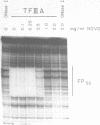
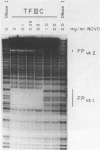
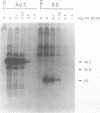
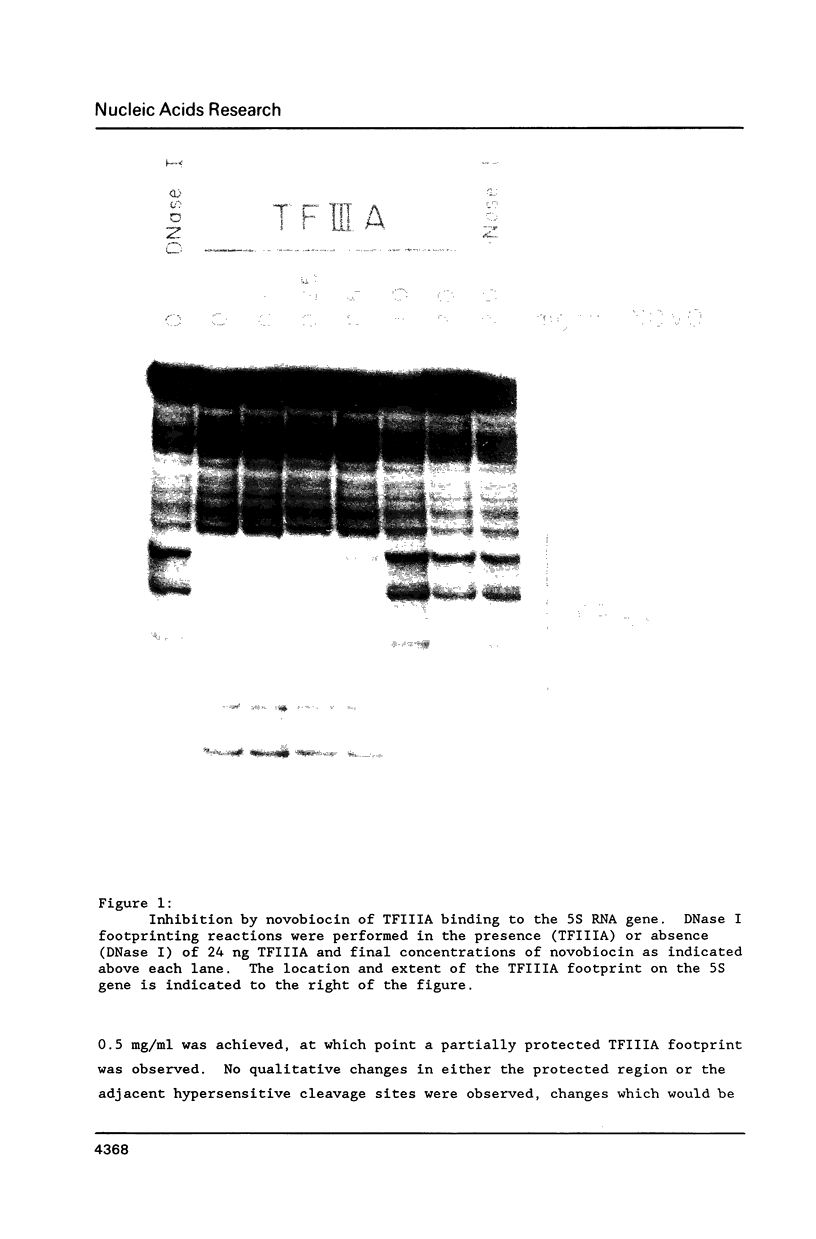
Abstract
Novobiocin has been shown to inhibit class III gene transcription from both chromatin and non-chromatin templates. Since novobiocin is a well characterized inhibitor of type II DNA topoisomerases, it has been postulated that a gyrase activity is necessary for transcription. Using DNase I footprinting, we show here that novobiocin inhibits the specific binding of polymerase III transcription factors TFIIIA and TFIIIC to the promoters of the 5S RNA and VA RNA genes, respectively. Concentrations of novobiocin employed were comparable to those necessary to inhibit HeLa topoisomerase II. In vitro transcription assays, performed under equivalent conditions, demonstrated that similar novobiocin concentrations were necessary for transcription inhibition. These results strongly suggest that novobiocin interferes with transcription by inhibiting specific protein-DNA interactions.
