Abstract
Gastric carcinogenesis is a multistep process orchestrated by aberrancies in the genetic and epigenetic regulation of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Chronic infection with Helicobacter pylori is the strongest known risk factor for the development of gastric cancer. H. pylori expresses a spectrum of virulence factors that dysregulate host intracellular signaling pathways that lower the threshold for neoplastic transformation. In addition to bacterial determinants, numerous host and environmental factors increase the risk of gastric carcinogenesis. Recent discoveries have shed new light on the involvement of microRNAs (miRNAs) in gastric carcinogenesis. miRNAs represent an abundant class of small, non-coding RNAs involved in global post-transcriptional regulation and, consequently, play an integral role at multiple steps in carcinogenesis, including cell cycle progression, proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and metastasis. Expression levels of miRNAs are frequently altered in malignancies, where they function as either oncogenic miRNAs or tumor suppressor miRNAs. This review focuses on miRNAs dysregulated by H. pylori and potential etiologic roles they play in H. pylori-mediated gastric carcinogenesis.
Keywords: gastric cancer, Helicobacter pylori, microRNA, cell cycle, proliferation, apoptosis
Introduction
Microbial infections are among the most significant causes of cancer worldwide with nearly one in five malignancies resulting from infectious agents (Parkin, 2006). Gastrointestinal cancers represent a major global health concern and account for nearly 20% of all cancer-related deaths (Ferlay et al., 2007). Despite the decreasing incidence of gastric cancer in developed countries, it remains the second leading cause of cancer-related death throughout the world, with ∼700,000 deaths attributed to this malignancy annually (Parkin et al., 2005). The major contributing factor to the development of gastric cancer is colonization and chronic infection by the bacterial pathogen, Helicobacter pylori. H. pylori selectively colonizes the gastric epithelium of over 50% of the world’s population and typically persists for the lifetime of the host. Among colonized individuals, however, only a fraction develop gastric adenocarcinoma, emphasizing the importance of understanding the pathogenic mechanisms by which H. pylori promotes chronic inflammation and the progression to gastric cancer.
Virulence Factors that Mediate Helicobacter pylori Pathogenesis
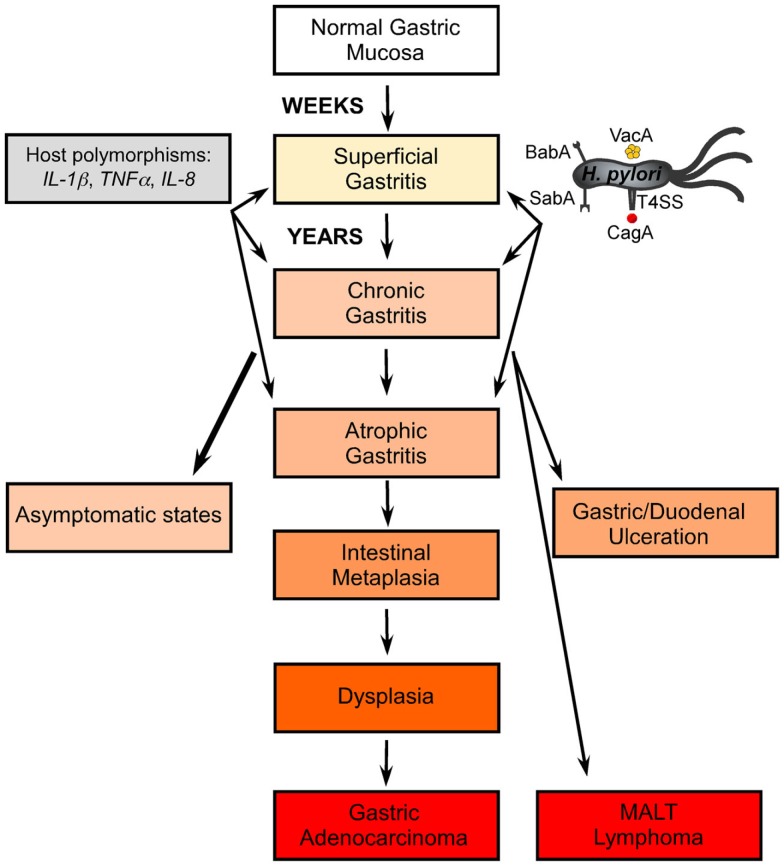
Chronic gastric inflammation induced by the bacterial pathogen, H. pylori, is the strongest known risk factor for the development of atrophic gastritis, metaplasia, dysplasia, and ultimately gastric adenocarcinoma (Figure 1). H. pylori is a Gram-negative, helical-shaped bacterium specifically adapted to persist within the human gastric niche. H. pylori possesses numerous elements to successfully colonize the gastric mucosa, establish chronic infection, and induce gastric pathology. In vivo, approximately 20% of H. pylori adhere to the gastric epithelium (Hessey et al., 1990). The large repertoire of adhesins expressed by H. pylori likely contribute to its specific adaptation to the gastric niche, allowing flexibility to target specific host cells and to exert a dynamic range of effector functions on host cells. H. pylori expresses a number of adhesins that have been linked to virulence. SabA (sialic acid-binding adhesin), which binds host sialyl-Lewisx, contributes to H. pylori persistence and mediates chronic gastric inflammation and injury (Mahdavi et al., 2002). The presence of blood group antigen-binding adhesin (BabA), which binds the host Lewisb blood group antigen, increases the risk of gastric cancer in a synergistic fashion with other virulence factors, such as CagA (Ilver et al., 1998; Gerhard et al., 1999).
Figure 1.
Progression to gastric adenocarcinoma. H. pylori colonizes the human gastric mucosa and causes superficial gastritis and chronic inflammation over weeks to months. H. pylori expressing key virulence factors, such as the cag type 4 secretion system (T4SS), and host genetic polymorphisms in IL-1β, TNFα, and IL-8 promoters that promote high expression of proinflammatory cytokines, augment the risk for developing atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and ultimately, gastric adenocarcinoma.
Following adherence and colonization of the gastric mucosa, H. pylori induces chronic gastritis and gastric injury, which are characterized by both neutrophilic and lymphocytic inflammation (Marshall et al., 1985; Goodwin et al., 1986). H. pylori expresses a number of factors capable of modulating the host immune system and eliciting proinflammatory immune responses. Some of these virulence factors include vacuolating cytotoxin (VacA) and the cag (cytotoxin associated gene) pathogenicity island. VacA is coded by the gene vacA, which is present in all strains of H. pylori, and which exhibits vacuolating activity (Leunk et al., 1988; Cover and Blaser, 1992; Cover et al., 1994; Phadnis et al., 1994; Schmitt and Haas, 1994; Telford et al., 1994). Additionally, VacA can induce apoptosis of host cells (Kuck et al., 2001; Xia and Talley, 2001) and suppress proliferation of T and B lymphocytes (Boncristiano et al., 2003; Gebert et al., 2003; Sundrud et al., 2004), which may contribute to the persistence of H. pylori through dysregulation of the host immune response. The cag pathogenicity island is present in ∼60% of all H. pylori strains and its presence is strongly associated with an increased risk of severe gastritis, ulcer disease, and gastric cancer (Censini et al., 1996; Tomb et al., 1997; Akopyants et al., 1998; Alm et al., 1999). The cag island encodes a type 4 secretion system (T4SS), which injects effector molecules, such as CagA, into host cells. CagA is a 120- to 140-kD protein that contains a number of tyrosine phosphorylation motifs (Covacci et al., 1993; Tummuru et al., 1993). Following its injection into host cells, CagA exerts a wide range of phosphorylation-dependent and independent effects, such as cytoskeletal rearrangements, disruption of cell polarity, and mitogenic and proinflammatory responses (Polk and Peek, 2010). Cumulatively, these bacterial factors contribute to adherence, persistence, host immune modulation, and virulence of H. pylori within the gastric niche, ultimately resulting in H. pylori-mediated chronic inflammation and a series of pathological outcomes that facilitate the development of gastric cancer.
Host Factors that Contribute to Gastric Carcinogenesis
In addition to microbial factors that potentiate gastric disease, there are a number of host factors that contribute to chronic gastritis and the progression to gastric adenocarcinoma. Cyclooxygenases (COX) are key enzymes that catalyze prostaglandin synthesis. Of the three isoforms identified, COX-2 is upregulated in gastric epithelial cells upon co-culture with H. pylori (Romano et al., 1998; Juttner et al., 2003; Meyer et al., 2003; Wu et al., 2005) and within the gastric mucosa of H. pylori-infected individuals (Sawaoka et al., 1998; Fu et al., 1999; McCarthy et al., 1999). In vivo studies show that COX-2 is further upregulated in H. pylori-mediated adenocarcinoma (Ristimaki et al., 1997; Sung et al., 2000). COX-2 expression levels are considered an independent factor for poor prognosis and correlate with reduced patient survival, suggesting that H. pylori-induced COX-2 overexpression is a risk factor for the development of gastric cancer.
Other host factors that increase the propensity for chronic inflammation and gastric adenocarcinoma are polymorphisms within human IL-1β (interleukin-1), TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor), and IL-8 promoters (El-Omar et al., 2000, 2003; Machado et al., 2001; Furuta et al., 2002), which lead to increased expression of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-8 (Figure 1). These polymorphisms in combination with H. pylori virulent genotypes increase the risk of gastric cancer up to 87-fold over baseline (Figueiredo et al., 2002), emphasizing the importance of microbial–host interactions in the development of gastric cancer. Collectively, data demonstrate that H. pylori virulence factors, host genetics, and environmental factors interact to induce and maintain the persistent inflammatory immune response that initiates the multistep process leading to gastric cancer.
microRNAs
Recent discoveries have shed new light on the involvement of host microRNAs (miRNAs) in gastric carcinogenesis. miRNAs are small, non-coding RNAs ∼20–25 nucleotides in length, which function as critical post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression (Bartel, 2009). miRNAs were first characterized in 1993 (Lee et al., 1993), but their distinct role in transcriptional regulation was not recognized until the early 2000s. Most miRNAs are found in intergenic regions and contain their own promoter and regulatory units. Processed miRNAs function by binding to the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of messenger RNAs (mRNAs), typically resulting in mRNA degradation and gene silencing or translational repression (Bartel, 2009). It is estimated that the human genome encodes thousands of miRNAs, targeting ∼30–60% of all protein-coding genes (Lewis et al., 2003). miRNAs are involved in many biological processes, including development, differentiation, angiogenesis, cell cycle progression, proliferation, apoptosis, and signal transduction pathways (Ambros, 2004). Dysregulation of miRNA expression with subsequent disruption of these biological processes can result in disease states. There is an increasing body of evidence regarding the regulatory roles of miRNAs in immune and inflammatory disorders (Wu et al., 2008; Sonkoly and Pivarcsi, 2009), and aberrant expression of miRNAs is observed in many cancers (Lu et al., 2005; Volinia et al., 2006). Thus, recent studies have begun to dissect the mechanisms by which miRNAs function as either oncogenic miRNAs (oncomiRs) or tumor suppressors to promote or prevent tumorigenesis.
Dysregulation of miRNAs in H. pylori-induced Gastric Carcinogenesis
The number of studies analyzing miRNA expression profiles in gastric cancer is rapidly increasing and a comprehensive list of miRNAs dysregulated in gastric cancer, confirmed mRNA targets, and the biological processes affected is shown in Tables A1 and A2 in the Appendix. The first study to address miRNA expression profiles in various cancers, including gastric cancer, was performed in 2005 (Lu et al., 2005). Subsequent studies have not only focused on miRNA expression profiles in gastric cancer, but also those that are altered in response to H. pylori.
Matsushima et al. (2011) conducted a study to characterize miRNA expression signatures in H. pylori-infected human gastric mucosa. Using high throughput profiling analysis, 31 miRNAs were identified as being differentially expressed between H. pylori-infected and H. pylori-uninfected gastric mucosa. The relationship between miRNA expression levels and H. pylori-induced acute inflammation, characterized by neutrophil infiltration, and chronic inflammation, characterized by mononuclear cell infiltration were also determined. Expression levels of many miRNAs correlated with either the degree of acute or chronic inflammation and in some cases both (Tables 1 and 2). The relationship between miRNA expression and extent of glandular atrophy, and intestinal metaplasia was also assessed, but no significant correlations were found (Matsushima et al., 2011). A comprehensive list of miRNAs dysregulated by H. pylori, confirmed mRNA targets, and biological processes affected is shown in Tables 1 and 2. These data suggest that H. pylori infection affects global miRNA expression in human gastric mucosa, and this effect is, in part, linked to H. pylori-induced host inflammatory immune responses.
