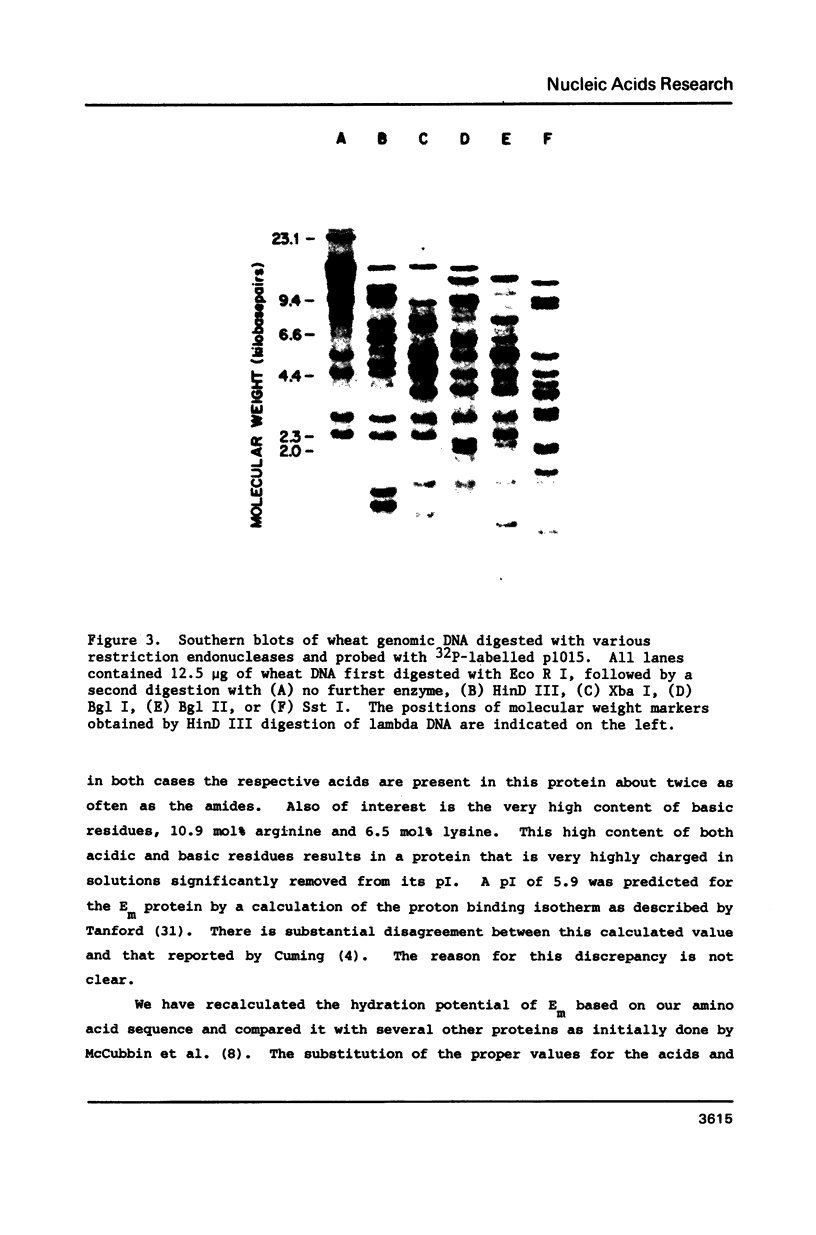
The nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone isolated from developing wheat embryos and encoding the Em protein is reported. The entire coding region for Em and the 3' non-translated flank are contained within this clone. The amino acid sequence deduced for Em is very rich in glycine (18 mol%) as well as both basic and acidic residues. The molecular weight of the protein is ca. 9,900 daltons. The deduced sequence is supported by direct amino acid sequencing of cyanogen bromide cleavage fragments obtained from purified Em protein. Em is shown by Southern blots to be a product of a gene family of approximately ten members.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson O. D., Litts J. C., Gautier M. F., Greene F. C. Nucleic acid sequence and chromosome assignment of a wheat storage protein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8129–8144. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. D., Smith J. B. Nuclear dna amounts in angiosperms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 May 27;274(933):227–274. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1976.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuming A. C. Developmental regulation of gene expression in wheat embryos. Molecular cloning of a DNA sequence encoding the early-methionine-labelled (Em) polypeptide. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):351–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuming A. C., Lane B. G. Protein synthesis in imbibing wheat embryos. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(2):217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Herdt E., De Voeght F., Clauwaert J., Kondo M., Slegers H. A cryptobiosis-specific 19S protein complex of Artemia salina gastrulae. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):9–17. doi: 10.1042/bj1940009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn R., McCoy J., Simsek M., Majumdar A., Chang S. H., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. The bacteriorhodopsin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6744–6748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fristensky B., Lis J., Wu R. Portable microcomputer software for nucleotide sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6451–6463. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzelczak Z. F., Sattolo M. H., Hanley-Bowdoin L. K., Kennedy T. D., Lane B. G. Synthesis and turnover of proteins and mRNA in germinating wheat embryos. Can J Biochem. 1982 Mar;60(3):389–397. doi: 10.1139/o82-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa Y., Nojima H., Nukiwa N., Ishizuka M., Nakajima T., Yasuhara T., Tanaka T., Oshima T. High guanine plus cytosine content in the third letter of codons of an extreme thermophile. DNA sequence of the isopropylmalate dehydrogenase of Thermus thermophilus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):2956–2960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislev N., Rubenstein I. Utility of ethidium bromide in the extraction from whole plants of high molecular weight maize DNA. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1140–1143. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson R., Messing J. Apple II software for M13 shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):39–49. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthe D. S., Quatrano R. S. Transcription in Isolated Wheat Nuclei: I. ISOLATION OF NUCLEI AND ELIMINATION OF ENDOGENOUS RIBONUCLEASE ACTIVITY. Plant Physiol. 1980 Feb;65(2):305–308. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Rafalski A., Peterson D., Söll D. A wheat HMW glutenin subunit gene reveals a highly repeated structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8729–8737. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. W., Lane B. G. Relation of protein synthesis in imbibing wheat embryos to the cell-free translational capacities of bulk mRNA from dry and imbibing embryos. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5965–5970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L. A simple method to recover intact high molecular weight RNA and DNA after electrophoretic separation in low gelling temperature agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. D., Quatrano R. S., Cuming A. C. Em polypeptide and its messenger RNA levels are modulated by abscisic acid during embryogenesis in wheat. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):501–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]