Abstract
Per definition, ER exit sites are COPII vesiculation events at the surface of the ER and in higher plants are only visualizable in the electron microscope through cryofixation techniques. Fluorescent COPII labeling moves with Golgi stacks and locates to the interface between the ER and the Golgi. In contrast, the domain of the ER where retrograde COPI vesicles fuse, i.e., ER import sites (ERIS), has remained unclear. To identify ERIS we have employed ER-located SNAREs and tethering factors. We screened several SNAREs (SYP81, the SYP7 family, and USE1) to find a SNARE whose overexpression did not disrupt ER-Golgi traffic and which gave rise to discrete fluorescent punctae when expressed with an XFP tag. Only the Qc-SNARE SYP72 fulfilled these criteria. When coexpressed with SYP72-YFP, both the type I-membrane protein RFP-p24δ5 and the luminal marker CFP-HDEL whose ER localization are due to an efficient COPI-mediated recycling, form nodules along the tubular ER network. SYP72-YFP colocalizes with these nodules which are not seen when RFP-p24δ5 or CFP-HDEL is expressed alone or when SYP72-YFP is coexpressed with a mutant form of RFP-p24δ5 that cannot exit the ER. SYP72-YFP does not colocalize with Golgi markers, except when the Golgi stacks are immobilized through actin depolymerization. Endogenous SYP7 SNAREs, also colocalize with immobilized COPII/Golgi. In contrast, XFP-tagged versions of plant homologs to TIP20 of the Dsl1 COPI-tethering factor complex, and the COPII-tethering factor p115 colocalize perfectly with Golgi stacks irrespective of the motile status. These data suggest that COPI vesicle fusion with the ER is restricted to periods when Golgi stacks are stationary, but that when moving both COPII and COPI vesicles are tethered and collect in the ER-Golgi interface. Thus, the Golgi stack and an associated domain of the ER thereby constitute a mobile secretory and recycling unit: a unique feature in eukaryotic cells.
Keywords: ER export sites, ER import sites, Golgi motility, secretory unit, SNAREs, tobacco
Introduction
In all eukaryotic organisms protein trafficking between the ER and the Golgi apparatus is bidirectional and dependent on the COPI and COPII vesiculation machineries (Lee et al., 2004; Jürgens and Geldner, 2007). ER export (or exit) sites (ERES) are discrete domains of the ER characterized by local accumulations of COPII proteins (heterodimers of Sec23/24 and heterotetramers of Sec31/13) forming vesicles through which secretory proteins leave the ER (Budnik and Stephens, 2009; Marti et al., 2010; Miller and Barlowe, 2010; Zanetti et al., 2012). ERES and their relationship to the Golgi apparatus are fundamentally different in mammalian and higher plant cells. In mammals, ERES are found at regions of the ER, termed transitional ER, characterized by a lack of ribosomes and the presence of Sec16 in addition to COPII dimers (Hughes et al., 2009). Each ERES then gives rise to a single intermediate compartment termed ER-Golgi Intermediate Compartment (ERGIC) or Vesicular Tubular Complex (VTC) through the homotypic fusion of COPII-carriers (Zeuschner et al., 2006; Hughes et al., 2009). This structure then transports secretory cargo to a sessile peri-nuclear Golgi complex several μm distant along microtubules (Appenzeller-Herzog and Hauri, 2006). In contrast, the higher plant Golgi apparatus is polydisperse with individual Golgi stacks moving rapidly (several μm min−1) along actin microfilaments that lie parallel to ER tubules (Boevink et al., 1998; Nebenführ et al., 1999). Since, there is no ERGIC in higher plants homotypic COPII vesicle fusion is thought to create the first cis-cisterna of the Golgi stack (Yang et al., 2005; Kang and Staehelin, 2008).
COPII fluorescence has been shown on several occasions to colocalize with Golgi stacks in higher plants (daSilva et al., 2004; Hanton et al., 2006; Marti et al., 2010). Significantly, as a Golgi stack moves, the COPII fluorescent signal moves with it suggesting a tight coupling between ERES and Golgi stacks (Sparkes et al., 2009; Hawes, 2012). Consequently, ERES and Golgi stacks in plants have been described as constituting a “secretory unit” (daSilva et al., 2004; Hawes et al., 2008). However, it has been recently shown that this COPII fluorescence does not locate to the surface of the ER, i.e., does not represent ERES sensu stricto, but instead reflects a temporary accumulation of COPII-coated carriers in the narrow (<500 nm) interface between the ER and the overlying Golgi stack (Langhans et al., 2012).
The acknowledged vehicle for retrograde transport into the ER is the COPI vesicle, valid for mammals (Beck et al., 2009; Hsu and Yang, 2009), as well as for plants (Pimpl et al., 2000; Robinson et al., 2007). However, there is virtually no information concerning the actual sites of COPI vesicle fusion with the ER: so-called ER import sites (ERIS). Investigations into retrograde Golgi-ER traffic have been carried out on mammalian cells after brefeldin A (BFA) treatment when COPI vesicles are no longer formed. Under these artificial conditions, tubules emanate from cis-Golgi cisternae which fuse with the ER at ERES (Mardones et al., 2006). Interestingly, and in contrast to the situation in mammalian cells, BFA-induced Golgi stack disassembly in plants proceeds from trans-Golgi cisternae (Schoberer et al., 2010), but neither the modus nor the site of entry into the ER have been established.
Successful vesicle transport between the ER and the Golgi apparatus entails both vesicle capture, which is achieved by long range tethering factors (Sztul and Lupashin, 2009), and the actual fusion event mediated by cognate SNARE interactions (Cai et al., 2007). The tethering factor complex Dsl1 (yeast)/Zw10 (mammals), is responsible for capturing incoming COPI vesicles prior to assembly of a trans-SNARE complex (Ren et al., 2009; Zink et al., 2009; Schmitt, 2010). The latter consists of a Qa- (Ufe1p/Syn18), a Qb- (Sec20), and a Qc-SNARE (Use1; Ballensiefen et al., 1998; Patel et al., 1998; Dilcher et al., 2003).
In this paper we have examined the suitability of several of the plant-specific ER-based plant SNAREs as ERIS markers: AtUse1, and the three members of the SYP7 family (SYP71, SYP72, SYP73) for which no yeast or animal orthologs exist (Sanderfoot et al., 2000). These candidates were screened to find one which was not disruptive to ER-Golgi transport when overexpressed, but could nevertheless mark ERIS as indicated by punctae on the ER when fluorescently tagged. Among the SNAREs tested only SYP72 fulfilled these criteria. SYP72 expression caused the ER to form nodules. Under normal conditions Golgi stacks travel over SYP72 nodules, but upon immobilization through latrunculin B (lat B) treatment, they stop specifically at SYP72 nodules which we therefore interpret as docking sites for retrograde transport. In contrast to the more-or-less stationary SYP72 docking sites, Tip20 (a component of the ER-based tethering factor complex Dsl1) colocalized with Golgi markers under both mobile and immobilized conditions. These data indicate (a) that whereas ER export appears to be a continual ongoing event, ER import is restricted to brief periods of Golgi immobility, and (b) that mobile Golgi stacks are accompanied by a domain of the ER containing COPI-tethering factors. These features are unique to higher plants.
Results
SYP72 is a non-disruptive SNARE that localizes to the ER in punctae
Taking into account the narrow ER-Golgi interface we made the assumption that ERIS would be restricted to domains of the ER similar in size to the diameter of a Golgi stack, i.e., would be visualized as punctae when the correct (X)-FP tagged SNARE was expressed. According to Uemura et al. (2004) and Moreau et al. (2007), the Qa-SNARE SYP81 (=AtUfe1), three Qc-SNAREs (SYP71, SYP72, SYP73), and two R-SNAREs (SEC22 and VAMP723) localize to the ER. However, as previously shown by Chatre et al. (2005) and Bubeck et al. (2008), SEC22 is present in both the Golgi apparatus and ER. Since the images of VAMP723 and SEC22 in the paper of Uemura et al. (2004) are almost identical, we assume that VAMP723 also has a dual localization. In addition to the SYP7 family, there is another SNARE localized to the ER: USE1 (Unconventional SNARE in the ER) which was originally identified in yeast by Dilcher et al. (2003) as a Qb-SNARE interacting with Ufe1p, Sec20p, and Sec22p. Due to the unconventional domain structure of this SNARE the Arabidopsis homolog of Use1p was not included in the earlier plant SNARE classifications (Sanderfoot et al., 2000; Uemura et al., 2004; Moreau et al., 2007).
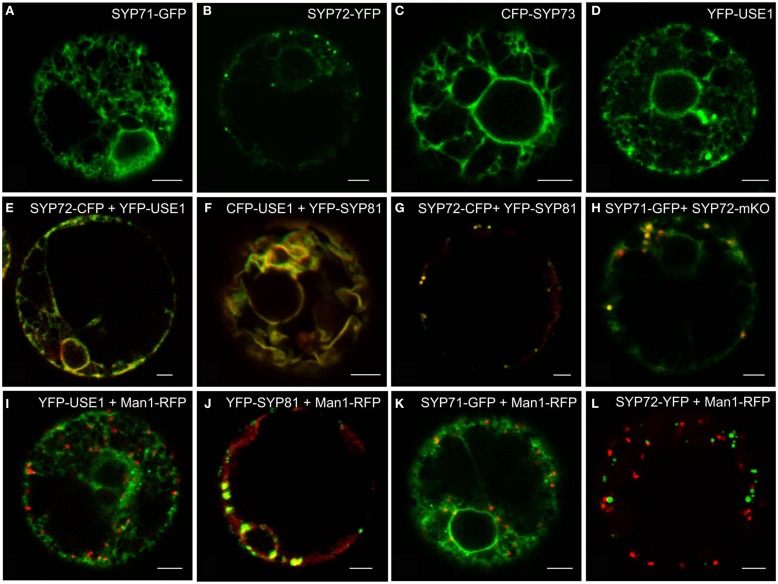
Using the tobacco mesophyll protoplast expression system (Phillipson et al., 2001; Bubeck et al., 2008) we examined the subcellular distributions of USE1 and the SYP7 SNARE family and also monitored the effects of their overexpression on the behavior of different neutral reporters for intracellular transport: barley α-amylase for anterograde transport and its derivative amylase-HDEL for retrograde Golgi-to-ER transport. Only the fluorescently tagged versions of SYP72 (Figure 1B) fulfilled the criterion of producing a punctate signal on the surface of the ER. By comparison, in addition to punctate signals SYP71 and USE1 also labeled the tubular ER network (Figures 1A,D). The signal from SYP73 was also distributed throughout the ER but without punctae (Figure 1C). In contrast to the localization in Arabidopsis (Suwastika et al., 2008; reviewed in Kim and Brandizzi, 2012) SYP71 did not localize to the plasma membrane in tobacco (Figure 1A). When coexpressed, the fluorescent versions of USE1 and SYP72 were distributed throughout the ER (Figure 1E), as was the case with USE1 and SYP81 (Figure 1F). In contrast, the fluorescent punctae of SYP72 and SYP81 colocalized (Figure 1G), as did SYP71 with SYP72 (Figure 1H). Thus while not proving that these different ER-based SNAREs interact with one another, these data at least indicate a close spatial relationship between the Qa-SNARE SYP81 and the Qc-SNARE SYP72.
Figure 1.
Screening for punctate ER-localized SNAREs in tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Protoplasts were electroporated with plasmid DNA (up to 30 μg) encoding for SYP71-GFP (A,H), SYP72-(X)FP (B,E,G,H,K), CFP-SYP73 (C), or (X)FP-USE1 (D–F,I), either alone, in various combinations or electroporated together with the cis-Golgi marker Man1-RFP (I–K). CFP fluorescence is depicted in green (E–G), YFP in red (E–G), GFP in green (H), mKO in red (H). Man1-RFP signals are always shown in red (I–L). All images are of single optical sections. Magnification bars = 5 μm.