Table 1.
miRNAs downregulated in response to H. pylori.
| miRNAs | Target mRNAs | Biological process targeted | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| let-7a+ | RAB40C | Cell cycle progression | Matsushima et al. (2011), Motoyama et al. (2008), Yang et al. (2011) |
| Proliferation | |||
| HMGA2 | Invasion | ||
| let-7b* | HMGA2 | Invasion | Matsushima et al. (2011), Motoyama et al. (2008) |
| let-7d | HMGA2 | Invasion | Matsushima et al. (2011), Motoyama et al. (2008) |
| let-7e | HMGA2 | Invasion | Matsushima et al. (2011), Motoyama et al. (2008) |
| let-7f | HMGA2 | Invasion | Matsushima et al. (2011), Motoyama et al. (2008) |
| miR-1 | ND | Proliferation | Saito et al. (2011) |
| miR-31+ | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-32 | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-34b | ND | ND | Suzuki et al. (2010) |
| miR-34c | ND | ND | Suzuki et al. (2010) |
| miR-101 | COX-2, FOS | Proliferation | Matsushima et al. (2011), Varambally et al. (2008), Wang et al. (2010) |
| MCL1 | Apoptosis | ||
| EZH2 | Invasion migration | ||
| miR-103# | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-106b | p21 | Cell cycle progression | Kan et al. (2009), Matsushima et al. (2011), Petrocca et al. (2008) |
| Proliferation | |||
| BIM | Apoptosis | ||
| miR-125a | ERBB2 | Proliferation | Matsushima et al. (2011), Nishida et al. (2011) |
| miR-130a | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-133 | ND | Proliferation | Saito et al. (2011) |
| miR-141# | FGFR2 | Proliferation | Du et al. (2009), Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-200a+ | ZEB1, ZEB2 | Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) | Ahn et al. (2011), Matsushima et al. (2011), Shinozaki et al. (2010) |
| miR-200b+ |
BCL2, XIAP ZEB1, ZEB2 |
Apoptosis EMT |
Ahn et al. (2011), Matsushima et al. (2011), Shinozaki et al. (2010), Zhu et al. (2011a) |
| miR-200c+ | BCL2, XIAP | Apoptosis | Matsushima et al. (2011), Shinozaki et al. (2010), Zhu et al. (2011a) |
| EMT | |||
| miR-203 | ABL1 | Proliferation | Craig et al. (2011b), Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| Invasion | |||
| miR-204 | EZR | Proliferation | Lam et al. (2011), Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-210 | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-214 | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-218 | ECOP | Proliferation | Gao et al. (2010), Tie et al. (2010) |
| Apoptosis | |||
| ROBO1 | Invasion and metastasis | ||
| miR-320+ | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-372 | LATS2 | Cell cycle progression | Belair et al. (2011) |
| miR-373 | LATS2 | Cell cycle progression | Belair et al. (2011) |
| miR-375+ | PDK1, 14-3-3 | Apoptosis | Ding et al. (2010), Matsushima et al. (2011), Tsukamoto et al. (2010) |
| JAK2 | Proliferation | ||
| miR-377 | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-379 | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-429+ | BCL2, XIAP | Apoptosis | Matsushima et al. (2011), Sun et al. (2011), Zhu et al. (2011a) |
| MYC | Proliferation | ||
| miR-449 | GMNN, CCNE2 | Cell cycle progression | Bou Kheir et al. (2011), Lize et al. (2011) |
| MET, SIRT1 | Proliferation | ||
| miR-455 | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-491-5p | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-500 | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-532# | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
| miR-652# | ND | ND | Matsushima et al. (2011) |
Target criteria included (1) reduced protein expression upon miRNA transfection in gastric cells or expression inversely correlated with miRNA in gastric tissue or (2) presence of miRNA binding site on the 3′UTR of target mRNA confirmed by luciferase reporter assay. ND, target mRNA or biological process not determined. *, miRNA expression correlates with acute inflammation. #, miRNA expression correlates with chronic inflammation. +, miRNA expression correlates with both acute and chronic inflammation. Bold indicates miRNA also downregulated in gastric cancer.
Table 2.
miRNAs upregulated in response to H. pylori infection.
| miRNAs | Target mRNAs | Biological process targeted | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-17∧ | p21 | Cell cycle progression | Saito et al. (2010) |
| miR-20a∧ | p21 | Cell cycle progression | Saito et al. (2010) |
| miR-21 | PDCD4 | Proliferation | Zhang et al. (2008) |
| RECK | Apoptosis | ||
| PTEN | Invasion | ||
| miR-146a | IRAK1, TRAF6 | Immune response | Li et al. (2011a), Liu et al. (2010), Xiao et al. (2011) |
| Proliferation | |||
| SMAD4 | Apoptosis | ||
| miR-155 | IKK-ε, SMAD2 | Immune response | Fassi Fehri et al. (2010), Oertli et al. (2011), Tang et al. (2010), Xiao et al. (2009b) |
| FADD, PKIα | Apoptosis | ||
| miR-223* | EPB41L3 | Invasion and metastasis | Li et al. (2011b), Matsushima et al. (2011) |
Target criteria included (1) reduced protein expression upon miRNA transfection in gastric cells or expression inversely correlated with miRNA in gastric tissue or (2) presence of miRNA binding site on the 3′UTR of target mRNA confirmed by luciferase reporter assay. ND, target mRNA or biological process not determined. ∧, miRNA expression induced by CagA overexpression, not H. pylori infection (Saito et al., 2010). *, miRNA expression correlates with acute inflammation. Bold indicates miRNA also upregulated in gastric cancer.
miRNAs that are dysregulated in response to H. pylori infection may not be the same miRNAs that are dysregulated in later stages of gastric disease. A comprehensive review of the literature, however, revealed that there is a select subset of miRNAs dysregulated both following H. pylori infection as well asin gastric cancer. These include downregulated miRNAs, let-7a, miR-31, miR-101, miR-141, miR-203, miR-210, miR-218, miR-375, and miR-449 as well as upregulated miRNAs, miR-17, miR-20a, miR-21, miR-146a, miR-155, and miR-223. These miRNAs may be more biologically relevant to H. pylori-induced gastric inflammation and carcinogenesis and represent fruitful targets for studies focused on cancer that develops in the context of H. pylori infection.
The next sections will discuss miRNA dysregulation in H. pylori-induced disease and how specific miRNAs control various biological processes related to (1) host inflammatory immune response, (2) cell cycle progression, and (3) apoptosis and proliferation.
Helicobacter pylori-induced miRNA Dysregulation to Control Host Inflammatory Responses
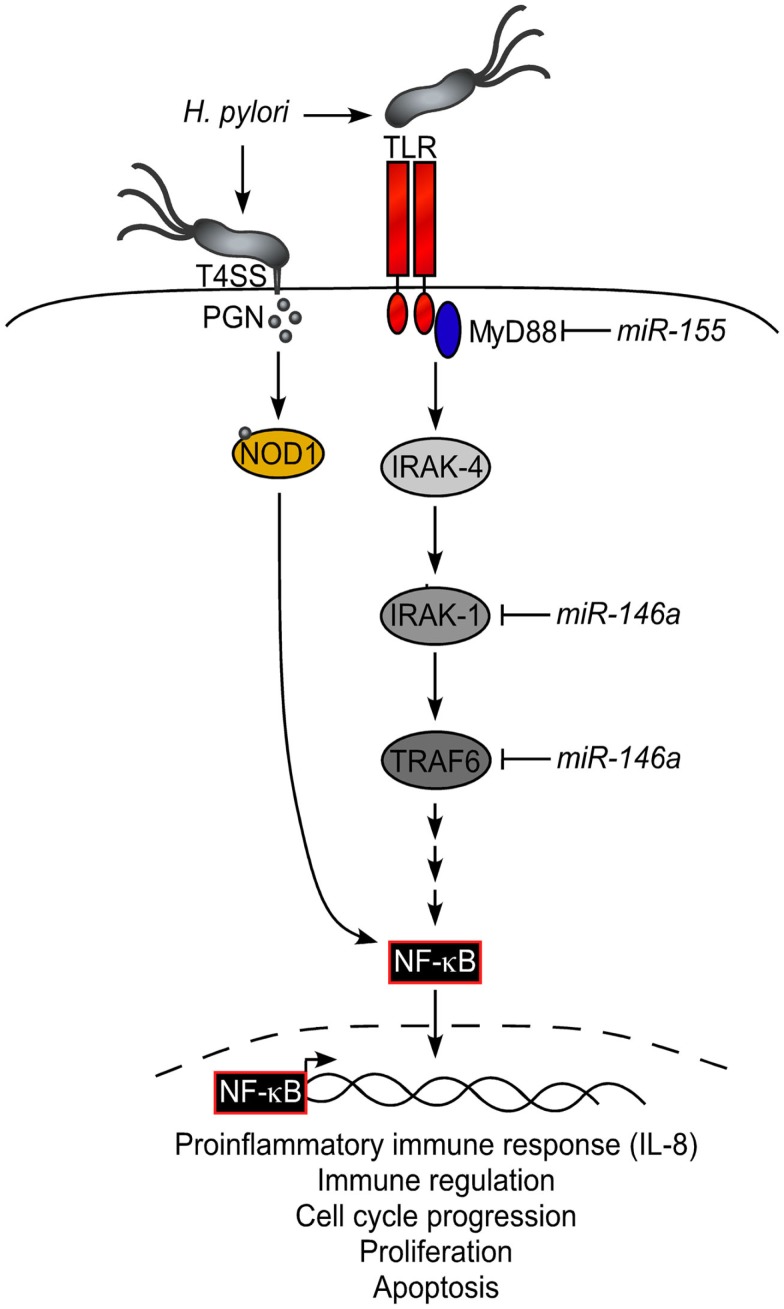
Host cells recognize invading pathogens and/or pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) through membrane-associated or cytoplasmic pathogen recognition molecules known as Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and Nod-like receptors (NLRs), respectively. PAMPs activate adaptor proteins and transcription factors that mediate host innate immunity through activation of NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) signaling (Figure 2). Gastric epithelial cells are the initial host element encountered by H. pylori. The innate immune response induced in epithelial cells is characterized by NOD1-dependent activation of NF-κB in response to H. pylori peptidoglycan (PGN), which is injected into host cells via the cag T4SS (Viala et al., 2004). Activation of NF-κB by H. pylori leads to induction of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-8 and likely contributes to carcinogenesis through activation of downstream targets that mediate inflammation, cell cycle progression, proliferation, and apoptosis. Myeloid cells constitute a second line of defense and secrete proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-1, and TNF-α to establish T and B lymphocyte-mediated adaptive immunity.
Figure 2.
TLR, NOD, and the NF-κB signaling pathways. Host cells recognize invading pathogens through extracellular Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and intracellular Nod-like receptors (NOD). Pathogens, such as H. pylori, activate TLRs and adaptor molecules that ultimately lead to NF-κB activation and a proinflammatory immune response. The key adaptor molecule responsible for signaling by TLRs is MyD88. MyD88 and other adaptor proteins (IRAK-1 and TRAF6) in this signaling cascade are targeted by miRNAs to dampen the host immune response.
The involvement of miRNAs in modulating both the innate and adaptive immune responses is well established (Chen et al., 2004) and H. pylori can dysregulate miRNA expression to evade host defenses and successfully persist in the gastric niche. miR-146a and miR-155 are specifically involved in H. pylori-induced negative regulation of the proinflammatory immune response (Figure 2). Changes in miR-146a expression occur in the development of gastric cancer and in the negative regulation of the innate inflammatory immune response. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in miR-146a are associated with an increased susceptibility to gastric cancer (Okubo et al., 2010) and H. pylori upregulates miR-146a in vitro and in vivo in a CagA-independent and an NF-κB-dependent manner (Liu et al., 2010; Li et al., 2011a). miR-146a targets the TLR-signaling adaptor molecules IRAK1 (interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase) and TRAF6 (TNF receptor-associated factor), resulting in negative regulation of TLR and downstream proinflammatory signaling (Figure 2; Liu et al., 2010; Li et al., 2011a). As a result, miR-146a overexpression negatively regulates H. pylori-induced IL-8, TNF-α, IL-1β, GRO-α [CXCL1, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand], and MIP-3α (macrophage inflammatory protein) expression, all key components to the proinflammatory innate and adaptive immune responses (Liu et al., 2010; Li et al., 2011a).
The second miRNA involved in H. pylori-induced downregulation of the host inflammatory immune response, miR-155, plays a critical role in regulating lymphocyte homeostasis and tolerance (Thai et al., 2007). miR-155 is increased in many malignancies of B cell or myeloid origin (Volinia et al., 2006). In transgenic murine models of miR-155 overexpression, mice develop spontaneous B cell lymphomas (Costinean et al., 2006). miR-155 is induced during both bacterial and viral infections in myeloid cells through activation of TLR-signaling pathways. H. pylori upregulates miR-155 expression in vitro and in vivo, which occurs in an NF-κB-dependent manner, and ultimately results in decreased induction of the proinflammatory cytokines, IL-8, and GRO-α (Xiao et al., 2009b; Tang et al., 2010). miR-155 targets MyD88 (myeloid differentiation primary response gene), the universal adapter protein used by TLRs to activate NF-κB (Figure 2; Xiao et al., 2009b; Tang et al., 2010). Decreased levels of MyD88 subsequently result in decreased NF-κB activation and dampening of the host inflammatory response (Xiao et al., 2009b; Tang et al., 2010). Therefore, these data demonstrate that H. pylori dysregulates host miRNA expression to manipulate the host inflammatory immune response, which may promote bacterial survival and persistence within the gastric mucosa. Because these miRNAs have established roles in carcinogenesis as well as innate immunity, they could serve as an important link between H. pylori-induced inflammation and carcinogenesis.
