Abstract
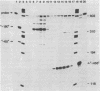
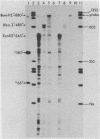
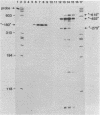
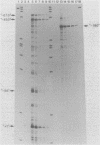
We have developed an homologous in vitro system from spinach chloroplasts that correctly initiates transcription of the plastid genes for the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (rbcL) and the beta subunit of the plastid ATPase (atpB). The transcriptionally active extracts from spinach chloroplasts require circular DNA templates for specific initiation. The RNA polymerase activity is insensitive to rifampicin. The extent of transcription in vitro is a function of the extract:template ratio. The efficiency of the rbcL transcription in vitro is more than one transcript per one hundred templates per hour.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry-Lowe S. L., Mc Knight T. D., Shah D. M., Meagher R. B. The nucleotide sequence, expression, and evolution of one member of a multigene family encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in soybean. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):483–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley W., Smith H. J., Bogorad L. RNA polymerases of maize: partial purification and properties of the chloroplast enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Miller C. A. Non-chromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria. II. Molecular nature of R-factors isolated from Proteus mirabilis and Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):671–687. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossland L. D., Rodermel S. R., Bogorad L. Single gene for the large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase in maize yields two differentially regulated mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4060–4064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Delimitation of far upstream sequences required for maximal in vitro transcription of an H2A histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
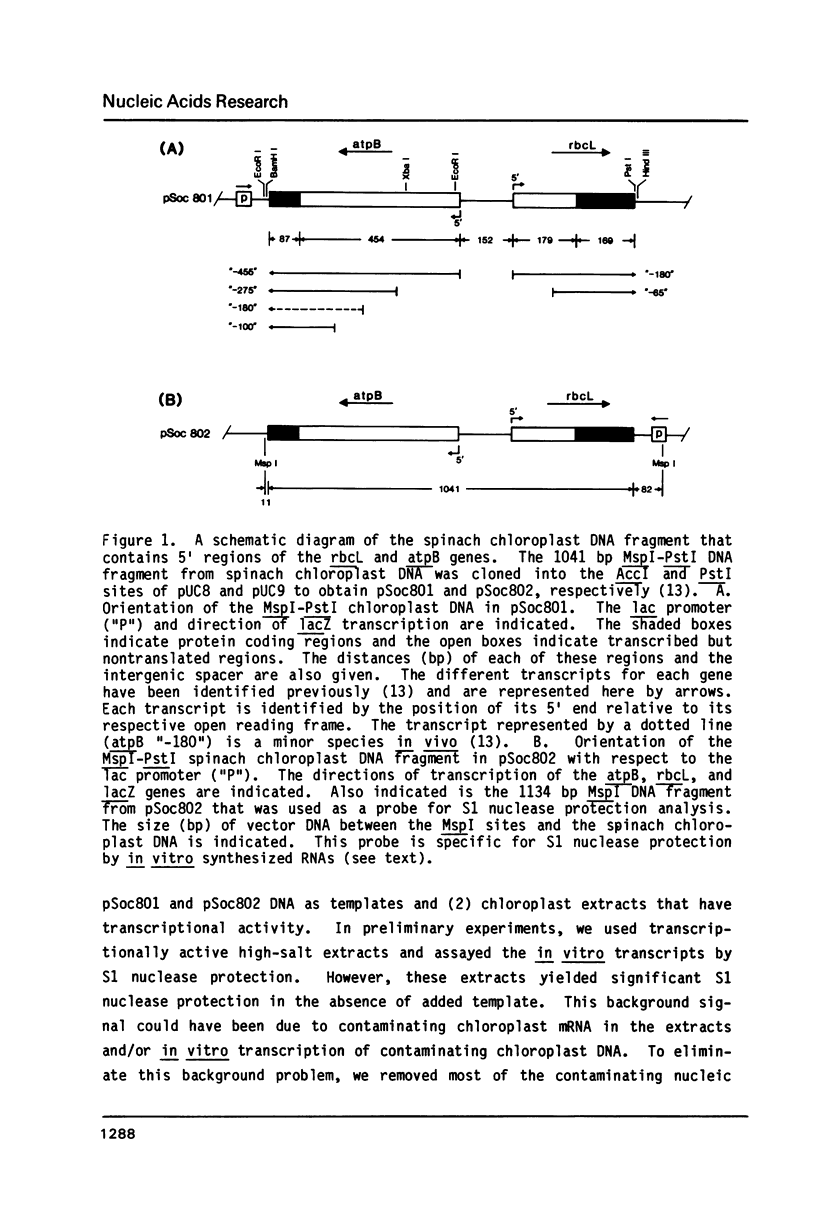
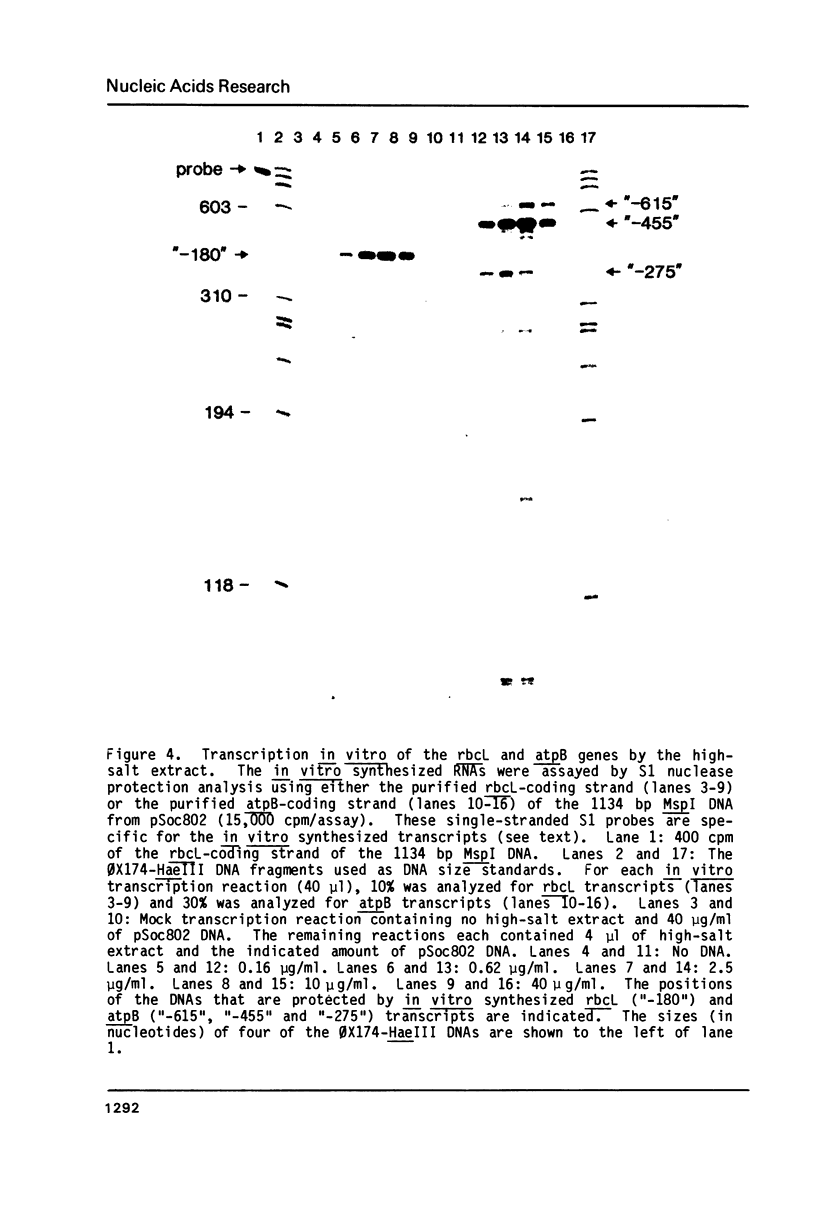
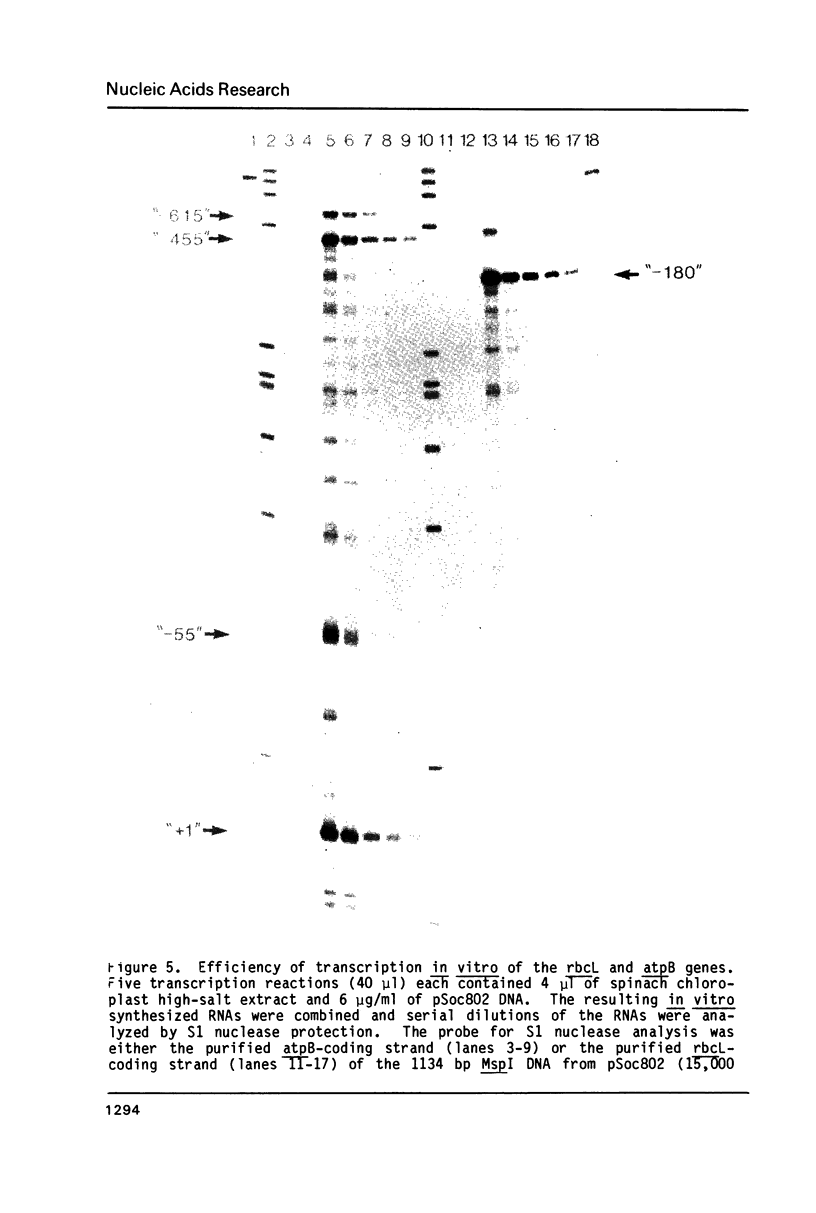
- Gruissem W., Greenberg B. M., Zurawski G., Prescott D. M., Hallick R. B. Biosynthesis of chloroplast transfer RNA in a spinach chloroplast transcription system. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):815–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Tenen D. G., Livingston D. M., Sharp P. A. T antigen repression of SV40 early transcription from two promoters. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly S. O., McIntosh L., Link G., Bogorad L. Differential transcription in vivo and in vitro of two adjacent maize chloroplast genes: The large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase and the 2.2-kilobase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6821–6825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link G. DNA sequence requirements for the accurate transcription of a protein-coding plastid gene in a plastid in vitro system from mustard (Sinapis alba L.). EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1697–1704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polya G. M., Jagendorf A. T. Wheat leaf RNA polymerases. I. Partial purification and characterization of nuclear, chloroplast and soluble DNA-dependent enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Oct;146(2):635–648. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz Z., Jolly S. O., Steinmetz A. A., Bogorad L. Overlapping divergent genes in the maize chloroplast chromosome and in vitro transcription of the gene for tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3423–3427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suissa M. Spectrophotometric quantitation of silver grains eluted from autoradiograms. Anal Biochem. 1983 Sep;133(2):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis R. H., Rubin H. Calcium protects DNase I from proteinase K: a new method for the removal of contaminating RNase from DNase I. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):260–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. Structures of the genes for the beta and epsilon subunits of spinach chloroplast ATPase indicate a dicistronic mRNA and an overlapping translation stop/start signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6260–6264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Perrot B., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. The structure of the gene for the large subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from spinach chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3251–3270. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]