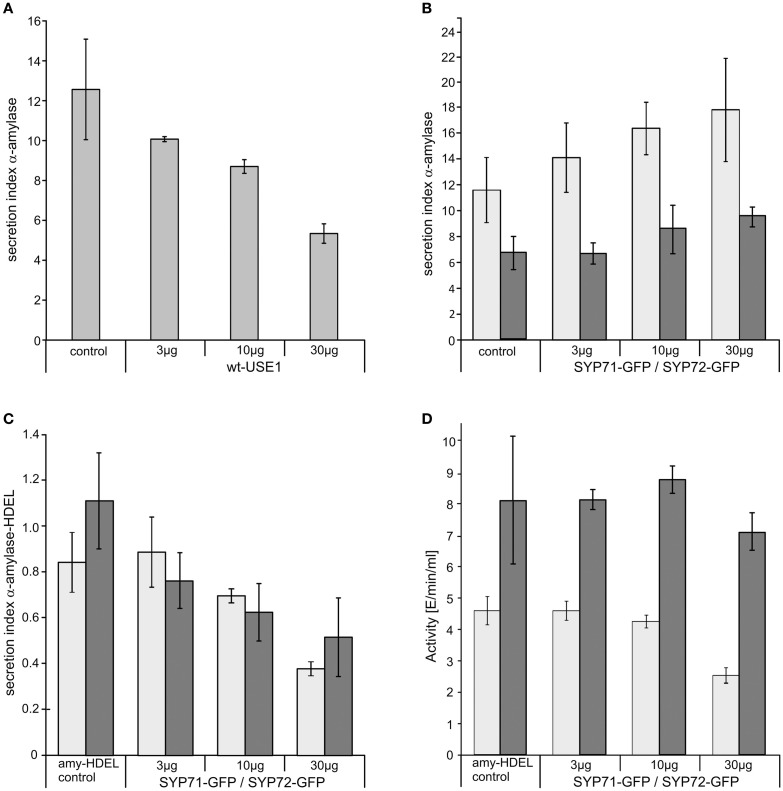
Significantly, and unlike SYP81 (Figure 1J) the expression of fluorescently tagged USE1 (Figure 1I), SYP71 (Figure 1K), and SYP72 (Figure 1L) did not lead to a redistribution of the Golgi marker Man1-RFP into the ER, suggesting that ER-Golgi transport was still functional in these cases. The collapse of the Golgi into the ER through overexpression of SYP81 was confirmed biochemically. The efficiency of α-amylase transport was expressed as the secretion index (SI) which is the ratio of the reporter’s activity detected in the culture medium and within the cells. Changes in the SI therefore indicate directly whether anterograde ER-to-Golgi transport is altered. Curiously, overexpression of USE1 also resulted in a dosage-dependent inhibition of secretion, as evident by a decreasing SI (Figure 2A) although punctate Man1-RFP fluorescence was still observed (Figure 1I). In contrast, overexpression of C-tagged fluorescent forms of SYP71/72 did not inhibit secretion (Figure 2B). In order to estimate the effects of SYP71/SYP72 on retrograde Golgi-to-ER traffic, transport assays with α-amylase-HDEL were performed. Should retrograde transport be inhibited an increase in the SI for this reporter would be expected. However a dosage-dependent decrease of the SI indicates that less reporter molecules are released to the culture medium, meaning that recycling to the ER is more efficient. By decreasing the SI our results suggest that SYP71/72 expression are enhancing retrograde transport (Figure 2C). However, the comparison of the total amylase-HDEL activities revealed that the reduction in SI at higher plasmid concentrations was rather due to a decrease in total activity than due to enhanced recycling. This was especially true when high plasmid concentrations for SYP71 were used (Figure 2D). Due to their disruptive effects on ER-Golgi transport, USE1 and SYP81 were therefore deemed unsuitable for use as ERIS markers. Of the two SYP7 family members which did not inhibit anterograde ER-Golgi transport, SYP72 was deemed the less toxic of the two and was chosen as the more appropriate ERIS marker because it was the only one that formed exclusively punctate signals.
Figure 2.
The effects of ER-SNARE overexpression on secretion and retrograde Golgi-ER transport in tobacco protoplasts. Protoplasts were co-electroporated with a constant amount of plasmid DNA encoding for α-amylase and increasing amounts of plasmid DNA encoding for full-length wtUSE1 (A), SYP71-GFP [(B) light gray], or SYP72-GFP [(B) dark gray]. SYP71-GFP [(C) light gray], and SYP72-GFP [(C) dark gray], respectively, were also coexpressed with α-amylase-HDEL which is normally retained in the ER by efficient COPI-mediated retrograde transport from the Golgi. Secreted and protoplast retained levels of α-amylase activity were measured and the secretion index calculated as described in Materials and Methods. The first column shows as a control the expression of the reporter alone, the other columns the coexpression with constructs in different concentrations as indicated below the axis. USE1 inhibits secretion (A) while SYP71, SYP72 do not (B). Expression of either SYP71-GFP or SYP72-GFP lowers the secretions index of α-amylase-HDEL indicating a more efficient retrograde Golgi-ER transport (C). Total activity for SYP71-GFP [(D) light gray] or SYP72-GFP [(D) dark gray] decreased only at very high amounts of electroporated DNA. Standard deviations are given as vertical lines in each column.
SYP72 expression causes the wild type ER membrane marker RFP-p24δ5 and CFP-HDEL to form nodules
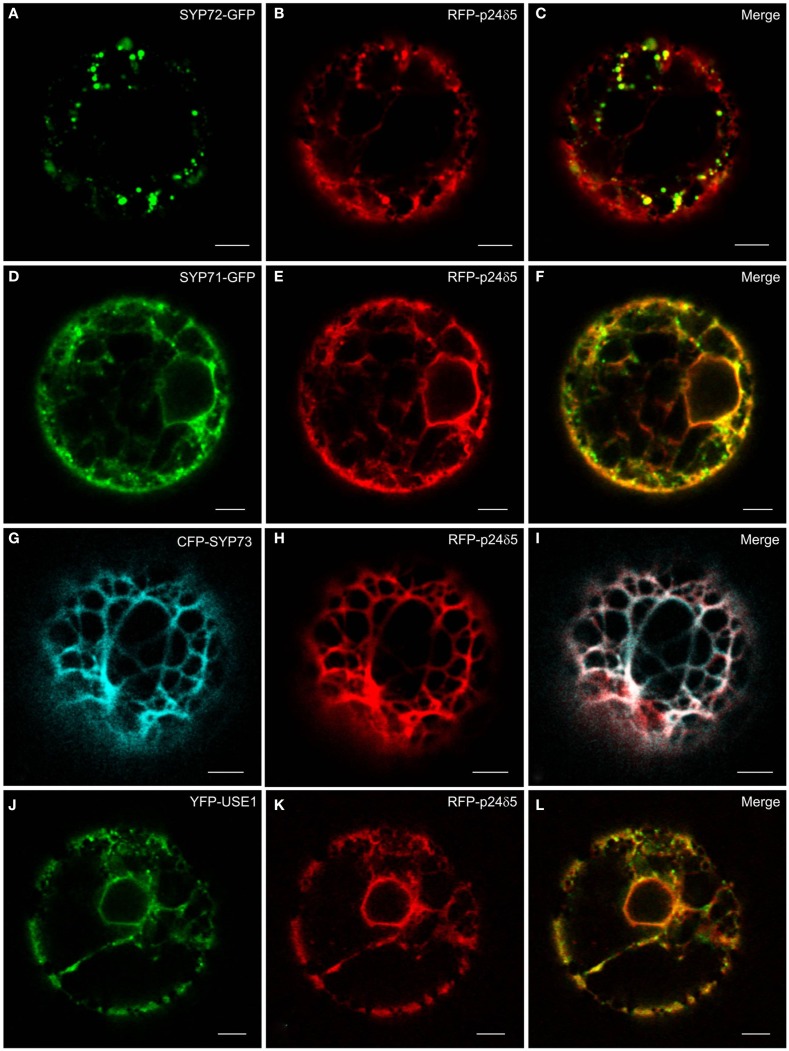
The principle ER marker p24 used in this study is p24δ5. This is a type I-membrane protein and has canonical COPI- and COPII-binding motifs in its cytosolic tail (Contreras et al., 2004; Montezinos et al., 2012). Under steady-state conditions RFP-p24δ5 localizes almost completely to the ER. This distribution is a consequence of a highly efficient COPI-mediated recovery from the Golgi apparatus (Langhans et al., 2008). Normally, RFP-p24δ5 is not detectable in the Golgi apparatus, but can be visualized there when an ARF1-GTP fixed mutant is expressed at low-dose which slows down COPI recycling (Langhans et al., 2008, 2012). p24δ5 is therefore a membrane protein which cycles between the ER and the Golgi, and represents both antero- and retrograde membrane cargo. We noted that when SYP72-GFP was coexpressed with RFP-p24δ5 in tobacco protoplasts the green SYP72-GFP signals colocalized with red punctae on the ER (Figures 3A–C). This effect was partially recognizable with SYP71-GFP and YFP-USE1, but due to the considerable staining of the ER network was not as dramatic as with SYP72-GFP (Figures 3D–F,J–L). It was not seen at all with CFP-SYP73 (Figures 3G–I).
Figure 3.
The ER marker RFP-p24δ5 forms nodules in the presence of SYP72. Tobacco mesophyll protoplasts were co-electroporated with RFP-p24δ5 (10 μg) and 15 μg of one ER-SNARE [SYP72-GFP (A–C), SYP71-GFP (D–F), CFP-SYP73 (G–I), or YFP-USE1 (J–L)]. In addition to a general staining of the ER network the red RFP-p24δ5 signal is also present as punctae which colocalize exactly with the punctate green SYP72-GFP signals. This phenomenon was partially recognizable in the case of SYP71 and USE1 but was not at all visible with SYP73. All images are of single optical sections. Magnification bars = 5 μm.
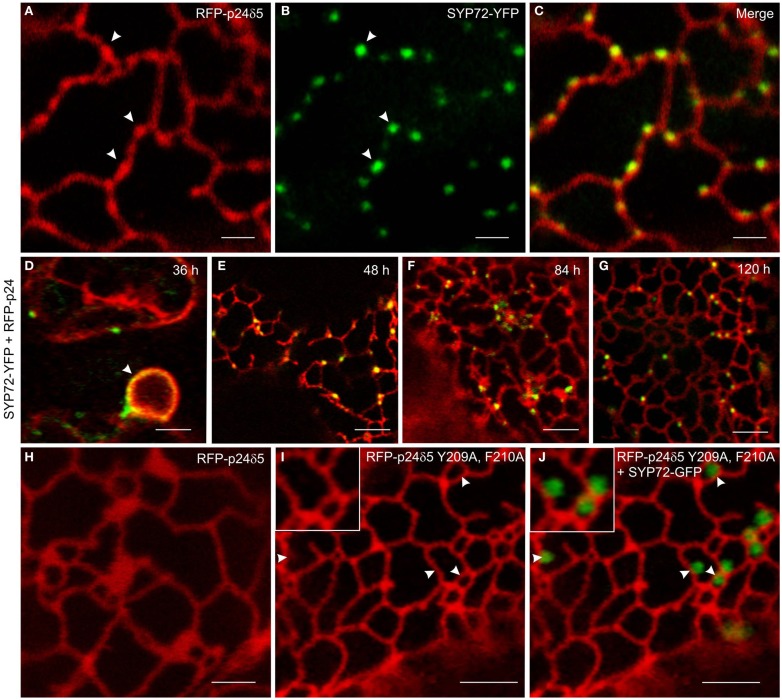
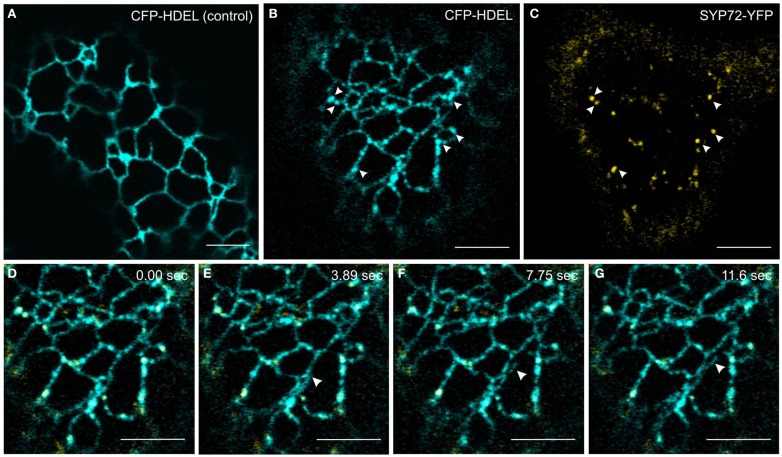
In order to investigate this phenomenon further we therefore switched to Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of tobacco leaf epidermal cells which affords a higher degree of resolution in the CLSM. In this system coexpression of SYP72-YFP and RFP-p24δ5 also caused the formation distinct nodules in the network of tubular ER. These nodules colocalized exactly with SYP72-YFP punctae (Figures 4A–C). A time-course study of SYP72-YFP expression in Agroinfiltrated tobacco leaves revealed that after 36 h incubation SYP72-YFP signals were first seen at the nuclear envelope (Figure 4D), but after 48 h became visible throughout the whole of the ER (Figure 4E). The frequency of SYP72-GFP punctae did not significantly alter over a further 3 days incubation period (Figures 4F,G). Nodules were not seen in the ER when RFP-p24δ5 was expressed alone (Figure 4H; see also Lerich et al., 2011; Langhans et al., 2012). They were also not observed when a mutant form of RFP-p24δ5 lacking the diaromatic (YF) motif in the cytoplasmic tail was coexpressed with SYP72-GFP (Figures 4I,J). This mutant (mutant 2 in Langhans et al., 2008) cannot interact with COPII and therefore cannot be exported out of the ER, and obviously is not recycled back to the ER from the Golgi like the wild type protein. Thus, although the mechanism of SYP72 induced nodule formation is unclear, it is clearly related to retrograde traffic into the ER. Surprisingly, nodules were also formed when CFP-HDEL (which also cycles between the ER and the Golgi) rather than RFP-p24δ5 was used to label the ER (Figures 5A–C). Movement of the luminal marker was however still observable (Figures 5D–G; Movie S1 in Supplementary Material).