Helicobacter pylori and miRNAs Regulate Cell Cycle Progression
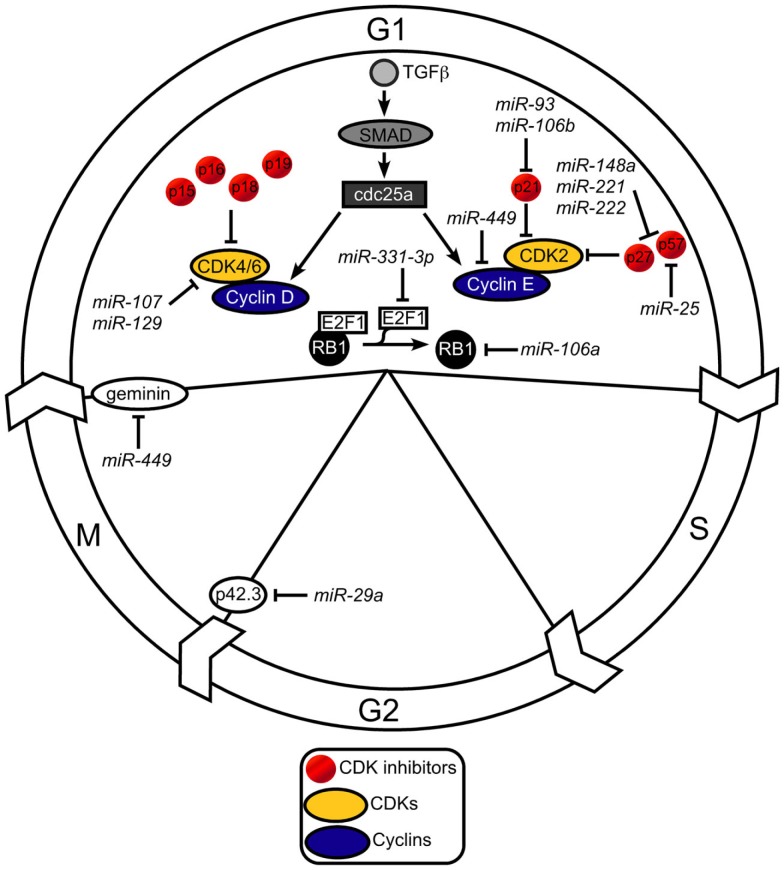
Disruption of cell cycle progression and increased cellular proliferation are common features of malignancies. Cell cycle progression requires coordinated expression of cyclins, which results in sequential activation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). miRNA dysregulation promotes cell cycle progression by upregulating cyclin expression and/or downregulating expression of CDK inhibitors (p15, p16, p18, p19, p21, p27, p28, p57) in various cancers, including gastric cancer (Figure 3). miR-449, a miRNA downregulated in H. pylori-infected gastric tissue and in gastric cancer, targets GMNN (geminin) and CCNE2 (cyclin E2; Figure 3). Both geminin and cyclin E2 are overexpressed in numerous malignancies and promote M/G1 and G1/Scell cycle progression and cell proliferation (Bou Kheir et al., 2011; Lize et al., 2011). Consequently, downregulation of miR-449, as occurs following H. pylori infection, promotes cell cycle progression and proliferation through upregulation of geminin and cyclin E2.
Figure 3.
Regulation of cell cycle progression. The cell cycle consists of four distinct phases: G1, S, G2, and M. Two key classes of regulatory molecules, cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), determine a cells progress through the cell cycle. CDK inhibitors prevent the progression of cell cycle and function as tumor suppressors. miRNAs target the key regulatory molecules, cyclins and CDKs, as well as CDK inhibitors to disrupt normal cell cycle progression.
p42.3, a recently identified protein significantly upregulated in gastric cancer, regulates G2/M cell cycle progression and proliferation in gastric cancer cells (Xu et al., 2007). miR-29a, a miRNA significantly downregulated in gastric cancer, targets p42.3 (Cui et al., 2011; Figure 3). Thus, the downregulation of miR-29a results in a reciprocal increase in p42.3 expression, promoting increased cell cycle progression and proliferation.
The retinoblastoma protein (RB1) is a tumor suppressor dysregulated in many cancers. RB1 functions to prevent excessive cell proliferation by inhibiting G1/S cell cycle progression. RB1 binds and inhibits transcription factors of the E2F family. When RB1 is bound to E2F the complex acts as a growth suppressor and prevents progression through cell cycle. A number of miRNAs target these factors. For instance, miR-106a is upregulated in gastric cancer and targets RB1 (Volinia et al., 2006), while miR-331-3p is downregulated in gastric cancer and targets E2F1 (Guo et al., 2010; Figure 3).
TGFβ suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation via the transcriptional upregulation of the CDK inhibitor, p21 (Yoo et al., 1999). miR-93 and miR-106b directly target p21, resulting in its transcriptional silencing and impairment of the tumor-suppressing activity of TGFβ (Petrocca et al., 2008; Kan et al., 2009; Figure 3). In addition, miR-25 targets the CDK inhibitor, p57, while miR-221 and miR-222 target the CDK inhibitors, p27 and p57 (Kim et al., 2009; Figure 3). These oncogenic miRNA clusters are also significantly upregulated in gastric cancer (Volinia et al., 2006; Petrocca et al., 2008; Guo et al., 2009; Kim et al., 2009; Yao et al., 2009). Overexpression of most of these miRNAs results in activation of CDK2, thereby promoting G1/S phase progression. Since numerous reports have described the role of H. pylori in the modulation of cyclins, CDKs, and CDK inhibitors and their link to gastric carcinogenesis (Shirin et al., 2001), these data suggest that H. pylori modulates expression of cyclins, CDKs, and CDK inhibitors through dysregulation of host miRNAs, which may increase the propensity for gastric transformation.
Helicobacter pylori and miRNA Dysregulation Inhibit Apoptosis and Promote Cell Survival
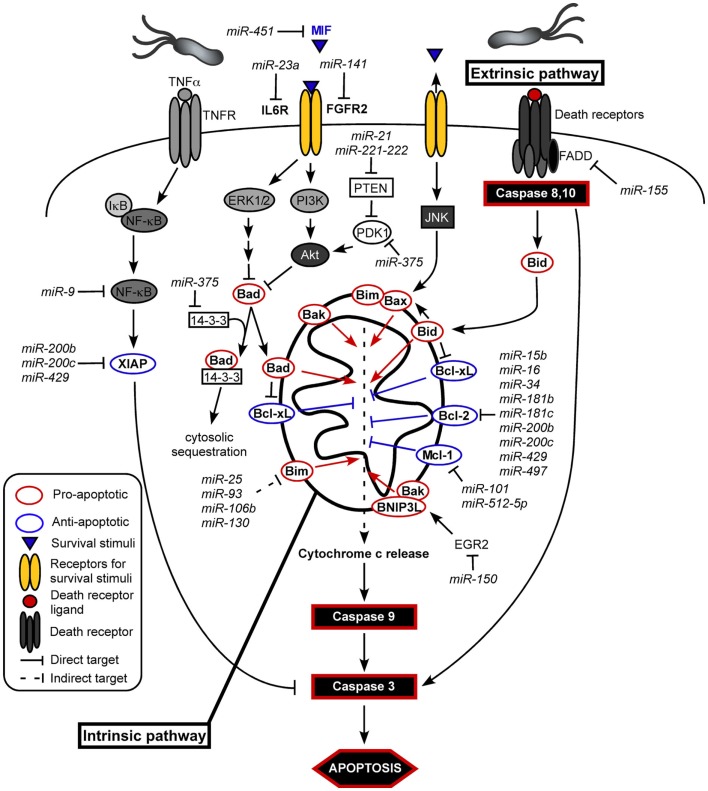
Increased cellular proliferation and evasion of apoptosis are hallmarks of cellular transformation. Apoptosis can be classified as being dependent on either the intrinsic or extrinsic pathways. The intrinsic pathway is initiated within cells and hinges on the balance of activity between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 (B cell lymphoma 2) superfamily of proteins, which act to regulate the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane. miRNAs regulate apoptosis by altering expression and balance of members of the pro-apoptotic (e.g., Bax, Bak, Bim, Bad, Bid, and BNIP3L) and anti-apoptotic (e.g., Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1) Bcl-2 protein family (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Signaling cascades that regulate the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis. TNFα signaling leads to activation of NF-κB and the anti-apoptotic protein XIAP. Other receptors that detect survival factors, such as growth factors and cytokines, induce ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt signaling cascades that ultimately result in the inhibition of the pro-apoptotic protein, Bad. In contrast, upon removal of survival factors, these receptors can signal via JNK to induce the pro-apoptotic protein, Bax. Pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins govern the intrinsic pathway of cell death, which results in the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria and induction of the caspase cascade. Signaling through death receptors initiate the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis, leading to the induction of caspases and cell death. There are numerous miRNAs that regulate each of these pathways and dysregulation of these miRNAs can lead to anti-apoptotic and tumorigenic responses.
Numerous miRNAs overexpressed in gastric cancer function as oncomiRs by targeting members of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein family. In addition to their role in regulating cell cycle progression, miR-25, miR-93, and miR-106b also inhibit apoptosis by preventing expression of the pro-apoptotic protein, Bim (Kan et al., 2009; Figure 4). Overexpression of miR-130b also contributes to suppression of Bim and apoptosis by targeting RUNX3 (runt-related transcription factor; Lai et al., 2010), a known tumor suppressor frequently silenced in gastric cancer (Li et al., 2002). miR-150 targets the EGR2 (early growth response protein; Wu et al., 2010), a tumor-suppressive transcription factor that induces apoptosis by direct transactivation of pro-apoptotic factors, Bak, and BNIP3L (Unoki and Nakamura, 2003).
Numerous tumor suppressor miRNAs target members of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein family and are consequently downregulated in gastric cancer. miR-15b, miR-16, miR-34, miR-181b, miR-181c, and miR-497 directly target anti-apoptotic BCL2 (Ji et al., 2008; Xia et al., 2008; Zhu et al., 2010b, 2011b; Figure 4). These miRNA clusters are downregulated in gastric cancer cells (Guo et al., 2009), leading to increased expression of Bcl-2 and inhibition of apoptosis. The miR-200bc/429 cluster is downregulated in gastric cells, and these miRNAs directly target BCL2 and XIAP (x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis), leading to reduced expression and increased apoptosis (Zhu et al., 2011a; Figure 4). miR-101 and miR-512-5p target another anti-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family, MCL1 (myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein; Saito et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2010; Figure 4). Both miR-101 and miR-512-5p are downregulated in gastric cancer, leading to increased levels of Mcl-1 and an anti-apoptotic phenotype. In addition, miR-101 is downregulated by H. pylori (Matsushima et al., 2011). miR-449 is also likely involved in mediating the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis and has been classified as a potent inducer of cell cycle arrest and cell death. miR-449 expression is reduced in H. pylori-infected gastric tissue, and its expression is lost in gastric tumors (Bou Kheir et al., 2011; Lize et al., 2011). Conversely, overexpression of miR-449 inhibits cellular proliferation and induces significant levels of apoptosis, and since miR-449 belongs to the family of p53-responsive miRNAs, its overexpression also results in activation of p53 and apoptosis-specific marker, caspase 3.
In contrast to the intrinsic pathway, the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis is initiated on the cell surface through the activation of specific pro-apoptotic, death receptors. Specific pro-apoptotic ligands are known to activate the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis via specific receptor binding. Ligand binding induces receptor clustering and the recruitment of the adaptor protein Fas-associated death domain (FADD), leading to induction of caspases and ultimately cell death. In addition to its role in regulating the host immune response, miR-155 targets FADD (Figure 4), leading to decreased expression of this key adaptor molecule (Xiao et al., 2009b). Therefore, the upregulation of miR-155 by H. pylori and during carcinogenesis results in downregulation of FADD and inhibition of apoptosis.
In addition to targeting proteins directly involved in the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of cell death, miRNAs target other factors that ultimately lead to inhibition of apoptosis and increased proliferation. miR-375 targets 14-3-3 zeta, an anti-apoptotic protein that mediates cell survival by binding the pro-apoptotic protein Bad and sequestering it to the cytosol (Tsukamoto et al., 2010; Figure 4). miR-375 also targets PDK1 (3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase), a kinase that directly phosphorylates Akt, thereby regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway (Figure 4). Overexpression of miR-375 was shown to substantially reduce cell viability through induction of the caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway. miR-375 is one of the most highly downregulated miRNAs in gastric cancer (Tsukamoto et al., 2010), suggesting its role as a potent tumor suppressor that contributes to the development of gastric carcinoma.
In contrast, miR-21, a known oncomir that targets many known tumor suppressors, is consistently upregulated in various human cancers, including gastric cancer (Volinia et al., 2006; Chan et al., 2008; Petrocca et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2008; Guo et al., 2009), and miR-21 expression is increased in H. pylori-infected gastric tissues (Zhang et al., 2008). Overexpression of miR-21 shifts the balance between proliferation and apoptosis, increasing cellular proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis. Specifically, miR-21 targets PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog), a tumor suppressor and negative regulator of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway (Yamanaka et al., 2009), which is involved in both apoptotic and proliferative pathways (Figure 4). Mutations in PTEN are important in the progression of many cancers, including gastric carcinoma (Kang et al., 2002). miR-21 likely also contributes to apoptosis by targeting PDCD4 (programmed cell death protein 4), which is localized to the nucleus of proliferating cells; however, its direct role in apoptosis has not been elucidated (Lu et al., 2008; Motoyama et al., 2010).
