Abstract
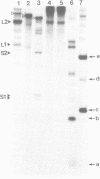
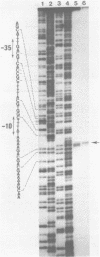
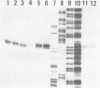
In order to find the promoter region of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase [EC 4.1.1.31] gene (ppc), in vitro transcription was performed using truncated DNA fragments as templates. Transcription mapping showed three promoters as candidates, but only one of them could be assigned to the promoter of ppc gene, considering the nucleotide sequence of its coding region (Fujita, N., Miwa, T., Ishijima, S., Izui, K. and Katsuki, H. (1984) J. Biochem. 95, 909-916). Nuclease S1 mapping showed that the in vivo and in vitro transcription initiation sites are identical and that the site lies 91 or 92 nucleotides upstream the translation initiation site. No alteration of the transcription initiation site was observed whether the cells were starved for an amino acid or grown on various carbon sources. The sequences of the -10 and -35 regions were fairly in accordance with the consensus sequences hitherto reported. Some features of the sequence around the promoter region were discussed.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H. Autoregulation of the Escherichia coli crp gene: CRP is a transcriptional repressor for its own gene. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90504-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Kawamukai M., Ishihama A. Cloning and promoter analysis of the Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3451–3465. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiil N., Friesen J. D. Isolation of "relaxed" mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):729–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.729-731.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita N., Miwa T., Ishijima S., Izui K., Katsuki H. The primary structure of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence of the ppc gene and deduced amino acid sequence. J Biochem. 1984 Apr;95(4):909–916. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda R., Iwakura Y., Ishihama A. Heterogeneity of RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli. I. A new holoenzyme containing a new sigma factor. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar;83(3):353–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant J. A. Stringent control in E. coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:393–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez N., Wiggs J., Chamberlin M. J. A simple procedure for resolution of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme from core polymerase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90521-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui K., Sabe H., Katsuki H. Increased synthesis of phosphoenolypyruvate carboxylase in a strain of Escherichia coli bearing a ColE1-ppc+ hybrid plasmid. FEBS Lett. 1981 Oct 26;133(2):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80531-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajitani M., Ishihama A. Determination of the promoter strength in the mixed transcription system. II. Promoters of ribosomal RNA, ribosomal protein S1 and recA protein operons from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3873–3888. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajitani M., Ishihama A. Determination of the promoter strength in the mixed transcription system: promoters of lactose, tryptophan and ribosomal protein L10 operons from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):671–686. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajitani M., Ishihama A. Promoter selectivity of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Differential stringent control of the multiple promoters from ribosomal RNA and protein operons. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1951–1957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Nierman W. C., Chamberlin M. J. A direct effect of guanosine tetraphosphate on pausing of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase during RNA chain elongation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2787–2797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaki T., Murakami H., Taguchi M., Izui K., Katsuki H. Stringent control of intermediary metabolism in Escherichia coli: pyruvate excretion by cells grown on succinate. J Biochem. 1981 Nov;90(5):1437–1444. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlarz D., Garreau H., Buc H. Regulation of the amount and of the activity of phosphofructokinases and pyruvate kinases in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 13;381(2):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marko M. A., Chipperfield R., Birnboim H. C. A procedure for the large-scale isolation of highly purified plasmid DNA using alkaline extraction and binding to glass powder. Anal Biochem. 1982 Apr;121(2):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90497-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Flavell R. A. A method for the recovery of DNA from agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2321–2332. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi M., Izui K., Katsuki H. Activation of Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase by guanosine-5'-diphosphate-3'-diphosphate. FEBS Lett. 1977 May 15;77(2):270–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Nishikido T., Izui K., Katsuki H. Control of the synthesis of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1970 Apr;67(4):567–575. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]