Figure 4.
Overexpression of SYP72 enhances retrograde Golgi-ER traffic and leads to the formation of p24δ5 nodules in the ER. (A–C) Coexpression of RFP-p24δ5 and SYP72-YFP in agroinfiltrated tobacco leaf epidermal cells leads to production of nodules in the RFP-p24δ5 stained ER tubular network. These nodules label positively with SYP72-YFP (indicated by arrowheads). (D–G) SYP72-YFP and RFP-p24δ5 fluorescence are first detected after 36 h in the nuclear envelope (arrow) and persist for at least 120 h post-infiltration. For images (A–G), the YFP signal is presented in green for easier viewing. (H–J) Coexpression of SYP72-GFP with a mutant form of RFP-p24δ5 (which cannot be exported out of the ER – see Materials and Methods) in tobacco leaf epidermal cells. As with leaf cells expressing only RFP-p24δ5, nodules in the ER tubular network are not present [compare (H) with (I)], and the SYP72-GFP punctate signals are distributed randomly on the surface of the ER (J). Magnification bars = 2 μm (A–C,H); 5 μm (D–G,I,J).
Figure 5.
CFP-HDEL forms nodules only when coexpressed with SYP72-YFP. (A–C) CFP-HDEL expressed alone labels the ER uniformly (A) but forms nodules when coexpressed with SYP72-YFP (B,C) in tobacco leaf epidermal cells. Arrows point to colocalization of nodules with SYP72-YFP punctae. (D–G) Frames of a movie (CFP-HDEL in cyan; SYP72-YFP in yellow) depicting a growing tubule (arrowhead; Movie S1 in Supplementary Material). Magnification bars = 5 μm (A–G).
COPII/Golgi markers and SYP72 colocalize only when the Golgi is stationary
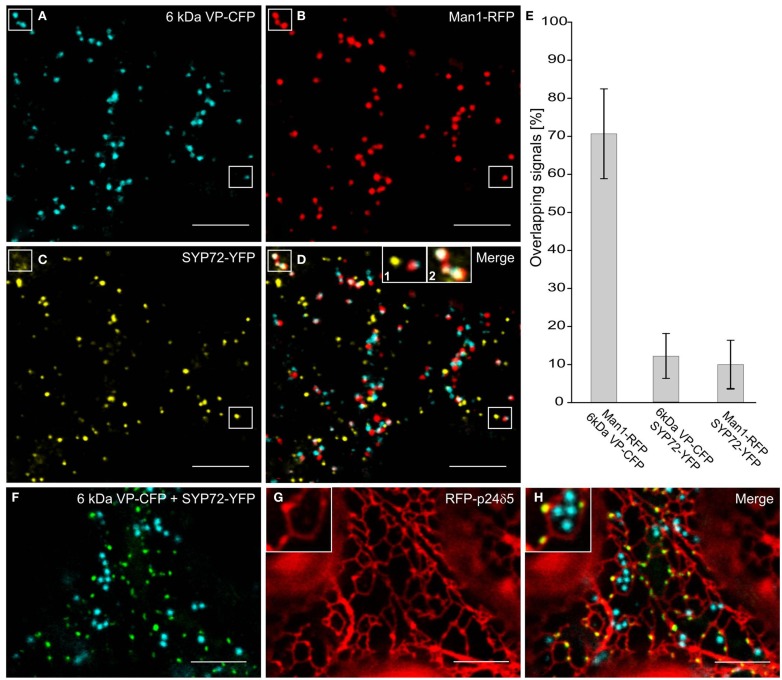
In the course of analyzing SYP72 expression, we noted that in tobacco leaf protoplasts the punctate signals for SYP72 and the Golgi marker Man1-RFP did not colocalize (Figure 1K). This situation was confirmed in leaf epidermal cells when Man1-RFP, SYP72-YFP, and 6 kDa VP-CFP (a membrane marker for COPII; Lerich et al., 2011; Langhans et al., 2012) were transiently coexpressed via Agroinfiltration (Figures 6A–D). Whereas there was a good fluorescence overlap between the 6-kDa VP-CFP and Man1-RFP, there was generally very little overlap between these and SYP72-YFP (Figures 6D–E and inset 1; see also Table 1). Nevertheless, occasional images showing an overlap between the Man1-RFP and the SYP72-YFP were found (see rectangles in Figures 6B–D, plus inset 2 in Figure 6D). When in triple coexpression experiments the ER marker RFP-p24 was agroinfiltrated together with 6 kDa VP-CFP and SYP72-YFP, the 6-kDa VP-CFP punctae were invariably seen adjacent to the tubules of the ER network in contrast to the punctate signals of SYP72-YFP which were always found directly on the nodules in the ER network (Figures 6F–H).
Figure 6.
Punctate SYP72-YFP signals seldom colocalize with ERES and Golgi markers in normal cells. Tobacco leaves were triple agroinfiltrated with 6 kDa VP-CFP (A), Man1-RFP (B), SYP72-YFP (C). Although a high degree of colocalization between the blue COPII (6 kDa VP-CFP) and red Golgi (Man1-RFP) markers was observed, there was little overlap between the signals for SYP72-YFP (yellow) and the COPII and Golgi markers (D–E). A case of colocalization between SYP72-YFP and Man1-RFP punctae is indicated in the rectangles in (A–C), and in inset 2 in (D) When tobacco leaves were triple agroinfiltrated with 6 kDa VP-CFP, SYP72-YFP, and RFP-p24δ5 a clear distinction can be made between the punctate SYP72-YFP signals which lie directly on the tubular ER network (see insets in (G,H) for nodules) and the Golgi-associated ERES marker [6 kDa VP-CFP; (F–H)]. Magnification bars = 10 μm (A–D,F–H).
Table 1.
Degrees of overlap of Golgi, ERES, and ERIS markers in tobacco leaf epidermal cells*.
| Combinations of fluorescent markers | Degree of overlap (%) | Standard deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Man1-RFP/6 kDa VP-CFP | 71 | ±11.8 |
| Man1-RFP/SYP72-YFP | 10 | ±6.3 |
| 6 kDa VP-CFP/SYP72-YFP | 12 | ±5.9 |
*Measurements made on 10 separate cells, and calculated with ImageJ 1.46f and the plugins Colocalization (Pierre Bourdoncle, http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/plugins/colocalization.html) and ColocalizeRGB (Sergio Caballero, http://grove.ufl.edu/∼ksamn2/plugins.html#COLOC).
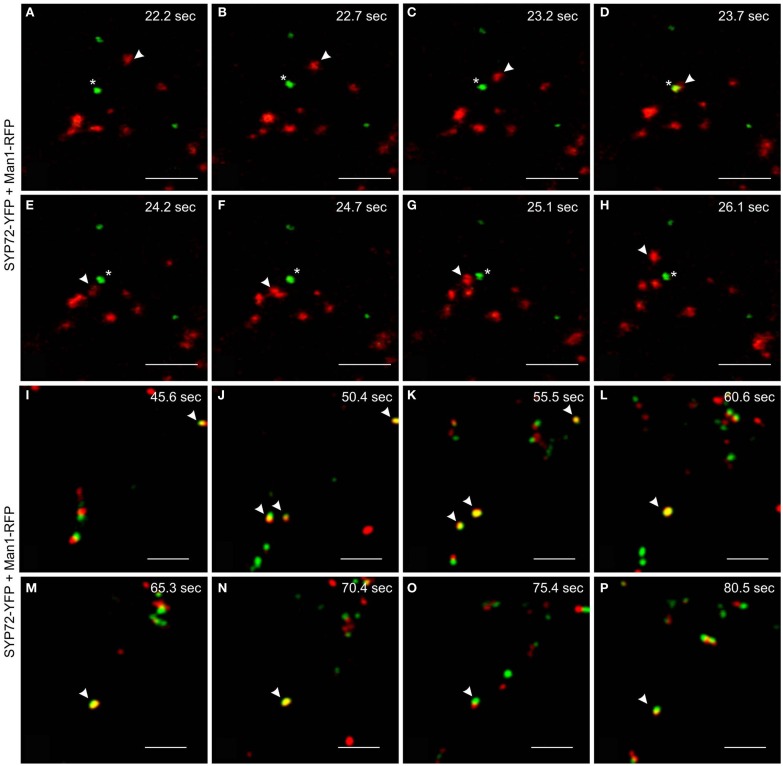
We have performed live cell imaging to determine the relative mobilities of the SYP72-YFP and Man1-RFP signals. As expected for a Golgi marker the Man1-RFP signals are generally very mobile, whereas the SYP72-YFP signals are relatively immobile. Interestingly, individual Golgi stacks were occasionally seen moving over stationary SYP72-YFP punctae (Figures 7A–H; Movie S2 in Supplementary Material). We have also been able to observe examples where the Man1-RFP and SYP72-YFP signals colocalize, and in such cases the punctae were for a short time immobile (Figures 7I–P; Movie S3 in Supplementary Material). Since such colocalizations were difficult to find we cannot give statistically sound values for the length of the stationary period, however from the data presented it is in the range of 10–15 s. These two key observations suggest that the SYP72-YFP signals represent docking sites for Golgi stacks, although the Golgi stacks do not always make a halt at these sites.
Figure 7.
Mobilities and transient colocalization of Man1-RFP and SYP72-YFP as observed in videos of untreated tobacco leaf epidermal cells. (A–H) Eight frames taken at 0.5–1 s intervals from a movie sequence of the SYP72-YFP (shown in green) and Man1-RFP (in red) images (movie available as Movie S2 in Supplementary Material). A Man1-RFP puncta (arrowhead) is seen moving toward and over a SYP72-YFP puncta (star). (I–P) SYP72-YFP (in green) and Man1-RFP (in red) are shown in these eight frames (5 s interval; movie available as Movie S3 in Supplementary Material). Several examples of temporary colocalization between SYP72-YFP and Man1-RFP signals are to be seen (arrowhead). Magnification bars = 5 μm (A–P).