Similar to PI3K/Akt signaling, the NF-κB signaling pathway is important in inhibition of apoptosis and cell survival. The NF-κB signaling cascade is activated during H. pylori-induced gastritis and is constitutively active in gastric cancer (Sasaki et al., 2001). miR-218 expression is reduced in numerous cancers, including gastric cancer. H. pylori infection also reduces the expression of miR-218 in vitro and in vivo. miR-218 induces apoptosis in gastric cancer cells through direct targeting of ECOP (epidermal growth factor receptor-co-amplified and overexpressed protein), a known positive regulator of NF-κB transcriptional activity. Downregulation of miR-218 leads to overexpression of ECOP, inhibition of NF-κB transcriptional activation, and transcription of a downstream target COX-2, ultimately inhibiting apoptosis, and inducing cell proliferation (Gao et al., 2010). Another miRNA important in regulating NF-κB signal transduction pathways is miR-9, which directly targets NF-κB1, thereby suppressing NF-κB transcriptional activity (Figure 4). miR-9 is downregulated in gastric cancer and in vitro studies have shown that restoration of miR-9 expression suppresses proliferation of gastric cancer cells (Luo et al., 2009; Wan et al., 2010). Cumulatively, these studies demonstrate that aberrant activation of NF-κB signaling as a result of H. pylori-induced miRNA dysregulation results in inhibition of apoptosis and increased proliferation, thereby sensitizing cells for subsequent mutagenesis.
miR-451, another downregulated miRNA in H. pylori-infected gastric mucosa and gastric cancer, targets MIF (macrophage migration inhibitory factor; Bandres et al., 2009), a lymphokine involved in cell-mediated immunity that is expressed in response to H. pylori infection and during gastric carcinogenesis (He et al., 2006). Overexpression of miR-451 results in targeted downregulation of MIF, which is accompanied by a decrease in cell proliferation and increased apoptosis (Figure 4). Furthermore, there is an inverse correlation between miR-451 and MIF expression in gastric cancer, suggesting that miR-451 functions as a tumor suppressor by silencing MIF expression, leading to a proliferative and anti-apoptotic phenotype (Bandres et al., 2009). miR-141, another miRNA significantly decreased in H. pylori-infected gastric tissue (Matsushima et al., 2011) as well as gastric carcinoma, targets FGFR2 (fibroblast growth factor receptor), and overexpression of miR-141 leads to decreased FGFR2 expression and inhibition of proliferation (Du et al., 2009; Figure 4). miR-23a functions as a growth-promoting and anti-apoptotic factor. It is significantly upregulated in gastric adenocarcinoma and targets IL-6R (interleukin-6 receptor), which promotes increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis in gastric adenocarcinoma cells (Zhu et al., 2010a; Figure 4).
Helicobacter pylori and miRNA Dysregulation Promotes Cell Invasion and Metastasis
Invasion and metastasis are hallmarks of cancer cells. Several intracellular signaling pathways, such as those mediated by TGFβ and hepatocyte growth factor/Met signaling, promote metastasis. In addition to its role in regulating cell cycle progression, the H. pylori downregulated miR-449 also targets Met, a known proto-oncogene that encodes the hepatocyte growth factor receptor. Aberrant activation of Met triggers oncogenic processes, such as proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis (Bou Kheir et al., 2011; Lize et al., 2011). Thus, the targeted downregulation of miR-449 by H. pylori and during gastric carcinogenesis results in upregulation of Met, increased cell proliferation, and likely other oncogenic processes.
The metastatic potential of cancer cells is also regulated by mechanisms that control cell survival, cytoskeletal changes, as well as the activity of extracellular matrix-degrading proteinases (MMPs). Many miRNAs known to regulate cell cycle progression, proliferation, and apoptosis pathways are also involved in metastasis. For example, overexpression of miR-21 has been shown to increase the invasiveness of gastric cancer cells. In addition to its known tumor suppressor targets, miR-21 also targets RECK (reversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs), a tumor and metastasis suppressor that inhibits tumor metastasis and angiogenesis through modulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs; Zhang et al., 2008). H. pylori induces expression of MMPs, including MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-7, MMP-9, which have been linked to H. pylori-induced disease and carcinogenesis (Elkington et al., 2005). These data suggest that H. pylori has the potential to modulate expression of MMPs through dysregulation of host miRNAs and these disruptions may increase the propensity for gastric transformation.
miR-106a is significantly upregulated in cancer cells (Volinia et al., 2006) and is known to correlate with increased lymphatic and distant metastasis (Xiao et al., 2009a). Conversely, miR-218, a tumor suppressor miRNA, is downregulated in gastric cancer (Volinia et al., 2006), which correlates with increased metastasis and invasion. This is thought to occur through direct targeting of ROBO1 (roundabout homolog), which leads to enhanced signaling through the ROBO1 receptor. The SLIT/ROBO signaling pathway has been implicated in many biological responses through regulation of cell migration (Tie et al., 2010). Thus, disruption of this signaling cascade can result in increased invasion and metastasis.
Conclusion
The discovery of miRNAs just over a decade ago has challenged the central dogma of genetic and epigenetic regulation. Although extensive work has been dedicated to identifying miRNAs, mRNA targets, and their contribution to accepted regulatory networks, we have only begun to scratch the surface. With thousands of miRNAs within the human genome, and the ability of each miRNA to target and regulate numerous protein-coding mRNAs, affected regulatory networks are likely to be modified by countless miRNA contributors and will continue to evolve.
Many questions arise when comparing miRNA expression profiles in different model systems in vitro and in vivo and when comparing miRNA expression profiles in H. pylori-infected gastric tissue and gastric cancer. For example, miR-106b, a known oncogenic miRNA, upregulated in various malignancies including gastric cancer, is decreased in H. pylori-infected gastric mucosa. Similarly, miR-34b, miR-34c, miR-103, miR-200a, miR-200b, miR-214, and miR-372 are all overexpressed in gastric cancer, while in H. pylori-infected gastric mucosa these miRNAs are significantly downregulated. In contrast, miR-146a is significantly decreased in gastric cancer, but upregulated in H. pylori-infected gastric tissue. However, a recent report has shown that miR-146a is upregulated in a subset of gastric cancers. Although examining miRNA expression signatures in gastric cancer is clearly important in understanding the disease, development of novel therapeutics requires greater insight into the miRNA profiles in precancerous gastric tissues. Since the majority of gastric cancers arise within the context of chronic inflammation, it will be particularly important to discriminate between preneoplastic and tumor-specific miRNA expression profiles. A more comprehensive understanding of the roles of miRNAs in normal biological processes and disease is needed to fully appreciate miRNA dysregulation by pathogens, such as H. pylori. Furthermore, the relationship between single miRNAs and their targets are important to consider, but many of these relationships are cell and context specific. Thus, it is critically important to dissect these intricate pathways and understand how host–pathogen interactions disrupt these encompassing regulatory pathways.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge James Patton from Vanderbilt University for his expertise and guidance in the subject matter of miRNAs. We would like to acknowledge the following funding sources through National Institutes of Health: NCI F32CA153539 (Jennifer M. Noto), NCI P01CA116087 (Richard M. Peek), NCI R01CA077955 (Richard M. Peek), NIDDK R01DK058587 (Richard M. Peek), and NIDDK P30DK058404 (Richard M. Peek).
Appendix
Table A1.
miRNAs downregulated in gastric cancer.
| miRNAs | Target mRNAs* | Biological processes targeted | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| let-7a | RAB40C | Cell cycle progression Proliferation |
Li et al. (2010, 2011c), Motoyama et al. (2008), Tsujiura et al. (2010), Yang et al. (2011), Zhang et al. (2007), Zhu et al. (2010c) |
| HMGA2 | Invasion | ||
| miR-9 | CDX2 | Cell cycle progression NFκB1 |
Luo et al. (2009), Rotkrua et al. (2011), Tsai et al. (2011a), Wan et al. (2010) |
| GRB2, RAB34 | Proliferation | ||
| miR-15b | BCL2 | Apoptosis | Xia et al. (2008) |
| miR-16 | BCL2 | Apoptosis | Shin et al. (2011), Xia et al. (2008) |
| miR-29a | p42.3 | Cell cycle progression | Cui et al. (2011), Lang et al. (2010) |
| Proliferation | |||
| CDC42 | Invasion | ||
| miR-29b | CDC42 | Proliferation | Lang et al. (2010) |
| Invasion | |||
| miR-29c | CDC42 | Proliferation | Lang et al. (2010) |
| Invasion | |||
| miR-30a | ND | ND | Li et al. (2010) |
| miR-30b | ND | ND | Ueda et al. (2010) |
| miR-30c | ND | ND | Ueda et al. (2010) |
| miR-31 | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009), Zhang et al. (2010b) |
| miR-33b | ND | ND | Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-34 | BCL2 | Apoptosis | Ji et al. (2008) |
| miR-96 | ND | ND | Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-101 | COX-2, FOS | Proliferation | Varambally et al. (2008), Wang et al. (2010) |
| MCL1 | Apoptosis | ||
| EZH2 | Invasion migration | ||
| miR-126 | CRK | Cell cycle progression | Feng et al. (2010), Li et al. (2010, 2011c), Otsubo et al. (2011) |
| Proliferation | |||
| Invasion and metastasis | |||
| SOX2 | Proliferation | ||
| miR-128b | ND | ND | Katada et al. (2009) |
| miR-129 | CDK6 | Cell cycle progression Proliferation |
Katada et al. (2009), Shen et al. (2010), Tsai et al. (2011b), Wu et al. (2010a) |
| SOX4 | Apoptosis | ||
| miR-133b | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009), Wu et al. (2011a) |
| miR-136 | ND | ND | Ueda et al. (2010) |
| miR-138 | ND | ND | Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-139-5p | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009) |
| miR-141 | FGFR2 | Proliferation | Du et al. (2009) |
| miR-143 | ND | Proliferation | Li et al. (2011a), Takagi et al. (2009), Wu et al. (2011a) |
| miR-145 | ND | ND | Li et al. (2011a), Takagi et al. (2009), Tchernitsa et al. (2010) |
| miR-146a | IRAK1, TRAF6 | Immune response Proliferation |
Hou et al. (2011), Kogo et al. (2011), Li et al. (2011a,d), Okubo et al. (2010), Tchernitsa et al. (2010) |
| Apoptosis | |||
| miR-148 | ND | ND | Katada et al. (2009) |
| miR-148a | CCKBR | Proliferation | Chen et al. (2010), Guo et al. (2011), Zheng et al. (2011) |
| p27 | Cell cycle progression | ||
| ROCK1 | Invasion and metastasis | ||
| miR-148b | CCKBR | Proliferation | Song et al. (2011) |
| miR-152 | CCKBR | Proliferation | Chen et al. (2010), Ueda et al. (2010) |
| miR-181b | BCL2 | Apoptosis | Jiang et al. (2011), Li et al. (2011c), Zhu et al. (2010b) |
| miR-181c | NOTCH4, KRAS | Proliferation | Hashimoto et al. (2010), Zhu et al. (2010b) |
| BCL2 | Apoptosis | ||
| miR-195 | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009), Wu et al. (2011a) |
| miR-197 | ND | ND | Li et al. (2011c) |
| miR-203 | ABL1 | Proliferation | Chiang et al. (2011), Craig et al. (2011b) |
| Invasion | |||
| miR-210 | ND | ND | Li et al. (2011c) |
| miR-212 | MECP2 | Proliferation MYC |
Volinia et al. (2006), Wada et al. (2010), Wu et al. (2011a), Xu et al. (2010) |
| miR-218 | ECOP |
Proliferation Apoptosis |
Gao et al. (2010), Tie et al. (2010), Ueda et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| ROBO1 | Invasion and metastasis | ||
| miR-331-3p | E2F1 | Cell cycle progression | Guo et al. (2010) |
| Proliferation | |||
| miR-339 | ICAM-1 | Immune response | Ueda et al. (2009) |
| miR-375 |
PDK1, 14-3-3 JAK2 |
Apoptosis Proliferation |
Ding et al. (2010), Tsukamoto et al. (2010), Ueda et al. (2010), Xu et al. (2011) |
| miR-378 | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009), Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-433 | GRB2 | Proliferation | Luo et al. (2009) |
| miR-449 | GMNN, CCNE2 | Cell cycle progression | Bou Kheir et al. (2011), Lize et al. (2011) |
| MET, SIRT1 | Proliferation | ||
| miR-451 | MIF | Proliferation | Bandres et al. (2009) |
| Apoptosis | |||
| miR-497 | BCL2 | Apoptosis | Guo et al. (2009), Zhu et al. (2011b) |
| miR-512-5p | MCL1 | Apoptosis | Saito et al. (2009) |
| miR-638 | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-768-3p | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009) |
*Target criteria included (1) reduced protein expression upon miRNA transfection in gastric cells or expression inversely correlated with miRNA in gastric tissue or (2) presence of miRNA binding site on the 3′UTR of target mRNA confirmed by luciferase reporter assay. ND, target mRNA or biological process not determined. Bold indicates miRNA also downregulated following H. pylori infection.