Full text
PDF


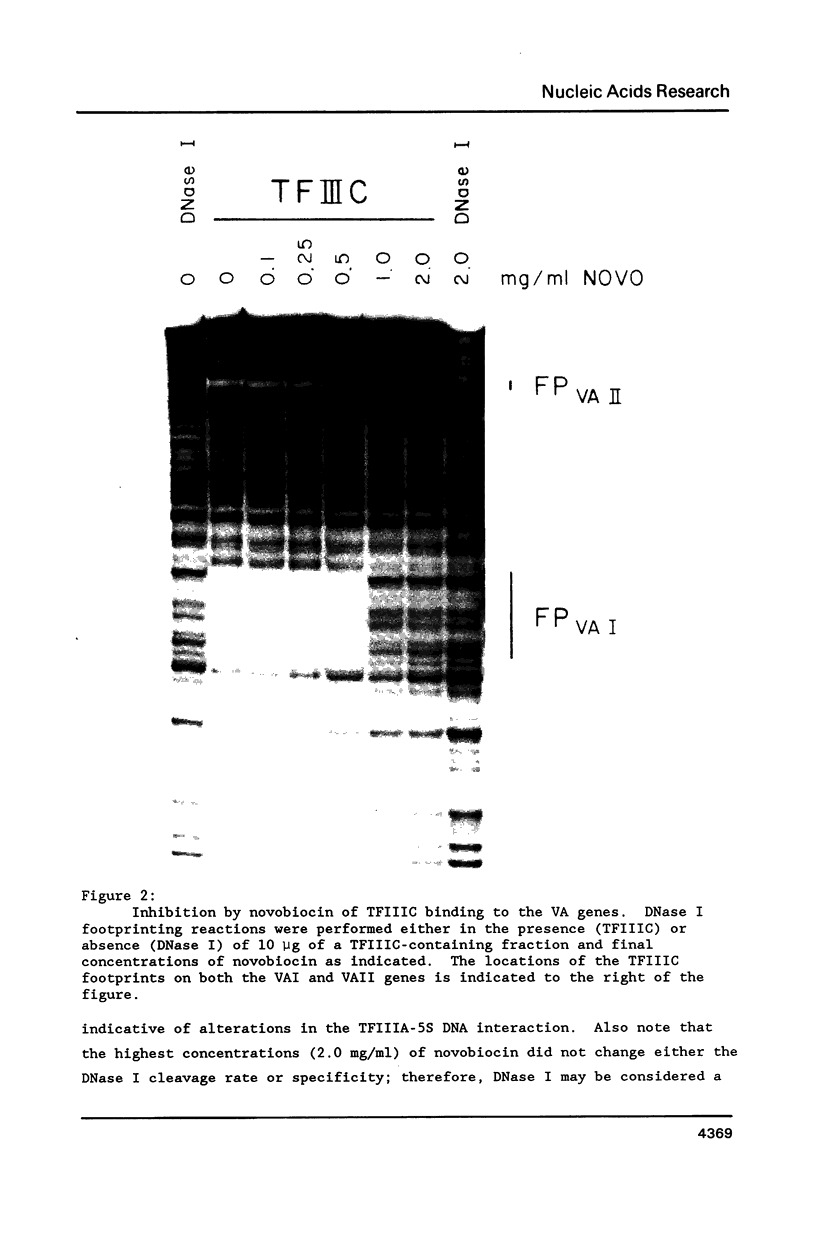
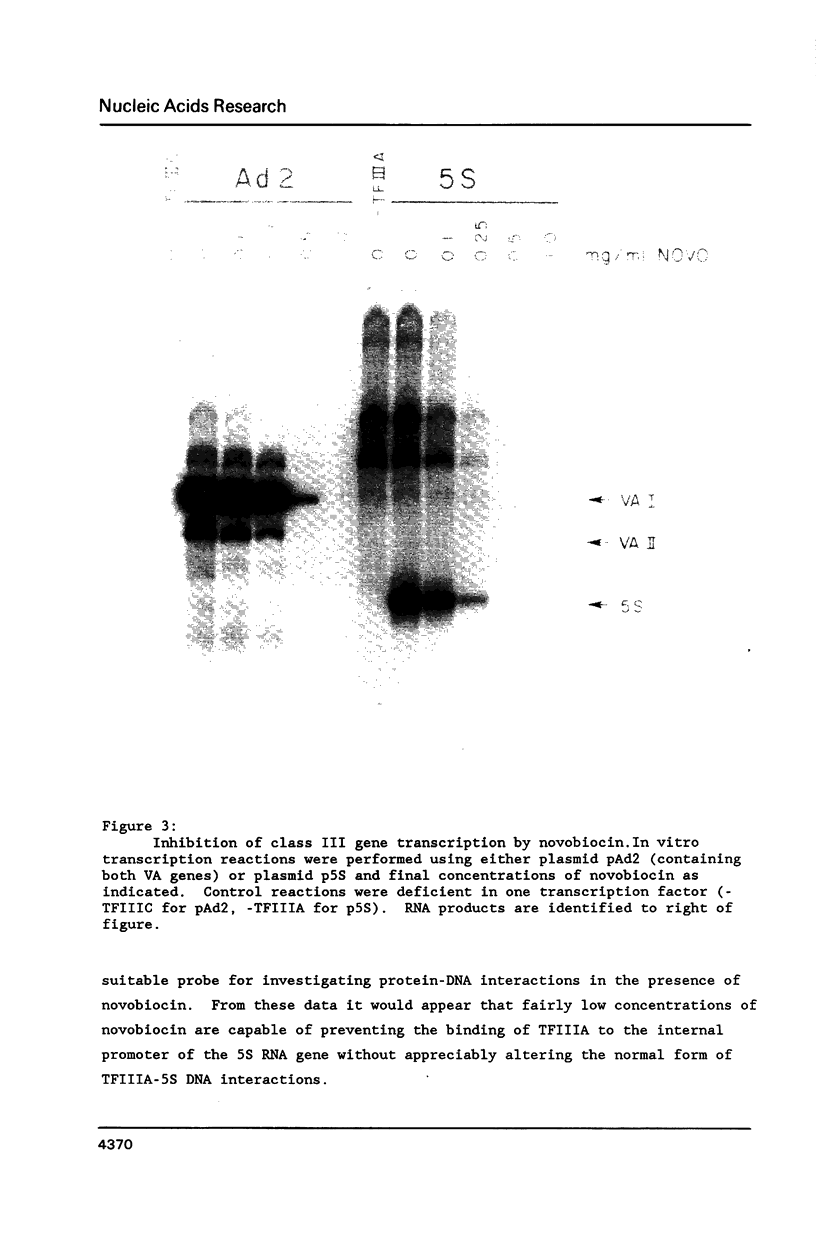
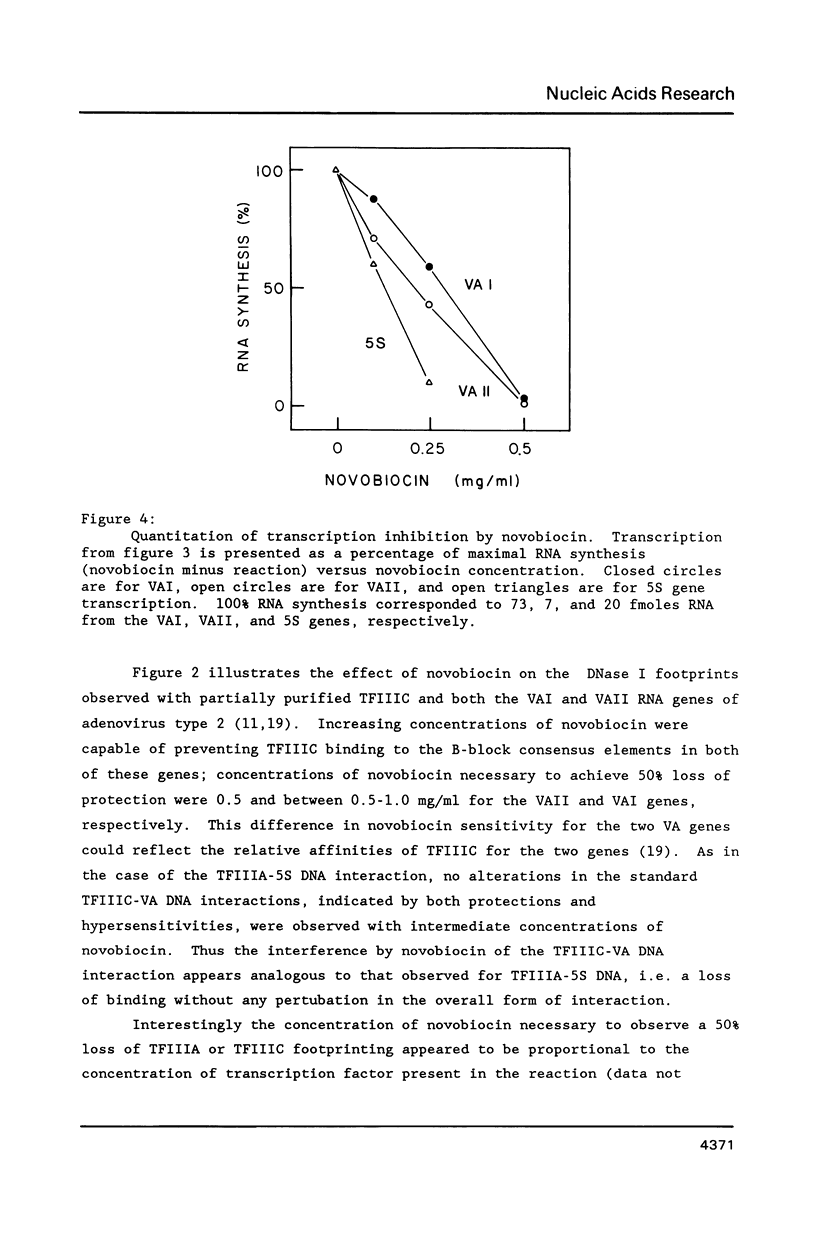



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieker J. J., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Formation of a rate-limiting intermediate in 5S RNA gene transcription. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. F., Gerrard S. P., Cozzarelli N. R. Analysis of RNA polymerase III transcription complexes by gel filtration. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4309–4317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Bresnahan D., Thompson S., Sealy L., Chalkley R. Novobiocin precipitates histones at concentrations normally used to inhibit eukaryotic type II topoisomerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3671–3686. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felts S. J., Weil P. A., Chalkley R. Novobiocin inhibits interactions required for yeast TFIIIB sequestration during stable transcription complex formation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1493–1506. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Novobiocin and coumermycin inhibit DNA supercoiling catalyzed by DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Blangy D. In vitro transcription by Xenopus oocytes RNA polymerase III requires a DNA topoisomerase II activity. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):151–155. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M. Novobiocin inhibits RNA polymerase III transcription in vitro by a mechanism distinct from DNA topoisomerase II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2075–2088. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. Binding of Xenopus transcription factor A to 5S RNA and to single stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2745–2758. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T., Brutlag D. ATP-dependent DNA topoisonmerase from D. melanogaster reversibly catenates duplex DNA rings. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Ryoji M., Worcel A. Gyration is required for 5S RNA transcription from a chromatin template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1305–1309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Liu L. F., Englund P. T. A homogeneous type II DNA topoisomerase from HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9334–9339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Cotten M., Chalkley R. Novobiocin inhibits passive chromatin assembly in vitro. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3305–3311. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., Brown D. D. Formation and stability of the 5 S RNA transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2483–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Higgins N. P., Brown P. O., Peebles C. L., Cozzarelli N. R. Energy coupling in DNA gyrase and the mechanism of action of novobiocin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4838–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G. Multiple proteins bind to VA RNA genes of adenovirus type 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1021–1031. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]