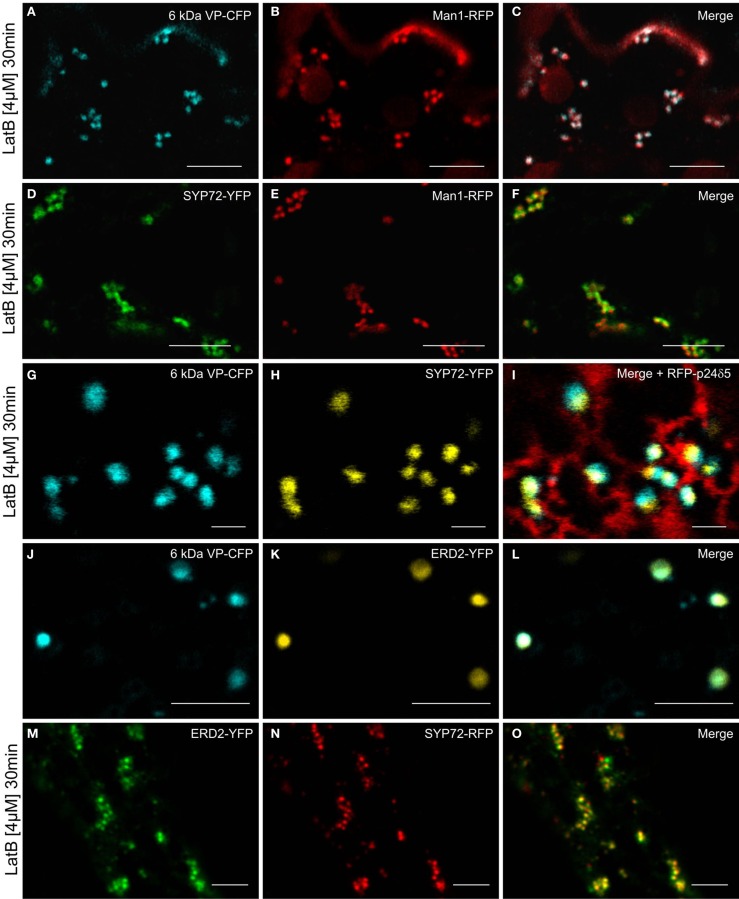
Since the movement of Golgi stacks across the surface of the ER is dependent on the actin cytoskeleton (Hawes et al., 2008), we wanted to determine how their immobilization would affect the distribution of fluorescent COPII/Golgi and SYP72 signals in leaf epidermal cells. As previously shown by Boevink et al. (1998), after actin depolymerization, Golgi stacks tended to group together sometimes lying on or adjacent to small islands of cisternal ER. We therefore applied latrunculin B (latB) to segments of tobacco leaves transiently expressing the COPII/cis-Golgi (6 kDa VP-CFP/Man1-RFP) markers as well as SYP72-YFP. After 1 h of latB treatment we found that the colocalized 6 kDa VP-CFP/Man1-RFP punctae did indeed form small clusters (Figures 8A–C). However, under these conditions so did the SYP72-YFP punctae, and these colocalized with both the Golgi (Man1-RFP) and ERES (6 kDa VP-CFP) signals (Figures 8D–I). The recycling receptor ERD2-YFP, which also locates to the cis-Golgi, behaved like Man1-RFP: it colocalized perfectly with the 6-kDa VP-CFP signal irrespective of Golgi mobility (Figures 8J–L) and only colocalized with SYP72-GFP when the Golgi was stationary (Figures 8M–O).
Figure 8.
Actin depolymerization causes SYP72, Golgi, and ERES signals to colocalize in clusters. Tobacco leaves were double agroinfiltrated with either 6 kDa VP-CFP and Man1-RFP (A–C), or with SYP72-YFP and Man1-RFP (D–F), or triple agroinfiltrated with 6 kDa VP-CFP, SYP72-YFP, and RFP-p24δ5 (G–I). ERD2-YFP and 6 kDa VP-CFP signals were observed in untreated cells (J–L) and ERD2-YFP and SYP72-RFP fluorescence after latrunculin B treatment (M–O). Segments of the agroinfiltrated leaves were cut out 2 days post-infiltration and incubated for 30 min with latrunculin B (4 μM) before observation in the CLSM. Magnification bars = 10 μm (A–F); 1 μm (G–I); 5 μm (J–O).
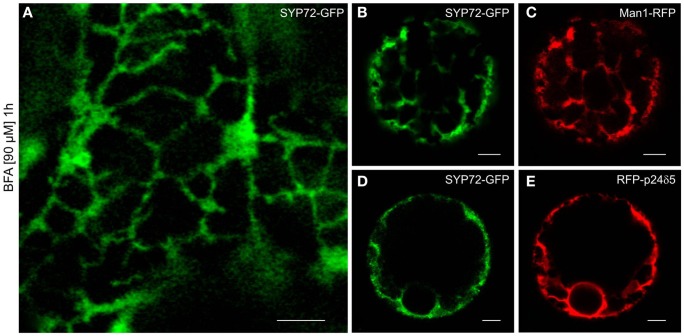
Although in normal leaf epidermal cells SYP72-YFP and ERES/Golgi signals generally did not colocalize, in response to BFA treatment they nevertheless showed the same phenotype: a uniform ER-labeling. This was obtained with both leaf epidermal cells (Figure 9A) and mesophyll protoplasts (Figures 9B–E). The effect of BFA on the redistribution of Golgi marker proteins into the ER in tobacco cells is well-known (Robinson et al., 2008; Langhans et al., 2011), and has been explained in terms of a randomization of SNAREs in Golgi and ER membranes (see Nebenführ et al., 2002). Accordingly, SNAREs which normally gather in transport vesicles and are present at fusion sites no longer do so because BFA inhibits vesicle formation (initially COPI but subsequently also COPII). The observation that the SNARE SYP72 is no longer visible in concentrated punctae after BFA treatment may be taken as supportive evidence of this scenario.
Figure 9.
BFA prevents formation of SYP72 punctae. Pretreatment with BFA (90 μM; 1 h) leads to a general ER distribution of SYP72-GFP signals in leaf epidermal cells (A), and protoplasts (B–E) when coexpressed with the Golgi marker Man1-RFP (C) or the ER marker RFP-p24δ5 (E). Magnification bars (A–E) = 5 μm.
Endogenous SYP7 SNAREs colocalize with COPII and Golgi markers
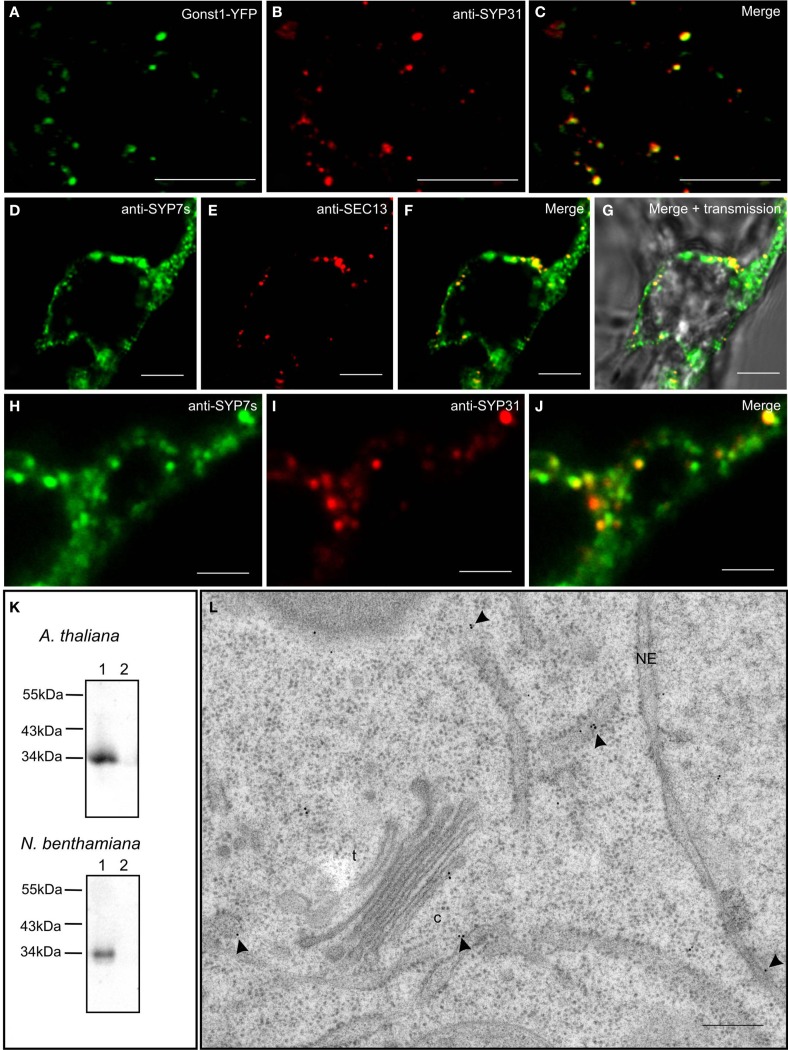
In order to test the validity of our transient expression data, we performed double immunofluorescence on tobacco BY-2 cells with immobilized Golgi stacks using antibodies generated against the Arabidopsis SYP7 family of SNAREs (Figure 10K; see also Suwastika et al., 2008), and antibodies directed against either SEC13, a plant COPII protein (Yang et al., 2005), or SYP31 (=AtSED5), a Golgi localized syntaxin (Bubeck et al., 2008). The specificity of SYP31 was demonstrated in stably transformed BY-2 cells expressing the Golgi marker GONST1-YFP (Tse et al., 2004; Figures 10A–C). With both combinations of antibodies (anti-SYP7s vs. anti-SYP31; anti-SYP7s vs. anti-SEC13) punctate signals with a high degree of overlap were obtained (Figures 10D–J). This is supported by statistical analyses involving the calculation of the Mander’s coefficient (Table 2).
Figure 10.
Endogenous SYP7 proteins colocalize with ERES and Golgi stacks. (A–C) Immunofluorescent localization of the syntaxin SYP31 to Golgi stacks in transgenic tobacco BY-2 cells expressing the Golgi marker GONST1-YFP. (D–J) Double immunofluorescence on tobacco BY-2 cells using antibodies against the SYP7 family and the COPII protein SEC13 (D–G) or the syntaxin SYP31 (H–J). (K) Western blots showing the specificity of the SYP7 antiserum in total membrane preparations (lanes 1) from Arabidopsis and tobacco leaves (lane 2 is the 100,000-g supernatant as a negative control). (L) Immunogold labeling with SYP7 antibodies of a thin section cut from a high pressure frozen Arabidopsis root tip. Arrowheads point to gold particles. c, cis-Golgi; t, trans-Golgi; NE, nuclear envelope. Magnification bars = 5 μm (A–G); 1 μm (H–J); 300 nm (L).
Table 2.
Colocalization of endogenous Golgi (anti-SYP31), COPII (anti-SEC13), and ERIS (anti-SYP7s) in tobacco BY-2 suspension culture cells*.
| Combinations of antibodies |
Manders coefficient |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | M1 (A overlapping with B) | M2** (B overlapping with A) |
| anti-SYP31 | anti-SYP7s | 0.93 ± 0.08 | 0.18 ± 0.05 |
| anti-SEC13 | anti-SYP7s | 0.86 ± 0.07 | 0.18 ± 0.14 |
*Measurements made on 10 separate cells, and calculated with ImageJ 1.46f and the plugins JACoP (Bolte S, Cordelieres FP 2006) and PSC Colocalization (French et al., 2008]).
**The SYP7s antibody recognizes epitopes on the entire ER (green signal) whereas anti-SYP31 or anti-SEC13 signals are only present as punctae. Thus the low value for M2 is to be expected since only a fraction of the green signal (anti-SYP7s; found over the entire ER) overlaps with the red fluorescence (anti-SEC13/anti-SYP31; only punctae). However, as shown for M1 almost all of the red signals overlap with the green.
