Abstract
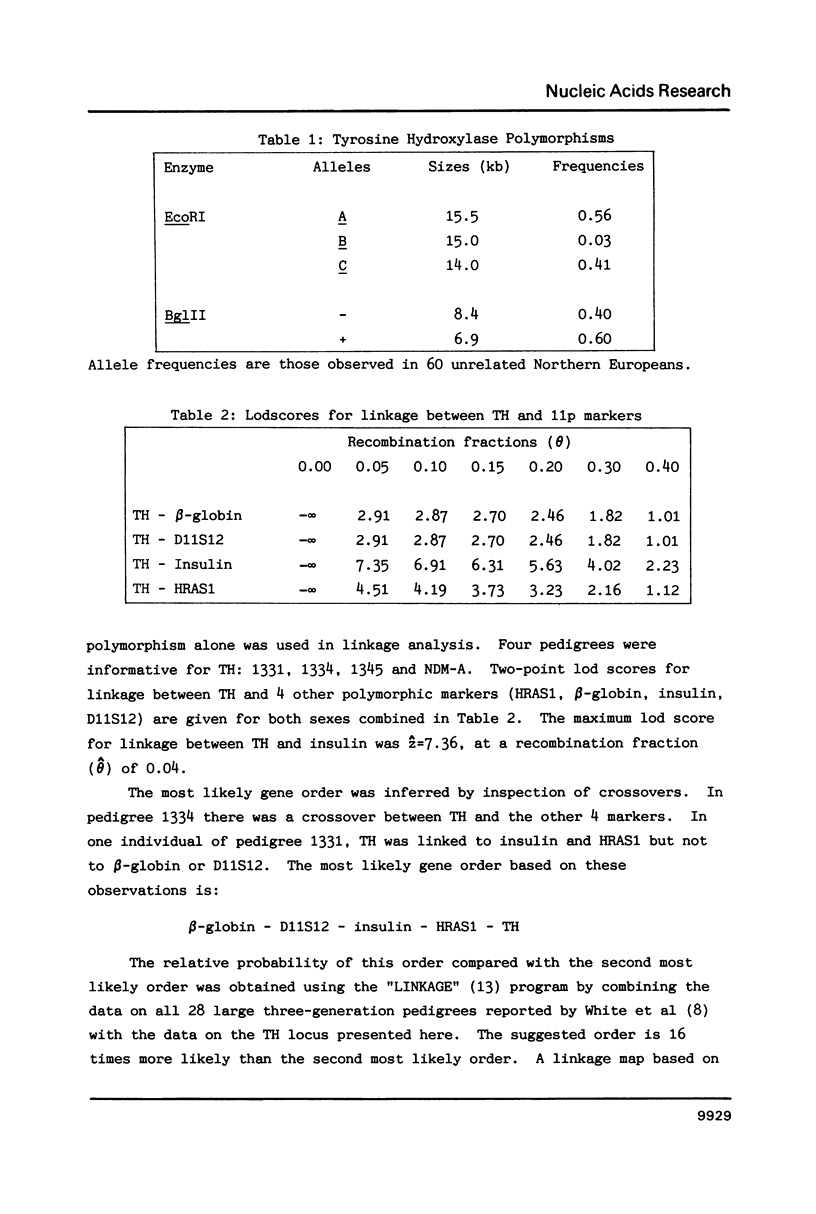
Tyrosine hydroxylase is the rate-limiting enzyme in catecholamine synthesis; the gene has previously been cloned and localised to the short arm of chromosome 11. Because of the interest in tyrosine hydroxylase as a candidate gene for manic-depressive psychosis and other affective disorders, we carried out family studies to determine the linkage of tyrosine hydroxylase with insulin, beta-globin, D11S12 and Harvey-ras 1, members of a linkage group which has previously been localised to 11p. Using DNA from the Centre d'Etude du Polymorphisme Humain (CEPH) and from two large British pedigrees, we show that tyrosine hydroxylase is closely linked to these four loci (z = 7.36, theta = 0.04 for linkage to insulin) and suggest a gene order based on multipoint mapping.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Gerhard D. S., Fong N. M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Rall L. B. Isolation of the human insulin-like growth factor genes: insulin-like growth factor II and insulin genes are contiguous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Selby M. J., Rutter W. J. The highly polymorphic region near the human insulin gene is composed of simple tandemly repeating sequences. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):31–35. doi: 10.1038/295031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissenden J. E., Ullrich A., Francke U. Human chromosomal mapping of genes for insulin-like growth factors I and II and epidermal growth factor. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):781–784. doi: 10.1038/310781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzeschik K. H., Kazazian H. H. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of Chromosomes 10, 11, and 12. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):179–205. doi: 10.1159/000132174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidksy A. S., Robson K. J., Thirumalachary C., Barker P. E., Ruddle F. H., Woo S. L. The PKU locus in man is on chromosome 12. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):527–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeders S. T., Breuning M. H., Davies K. E., Nicholls R. D., Jarman A. P., Higgs D. R., Pearson P. L., Weatherall D. J. A highly polymorphic DNA marker linked to adult polycystic kidney disease on chromosome 16. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):542–544. doi: 10.1038/317542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Leppert M., Bishop D. T., Barker D., Berkowitz J., Brown C., Callahan P., Holm T., Jerominski L. Construction of linkage maps with DNA markers for human chromosomes. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):101–105. doi: 10.1038/313101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


