Abstract
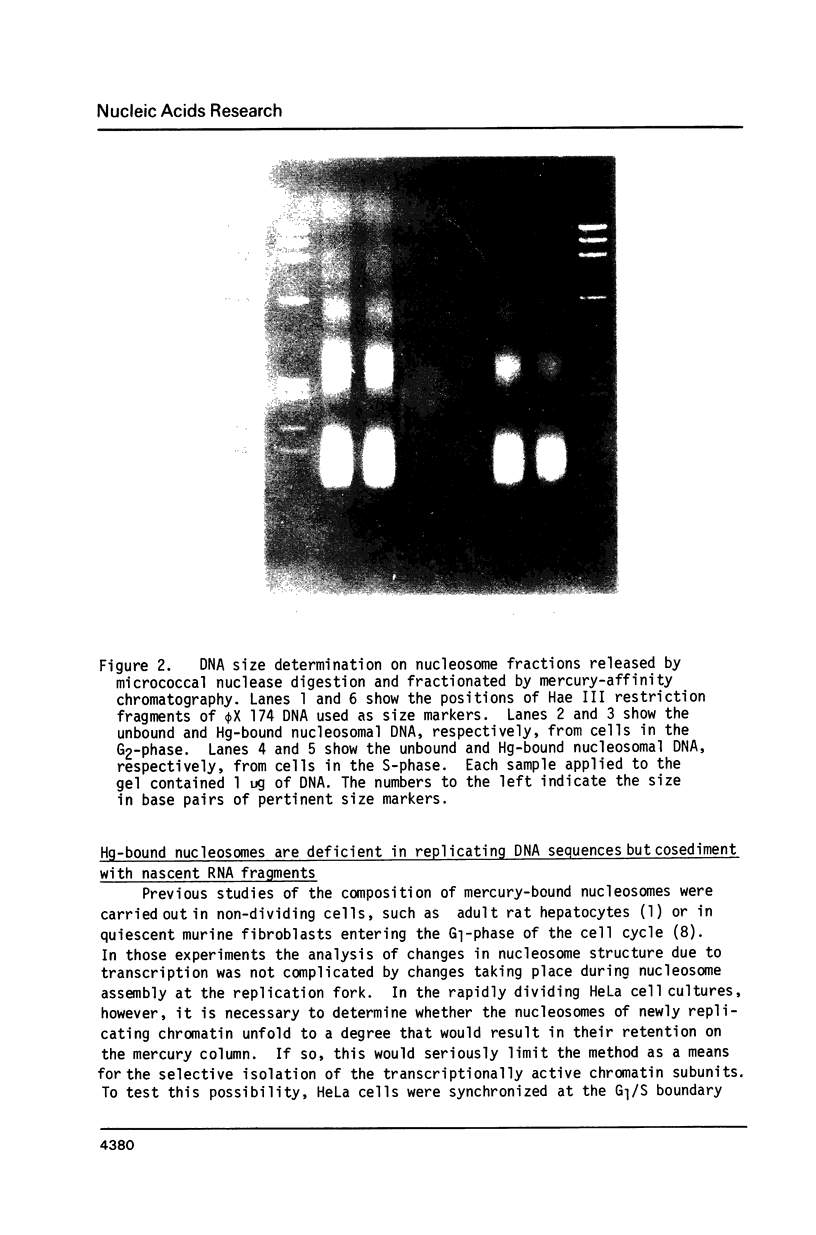
Unfolding of the nucleosomes in transcriptionally active chromatin uncovers the sulfhydryl groups of histone H3 and permits the selective recovery of the unfolded nucleosomes by mercury-affinity chromatography. This new technique has been used to compare the nucleosomal proteins and their postsynthetic modifications in the unfolded and the compactly beaded nucleosomes of HeLa cells in logarithmic growth, and at different stages of the growth cycle. The Hg-bound nucleosomes are shown to be deficient in replicating DNA sequences, but to remain associated with fragments of nascent RNA chains (or RNP particles) during gradient centrifugations. Both nucleosome fractions contain a full complement of "core" histones but differ with respect to postsynthetic modifications. The Hg-bound nucleosomes contain high levels of the tri- and tetra-acetylated forms of histones H3 and H4. The unbound nucleosomes are deficient in acetylated histones but enriched in phosphorylated H2A. In synchronized HeLa cells, histone H2A and H4 gene sequences occur in the Hg-bound nucleosomes during the S-phase when their transcription takes place, but not in the G2-phase when the genes are repressed.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLFREY V. G., FAULKNER R., MIRSKY A. E. ACETYLATION AND METHYLATION OF HISTONES AND THEIR POSSIBLE ROLE IN THE REGULATION OF RNA SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:786–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfageme C. R., Zweidler A., Mahowald A., Cohen L. H. Histones of Drosophila embryos. Electrophoretic isolation and structural studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3729–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Schwab M., Lin C. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Homogeneously staining chromosomal regions contain amplified copies of an abundantly expressed cellular oncogene (c-myc) in malignant neuroendocrine cells from a human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., Sasi R., Fasman G. D. Biochemical and physiochemical characterization of chromatin fractions with different degrees of solubility isolated from chicken erythrocyte nuclei. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):1981–1988. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., van Holde K. E. Histone hyperacetylation: its effects on nucleosome conformation and stability. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1421–1428. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach L. L., Marashi F., Plumb M., Stein G., Stein J. Inhibition of DNA replication coordinately reduces cellular levels of core and H1 histone mRNAs: requirement for protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1618–1625. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavykin S. G., Usachenko S. I., Lishanskaya A. I., Shick V. V., Belyavsky A. V., Undritsov I. M., Strokov A. A., Zalenskaya I. A., Mirzabekov A. D. Primary organization of nucleosomal core particles is invariable in repressed and active nuclei from animal, plant and yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3439–3459. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode J., Henco K., Wingender E. Modulation of the nucleosome structure by histone acetylation. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(1):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. W., Love W. E., Wang B. C., Hamlin R., Nguyen H. X., Moudrianakis E. N. Crystallographic structure of the octameric histone core of the nucleosome at a resolution of 3.3 A. Science. 1985 May 3;228(4699):546–553. doi: 10.1126/science.3983639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Histone H3 disulfide dimers and nucleosome structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5519–5523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candido E. P., Reeves R., Davie J. R. Sodium butyrate inhibits histone deacetylation in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron F., Thomas J. O. Exchange of histone H1 between segments of chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 15;146(4):513–537. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Abmayr S. M., Fleischmann G., Lowenhaupt K., Elgin S. C., Keene M. A., Howard G. C. Chromatin structure and gene activity: the role of nonhistone chromosomal proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;13(1):1–86. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrysogelos S., Riley D. E., Stein G., Stein J. A human histone H4 gene exhibits cell cycle-dependent changes in chromatin structure that correlate with its expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7535–7539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criado M., Sarin V., Fox J. L., Lindstrom J. Evidence that the acetylcholine binding site is not formed by the sequence alpha 127-143 of the acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):2839–2846. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. R., Saunders C. A. Chemical composition of nucleosomes among domains of calf thymus chromatin differing in micrococcal nuclease accessibility and solubility properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12574–12580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieterich A. E., Axel R., Cantor C. R. Dynamics of nucleosome structure studied by fluorescence. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):199–206. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebralidse K. K., Mirzabekov A. D. One-domain interaction of histone H4 with nucleosomal core DNA is restricted to a narrow DNA segment. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 1;194(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan P. A., Levy-Wilson B. Structure of transcriptionally active and inactive nucleosomes from butyrate-treated and control HeLa cells. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3695–3702. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C., Weintraub H. Chromosomal proteins and chromatin structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:725–774. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshaghpour H., Dieterich A. E., Cantor C. R., Crothers D. M. Singlet-singlet energy transfer studies of the internal organization of nucleosomes. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1797–1805. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halleck M. S., Gurley L. R. Histone H2A subfractions and their phosphorylation in cultured Peromyscus cells. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Feb;125(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halleck M. S., Gurley L. R. Histone variants and histone modifications in chromatin fractions from heterochromatin-rich Peromyscus cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Apr;138(2):271–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno M. L., Chrysogelos S. A., Stein G. S., Stein J. L. Reversible changes in the nucleosomal organization of a human H4 histone gene during the cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5364–5370. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S., Erard M., Burggraf E., Couppez M., Sautière P., Champagne M., Van Regenmortel M. H. Immunochemical detection of changes in chromatin subunits induced by histone H4 acetylation. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):939–944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01275.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Stein J., Stein G. Coordinate regulation of multiple histone mRNAs during the cell cycle in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2391–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior C. P., Cantor C. R., Johnson E. M., Allfrey V. G. Incorporation of exogenous pyrene-labeled histone into Physarum chromatin: a system for studying changes in nucleosomes assembled in vivo. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):597–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior C. P., Cantor C. R., Johnson E. M., Littau V. C., Allfrey V. G. Reversible changes in nucleosome structure and histone H3 accessibility in transcriptionally active and inactive states of rDNA chromatin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90561-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. Transcriptionally active chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 10;782(4):343–393. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs M. G., Whittaker R. G., Neumann J. R., Ingram V. M. n-Butyrate causes histone modification in HeLa and Friend erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):462–464. doi: 10.1038/268462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha E., Davie J. R., van Holde K. E., Weintraub H. Differential salt fractionation of active and inactive genomic domains in chicken erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8558–8563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. M., Garrard W. T. Differentiation-dependent chromatin alterations precede and accompany transcription of immunoglobulin light chain genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8534–8544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargan D. R., Butterworth P. H. Eukaryotic ternary transcription complexes: transcription complexes of RNA polymerase II are associated with histone-containing, nucleosome-like particles in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):3805–3822. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. DNA associated with hyperacetylated histone is preferentially digested by DNase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):1863–1876. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. The effect of sodium butyrate on histone modification. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Structure of chromatin containing extensively acetylated H3 and H4. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Levels of c-myc oncogene mRNA are invariant throughout the cell cycle. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):363–366. doi: 10.1038/314363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Augustine R., Schulman H. Calcium-dependent phosphorylation of histone H3 in butyrate-treated HeLa cells. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):74–76. doi: 10.1038/287074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Wilson L. B., deRiel J. K., Villa-komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Insertion of synthetic copies of human globin genes into bacterial plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):563–581. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong N. T., Candido E. P. Histone H3 thiol reactivity as a probe of nucleosome structure. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8263–8268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau P., Thorne A. W., Imai B. S., Matthews H. R., Bradbury E. M. Thermal denaturation studies of acetylated nucleosomes and oligonucleosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zama M., Olins D. E., Wilkinson-Singley E., Olins A. L. Reversibility of nucleosome conformation perturbed by urea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 29;85(4):1446–1452. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong R., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. The primary structure and expression of four cloned human histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7409–7425. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]