We also performed immunogold electron microscopy with the SYP7s antibodies on sections cut from high pressure frozen/freeze-substituted samples of Arabidopsis roots (because of their highly vacuolated condition tobacco leaf epidermal cells are not suitable for this purpose). The expected size of a single SYP7X polypeptide (33 kDa) matches the signal recognized by the SYP7s antibodies in microsomal membranes isolated from both Arabidopsis roots and tobacco leaves (Figure 10K lane 1; lane 2 represents a negative control). Ultrastructural analysis showed a positive labeling of the ER and the cis-Golgi (Figure 10L) with comparatively little background label in the cytosol or over other organelles. This type of labeling was also previously described for the Qa-SNARE SYP81 in Arabidopsis roots (Bubeck et al., 2008). In neither case was a clustering of gold particles observed, as might be expected from the CLSM data described above. There are several reasons for this. Firstly, the SYP7s antibodies recognize all three SYP7 family members, which between themselves have at least a 50% identity (Suwastika et al., 2008). This means that SYP71 and SYP73, which show a more general labeling of ER tubules when expressed as XFP-constructs, will also be recognized. Secondly, it is generally accepted that despite the use of rapid freeze fixation techniques it is extremely difficult to visualize vesicle fusion events. Even in cases where massive exocytotic fusions occur, e.g., at the tips of growing pollen tubes, fusion profiles are rarely seen in sections (Lancelle and Hepler, 1992). Indeed convincing visualization of vesicle fusion events in the EM have only been obtained in surface view by freeze-fracturing chemically stimulated synapses (Heuser et al., 1979). Thus, since profiles of COPII vesicle budding in higher plants have rarely been obtained (see Langhans et al., 2012 for a discussion) the ideal situation of visualizing COPII budding and COPI fusion events next to one another on the ER directly beneath a Golgi stack is virtually impossible to achieve.
ER and Golgi tethering factors colocalize with Golgi stacks irrespective of the motile status of the Golgi
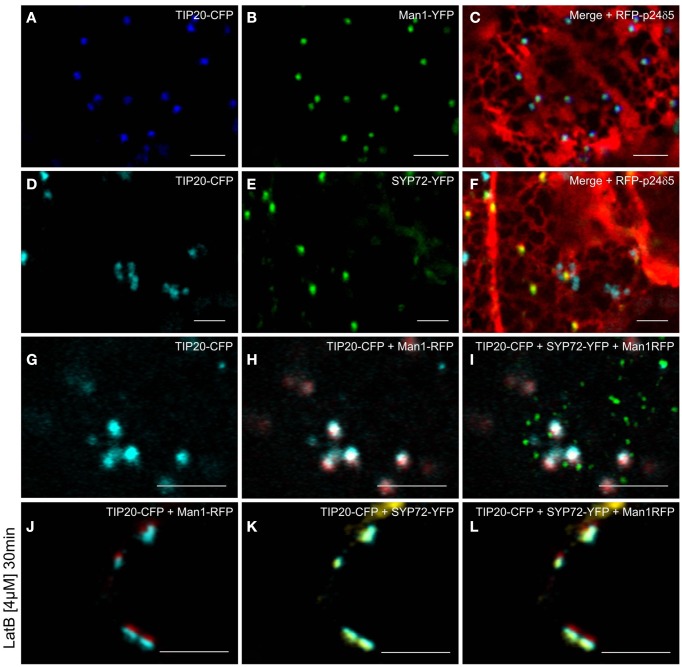
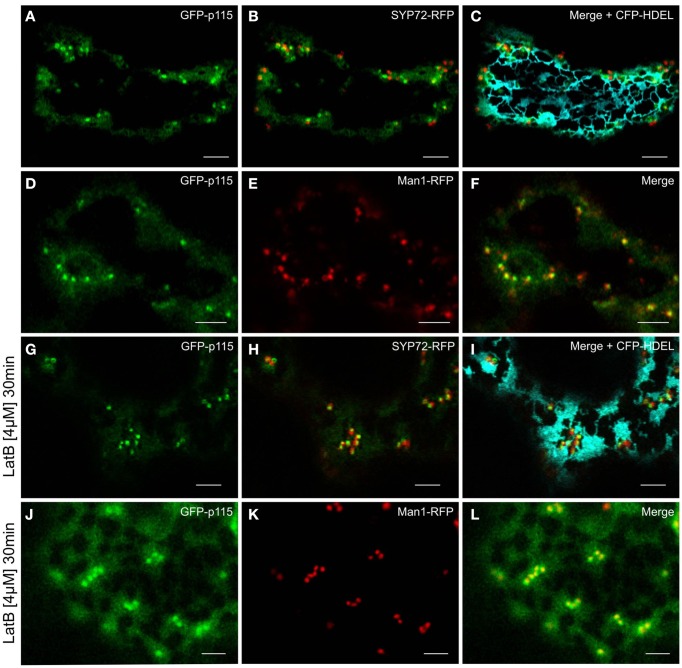
Prior to the SNARE-mediated fusion process, incoming vesicles are captured by tethering factors. The tethering factor complex Dsl1 (yeast)/ZW10 (mammals), is responsible for capturing the incoming COPI vesicles prior to assembly of a trans-SNARE complex, and is attached to the ER membrane (Ren et al., 2009; Zink et al., 2009; Schmitt, 2010; Meiringer et al., 2011). The Dsl1 complex has three proteins: Sec39p, Dsl1p, and Tip20p. The latter has a plant homolog (Schmitt, 2010) which we cloned as a CFP fusion for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of tobacco leaves. Imaging of leaf epidermal cells with mobile Golgi stacks, surprisingly revealed that TIP20-CFP colocalizes perfectly with the Golgi marker Man1-RFP (Figures 11A–C,G–I). However, consistent with the fact that SYP72 and COPII/Golgi markers do not colocalize when the Golgi is mobile, the signals for TIP20-CFP and SYP72-YFP were clearly separate from one another (Figures 11D–I). We also looked into the situation with the coiled-coil tethering factor p115 (in yeast, Uso1p) which together with the TRAPPI/II complexes is responsible for capturing COPII vesicles at the cis-Golgi (in yeast, Cao et al., 1998) or at the ERGIC (in mammals, Allan et al., 2000). A plant homolog to p115/Uso1p has been cloned and shown by immunogold electron microscopy to localize near to the cis-face of Golgi stacks in Arabidopsis root cells (Kang and Staehelin, 2008). When coexpressed with Man1-RFP in tobacco leaf epidermal cells, GFP-Atp115 colocalizes exactly with Man1-RFP, but not SYP72-RFP in normal cells with mobile Golgi stacks (Figures 12A–F). In latB-treated cells with immobile Golgi stacks both sets of fluorescently tagged tethering factors (Tip20-CFP; GFP-p115) colocalize with Man1-RFP (Figures 11J–L, 12J–L). Under these conditions even SYP72 overlaps considerably with both tethering factors (Figures 11J–L, 12G–I). Thus, irrespective of the motile status of the Golgi apparatus, fluorescently tagged tethering factors for both antero- and retrograde ER-Golgi vesicle trafficking in plants are spatially confined to the interface between the ER and the overlying Golgi stack.
Figure 11.
Golgi and ER-tethering factors colocalize to mobile Golgi stacks. Tobacco leaves were triple agroinfiltrated with either TIP20-CFP (A), Man1-YFP (B), and RFP-p24δ5 (C) or TIP20-CFP (D), SYP72-YFP (E), and RFP-p24δ5 (F). Triple infiltration of TIP20-CFP, Man1-RFP, and SYP72 was observed in untreated (G–I) and latrunculin B (4 μM, 30 min) treated cells (J–L). Magnification bars = 5 μm.
Figure 12.
GFP-p115 colocalizes with a cis-Golgi marker but not with SYP72. In agroinfiltrated tobacco leaves GFP-p115 and SYP72-RFP only overlapped in latrunculin B treated cells [compare (A–C) with(G–I)]. A high degree of colocalization was detected between GFP-p115 and Man1-RFP before (D–F) and after latrunculin B treatment (J–L). Magnification bars = 5 μm.
Discussion
Are SYP72-(X)FP and TIP20-(X)FP bona fide ERIS markers?
After tethering, vesicle fusion is mediated by cognitive SNARE–SNARE interactions whereby typically a vesicular R-SNARE interacts with three SNAREs (Qa, Qb, and Qc-SNAREs), at the acceptor membrane together forming a quadruple “cis-SNARE” helix after successful fusion (Jahn and Scheller, 2006). The Q-SNAREs are therefore faithful indicators of vesicle fusion events. The ER-tethering factor complex Dsl1 which is responsible for the long range capturing of COPI vesicles also interacts with individual SNARE proteins. For example, Sec39 binds to Use1, and Tip20 binds to Sec20 (Reilly et al., 2001; Aoki et al., 2008; Tripathi et al., 2009; Meiringer et al., 2011), and actually cause an acceleration of SNARE complex assembly (Ren et al., 2009). According to Schmitt (2010) the Tip20p-RINT1 family is the evolutionary the most conserved protein family belonging to the ER-tethering factor complex. Interestingly, in common with some other tethering factor proteins (sec6 of the exocyst complex; Vps53 of the GARP complex) Tip20p possesses a so-called MUN domain (Pei et al., 2009). While this maybe of importance when performing immunolocalizations if some antibodies are directed to this domain, it is irrelevant to our investigation since we cloned a full-length fluorescently tagged plant TIP20 homolog. In conclusion: fluorescently tagged versions of either the Q-SNARES or a Dsl1 component, provided their expression has no deleterious effects on transport, should be faithful indicators of vesicle fusion sites.
As shown above, only SYP72 fulfilled the criteria of being (a) non-disruptive toward the secretory pathway when overexpressed, and (b) producing punctate fluorescent signals on the surface of the ER. The sizes of the punctate fluorescent SYP72 and COPII/Golgi signals were also similar, suggesting that they could be structurally related to one another. However, in both mesophyll protoplasts and in intact epidermal cells of tobacco plants only rarely were the punctate SYP72 signals seen to colocalize with fluorescent cis-Golgi markers (Man1-RFP, ERD2-YFP, or COPII/ERES-markers (6 kDa VP-CFP). Nevertheless, in seldom cases we were able to visualize a colocalization of the Man1-RFP and SYP72 signals in normal cells, but colocalization was complete in cells treated with latB. Under this condition all three types of signal (i.e., SYP72, COPII/ERES, Golgi) colocalized. This suggests that SYP72 punctae represent predetermined docking sites for Golgi stacks and that retrograde COPI-mediated traffic only occurs when Golgi stacks are temporarily sessile. If this scenario is correct, we would have expected that TIP20, as a component of the ER-tethering factor complex Dsl1, would also be restricted to the docking sites. Surprisingly it was not, but was constitutively linked to Golgi stacks irrespective of their motile status. Since the Dsl1 complex is anchored to the membrane of the ER via SNAREs, this means that its movement must also be accompanied by a SNARE, possibly SEC20. Thus a domain of the ER is constantly moving with the overlying Golgi stack. This is not a new idea, since Runions et al. (2006) have previously demonstrated that calnexin, when tagged with photoactivatable GFP, also moves in a coordinated manner with Golgi stacks in the plane of the ER membrane in tobacco leaf epidermal cells.
A new model for ER-Golgi trafficking in higher plants
Higher plant Golgi stacks are propelled (via actomyosin interactions, Avisar et al., (2008, 2009) across the surface of the ER in a perpetual stop-and-go fashion (Boevink et al., 1998; Nebenführ et al., 1999). Although there are still doubts as to the mode of transport (vesicles versus tubules, see Hawes, 2012), several models have been proposed to explain ER-Golgi transport under these unique conditions. However, the major issue still remains unresolved as to whether cargo delivery to and from the Golgi stack occurs continuously during Golgi movement or is restricted to brief stationary periods (Boevink et al., 1998; Nebenführ et al., 1999; Neumann et al., 2003; daSilva et al., 2004; Hawes and Satiat-Jeunemaitre, 2005; Staehelin and Kang, 2008). In a recent paper (Langhans et al., 2012) we presented data implicating that COPII vesicle scission from the ER is not immediately followed by COPII vesicle fusion with the Golgi, and that tethered COPII vesicles might move with the Golgi stacks for a time until fusion occurs. This explains the close association of COPII-based fluorescence with Golgi stacks rather than the ER surface. Essentially what is visualized is a post-ERES, pre-Golgi intermediate, in a location analogous to the ERGIC of mammalian cells. In our opinion, the failure to detect COPII fluorescence at the surface of the ER is probably due to the fact that COPII vesicle release are individual budding events which occur quickly and consequently there are insufficient fluorescent COPII proteins on the ER membrane to produce a signal. We feel it is therefore important to distinguish between COPII-mediated release (ERES sensu stricto), the accumulation of fluorescent COPII-carriers, and COPII-fusion at the cis-Golgi since these are temporally separate events. We do not know for certain if COPII-fusion occurs continuously during Golgi movement or is restricted to periods when the Golgi is stationary.