Table A2.
miRNAs upregulated in gastric cancer.
| miRNAs | Target mRNAs* | Biological processes targeted | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-7 | ND | ND | Volinia et al. (2006), Wu et al. (2011b) |
| miR-17 | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009), Volinia et al. (2006), Yao et al. (2009), Zhou et al. (2010) |
| miR-17-5p | ND | ND | Petrocca et al. (2008), Tsujiura et al. (2010), Ueda et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-18a | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009), Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-18b | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009) |
| miR-19a | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009), Ueda et al. (2010) |
| miR-20a | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-20b | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009), Katada et al. (2009), Ueda et al. (2010) |
| miR-21 |
PDCD4 RECK |
Proliferation Apoptosis |
Chan et al. (2008), Guo et al. (2009), Li et al. (2010, 2011c), Lu et al. (2008), Motoyama et al. (2010), Petrocca et al. (2008), Shin et al. (2011), Tsujiura et al. (2010), Ueda et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006), Zhang et al. (2008) |
| PTEN | Invasion | ||
| miR-23a | IL-6R | Proliferation | Li et al. (2011c), Volinia et al. (2006), Zhu et al. (2010a) |
| Apoptosis | |||
| miR-23b | ND | ND | Li et al. (2011c) |
| miR-24 | AE1 | Proliferation | Chan et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006), Wu et al. (2010b) |
| Differentiation | |||
| miR-25 |
p57 BIM |
Cell cycle progression Apoptosis |
Kan et al. (2009), Kim et al. (2009), Li et al. (2011c), Petrocca et al. (2008), Ueda et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-27 | APC | Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) | Zhang et al. (2011) |
| miR-27a |
PHB ZBTB10 |
Proliferation Metastasis |
Katada et al. (2009), Li et al. (2011a; Liu et al. 2009), Sun et al. (2010), Zhao et al. (2011) |
| miR-34a | SIRT1 | Cell cycle progression | Craig et al. (2011a), Yamakuchi and Lowenstein (2009), Yao et al. (2009) |
| FOXP1 | Proliferation | ||
| miR-34b | ND | ND | Katada et al. (2009), Suzuki et al. (2010), Tsai et al. (2011b) |
| miR-34c | ND | ND | Katada et al. (2009), Suzuki et al. (2010) |
| miR-92 | ND | ND | Li et al. (2011c), Petrocca et al. (2008), Ueda et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-93 | p21 | Cell cycle progression | Kim et al. (2009), Petrocca et al. (2008), Ueda et al. (2010) |
| BIM | Apoptosis | ||
| miR-98 | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-99a | ND | ND | Li et al. (2011c) |
| miR-99b | ND | ND | Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-103 | ND | ND | Li et al. (2011c), Tchernitsa et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-106a | RB1 | Cell cycle progression Proliferation |
Guo et al. (2009), Petrocca et al. (2008), Tsujiura et al. (2010), Ueda et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006), Xiao et al. (2009a), Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-106b |
p21 BIM |
Cell cycle progression Apoptosis |
Guo et al. (2009), Kim et al. (2009), Petrocca et al. (2008), Tsujiura et al. (2010), Ueda et al. (2010), Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-107 | CDK6 | Proliferation | Feng et al. (2011), Li et al. (2011b,c), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| DICER | Invasion and metastasis | ||
| miR-125b | ND | ND | Li et al. (2011c), Ueda et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-128a | ND | ND | Katada et al. (2009) |
| miR-130b | RUNX3 | Apoptosis | Li et al. (2002), Lai et al. (2010), Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-135a | ND | ND | Ueda et al. (2010) |
| miR-138 | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-146a | SMAD4 | Proliferation | Xiao et al. (2011) |
| Apoptosis | |||
| miR-147 | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-150 | EGR2 | Apoptosis | Katada et al. (2009), Wu et al. (2010c) |
| miR-155 |
IKK-ε, SMAD2 FADD, PKIα |
Immune response Apoptosis |
Fassi Fehri et al. (2010), Oertli et al. (2011), Tang et al. (2010), Thai et al. (2007), Volinia et al. (2006), Xiao et al. (2009b), Yao et al. (2011) |
| miR-181a-2 | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-185 | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-191 | NDST1 | Proliferation | Li et al. (2011c), Shi et al. (2011), Ueda et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-192 | ALCAM | Proliferation | Jin et al. (2011), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-196a | ND | ND | Okubo et al. (2010), Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-200a | ZEB1, ZEB2 | Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) | Ahn et al. (2011) |
| miR-200b | ZEB1, ZEB2 | EMT | Ahn et al. (2011), Zhu et al. (2011a) |
| BCL2, XIAP | Apoptosis | ||
| miR-214 | ND | ND | Li et al. (2011c), Ueda et al. (2010), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| miR-215 | ALCAM | Proliferation | Jin et al. (2011), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| Apoptosis | |||
| miR-221 |
p27, p57 PTEN |
Cell cycle progression Proliferation |
Chun-Zhi et al. (2010), Kim et al. (2009), Li et al. (2011c), Volinia et al. (2006), Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-222 |
p27, p57 PTEN |
Cell cycle progression Proliferation |
Chun-Zhi et al. (2010), Kim et al. (2009), Li et al. (2011c), Ueda et al. (2009), Volinia et al. (2006) |
| ICAM-1 | Immune response | ||
| miR-223 | EPB41L3 | Invasion and metastasis | Li et al. (2011c), Petrocca et al. (2008), Volinia et al. (2006), Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-302f | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-337-3p | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-340 | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009), Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-345 | ND | ND | Ueda et al. (2010) |
| miR-372 | LATS2 | Cell cycle progression | Cho et al. (2009) |
| Apoptosis | |||
| miR-421 | CBX7, RBMXL1 | Proliferation | Guo et al. (2009), Jiang et al. (2010) |
| miR-520c-3p | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-575 | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-601 | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-616 | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
| miR-650 | ING4 | Apoptosis | Zhang et al. (2010a) |
| miR-658 | ND | ND | Guo et al. (2009) |
| miR-1259 | ND | ND | Yao et al. (2009) |
*Target criteria included (1) reduced protein expression upon miRNA transfection in gastric cells or expression inversely correlated with miRNA in gastric tissue or (2) presence of miRNA binding site on the 3′UTR of target mRNA confirmed by luciferase reporter assay. ND, target mRNA or biological process not determined. Bold indicates miRNA also upregulated following H. pylori infection.
References
- Ahn S. M., Cha J. Y., Kim J., Kim D., Trang H. T., Kim Y. M., Cho Y. H., Park D., Hong S. (2011). Smad3 regulates E-cadherin via miRNA-200 pathway. Oncogene. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1038/onc.2011.484 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akopyants N. S., Clifton S. W., Kersulyte D., Crabtree J. E., Youree B. E., Reece C. A., Bukanov N. O., Drazek E. S., Roe B. A., Berg D. E. (1998). Analyses of the cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 28, 37–53 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00770.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm R. A., Ling L. S., Moir D. T., King B. L., Brown E. D., Doig P. C., Smith D. R., Noonan B., Guild B. C., deJonge B. L., Carmel G., Tummino P. J., Caruso A., Uria-Nickelsen M., Mills D. M., Ives C., Gibson R., Merberg D., Mills S. D., Jiang Q., Taylor D. E., Vovis G. F., Trust T. J. (1999). Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 397, 176–180 10.1038/17837 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V. (2004). The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431, 350–355 10.1038/nature02871 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandres E., Bitarte N., Arias F., Agorreta J., Fortes P., Agirre X., Zarate R., Diaz-Gonzalez J. A., Ramirez N., Sola J. J., Jimenez P., Rodriguez J., Garcia-Foncillas J. (2009). microRNA-451 regulates macrophage migration inhibitory factor production and proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 2281–2290 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1818 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D. P. (2009). microRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136, 215–233 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belair C., Baud J., Chabas S., Sharma C. M., Vogel J., Staedel C., Darfeuille F. (2011). Helicobacter pylori interferes with an embryonic stem cell micro RNA cluster to block cell cycle progression. Silence 2, 7–23 10.1186/1758-907X-2-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boncristiano M., Paccani S. R., Barone S., Ulivieri C., Patrussi L., Ilver D., Amedei A., D’Elios M. M., Telford J. L., Baldari C. T. (2003). The Helicobacter pylori vacuolating toxin inhibits T cell activation by two independent mechanisms. J. Exp. Med. 198, 1887–1897 10.1084/jem.20030621 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bou Kheir T., Futoma-Kazmierczak E., Jacobsen A., Krogh A., Bardram L., Hother C., Gronbaek K., Federspiel B., Lund A. H., Friis-Hansen L. (2011). miR-449 inhibits cell proliferation and is down-regulated in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 10, 29–40 10.1186/1476-4598-10-29 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Censini S., Lange C., Xiang Z., Crabtree J. E., Ghiara P., Borodovsky M., Rappuoli R., Covacci A. (1996). cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I- specific and disease-associated virulence factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 14648–14653 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14648 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. H., Wu C. W., Li A. F., Chi C. W., Lin W. C. (2008). miR-21 microRNA expression in human gastric carcinomas and its clinical association. Anticancer Res. 28, 907–911 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Z., Li L., Lodish H. F., Bartel D. P. (2004). microRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303, 83–86 10.1126/science.1094226 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costinean S., Zanesi N., Pekarsky Y., Tili E., Volinia S., Heerema N., Croce C. M. (2006). Pre-B cell proliferation and lymphoblastic leukemia/high-grade lymphoma in E(mu)-miR155 transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 7024–7029 10.1073/pnas.0602266103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covacci A., Censini S., Bugnoli M., Petracca R., Burroni D., Macchia G., Massone A., Papini E., Xiang Z., Figura N., Rappuoli R. (1993). Molecular characterization of the 128-kDa immunodominant antigen of Helicobacter pylori associated with cytotoxicity and duodenal ulcer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 5791–5795 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5791 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Blaser M. J. (1992). Purification and characterization of the vacuolating toxin from Helicobacter pylori. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 10570–10575 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Tummuru M. K., Cao P., Thompson S. A., Blaser M. J. (1994). Divergence of genetic sequences for the vacuolating cytotoxin among Helicobacter pylori strains. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 10566–10573 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig V. J., Cogliatti S. B., Imig J., Renner C., Neuenschwander S., Rehrauer H., Schlapbach R., Dirnhofer S., Tzankov A., Muller A. (2011a). Myc-mediated repression of microRNA-34a promotes high-grade transformation of B-cell lymphoma by dysregulation of FoxP1. Blood 117, 6227–6236 10.1182/blood-2010-10-312231 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig V. J., Cogliatti S. B., Rehrauer H., Wundisch T., Muller A. (2011b). Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-203 dysregulates ABL1 expression and drives Helicobacter-associated gastric lymphomagenesis. Cancer Res. 71, 3616–3624 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui Y., Su W. Y., Xing J., Wang Y. C., Wang P., Chen X. Y., Shen Z. Y., Cao H., Lu Y. Y., Fang J. Y. (2011). miR-29a inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest through the downregulation of p42.3 in human gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 6, e25872. 10.1371/journal.pone.0025872 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding L., Xu Y., Zhang W., Deng Y., Si M., Du Y., Yao H., Liu X., Ke Y., Si J., Zhou T. (2010). miR-375 frequently downregulated in gastric cancer inhibits cell proliferation by targeting JAK2. Cell Res. 20, 784–793 10.1038/cr.2010.167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Y., Xu Y., Ding L., Yao H., Yu H., Zhou T., Si J. (2009). Down-regulation of miR-141 in gastric cancer and its involvement in cell growth. J. Gastroenterol. 44, 556–561 10.1007/s00535-009-0037-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkington P. T., O’Kane C. M., Friedland J. S. (2005). The paradox of matrix metalloproteinases in infectious disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 142, 12–20 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02840.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Omar E. M., Carrington M., Chow W. H., McColl K. E., Bream J. H., Young H. A., Herrera J., Lissowska J., Yuan C. C., Rothman N., Lanyon G., Martin M., Fraumeni J. F., Jr., Rabkin C. S. (2000). Interleukin-1 polymorphisms associated with increased risk of gastric cancer. Nature 404, 398–402 10.1038/35006081 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Omar E. M., Rabkin C. S., Gammon M. D., Vaughan T. L., Risch H. A., Schoenberg J. B., Stanford J. L., Mayne S. T., Goedert J., Blot W. J., Fraumeni J. F., Jr., Chow W. H. (2003). Increased risk of noncardia gastric cancer associated with proinflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms. Gastroenterology 124, 1193–1201 10.1016/S0016-5085(03)00157-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fassi Fehri L., Koch M., Belogolova E., Khalil H., Bolz C., Kalali B., Mollenkopf H. J., Beigier-Bompadre M., Karlas A., Schneider T., Churin Y., Gerhard M., Meyer T. F. (2010). Helicobacter pylori induces miR-155 in T cells in a cAMP-Foxp3-dependent manner. PLoS ONE 5, e9500. 10.1371/journal.pone.0009500 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferlay J., Autier P., Boniol M., Heanue M., Colombet M., Boyle P. (2007). Estimates of the cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2006. Ann. Oncol. 