Abstract
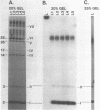
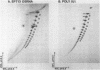
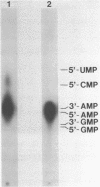
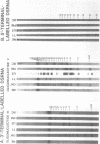
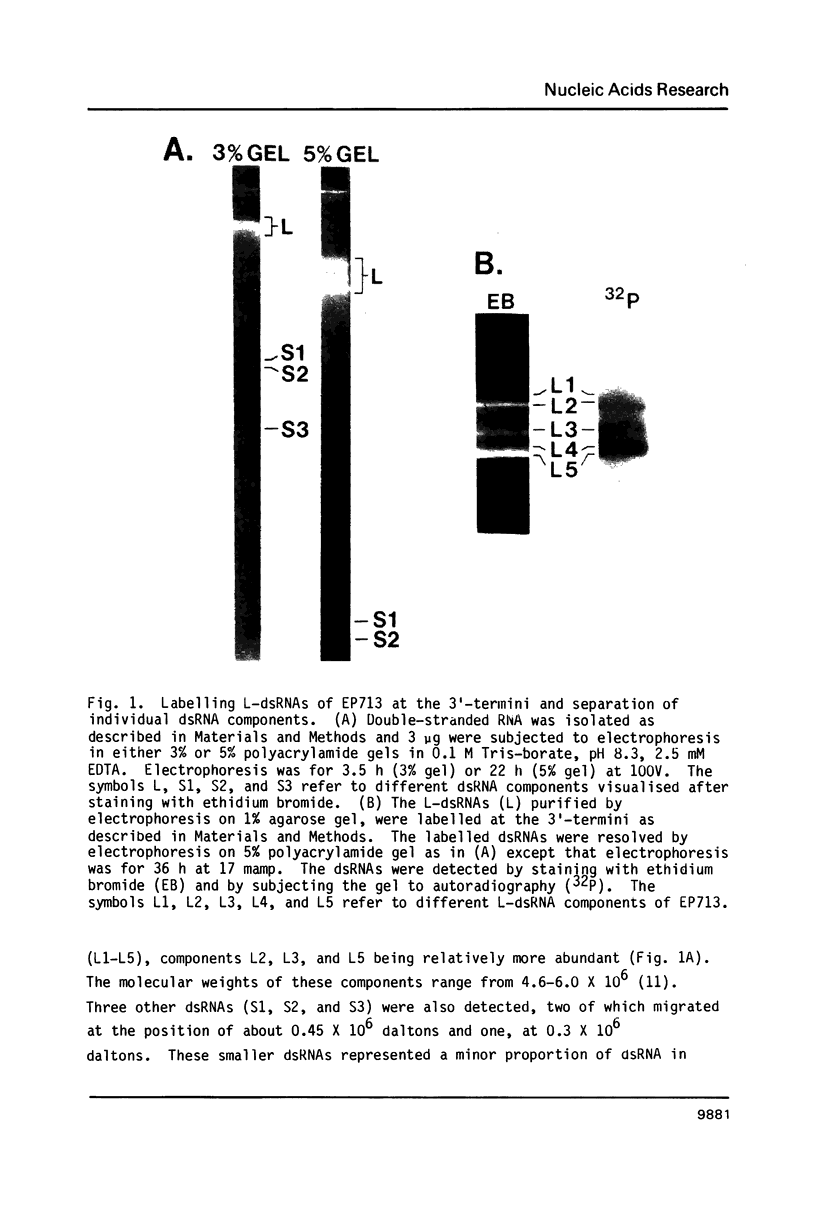
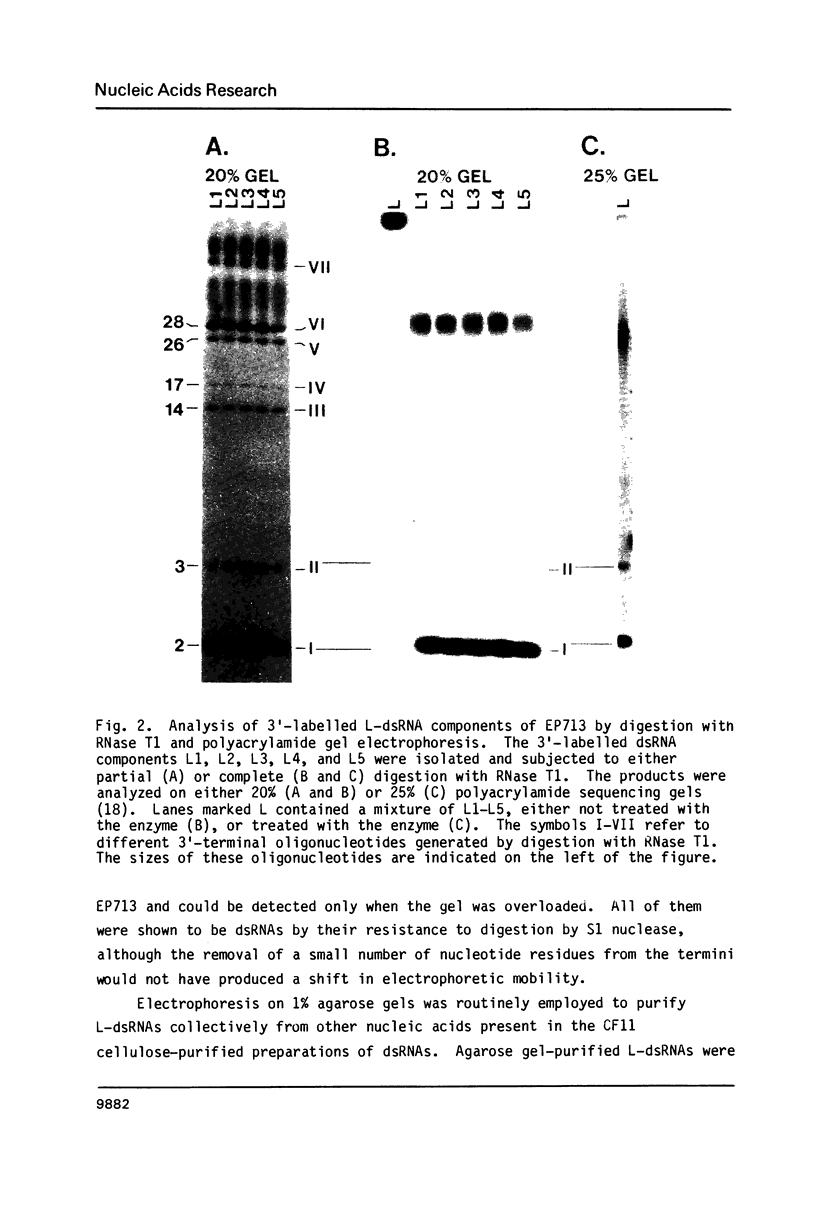
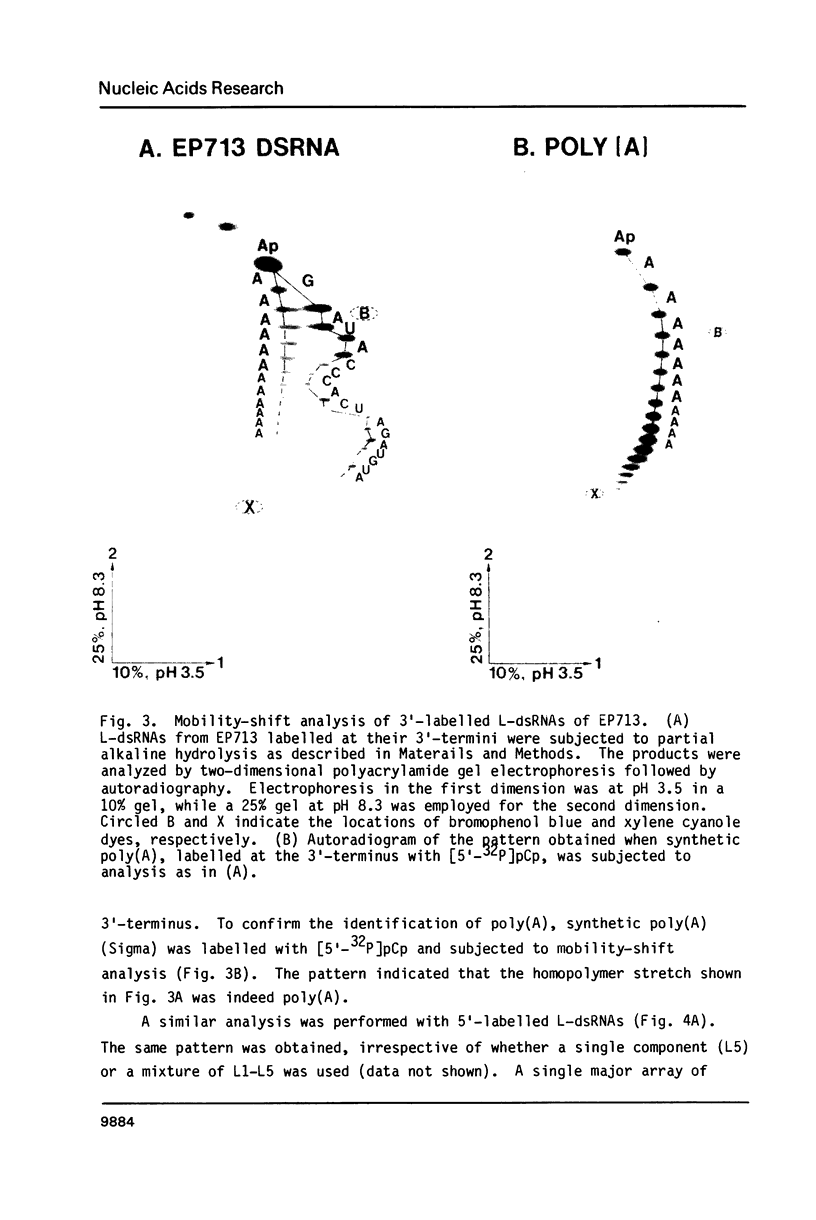
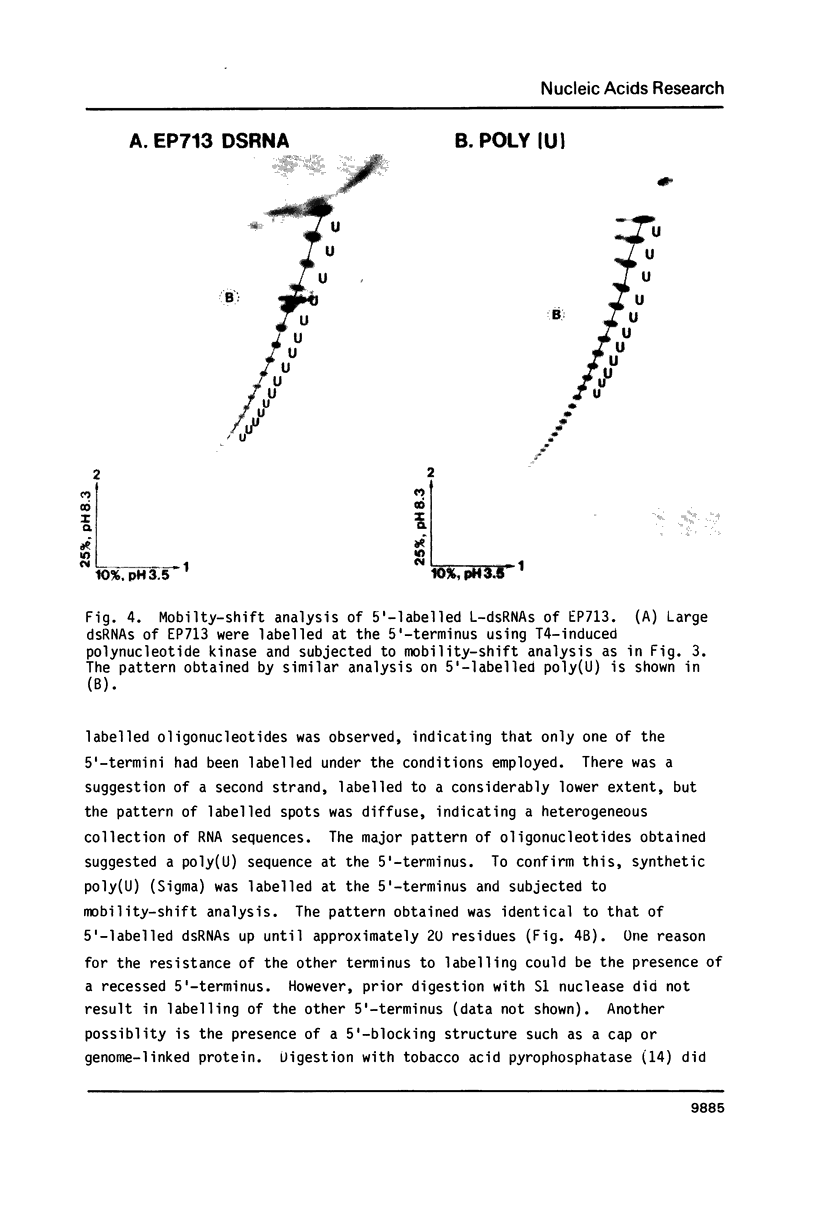
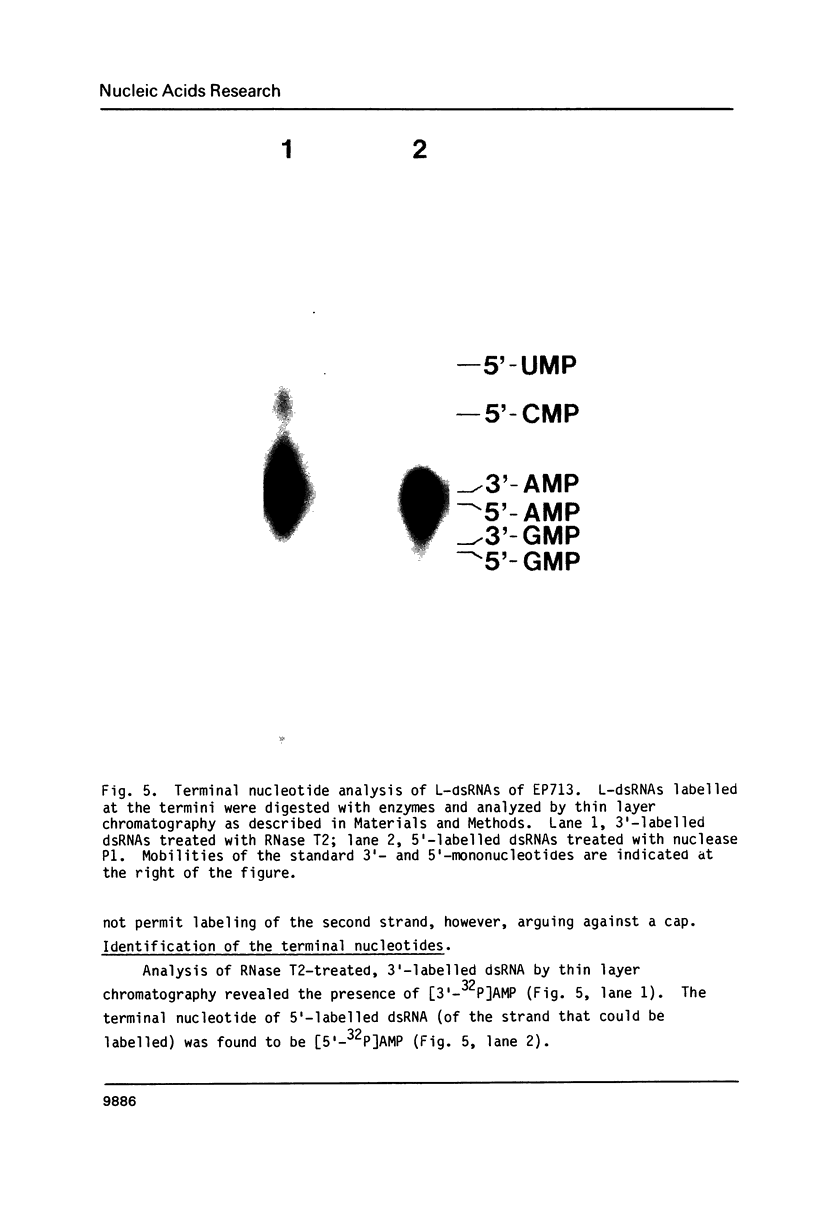
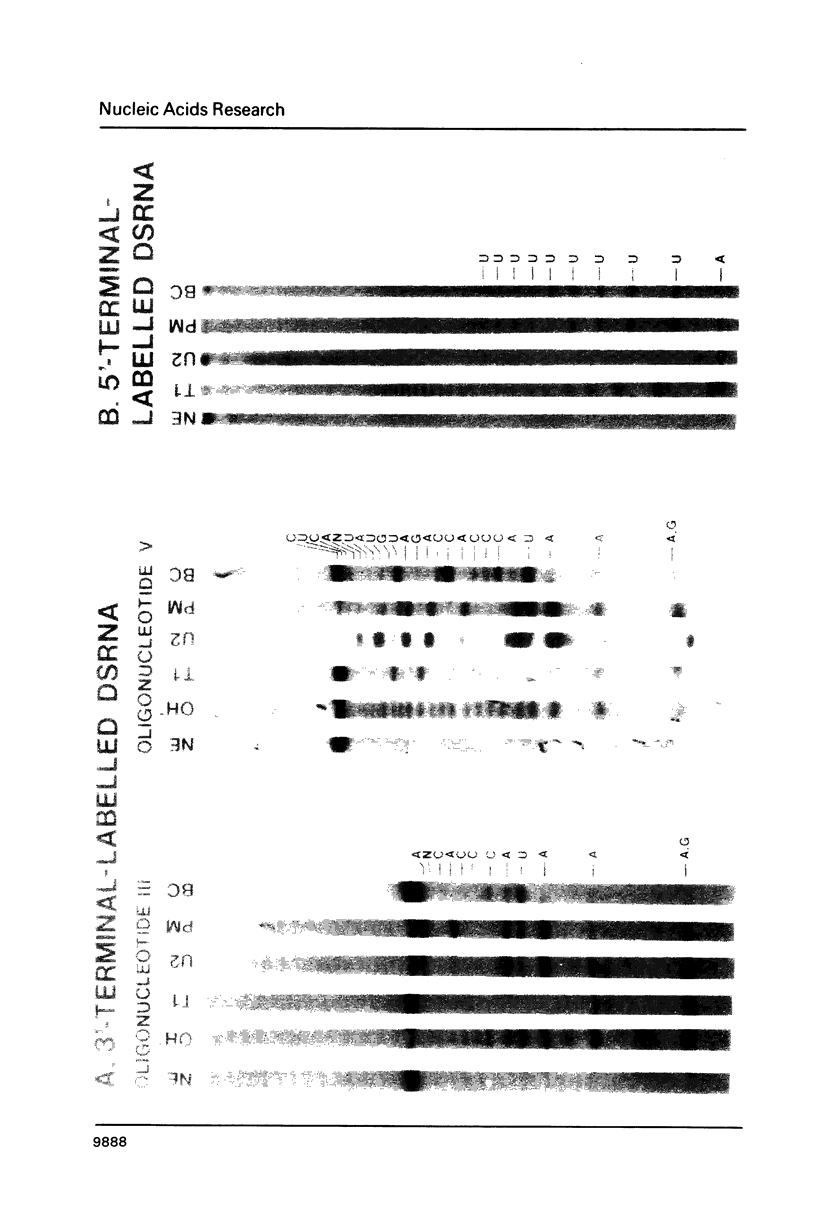
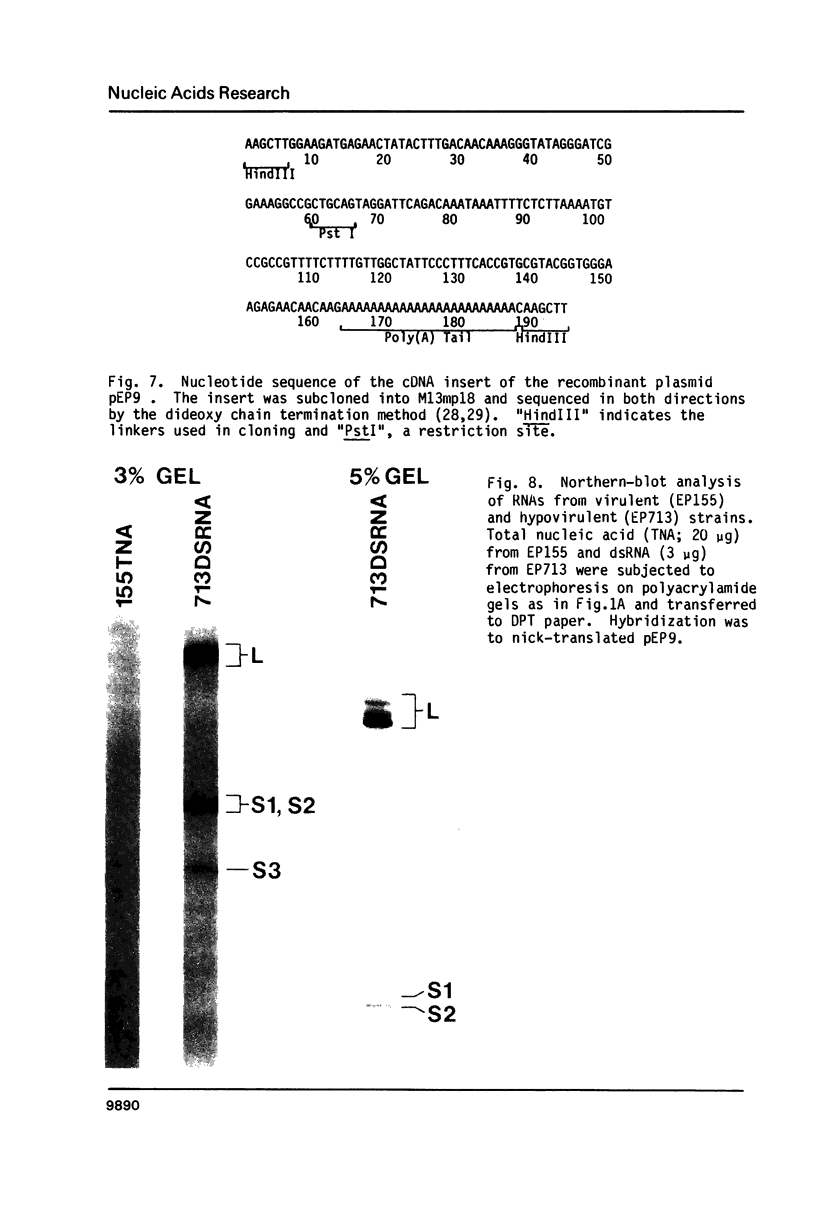
The 3'- and 5'-terminal sequences of the five large double-stranded RNA species (L-dsRNA; 4.5-6.0 X 10(6) daltons) of EP713, a hypovirulent strain of Endothia parasitica, were determined by mobility-shift and enzymatic methods. All the L-dsRNAs appeared to have identical terminal sequences. A heteropolymer sequence was found at one 3'-terminus and a poly(A) sequence of variable length at the other. It