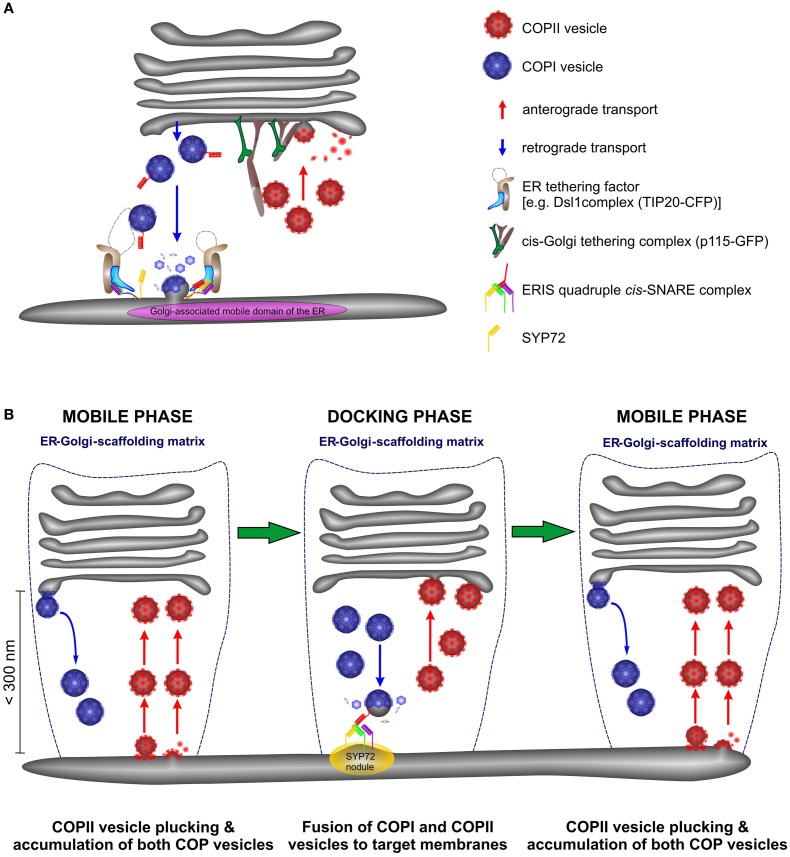
However, the data presented here allows us to speculate about retrograde transport. If COPII vesicles accumulate in the ER-Golgi interface this might also be the case for COPI vesicles and would explain why the ER-tethering factor TIP20-CFP moves together with the Golgi stacks. Consequently, COPI-retrograde carriers will be captured and carried with the Golgi stack during its mobile phase, until the Golgi docks at a predetermined fusion site, characterized by a SNARE fusion complex (the SYP72 nodules). We therefore propose a modification of the so-called “secretory unit” model of daSilva et al., (2004 by which ERES and Golgi stacks were considered to be tightly coupled and would move in tandem. We suggest that COPII vesicle release from the ER is a continuous event being triggered by an approaching Golgi stack but fusion with cis-Golgi cisternae is delayed until the Golgi stack is immobile (see Figure 13). Similarly COPI vesicle formation is continuous process, and the retrograde carriers can only fuse with the ER when the Golgi stack is stationary. This scenario might still be possible if ER-Golgi transport were to be accomplished by direct tubular connections as proposed by Hawes and colleagues (Hawes and Satiat-Jeunemaitre, 2005; Hawes, 2012). However, electron tomography of cryofixed specimens prepared from the yeast Pichia pastoris, whose stacked Golgi apparatus also lies very close to transitional ER revealed only vesicles, and no tubules in the ER-Golgi interface (Mogelsvang et al., 2003; Suda and Nakano, 2012). A similar situation also exists in Chlamydomonas (Hummel et al., 2007; Langhans et al., 2012). Of course these are two examples with stationary, positionally fixed Golgi stacks, but then the likelihood of tubular connections between the ER and the Golgi apparatus in such organisms would be greater than in these higher plant cells whose Golgi stacks move. In our opinion, this means that higher plants are unique among eukaryotic organisms in having a mobile, bidirectional, vesicle transport system, which by being encaged in a scaffold of tethering factors (Latijnhouwers et al., 2005; Hawes et al., 2008; Kang and Staehelin, 2008) ensures that transport vesicles do not get lost into the cytoplasm.
Figure 13.
Anterograde and retrograde traffic between the ER and the Golgi in higher plants is accomplished by a short-range secretory and recycling unit. (A) Cartoon showing the close proximity of ERES and ERIS in a domain of the ER which in size approximates the diameter of the Golgi stack. (B) This cartoon represents a new model for ER-Golgi transport in higher plants. Golgi stacks move intermittently over the surface of the ER. They are in tight association with the ER through a joint scaffolding matrix of tethering factors (dotted blue line). As Golgi stacks move they capture individual COPII vesicles released from ERES at the surface of the ER (“mobile phase”) and release COPI vesicles. Both types of vesicles accumulate in the ER-Golgi interface. When the Golgi stacks temporarily stop moving (“docking phase”) fusion of COPI and COPII vesicles to their respective target membranes occurs. Golgi stacks stop at ERIS as marked by the presence of “SYP72 nodules” on the ER.
Materials and Methods
Plant material and cultivation
Wild type Nicotiana tabacum and Nicotiana benthamiana were grown from surface-sterilized seeds either in soil or in Murashige and Skoog medium and 2% (w/w) sucrose in a controlled room at 22°C with a 16-h day length. Wild type tobacco BY-2 (N. tabacum var. Bright Yellow 2) cells were cultivated by shaking (100 rpm) in the dark in Murashige and Skoog’s (1962) medium at 25°C. Two different cell lines were used: wild type cells (obtained from Dr. Y. Moriyasu, Shizuoka University, Japan); cells transformed with a Gonst1-YFP fusion construct that localizes predominantly to the medial/trans-Golgi (Nebenführ et al., (1999).
Plasmid constructions
Primers for genes of interest were designed based on their sequence as found in the NCBI database (SYP71 = At3g09740, SYP72 = At3g45280, SYP73 = At3g61450, USE1 = At1g541110, plant Tip20 ortholog = At1g08400). All oligonucleotides were ordered from Sigma-Aldrich (Germany). Primers and vectors were used as listed in Table A1 in Appendix and published previously (Phillipson et al., 2001; Niemes et al., 2010). The expression of the gene of interest was under the control of the 35S promoter and was stopped by the NOS terminator or RBCS terminator. Gateway technology (Invitrogen) was used to generate binary vectors possessing the coding sequence for SYP72 (At3g45280) and the TIP20 ortholog (At1g08400). The primer sequences used for cloning into binary vectors are listed in Table A1 in Appendix. PCR was performed using the Phusion DNA polymerase (Fermentas). After purification the obtained DNA fragments were either cloned into the entry vector pDONR221 (Invitrogen) using BP clonase II (Invitrogen) following the supplier’s guide or into the pENTR1A via restriction enzymes. The LR reaction was carried out as recommended by the manufacturer (Invitrogen). The coding sequence for SYP72 and Tip20 was transferred by recombination into the binary destination vectors pJV-107, pJV-108, and pFK-242 (from the Gateway-compatible pGREEN-IIS vector series) to generate a plasmid encoding Tip20-CFP, SYP72-mCitrine (YFP), or SYP72-eGFP. The mutated p24δ5 as described in Langhans et al. (2008 was cloned into the binary vector pBIN20 using SacI and KpnI (Hennegan and Danna, 1998). All constructs were verified by sequencing.
Tobacco leaf agroinfiltration of markers used in this study
Agroinfiltration of tobacco leaves was performed exactly as described in Lerich et al. (2011).
Transient expression in protoplasts
Preparation of tobacco leaf protoplasts was done exactly as described in Scheuring et al. (2011). A total volume of 500 μl of the obtained protoplast suspension was pipetted into a disposable 1-ml plastic cuvette and mixed with an appropriate amount of plasmid DNA (p24-RFP (Langhans et al., 2008); YFP-SYP81 (Bubeck et al., 2008), YFP-USE1, SYP71-GFP, SYP72-XFP, CFP-SYP73 obtained as described above; Table A1 in Appendix). Incubation period for protoplasts was 16–24 h at 25°C in a dark chamber prior to CLSM analysis. All experiments were repeated several times.
Treatments with inhibitors
Experiments were performed with 4 μM latrunculin B (latB) and 90 μM brefeldin A (BFA). The inhibitors were dissolved in a stock solution in DMSO, leading to a final concentration of DMSO of 0.05%. As demonstrated in Langhans et al. (2007), this DMSO concentration is without any known cytological effect. In these experiments, plant material was pretreated 30–60 min before observing under the CLSM.
Confocal microscopy
Leaves (N. benthamiana) and protoplasts (N. tabacum var. SR1) were prepared for microscopy as specified in Lerich et al. 2011). Cells or plant material were observed under a Zeiss Axiovert LSM510 Meta microscope using a Plan-Neofluar 25×/0.8 Imm corr DIC or a C-Apochromat 63×/1.2 W corr water immersion objective. Special settings were designed for observing single-, double-, and triple-expression with different XFP-constructs. Fluorescence was detected by the metadetector using main beam splitter HFTs 488/543 and 458/514. Fluorophores were excited by frame switching in the multitracking mode of the microscope. Detection of eGFP and RFP was performed at excitation at 488 and 543 nm and an emission at 496–518 and 593–635 nm. Cerulean (CFP) and mCitrine (YFP) were detected at 464–486 and 529–550 nm, respectively, after excitation a 458- or 514-nm LASER beam. YFP and mRFP were detected using the HFT 488/543 at 529–550 and 593–635 nm. When observing CFP and eGFP in the same sample the eGFP detection range was shifted toward 507–529 nm. For movies or fast imaging, simultaneous scanning of GFP and RFP or CFP and YFP was used to exclude artifacts due to time shifting. Detection of Alexa Flour 488 and 546 was performed at 488 and 543 nm and an emission at 518–539 and 561–582 nm. Pinholes were adjusted to 1 Airy Unit for each wavelength except for CFP (1.3 Airy Units). Images were post-processed using the Zeiss LSM Image Browser (Version 4.2.0.121), Corel Draw X4 (Version 14.0.0.567), and ImageJ 1.46f.
α-Amylase assay and secretory index determinations
Preparation of protoplasts and determination of extracellular (secreted) and intracellular α-amylase and α-amylase-HDEL activities were performed as previously described (Bubeck et al., 2008).