18, 581–592 10.1093/annonc/mdl498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo C., Machado J. C., Pharoah P., Seruca R., Sousa S., Carvalho R., Capelinha A. F., Quint W., Caldas C., van Doorn L. J., Carneiro F., Sobrinho-Simoes M. (2002). Helicobacter pylori and interleukin 1 genotyping: an opportunity to identify high-risk individuals for gastric carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 94, 1680–1687 10.1093/jnci/94.22.1680 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu S., Ramanujam K. S., Wong A., Fantry G. T., Drachenberg C. B., James S. P., Meltzer S. J., Wilson K. T. (1999). Increased expression and cellular localization of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase 2 in Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gastroenterology 116, 1319–1329 10.1016/S0016-5085(99)70496-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta T., El-Omar E. M., Xiao F., Shirai N., Takashima M., Sugimurra H. (2002). Interleukin 1beta polymorphisms increase risk of hypochlorhydria and atrophic gastritis and reduce risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence in Japan. Gastroenterology 123, 92–105 10.1053/gast.2002.1230946 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao C., Zhang Z., Liu W., Xiao S., Gu W., Lu H. (2010). Reduced microRNA-218 expression is associated with high nuclear factor kappa B activation in gastric cancer. Cancer 116, 41–49 10.1002/cncr.24991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebert B., Fischer W., Weiss E., Hoffmann R., Haas R. (2003). Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin inhibits T lymphocyte activation. Science 301, 1099–1102 10.1126/science.1086871 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard M., Lehn N., Neumayer N., Boren T., Rad R., Schepp W., Miehlke S., Classen M., Prinz C. (1999). Clinical relevance of the Helicobacter pylori gene for blood-group antigen-binding adhesin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 12778–12783 10.1073/pnas.96.22.12778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Armstrong J. A., Marshall B. J. (1986). Campylobacter pyloridis, gastritis, and peptic ulceration. J. Clin. Pathol. 39, 353–365 10.1136/jcp.39.4.353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo J., Miao Y., Xiao B., Huan R., Jiang Z., Meng D., Wang Y. (2009). Differential expression of microRNA species in human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 24, 652–657 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05666.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X., Guo L., Ji J., Zhang J., Chen X., Cai Q., Li J., Gu Q., Liu B., Zhu Z., Yu Y. (2010). miRNA-331-3p directly targets E2F1 and induces growth arrest in human gastric cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 398, 1–6 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.05.082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. X., Yang J., Ding Y. W., Liu W., Shen Q. Y., Xia H. H. (2006). Increased epithelial and serum expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in gastric cancer: potential role of MIF in gastric carcinogenesis. Gut 55, 797–802 10.1136/gut.2005.078113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessey S. J., Spencer J., Wyatt J. I., Sobala G., Rathbone B. J., Axon A. T., Dixon M. F. (1990). Bacterial adhesion and disease activity in Helicobacter associated chronic gastritis. Gut 31, 134–138 10.1136/gut.31.2.134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilver D., Arnqvist A., Ogren J., Frick I. M., Kersulyte D., Incecik E. T., Berg D. E., Covacci A., Engstrand L., Boren T. (1998). Helicobacter pylori adhesin binding fucosylated histo-blood group antigens revealed by retagging. Science 279, 373–377 10.1126/science.279.5349.373 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji Q., Hao X., Meng Y., Zhang M., Desano J., Fan D., Xu L. (2008). Restoration of tumor suppressor miR-34 inhibits human p53-mutant gastric cancer tumorspheres. BMC Cancer 8, 266–277 10.1186/1471-2407-8-266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juttner S., Cramer T., Wessler S., Walduck A., Gao F., Schmitz F., Wunder C., Weber M., Fischer S. M., Schmidt W. E., Wiedenmann B., Meyer T. F., Naumann M., Hocker M. (2003). Helicobacter pylori stimulates host cyclooxygenase-2 gene transcription: critical importance of MEK/ERK-dependent activation of USF1/-2 and CREB transcription factors. Cell. Microbiol. 5, 821–834 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2003.00324.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan T., Sato F., Ito T., Matsumura N., David S., Cheng Y., Agarwal R., Paun B. C., Jin Z., Olaru A. V., Selaru F. M., Hamilton J. P., Yang J., Abraham J. M., Mori Y., Meltzer S. J. (2009). The miR-106b-25 polycistron, activated by genomic amplification, functions as an oncogene by suppressing p21 and Bim. Gastroenterology 136, 1689–1700 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.02.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y. H., Lee H. S., Kim W. H. (2002). Promoter methylation and silencing of PTEN in gastric carcinoma. Lab. Invest. 82, 285–291 10.1038/labinvest.3780422 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Yu J., Han T. S., Park S. Y., Namkoong B., Kim D. H., Hur K., Yoo M. W., Lee H. J., Yang H. K., Kim V. N. (2009). Functional links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 1672–1681 10.1093/nar/gkn813 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuck D., Kolmerer B., Iking-Konert C., Krammer P. H., Stremmel W., Rudi J. (2001). Vacuolating cytotoxin of Helicobacter pylori induces apoptosis in the human gastric epithelial cell line AGS. Infect. Immun. 69, 5080–5087 10.1128/IAI.69.8.5080-5087.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai K. W., Koh K. X., Loh M., Tada K., Subramaniam M. M., Lim X. Y., Vaithilingam A., Salto-Tellez M., Iacopetta B., Ito Y., Soong R. (2010). microRNA-130b regulates the tumour suppressor RUNX3 in gastric cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 46, 1456–1463 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.01.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E. K., Wang X., Shin V. Y., Zhang S., Morrison H., Sun J., Ng E. K., Yu J., Jin H. (2011). A microRNA contribution to aberrant Ras activation in gastric cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 3, 209–218 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. C., Feinbaum R. L., Ambros V. (1993). The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75, 843–854 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-Y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leunk R. D., Johnson P. T., David B. C., Kraft W. G., Morgan D. R. (1988). Cytotoxic activity in broth-culture filtrates of Campylobacter pylori. J. Med. Microbiol. 26, 93–99 10.1099/00222615-26-2-93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. P., Shih I. H., Jones-Rhoades M. W., Bartel D. P., Burge C. B. (2003). Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115, 787–798 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)01018-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Xu X., Xiao B., Zhu E. D., Li B. S., Liu Z., Tang B., Zou Q. M., Liang H. P., Mao X. H. (2011a). H. pylori related proinflammatory cytokines contribute to the induction of miR-146a in human gastric epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1007/s11033-011-1257-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Zhang Y., Zhang H., Liu X., Gong T., Li M., Sun L., Ji G., Shi Y., Han Z., Han S., Nie Y., Chen X., Zhao Q., Ding J., Wu K., Daiming F. (2011b). miRNA-223 promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting tumor suppressor EPB41L3. Mol. Cancer Res. 9, 824–833 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q. L., Ito K., Sakakura C., Fukamachi H., Inoue K., Chi X. Z., Lee K. Y., Nomura S., Lee C. W., Han S. B., Kim H. M., Kim W. J., Yamamoto H., Yamashita N., Yano T., Ikeda T., Itohara S., Inazawa J., Abe T., Hagiwara A., Yamagishi H., Ooe A., Kaneda A., Sugimura T., Ushijima T., Bae S. C., Ito Y. (2002). Causal relationship between the loss of RUNX3 expression and gastric cancer. Cell 109, 113–124 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00690-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Xiao B., Tang B., Li B., Li N., Zhu E., Guo G., Gu J., Zhuang Y., Liu X., Ding H., Zhao X., Guo H., Mao X., Zou Q. (2010). Up-regulated microRNA-146a negatively modulate Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammatory response in human gastric epithelial cells. Microbes Infect. 12, 854–863 10.1016/j.micinf.2010.06.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lize M., Klimke A., Dobbelstein M. (2011). microRNA-449 in cell fate determination. Cell Cycle 10, 2874–2882 10.4161/cc.10.17.17181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Getz G., Miska E. A., Alvarez-Saavedra E., Lamb J., Peck D., Sweet-Cordero A., Ebert B. L., Mak R. H., Ferrando A. A., Downing J. R., Jacks T., Horvitz H. R., Golub T. R. (2005). microRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435, 834–838 10.1038/nature03702 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Z., Liu M., Stribinskis V., Klinge C. M., Ramos K. S., Colburn N. H., Li Y. (2008). microRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene 27, 4373–4379 10.1038/onc.2008.72 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo H., Zhang H., Zhang Z., Zhang X., Ning B., Guo J., Nie N., Liu B., Wu X. (2009). Down-regulated miR-9 and miR-433 in human gastric carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 28, 82–91 10.1186/1756-9966-28-82 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machado J. C., Pharoah P., Sousa S., Carvalho R., Oliveira C., Figueiredo C., Amorim A., Seruca R., Caldas C., Carneiro F., Sobrinho-Simoes M. (2001). Interleukin 1B and interleukin 1RN polymorphisms are associated with increased risk of gastric carcinoma. Gastroenterology 121, 823–829 10.1053/gast.2001.28000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi J., Sonden B., Hurtig M., Olfat F. O., Forsberg L., Roche N., Angstrom J., Larsson T., Teneberg S., Karlsson K. A., Altraja S., Wadstrom T., Kersulyte D., Berg D. E., Dubois A., Petersson C., Magnusson K. E., Norberg T., Lindh F., Lundskog B. B., Arnqvist A., Hammarstrom L., Boren T. (2002). Helicobacter pylori SabA adhesin in persistent infection and chronic inflammation. Science 297, 573–578 10.1126/science.1069076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Armstrong J. A., McGechie D. B., Glancy R. J. (1985). Attempt to fulfill Koch’s postulates for pyloric Campylobacter. Med. J. Aust. 142, 436–439 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Isomoto H., Inoue N., Nakayama T., Hayashi T., Nakayama M., Nakao K., Hirayama T., Kohno S. (2011). microRNA signatures in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa. Int. J. Cancer 128, 361–370 10.1002/ijc.25348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy C. J., Crofford L. J., Greenson J., Scheiman J. M. (1999). Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in gastric antral mucosa before and after eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 94, 1218–1223 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01070.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Ramanujam K. S., Gobert A. P., James S. P., Wilson K. T. (2003). Cutting edge: cyclooxygenase-2 activation suppresses Th1 polarization in response to Helicobacter pylori. J. Immunol. 171, 3913–3917 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motoyama K., Inoue H., Mimori K., Tanaka F., Kojima K., Uetake H., Sugihara K., Mori M. (2010). Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of PDCD4 and microRNA-21 in human gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 36, 1089–1095 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motoyama K., Inoue H., Nakamura Y., Uetake H., Sugihara K., Mori M. (2008). Clinical significance of high mobility group A2 in human gastric cancer and its relationship to let-7 microRNA family. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 2334–2340 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida N., Mimori K., Fabbri M., Yokobori T., Sudo T., Tanaka F., Shibata K., Ishii H., Doki Y., Mori M. (2011). microRNA-125a-5p is an independent prognostic factor in gastric cancer and inhibits the proliferation of human gastric cancer cells in combination with trastuzumab. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 2725–2733 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertli M., Engler D. B., Kohler E., Koch M., Meyer T. F., Muller A. (2011). microRNA-155 is essential for the T cell-mediated control of Helicobacter pylori infection and for the induction of chronic gastritis and colitis. J. Immunol. 187, 3578–3586 10.4049/jimmunol.1101772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo M., Tahara T., Shibata T., Yamashita H., Nakamura M., Yoshioka D., Yonemura J., Ishizuka T., Arisawa T., Hirata I. (2010). Association between common genetic variants in pre-microRNAs and gastric cancer risk in Japanese population. Helicobacter 15, 524–531 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2010.00806.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin D. M. (2006). The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int. J. Cancer 118, 3030–3044 10.1002/ijc.21731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin D. M., Bray F., Ferlay J., Pisani P. (2005). Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J. Clin. 55, 74–108 10.3322/canjclin.55.2.74 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrocca F., Visone R., Onelli M. R., Shah M. H., Nicoloso M. S., de Martino I., Iliopoulos D., Pilozzi E., Liu C. G., Negrini M., Cavazzini L., Volinia S., Alder H., Ruco L. P., Baldassarre G., Croce C. M., Vecchione A. (2008). E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell 13, 272–286 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.02.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phadnis S. H., Ilver D., Janzon L., Normark S., Westblom T. U. (1994). Pathological significance and molecular characterization of the vacuolating toxin gene of Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 62, 1557–1565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk D. B., Peek R. M., Jr. (2010). Helicobacter pylori: gastric cancer and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10, 403–414 10.1038/nrc2903 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristimaki A., Honkanen N., Jankala H., Sipponen P., Harkonen M. (1997). Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. 