was possible to label only one 5'-terminus using polynucleotide kinase and [gamma-32P]ATP, and this was shown to be a poly(U) sequence of variable length. We propose that the dsRNAs have the following structure, where X represents a blocking group: (Formula: see text). A recombinant plasmid containing dsRNA-related sequences was constructed. Hybridization analysis using the recombinant probe indicated that the sequence homology among the L-dsRNAs extended beyond these terminal regions and was also shared by small dsRNAs (0.3-0.45 X 10(6) daltons).
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostakis S. L. Biological control of chestnut blight. Science. 1982 Jan 29;215(4532):466–471. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4532.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Reactions at the termini of tRNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3665–3677. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashdollar L. W., Esparza J., Hudson G. R., Chmelo R., Lee P. W., Joklik W. K. Cloning the double-stranded RNA genes of reovirus: sequence of the cloned S2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7644–7648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J. Four Drosophila heat shock genes at 67B: characterization of recombinant plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4441–4457. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Ruiz J. R., Kaper J. M. Cucumber mosaic virus-associated RNA 5. III. Little nucleotide sequence homology between CARNA 5 and helper RNA. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):204–213. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90393-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannig E. M., Williams T. L., Leibowitz M. J. The internal polyadenylate tract of yeast killer virus M1 double-stranded RNA is variable in length. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90380-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Alzner-Deweerd B., Heckman J. E., MacGee J., Tabor M. W., RajBhandary U. L. Sequence analysis of 5'[32P] labeled mRNA and tRNA using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):37–56. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek L. T., Eschenfeldt W. H., Munns T. W., Rhoads R. E. Heterogeneity of the 5' terminus of hen ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1657–1673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossop D. W., Francki R. I. Association of RNA 3 with aphid transmission of cucumber mosaic virus. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuss D. L., Summers D. Variant dsRNAs associated with transmission-defective isolates of wound tumor virus represent terminally conserved remnants of genome segments. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):276–288. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider I. R., White R. M. Tobacco ringspot virus codes for the coat protein of its satellite. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):244–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulder A., Darby G., Minson T. RNA-RNA hybridisation using 125I-labelled RNA from tobacco necrosis virus and its satellite. Nature. 1974 Oct 25;251(5477):733–735. doi: 10.1038/251733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekeres M., Brownstein B. H., Revel H. R., Haselkorn R. Terminal sequences of the bacteriophage phi 6 segmented dsRNA genome and its messenger RNAs. Virology. 1985 Apr 15;142(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90417-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiapalis C. M., Dorson J. W., De Sante D. M., Bollum F. J. Terminal riboadenylate transferase: a polyadenylate polymerase from calf thymus gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):737–743. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vary C. P., Vournakis J. N. RNase H-catalyzed site-specific deadenylylation of rabbit alpha- and beta- globin mRNAs. Secondary structure of 3'-noncoding regions. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3299–3307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wachter R., Fiers W. Preparative two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of 32 P-labeled RNA. Anal Biochem. 1972 Sep;49(1):184–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]