Antibodies against Sec13, SYP31, and SYP72 and their immunofluorescent localization
A polyclonal antiserum was raised in rabbits against a mixture of recombinant cytoplasmic tails of recombinant Arabidopsis SYP71, SYP72, and SYP73; this antibody recognizes a single band at 33 kDa in western blots (Suwastika et al., 2008). A polyclonal antiserum was raised in rats against recombinant Arabidopsis SEC13 (Yang et al., 2005). A polyclonal antiserum was raised in guinea pigs against the cytoplasmic tail of Arabidopsis SYP31 (=AtSed5). The recombinant protein was generated exactly as previously described for SYP81 (Bubeck et al., 2008). SYP31 locates to the Golgi apparatus, and the specificity of this antibody was demonstrated by immunofluorescence in a BY-2 cell line expressing a fluorescent Golgi marker. For immunolocalization 1.5 ml 3-day-old BY-2 cells were used and processed as documented previously in Ritzenthaler et al. 2002) with the following modifications. Cells were fixed with 0.25% glutaraldehyde and 4% paraformaldehyde for 30–45 min in culture medium. After two washes in culture medium and additionally two in PBS cells were transferred to 10 ml of freshly prepared PBS containing 0.1% (w/v) NaBH4 for 2 h to permeabilize cells and reduce autofluorescence. After two washes with PBS cells were treated with 2% driselase (Sigma) in dist. Water for 1 h at 28°C to partially digest cell walls. Directly afterward the cells were incubated in PBS containing 3% (v/v) NP-40 and 10% (v/v) DMSO. They were then washed in PBS containing 100 mM glycine as a blocking reagent or with blocking solution consisting of PBS, 5% (w/v) BSA, 2.5% (v/v) normal goat serum, and 0.1% (v/v) cold water fish skin gelatin (Aurion, Wageningen, The Netherlands) for 1 h at room temperature. The cells were incubated at 4°C overnight with the primary antibody in PBS at different dilutions SEC13 (1:100), SYP31 (1:100), or SYP7s serum (1:50). The cells were then washed twice in PBS, and incubated in the dark for 3 h at 37°C with Alexa-fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit IgG (Invitrogen) diluted 1:200 in PBS, Alexa-fluor 546 goat anti-rat IgG (Invitrogen) diluted 1:200 in PBS, Alexa-fluor 546 goat anti-guinea pig IgG (Invitrogen) diluted 1:200 in PBS.
High pressure freezing and immunogold electron microscopy
Samples were high pressure frozen, freeze-substituted, and embedded as described in Hillmer et al. 2012). Immunogold labeling was performed according to Scheuring et al. 2011) using SYP7 antiserum at a dilution of 1:200 in PBS. Sections were observed in a JEOL JEM1400 transmission electron microscope operating at 80 kV and images were taken with a Fastscan-F214 CCD camera (TVIPS, Gauting, Germany).
Western blotting and membrane isolation
Total membrane fractions were isolated from Arabidopsis thaliana and N. benthamiana leaves. After grinding the material in homogenization buffer [0.04 M HEPES; 0.01 M KCl; 0.4 M Sucrose; 100 mM EDTA; 0.003 M MgCl2-hexahydrate; 1 mM DTT; 1:100 protease inhibitor mix (Sigma)] the homogenate was centrifuged at 4500 g for 15 min (4°C) followed by the centrifugation of the supernatant at 4500 g for 20 min (4°C). Membranes were then enriched by centrifuging the supernatant at 100,000 g for 60 min (4°C). The pellet and the supernatant (negative control) were used for the following steps. Protein gel blots and immunodetection were performed as described previously (Bubeck et al., 2008) using rabbit antiserum raised against SYP7X (Suwastika et al., 2008).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Movies S1–S3 for this article can be found online at http://www.frontiersin.org/Plant_Cell_Biology/10.3389/fpls.2012.00143/abstract
Movie of live cell imaging of CFP-HDEL and SYP72-YFP. Corresponds to individual frames presented in Figures 5D–G.
Movie of Man1-RFP and SYP72-YFP in a tobacco leaf epidermal cell. Individual frames are shown in Figures 7A–H.
Man1-RFP and SYP72-YFP fluorescence is observed in this video. Figures 7I–P represents individual frames.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Joachim Forner (Department of Stem Cell Biology, Centre for Organismal Studies, University of Heidelberg, Germany) for providing vectors and for advice on cloning strategies. We thank Dr. Peter Pimpl (Centre for Plant Molecular Biology, University of Tübingen, Germany) for cloning RFP-p24 into a binary vector. We also thank Dr. Christophe Ritzenthaler (Institut de Biologie Moléculaire des Plantes du CNRS, Université de Strasbourg, France) for providing the binary Man1-RFP construct, Dr. Federica Brandizzi (MSU/DOE Plant Research Laboratory, East Lansing, Michigan, USA) for supplying us with the YFP-Sec24 construct, Dr. Aiming Wang (Southern Crop Protection and Food Research Centre, AAFC, Canada) for providing the 6-kDa VP-CFP plasmid, and Dr. Ikuko Hara-Nishimura for supplying the GFP-p115 construct. Barbara Jesenofsky is thanked for technical assistance. The financial support of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (RO 440/14-1) is gratefully acknowledged.
Appendix
Table A1.
Primers and vectors used in this investigation.
| Primer description | Sequence | Vector backbone |
|---|---|---|
| wtSYP72 sense ClaI | ACCACCATCGATATGCCGGTCATTGAT | pSar1 |
| wtSYP72 antisense BamHI | ACCACCGGATCCTTAGTTTAGAGCATT | pSar1 |
| YFP-SYP72 sense ClaI | ACCACCATCGATATGCCGGTCATTGAT | pDS13 |
| YFP-SYP72 antisense BamHI | ACCACCGGATCCTTAGTTTAGAGCATT | pDS13 |
| SYP72 gateway sense | GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTCTATGCCGGTCATTGATATC | pJV-108 |
| SYP72 gateway antisense | GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTCCGTTTAGAGCATTGTAAAT | pJV-108 |
| wtUSE1 sense ClaI | ACCACCATCGATGGGAATCGGCAAA | pSar1 |
| wtUSE1 antisense BamHI | ACCACCGGATCCCTATGTGACTCGGAT | pSar1 |
| YFP-USE1 sense sense ClaI | ACCACCATCGATGGGAATCGGCAAA | pDS13 |
| YFP-USE1 antisense BamHI | ACCACCGGATCCCTATGTGACTCGGAT | pDS13 |
| SYP71-GFP sense NheI | ACCACCGCTAGCATGACTGTGATCGAT | pDS13 |
| SYP71-GFP antisense NotI | ACCACCGCGGCCGCGCTTCAGTACATTGGTA | pDS13 |
| wtSYP73 sense ClaI | ACCACCATCGATATGGGCGTAATTGAT | pSar1 |
| wtSYP73 antisense BamHI | ACCACCGGATCCTCACTTCACAGAGTT | pSar1 |
| YFP-SYP73 sense ClaI | ACCACCATCGATATGGGCGTAATTGAT | pDS13 |
| YFP-SYP73 antisense BamHI | ACCACCGGATCCTCACTTCACAGAGTT | pDS13 |
| SYP72-GFP sense SmaI | ACCACCCCCGGGATGCCGGTCATTGAT | pSN9 |
| SYP72-GFP antisense Xba | ACCACCTCTAGATGCATGCCGGGGATC | pSN9 |
| RFP-SYP61 sense NheI | AGACTAGCTAGCATGGCCTCCTCCGAGGACG | pDS02 |
| RFP-SYP61 antisense ClaI | CTCACCATCGATGCGGCGCCGGTGGAGTGGCG | pDS02 |
| Tip20_SalI_fwd | tagcGTCGACatgcttccgatggaacat | pJV-107 |
| Tip20_NotI_w/oSTOP_rev | gctaGCGGCCGCgtaagacctacaaaattg | pJV-107 |
| Tip20_NcoI_fwd | actgCCATGGtctatctctacc | pJV-107 |
| Tip20_NcoI_rev | actgCCATGGtctatcaacctc | pJV-107 |
References
- Allan B. B., Moyer B. D., Balch W. E. (2000). Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science 289, 444–448 10.1126/science.289.5478.444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki T., Kojima M., Tani K., Tagaya M. (2008). Sec22b-dependent assembly of endoplasmic reticulum Q-SNARE proteins. Biochem. J. 410, 93–100 10.1042/BJ20071304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appenzeller-Herzog C., Hauri H.-P. (2006). The ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC): in search of its identity and function. J. Cell Sci. 119, 2173–2183 10.1242/jcs.03019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avisar D., Abu-Abied M., Belausov E., Sadot E., Hawes C., Sparkes I. A. (2009). A comparative study of the involvement of 17 Arabidopsis myosin family members on the motility of Golgi and other organelles. Plant Physiol. 150, 700–709 10.1104/pp.109.136853 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avisar D., Prokhnevsky A. I., Makarova K. S., Koonin E. V., Dolja V. V. (2008). Myosin XI-K is required for rapid trafficking of Golgi stacks, peroxisomes, and mitochondria in leaf cells of Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Physiol. 146, 1098–1108 10.1104/pp.107.113647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballensiefen W., Ossipov D., Schmitt H. D. (1998). Recycling of the yeast v-SNARE Sec22p involves COPI-proteins and the ER transmembrane proteins Ufe1p and Sec20p. J. Cell Sci. 111, 1507–1520 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck R., Ravet M., Wieland F. T., Cassel D. (2009). The COPI system: molecular mechanisms and function. FEBS Lett. 583, 2701–2709 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.07.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boevink P., Oparka K., Santa Cruz S., Martin B., Betteridge A., Hawes C. (1998). Stacks on tracks: the plant Golgi apparatus traffics on an actin/ER network. Plant J. 15, 441–447 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00208.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubeck J., Scheuring D., Hummel E., Langhans M., Viotti C., Foresti O., Denecke J., Banfield D. K., Robinson D. G. (2008). The syntaxins SYP31 and SYP81 control ER-Golgi trafficking in the plant secretory pathway. Traffic 9, 1629–1652 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00803.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budnik A., Stephens D. J. (2009). ER exit sites – localization and control of COPII vesicle formation. FEBS Lett. 583, 3796–3803 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai H., Reinisch K., Ferro-Novick S. (2007). Coats, tethers, Rabs, and SNAREs work together to mediate the intracellular destination of a transport vesicle. Dev. Cell 12, 671–682 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.04.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X., Ballew N., Barlowe C. (1998). Initial docking of ER-derived vesicles requires Uso1p and Ypt1p but is independent of SNARE proteins. EMBO J. 17, 2156–2165 10.1093/emboj/17.8.2156 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatre L., Brandizzi F., Hocquellet A., Hawes C., Moreau P. (2005). Sec22 and Memb11 are v-SNAREs of the anterograde endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi pathway in tobacco leaf epidermal cells. Plant Physiol. 139, 1244–1254 10.1104/pp.105.067447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras I., Yang Y., Robinson D. G., Aniento F. (2004). Sorting signals in the cytosolic tail of plant p24 proteins involved in the interaction with the COPII coat. Plant Cell Physiol. 45, 1779–1786 10.1093/pcp/pch200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- daSilva L. L. P., Snapp E. L., Denecke J., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Hawes C., Brandizzi F. (2004). Endoplasmic reticulum export sites and Golgi bodies behave as single mobile secretory units in plant cells. Plant Cell 16, 1753–1771 10.1105/tpc.022673 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilcher M., Veith B., Chidambaram S., Hartmann E., Schmitt H. D., von Mollard F. G. (2003). Use1p is a yeast SNARE protein required for retrograde traffic to the ER. EMBO J. 22, 3664–3674 10.1093/emboj/cdg339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French A. P., Mills S., Swarup R., Bennett M. J., Pridmore T. P. (2008). Colocalization of fluorescent markers in confocal microscope images of plant cells. Nat. Protocol. 3, 619–628 10.1038/nprot.2008.31 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanton S. L., Matheson L. A., Brandizzi F. (2006). Seeking a way out: export of proteins from the plant endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Plant Sci. 11, 335–343 10.1016/j.tplants.2006.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawes C. (2012). The ER/Golgi interface – is there anything in-between? Front. Plant Sci. 3:73 10.3389/fpls.2012.00073 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawes C., Osterrieder A., Hummel E., Sparkes I. (2008). The plant ER-Golgi interface. Traffic 9, 1571–1580 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00773.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawes C., Satiat-Jeunemaitre B. (2005). The plant Golgi apparatus – going with the flow. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1744, 93–107 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.03.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennegan K. P., Danna K. J. (1998). pBIN20: an improved binary vector for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 16, 129–131 10.1023/A:1007444100898 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. (1979). Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J. Cell Biol. 81, 275–300 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillmer S., Viotti C., Robinson D. G. (2012). An improved procedure for low-temperature embedding of high-pressure frozen and freeze-substituted plant tissues resulting in excellent structural preservation and contrast. J. Microsc. 247, 43–47 10.1111/j.1365-2818.2011.03595.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu V. W., Yang J.-S. (2009). Mechanisms of COPI vesicle formation. FEBS Lett. 583, 3758–3763 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.03.039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H., Budnik A., Schmidt K., Palmer K. J., Mantell J., Noakes C., Johnson A., Carter D. A., Verkade P., Watson P., Stephens D. J. (2009). Organisation of human ER-exit sites: requirements for the localisation of Sec16 to transitional ER. J. Cell Sci. 122, 2924–2934 10.1242/jcs.044032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel E., Schmickl R., Hinz G., Hillmer S., Robinson D. G. (2007). Brefeldin action and recovery in Chlamydomonas are rapid and involve fusion and fission of Golgi cisternae. Plant Biol. 9, 489–501 10.1055/s-2006-924759 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Scheller R. H. (2006). SNAREs – engines for membrane fusion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 631–643 10.1038/nrm2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G., Geldner N. (2007). The high road and the low road: trafficking choices in plants. Cell 130, 977–979 10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang B.