57, 1276–1280 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano M., Ricci V., Memoli A., Tuccillo C., Di Popolo A., Sommi P., Acquaviva A. M., Del Vecchio Blanco C., Bruni C. B., Zarrilli R. (1998). Helicobacter pylori up-regulates cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA expression and prostaglandin E2 synthesis in MKN28 gastric mucosal cells in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 28560–28563 10.1074/jbc.273.44.28560 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Murata-Kamiya N., Hirayama T., Ohba Y., Hatakeyama M. (2010). Conversion of Helicobacter pylori CagA from senescence inducer to oncogenic driver through polarity-dependent regulation of p21. J. Exp. Med. 207, 2157–2174 10.1084/jem.20100602 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Suzuki H., Tsugawa H., Nakagawa I., Matsuzaki J., Kanai Y., Hibi T. (2009). Chromatin remodeling at Alu repeats by epigenetic treatment activates silenced microRNA-512-5p with downregulation of Mcl-1 in human gastric cancer cells. Oncogene 28, 2738–2744 10.1038/onc.2009.140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Suzuki H., Tsugawa H., Suzuki S., Matsuzaki J., Hirata K., Hibi T. (2011). Dysfunctional gastric emptying with down-regulation of muscle-specific microRNAs in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Gastroenterology 140, 189–198 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.08.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki N., Morisaki T., Hashizume K., Yao T., Tsuneyoshi M., Noshiro H., Nakamura K., Yamanaka T., Uchiyama A., Tanaka M., Katano M. (2001). Nuclear factor-kappaB p65 (RelA) transcription factor is constitutively activated in human gastric carcinoma tissue. Clin. Cancer Res. 7, 4136–4142 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawaoka H., Kawano S., Tsuji S., Tsuji M., Sun W., Gunawan E. S., Hori M. (1998). Helicobacter pylori infection induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human gastric mucosa. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 59, 313–316 10.1016/S0952-3278(98)90079-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt W., Haas R. (1994). Genetic analysis of the Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin: structural similarities with the IgA protease type of exported protein. Mol. Microbiol. 12, 307–319 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01019.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki A., Sakatani T., Ushiku T., Hino R., Isogai M., Ishikawa S., Uozaki H., Takada K., Fukayama M. (2010). Downregulation of microRNA-200 in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. 70, 4719–4727 10.1158/1538-7445.AM10-4719 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirin H., Weinstein I. B., Moss S. F. (2001). Effects of H. pylori infection of gastric epithelial cells on cell cycle control. Front. Biosci. 6, E104–E118 10.2741/Shirin [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonkoly E., Pivarcsi A. (2009). Advances in microRNAs: implications for immunity and inflammatory diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 13, 24–38 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00534.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T., Wang C., Xing J., Wu D. (2011). miR-429 modulates the expression of c-myc in human gastric carcinoma cells. Eur. J. Cancer. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.05.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundrud M. S., Torres V. J., Unutmaz D., Cover T. L. (2004). Inhibition of primary human T cell proliferation by Helicobacter pylori vacuolating toxin (VacA) is independent of VacA effects on IL-2 secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 7727–7732 10.1073/pnas.0401528101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung J. J., Leung W. K., Go M. Y., To K. F., Cheng A. S., Ng E. K., Chan F. K. (2000). Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in Helicobacter pylori-associated premalignant and malignant gastric lesions. Am. J. Pathol. 157, 729–735 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64586-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Yamamoto E., Nojima M., Kai M., Yamano H. O., Yoshikawa K., Kimura T., Kudo T., Harada E., Sugai T., Takamaru H., Niinuma T., Maruyama R., Yamamoto H., Tokino T., Imai K., Toyota M., Shinomura Y. (2010). Methylation-associated silencing of microRNA-34b/c in gastric cancer and its involvement in an epigenetic field defect. Carcinogenesis 31, 2066–2073 10.1093/carcin/bgp179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang B., Xiao B., Liu Z., Li N., Zhu E. D., Li B. S., Xie Q. H., Zhuang Y., Zou Q. M., Mao X. H. (2010). Identification of MyD88 as a novel target of miR-155, involved in negative regulation of Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. FEBS Lett. 584, 1481–1486 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.02.063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford J. L., Ghiara P., Dell’Orco M., Comanducci M., Burroni D., Bugnoli M., Tecce M. F., Censini S., Covacci A., Xiang Z., Papini E., Montecucco C., Parente L., Rappuoli R. (1994). Gene structure of the Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin and evidence of its key role in gastric disease. J. Exp. Med. 179, 1653–1658 10.1084/jem.179.5.1653 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thai T. H., Calado D. P., Casola S., Ansel K. M., Xiao C., Xue Y., Murphy A., Frendewey D., Valenzuela D., Kutok J. L., Schmidt-Supprian M., Rajewsky N., Yancopoulos G., Rao A., Rajewsky K. (2007). Regulation of the germinal center response by microRNA-155. Science 316, 604–608 10.1126/science.1141229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tie J., Pan Y., Zhao L., Wu K., Liu J., Sun S., Guo X., Wang B., Gang Y., Zhang Y., Li Q., Qiao T., Zhao Q., Nie Y., Fan D. (2010). miR-218 inhibits invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting the Robo1 receptor. PLoS Genet. 6, e1000879. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000879 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomb J. F., White O., Kerlavage A. R., Clayton R. A., Sutton G. G., Fleischmann R. D., Ketchum K. A., Klenk H. P., Gill S., Dougherty B. A., Nelson K., Quackenbush J., Zhou L., Kirkness E. F., Peterson S., Loftus B., Richardson D., Dodson R., Khalak H. G., Glodek A., McKenney K., Fitzegerald L. M., Lee N., Adams M. D., Hickey E. K., Berg D. E., Gocayne J. D., Utterback T. R., Peterson J. D., Kelley J. M., Cotton M. D., Weidman J. M., Fujii C., Bowman C., Watthey L., Wallin E., Hayes W. S., Borodovsky M., Karp P. D., Smith H. O., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. (1997). The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 388, 539–547 10.1038/41483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto Y., Nakada C., Noguchi T., Tanigawa M., Nguyen L. T., Uchida T., Hijiya N., Matsuura K., Fujioka T., Seto M., Moriyama M. (2010). microRNA-375 is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta. Cancer Res. 70, 2339–2349 10.1158/1538-7445.AM10-2339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tummuru M. K., Cover T. L., Blaser M. J. (1993). Cloning and expression of a high-molecular-mass major antigen of Helicobacter pylori: evidence of linkage to cytotoxin production. Infect. Immun. 61, 1799–1809 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unoki M., Nakamura Y. (2003). EGR2 induces apoptosis in various cancer cell lines by direct transactivation of BNIP3L and BAK. Oncogene 22, 2172–2185 10.1038/sj.onc.1206222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varambally S., Cao Q., Mani R. S., Shankar S., Wang X., Ateeq B., Laxman B., Cao X., Jing X., Ramnarayanan K., Brenner J. C., Yu J., Kim J. H., Han B., Tan P., Kumar-Sinha C., Lonigro R. J., Palanisamy N., Maher C. A., Chinnaiyan A. M. (2008). Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science 322, 1695–1699 10.1126/science.1165395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viala J., Chaput C., Boneca I. G., Cardona A., Girardin S. E., Moran A. P., Athman R., Memet S., Huerre M. R., Coyle A. J., DiStefano P. S., Sansonetti P. J., Labigne A., Bertin J., Philpott D. J., Ferrero R. L. (2004). Nod1 responds to peptidoglycan delivered by the Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island. Nat. Immunol. 5, 1166–1174 10.1038/ni1131 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volinia S., Calin G. A., Liu C. G., Ambs S., Cimmino A., Petrocca F., Visone R., Iorio M., Roldo C., Ferracin M., Prueitt R. L., Yanaihara N., Lanza G., Scarpa A., Vecchione A., Negrini M., Harris C. C., Croce C. M. (2006). A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 2257–2261 10.1073/pnas.0510565103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan H. Y., Guo L. M., Liu T., Liu M., Li X., Tang H. (2010). Regulation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB1 by microRNA-9 in human gastric adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer 9, 16. 10.1186/1476-4598-9-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. J., Ruan H. J., He X. J., Ma Y. Y., Jiang X. T., Xia Y. J., Ye Z. Y., Tao H. Q. (2010). microRNA-101 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and involved in cell migration and invasion. Eur. J. Cancer 46, 2295–2303 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.07.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Y., Wang C. J., Tseng C. C., Chen H. P., Wu M. S., Lin J. T., Inoue H., Chen G. H. (2005). Helicobacter pylori promote gastric cancer cells invasion through a NF-kappaB and COX-2-mediated pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 11, 3197–3203 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F., Zikusoka M., Trindade A., Dassopoulos T., Harris M. L., Bayless T. M., Brant S. R., Chakravarti S., Kwon J. H. (2008). microRNAs are differentially expressed in ulcerative colitis and alter expression of macrophage inflammatory peptide-2 alpha. Gastroenterology 135, 1624–1635e24. 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.05.053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Q., Jin H., Yang Z., Luo G., Lu Y., Li K., Ren G., Su T., Pan Y., Feng B., Xue Z., Wang X., Fan D. (2010). miR-150 promotes gastric cancer proliferation by negatively regulating the pro-apoptotic gene EGR2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 392, 340–345 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.054 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia H. H., Talley N. J. (2001). Apoptosis in gastric epithelium induced by Helicobacter pylori infection: implications in gastric carcinogenesis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 96, 16–26 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03604.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia L., Zhang D., Du R., Pan Y., Zhao L., Sun S., Hong L., Liu J., Fan D. (2008). miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 123, 372–379 10.1002/ijc.23501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao B., Guo J., Miao Y., Jiang Z., Huan R., Zhang Y., Li D., Zhong J. (2009a). Detection of miR-106a in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Clin. Chim. Acta 400, 97–102 10.1016/j.cca.2008.10.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao B., Liu Z., Li B. S., Tang B., Li W., Guo G., Shi Y., Wang F., Wu Y., Tong W. D., Guo H., Mao X. H., Zou Q. M. (2009b). Induction of microRNA-155 during Helicobacter pylori infection and its negative regulatory role in the inflammatory response. J. Infect. Dis. 200, 916–925 10.1086/605443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao B., Zhu E. D., Li N., Lu D. S., Li W., Li B. S., Zhao Y. L., Mao X. H., Guo G., Yu P. W., Zou Q. M. (2011). Increased miR-146a in gastric cancer directly targets SMAD4 and is involved in modulating cell proliferation and apoptosis. Oncol. Rep. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.3892/or.2011.1514 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Li W., Fan X., Liang Y., Zhao M., Zhang J., Tong W., Wang J., Yang W., Lu Y. (2007). Identification and characterization of a novel p42.3 gene as tumor-specific and mitosis phase-dependent expression in gastric cancer. Oncogene 26, 7371–7379 10.1038/sj.onc.1210620 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka Y., Tagawa H., Takahashi N., Watanabe A., Guo Y. M., Iwamoto K., Yamashita J., Saitoh H., Kameoka Y., Shimizu N., Ichinohasama R., Sawada K. (2009). Aberrant overexpression of microRNAs activate AKT signaling via down-regulation of tumor suppressors in natural killer-cell lymphoma/leukemia. Blood 114, 3265–3275 10.1182/blood-2009-06-222794 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Jie Z., Cao H., Greenlee A. R., Yang C., Zou F., Jiang Y. (2011). Low-level expression of let-7a in gastric cancer and its involvement in tumorigenesis by targeting RAB40C. Carcinogenesis 32, 713–722 10.1093/carcin/bgr035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Y., Suo A. L., Li Z. F., Liu L. Y., Tian T., Ni L., Zhang W. G., Nan K. J., Song T. S., Huang C. (2009). microRNA profiling of human gastric cancer. Mol. Med. Report 2, 963–970 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo Y. D., Choi J. Y., Lee S. J., Kim J. S., Min B. R., Lee Y. I., Kang Y. K. (1999). TGF-beta-induced cell-cycle arrest through the p21(WAF1/CIP1)-G1 cyclin/Cdks-p130 pathway in gastric-carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 83, 512–517 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Li Z., Gao C., Chen P., Chen J., Liu W., Xiao S., Lu H. (2008). miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab. Invest. 88, 1358–1366 10.1038/labinvest.2008.94 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L. H., Liu T., Tang H., Tian R. Q., Su C., Liu M., Li X. (2010a). microRNA-23a promotes the growth of gastric adenocarcinoma cell line MGC803 and downregulates interleukin-6 receptor. FEBS J. 277, 3726–3734 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07773.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W., Shan X., Wang T., Shu Y., Liu P. (2010b). miR-181b modulates multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 127, 2520–2529 10.1002/ijc.25260 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W., Xu H., Zhu D., Zhi H., Wang T., Wang J., Jiang B., Shu Y., Liu P. (2011a). miR-200bc/429 cluster modulates multidrug resistance of human cancer cell lines by targeting BCL2 and XIAP. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1007/s00280-011-1752-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W., Zhu D., Lu S., Wang T., Wang J., Jiang B., Shu Y., Liu P. (2011b). miR-497 modulates multidrug resistance of human cancer cell lines by targeting BCL2. Med. Oncol. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1007/s12032-010-9797-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References