-H., Staehelin L. A. (2008). ER-to-Golgi transport by COPII vesicles in Arabidopsis involves a ribosome-excluding scaffold that is transferred with the vesicles to the Golgi matrix. Protoplasma 234, 51–64 10.1007/s00709-008-0015-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S.-J., Brandizzi F. (2012). News and views into the SNARE complexity in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 3:28 10.3389/fpls.2012.00028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancelle S. A., Hepler P. K. (1992). Ultrastructure of freeze-substituted pollen tubes of Lilium longiflorum. Protoplasma 167, 215–230 10.1007/BF01403385 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Langhans M., Förster S., Helmchen G., Robinson D. G. (2011). Differential effects of the brefeldin A analogue (6R)-hydroxy-BFA in tobacco and Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 62, 2949–2957 10.1093/jxb/err007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhans M., Hawes C., Hillmer S., Hummel E., Robinson D. G. (2007). Golgi regeneration after brefeldin A treatment in BY-2 cells entails stack enlargement and cisternal growth followed by division. Plant Physiol. 145, 527–538 10.1104/pp.107.104919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhans M., Marcote M. J., Pimpl P., Virgili-López G., Robinson D. G., Aniento F. (2008). In vivo trafficking and localization of p24 proteins in plant cells. Traffic 9, 770–785 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00719.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhans M., Meckel T., Kress A., Lerich A., Robinson D. G. (2012). ERES (ER exit sites) and the “Secretory Unit Concept.” J. Microsc. 10.1111/j.1365-2818.2011.03597.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latijnhouwers M., Hawes C., Carvalho C. (2005). Holding it all together? Candidate proteins for the plant Golgi matrix. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 8, 632–639 10.1016/j.pbi.2005.09.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. C. S., Miller E. A., Goldberg J., Orci L., Schekman R. (2004). Bi-directional protein transport between the ER and Golgi. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 20, 87–123 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.20.012103.135836 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerich A., Langhans M., Sturm S., Robinson D. G. (2011). Is the 6 kDa tobacco etch viral protein a bona fide ERES marker? J. Exp. Bot. 62, 5013–5023 10.1093/jxb/err200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardones G. A., Snyder C. M., Howell K. E. (2006). Cis-Golgi matrix proteins move directly to endoplasmic reticulum exit sites by association with tubules. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 525–538 10.1091/mbc.E05-05-0447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti L., Fornaciari S., Renna L., Stefano G., Brandizzi F. (2010). COPII-mediated traffic in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 15, 522–528 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.05.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiringer C. T. A., Rethmeier R., Auffarth K., Wilson J., Perz A., Barlowe C., Schmitt H. D., Ungermann C. (2011). The Dsl1 protein tethering complex is a resident endoplasmic reticulum complex, which interacts with five soluble NSF (N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor) attachment protein receptors (SNAREs): implications for fusion and fusion regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 25039–25046 10.1074/jbc.M110.215327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. A., Barlowe C. (2010). Regulation of coat assembly –sorting things out at the ER. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 22, 447–453 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.04.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogelsvang S., Gomez-Ospina N., Soderholm J., Glick B. S., Staehelin L. A. (2003). Tomographic evidence for continuous turnover of Golgi cisternae in Pichia pastoris. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 2277–2291 10.1091/mbc.E02-10-0697 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montezinos J. C., Sturm S., Langhans M., Hillmer S., Marcote M. J., Robinson D. G., Aniento F. (2012). Coupled transport of Arabidopsis p24 proteins at the ER-Golgi interface. J. Exp. Bot. 10.1093/jxb/ers112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Brandizzi F., Hanton S., Chatre L., Melser S., Hawes C., Satiat-Jeunemaitre B. (2007). The plant ER-Golgi interface: a highly structured and dynamic membrane complex. J. Exp. Bot. 58, 49–64 10.1093/jxb/erl135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murashige R., Skoog F. (1962). A revised medium for rapid growth and bio-assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Plant Physiol. 15, 473–497 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nebenführ A., Gallagher L. A., Dunahay T. G., Frohlick J. A., Mazurkiewicz A. M., Meehl J. B., Staehelin L. A. (1999). Stop-and-go movements of plant Golgi stacks are mediated by the acto-myosin system. Plant Physiol. 121, 1127–1142 10.1104/pp.121.4.1127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebenführ A., Ritzenthaler C., Robinson D. G. (2002). Brefeldin A: deciphering an enigmatic inhibitor of secretion. Plant Physiol. 130, 1102–1108 10.1104/pp.011569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann U., Brandizzi F., Hawes C. (2003). Protein transport in plant cells: in and out of the Golgi. Ann. Bot. 92, 167–180 10.1093/aob/mcg134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemes S., Langhans M., Viotti C., Scheuring D., San Wan Yan M., Jiang L., Hillmer S., Robinson D. G., Pimpl P. (2010). Retromer recycles vacuolar sorting receptors from the trans-Golgi network. Plant J. 61, 107–121 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04034.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. K., Indig F. E., Olivieri N., Levine N. D., Latterich M. (1998). Organelle membrane fusion: a novel function for the syntaxin homolog Ufe1p in ER membrane fusion. Cell 92, 611–620 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81129-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei J., Ma C., Rizo J., Grishin N. V. (2009). Remote homology between Munc13 MUN domain and vesicle tethering complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 391, 509–517 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.06.054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillipson B. A., Pimpl P., daSilva L. L., Crofts A. J., Taylor J. P., Movafeghi A., Robinson D. G., Denecke J. (2001). Secretory bulk flow of soluble proteins is efficient and COPII dependent. Plant Cell 13, 2005–2020 10.2307/3871424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimpl P., Movafeghi A., Coughlan S., Denecke J., Hillmer S., Robinson D. G. (2000). In situ localization and in vitro induction of plant COPI-coated vesicles. Plant Cell 12, 2219–2236 10.2307/3871116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly B. A., Kraynack B. A., VanRheenen S. M., Waters M. G. (2001). Golgi-to-endoplasmic reticulum (ER) retrograde traffic in yeast requires Dsl1p, a component of the ER target site that interacts with a COPI coat subunit. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 3783–3796 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren Y., Yip C. K., Tripathi A., Huie D., Jeffrey P. D., Walz T., Hughson F. M. (2009). A structure-based mechanism for vesicle capture by the multisubunit tethering complex Dsl1. Cell 139, 1119–1129 10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzenthaler C., Nebenführ A., Movafeghi A., Stussi-Garaud C., Behnia L., Pimpl P., Staehelin L. A., Robinson D. G. (2002). Reevaluation of the effects of brefeldin A on plant cells using tobacco bright yellow 2 cells expressing Golgi-targeted green fluorescent protein and COPI antisera. Plant Cell 14, 237–261 10.1105/tpc.010237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. G., Herranz M.-C., Bubeck J., Pepperkok R., Ritzenthaler C. (2007). Membrane dynamics in the early secretory pathway. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 26, 199–225 10.1080/07352680701495820 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. G., Langhans M., Saint-Jore-Dupas C., Hawes C. (2008). BFA effects are tissue and not just plant specific. Trends Plant Sci. 13, 405–408 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.05.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runions J., Brach T., Kuhner S., Hawes C. (2006). Photoactivation of GFP reveals protein dynamics within the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J. Exp. Bot. 57, 43–50 10.1093/jxb/eri289 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderfoot A. A., Assaad F. F., Raikhel N. V. (2000). The Arabidopsis genome. An abundance of soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor adaptor protein receptors. Plant Physiol. 124, 1558–1569 10.1104/pp.124.4.1558 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuring D., Viotti C., Krüger F., Künzl F., Sturm S., Bubeck J., Hillmer S., Frigerio L., Robinson D. G., Pimpl P., Schumacher K. (2011). Multivesicular bodies mature from the trans-Golgi network/early endosome in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23, 3463–3481 10.1105/tpc.111.086918 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D. (2010). Dsl1p/Zw10: common mechanisms behind tethering vesicles and microtubules. Trends Cell Biol. 20, 257–268 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.02.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoberer J., Runions J., Steinkellner H., Strasser R., Hawes C., Osterrieder A. (2010). Sequential depletion and acquisition of proteins during Golgi stack disassembly and reformation. Traffic 11, 1429–1444 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01106.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes I. A., Ketelaar T., de Ruijter N. C. A., Hawes C. (2009). Grab a Golgi: laser trapping of Golgi bodies reveals in vivo interactions with the endoplasmic reticulum. Traffic 10, 567–571 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00891.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin L. A., Kang B.-H. (2008). Nanoscale architecture of endoplasmic reticulum export sites and of Golgi membranes as determined by electron tomography. Plant Physiol. 147, 1454–1468 10.1104/pp.108.120618 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda Y., Nakano A. (2012). The yeast golgi apparatus. Traffic 13, 505–510 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01316.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwastika I. N., Uemura T., Shiina T., Sato M. H., Takeyasu K. (2008). SYP71, a plant-specific Qc-SNARE protein, reveals dual localization to the plasma membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis. Cell Struct. Funct. 33, 185–192 10.1247/csf.08024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E., Lupashin V. (2009). Role of vesicle tethering factors in the ER-Golgi membrane traffic. FEBS Lett. 583, 3770–3783 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi A., Ren Y., Jeffrey P. D., Hughson F. M. (2009). Structural characterization of Tip20p and Dsl1p, subunits of the Dsl1p vesicle tethering complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 114–123 10.1038/nsmb.1548 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse Y. C., Mo B., Hillmer S., Zhao M., Lo S. W., Robinson D. G., Jiang L. (2004). Identification of multivesicular bodies as prevacuolar compartments in Nicotiana tabacum BY-2 cells. Plant Cell 16, 672–693 10.1105/tpc.019703 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Ueda T., Ohniwa R. L., Nakano A., Takeyasu K., Sato M. H. (2004). Systematic analysis of SNARE molecules in Arabidopsis: dissection of the post-Golgi network in plant cells. Cell Struct. Funct. 29, 49–65 10.1247/csf.29.49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y.-d., Elamawi R., Bubeck J., Pepperkok R., Ritzenthaler C., Robinson D. G. (2005). Dynamics of COPII vesicles and the Golgi apparatus in cultured Nicotiana tabacum BY-2 cells provides evidence for transient association of Golgi stacks with endoplasmic reticulum exit sites. Plant Cell 17, 1513–1531 10.1105/tpc.104.026757 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti G., Pahuja K. B., Studer S., Shim S., Schekman R. (2012). COPII and the regulation of protein sorting in mammals. Nat. Cell Biol. 14, 20–28 10.1038/ncb2390 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeuschner D., Geerts W. J. C., van Donselaar E., Humbel B. M., Slot J. W., Koster A. J., Klumperman J. (2006). Immuno-electron tomography of ER exit sites reveals the existence of free COPII-coated transport carriers. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 377–383 10.1038/ncb1371 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink S., Wenzel D., Wurm C. A., Schmitt H. D. (2009). A link between ER tethering and COP-I vesicle uncoating. Dev. Cell 17, 403–416 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.07.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Movie of live cell imaging of CFP-HDEL and SYP72-YFP. Corresponds to individual frames presented in Figures 5D–G.
Movie of Man1-RFP and SYP72-YFP in a tobacco leaf epidermal cell. Individual frames are shown in Figures 7A–H.
Man1-RFP and SYP72-YFP fluorescence is observed in this video. Figures 7I–P represents individual frames.