- Ahn S. M., Cha J. Y., Kim J., Kim D., Trang H. T., Kim Y. M., Cho Y. H., Park D., Hong S. (2011). Smad3 regulates E-cadherin via miRNA-200 pathway. Oncogene. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1038/onc.2011.484 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandres E., Bitarte N., Arias F., Agorreta J., Fortes P., Agirre X., Zarate R., Diaz-Gonzalez J. A., Ramirez N., Sola J. J., Jimenez P., Rodriguez J., Garcia-Foncillas J. (2009). microRNA-451 regulates macrophage migration inhibitory factor production and proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 2281–2290 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1818 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bou Kheir T., Futoma-Kazmierczak E., Jacobsen A., Krogh A., Bardram L., Hother C., Gronbaek K., Federspiel B., Lund A. H., Friis-Hansen L. (2011). miR-449 inhibits cell proliferation and is down-regulated in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 10, 29–41 10.1186/1476-4598-10-29 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan M. C., Hilyard A. C., Wu C., Davis B. N., Hill N. S., Lal A., Lieberman J., Lagna G., Hata A. (2010). Molecular basis for antagonism between PDGF and the TGFbeta family of signalling pathways by control of miR-24 expression. EMBO J. 29, 559–573 10.1038/emboj.2009.370 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. H., Wu C. W., Li A. F., Chi C. W., Lin W. C. (2008). miR-21 microRNA expression in human gastric carcinomas and its clinical association. Anticancer Res. 28, 907–911 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Song Y., Wang Z., Yue Z., Xu H., Xing C., Liu Z. (2010). Altered expression of miR-148a and miR-152 in gastrointestinal cancers and its clinical significance. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 14, 1170–1179 10.1007/s11605-010-1202-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang Y., Song Y., Wang Z., Chen Y., Yue Z., Xu H., Xing C., Liu Z. (2011). Aberrant expression of miR-203 and its clinical significance in gastric and colorectal cancers. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 15, 63–70 10.1007/s11605-010-1367-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho W. J., Shin J. M., Kim J. S., Lee M. R., Hong K. S., Lee J. H., Koo K. H., Park J. W., Kim K. S. (2009). miR-372 regulates cell cycle and apoptosis of AGS human gastric cancer cell line through direct regulation of LATS2. Mol. Cells 28, 521–527 10.1007/s10059-009-0158-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun-Zhi Z., Lei H., An-Ling Z., Yan-Chao F., Xiao Y., Guang-Xiu W., Zhi-Fan J., Pei-Yu P., Qing-Yu Z., Chun-Sheng K. (2010). microRNA-221 and microRNA-222 regulate gastric carcinoma cell proliferation and radioresistance by targeting PTEN. BMC Cancer 10, 367–377 10.1186/1471-2407-10-367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig V. J., Cogliatti S. B., Imig J., Renner C., Neuenschwander S., Rehrauer H., Schlapbach R., Dirnhofer S., Tzankov A., Muller A. (2011a). Myc-mediated repression of microRNA-34a promotes high-grade transformation of B-cell lymphoma by dysregulation of FoxP1. Blood 117, 6227–6236 10.1182/blood-2010-10-312231 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig V. J., Cogliatti S. B., Rehrauer H., Wundisch T., Muller A. (2011b). Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-203 dysregulates ABL1 expression and drives Helicobacter-associated gastric lymphomagenesis. Cancer Res. 71, 3616–3624 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui Y., Su W. Y., Xing J., Wang Y. C., Wang P., Chen X. Y., Shen Z. Y., Cao H., Lu Y. Y., Fang J. Y. (2011). miR-29a inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest through the downregulation of p42.3 in human gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 6, e25872. 10.1371/journal.pone.0023219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding L., Xu Y., Zhang W., Deng Y., Si M., Du Y., Yao H., Liu X., Ke Y., Si J., Zhou T. (2010). miR-375 frequently downregulated in gastric cancer inhibits cell proliferation by targeting JAK2. Cell Res. 20, 784–793 10.1038/cr.2010.167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Y., Xu Y., Ding L., Yao H., Yu H., Zhou T., Si J. (2009). Down-regulation of miR-141 in gastric cancer and its involvement in cell growth. J. Gastroenterol. 44, 556–561 10.1007/s00535-009-0037-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fassi Fehri L., Koch M., Belogolova E., Khalil H., Bolz C., Kalali B., Mollenkopf H. J., Beigier-Bompadre M., Karlas A., Schneider T., Churin Y., Gerhard M., Meyer T. F. (2010). Helicobacter pylori induces miR-155 in T cells in a cAMP-Foxp3-dependent manner. PLoS ONE 5, e9500. 10.1371/journal.pone.0009500 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng L., Xie Y., Zhang H., Wu Y. (2011). miR-107 targets cyclin-dependent kinase 6 expression, induces cell cycle G1 arrest and inhibits invasion in gastric cancer cells. Med. Oncol. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1007/s12032-011-9823-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng R., Chen X., Yu Y., Su L., Yu B., Li J., Cai Q., Yan M., Liu B., Zhu Z. (2010). miR-126 functions as a tumour suppressor in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 298, 50–63 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.06.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao C., Zhang Z., Liu W., Xiao S., Gu W., Lu H. (2010). Reduced microRNA-218 expression is associated with high nuclear factor kappa B activation in gastric cancer. Cancer 116, 41–49 10.1002/cncr.24991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo J., Miao Y., Xiao B., Huan R., Jiang Z., Meng D., Wang Y. (2009). Differential expression of microRNA species in human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 24, 652–657 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05666.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo S. L., Peng Z., Yang X., Fan K. J., Ye H., Li Z. H., Wang Y., Xu X. L., Li J., Wang Y. L., Teng Y. (2011). miR-148a promoted cell proliferation by targeting p27 in gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 7, 567–574 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X., Guo L., Ji J., Zhang J., Chen X., Cai Q., Li J., Gu Q., Liu B., Zhu Z., Yu Y. (2010). miRNA-331-3p directly targets E2F1 and induces growth arrest in human gastric cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 398, 1–6 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.05.082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Akiyama Y., Otsubo T., Shimada S., Yuasa Y. (2010). Involvement of epigenetically silenced microRNA-181c in gastric carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 31, 777–784 10.1093/carcin/bgq013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Z., Xie L., Yu L., Qian X., Liu B. (2011). microRNA-146a is down-regulated in gastric cancer and regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis. Med. Oncol. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1007/s12032-011-9862-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji Q., Hao X., Meng Y., Zhang M., Desano J., Fan D., Xu L. (2008). Restoration of tumor suppressor miR-34 inhibits human p53-mutant gastric cancer tumorspheres. BMC Cancer 8, 266–278 10.1186/1471-2407-8-266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Zheng X., Xu X., Zhou Q., Yan H., Zhang X., Lu B., Wu C., Ju J. (2011). Prognostic significance of miR-181b and miR-21 in gastric cancer patients treated with S-1/oxaliplatin or doxifluridine/oxaliplatin. PLoS ONE 6, e23271. 10.1371/journal.pone.0023271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Z., Guo J., Xiao B., Miao Y., Huang R., Li D., Zhang Y. (2010). Increased expression of miR-421 in human gastric carcinoma and its clinical association. J. Gastroenterol. 45, 17–23 10.1007/s00535-009-0135-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Z., Selaru F. M., Cheng Y., Kan T., Agarwal R., Mori Y., Olaru A. V., Yang J., David S., Hamilton J. P., Abraham J. M., Harmon J., Duncan M., Montgomery E. A., Meltzer S. J. (2011). microRNA-192 and -215 are upregulated in human gastric cancer in vivo and suppress ALCAM expression in vitro. Oncogene 30, 1577–1585 10.1038/onc.2011.102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan T., Sato F., Ito T., Matsumura N., David S., Cheng Y., Agarwal R., Paun B. C., Jin Z., Olaru A. V., Selaru F. M., Hamilton J. P., Yang J., Abraham J. M., Mori Y., Meltzer S. J. (2009). The miR-106b-25 polycistron, activated by genomic amplification, functions as an oncogene by suppressing p21 and Bim. Gastroenterology 136, 1689–1700 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.02.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ishiguro H., Kuwabara Y., Kimura M., Mitui A., Mori Y., Ogawa R., Harata K., Fujii Y. (2009). microRNA expression profile in undifferentiated gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 34, 537–542 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Yu J., Han T. S., Park S. Y., Namkoong B., Kim D. H., Hur K., Yoo M. W., Lee H. J., Yang H. K., Kim V. N. (2009). Functional links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 1672–1681 10.1093/nar/gkn813 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogo R., Mimori K., Tanaka F., Komune S., Mori M. (2011). Clinical significance of miR-146a in gastric cancer cases. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 4277–4284 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2866 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai K. W., Koh K. X., Loh M., Tada K., Subramaniam M. M., Lim X., Vaithilingam A., Salto-Tellez M., Iacopetta B., Ito Y., Soong R. (2010). microRNA-130b regulates the tumour suppressor RUNX3 in gastric cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 46, 1456–1463 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.01.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang N., Liu M., Tang Q. L., Chen X., Liu Z., Bi F. (2010). Effects of microRNA-29 family members on proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cell lines. Chin. J. Cancer 29, 603–610 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q. L., Ito K., Sakakura C., Fukamachi H., Inoue K., Chi X. Z., Lee K. Y., Nomura S., Lee C. W., Han S. B., Kim H. M., Kim W. J., Yamamoto H., Yamashita N., Yano T., Ikeda T., Itohara S., Inazawa J., Abe T., Hagiwara A., Yamagishi H., Ooe A., Kaneda A., Sugimura T., Ushijima T., Bae S. C., Ito Y. (2002). Causal relationship between the loss of RUNX3 expression and gastric cancer. Cell 109, 113–124 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00690-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Luo F., Li Q., Xu M., Feng D., Zhang G., Wu W. (2011a). Identification of new aberrantly expressed miRNAs in intestinal-type. Oncol. Rep. 26, 1431–1439 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Zhang Y., Shi Y., Dong G., Liang J., Han Y., Wang X., Zhao Q., Ding J., Wu K., Fan D. (2011b). microRNA-107, an oncogene microRNA that regulates tumour invasion and metastasis by targeting DICER1 in gastric cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 15, 1887–1895 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01238.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Zhang Y., Zhang H., Liu X., Gong T., Li M., Sun L., Ji G., Shi Y., Han Z., Han S., Nie Y., Chen X., Zhao Q., Ding J., Wu K., Daiming F. (2011c). miRNA-223 promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting tumor suppressor EPB41L3. Mol. Cancer Res. 9, 824–833 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Xu X., Xiao B., Zhu E. D., Li B. S., Liu Z., Tang B., Zou Q. M., Liang H. P., Mao X. H. (2011d). H. pylori related proinflammatory cytokines contribute to the induction of miR-146a in human gastric epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1007/s11033-011-1257-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Zhang Y., Ding J., Wu K., Fan D. (2010). Survival prediction of gastric cancer by a seven-microRNA signature. Gut 59, 579–585 10.1136/gut.2008.171124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T., Tang H., Lang Y., Liu M., Li X. (2009). microRNA-27a functions as an oncogene in gastric adenocarcinoma by targeting prohibitin. Cancer Lett. 273, 233–242 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.07.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lize M., Klimke A., Dobbelstein M. (2011). microRNA-449 in cell fate determination. Cell Cycle 10, 2874–2882 10.4161/cc.10.17.17181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Z., Liu M., Stribinskis V., Klinge C. M., Ramos K. S., Colburn N. H., Li Y. (2008). microRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene 27, 4373–4379 10.1038/onc.2008.72 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo H., Zhang H., Zhang Z., Zhang X., Ning B., Guo J., Nie N., Liu B., Wu X. (2009). Down-regulated miR-9 and miR-433 in human gastric carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 28, 82–91 10.1186/1756-9966-28-82 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motoyama K., Inoue H., Mimori K., Tanaka F., Kojima K., Uetake H., Sugihara K., Mori M. (2010). Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of PDCD4 and microRNA-21 in human gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 36, 1089–1095 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motoyama K., Inoue H., Nakamura Y., Uetake H., Sugihara K., Mori M. (2008). Clinical significance of high mobility group A2 in human gastric cancer and its relationship to let-7 microRNA family. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 2334–2340 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertli M., Engler D. B., Kohler E., Koch M., Meyer T. F., Muller A. (2011). MicroRNA-155 is essential for the T cell-mediated control of Helicobacter pylori infection and for the induction of chronic gastritis and colitis. J. Immunol. 187, 3578–3586 10.4049/jimmunol.1101772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo M., Tahara T., Shibata T., Yamashita H., Nakamura M., Yoshioka D., Yonemura J., Ishizuka T., Arisawa T., Hirata I. (2010). Association between common genetic variants in pre-microRNAs and gastric cancer risk in Japanese population. Helicobacter 15, 524–531 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2010.00806.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsubo T., Akiyama Y., Hashimoto Y., Shimada S., Goto K., Yuasa Y. (2011). microRNA-126 inhibits SOX2 expression and contributes to gastric carcinogenesis. PLoS ONE 6, e16617. 10.1371/journal.pone.0016617 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrocca F., Visone R., Onelli M. R., Shah M. H., Nicoloso M. S., de Martino I., Iliopoulos D., Pilozzi E., Liu C. G., Negrini M., Cavazzini L., Volinia S., Alder H., Ruco L. P., Baldassarre G., Croce C. M., Vecchione A. (2008). E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell 13, 272–286 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.02.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotkrua P., Akiyama Y., Hashimoto Y., Otsubo T., Yuasa Y. (2011). miR-9 downregulates CDX2 expression in gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 129, 2611–2620 10.1002/ijc.25923 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Suzuki H., Tsugawa H., Nakagawa I., Matsuzaki J., Kanai Y., Hibi T. (2009). Chromatin remodeling at Alu repeats by epigenetic treatment activates silenced microRNA-512-5p with downregulation of Mcl-1 in human gastric cancer cells. Oncogene 28, 2738–2744 10.1038/onc.2009.140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen R., Pan S., Qi S., Lin X., Cheng S. (2010). Epigenetic repression of microRNA-129-2 leads to overexpression of SOX4 in gastric cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 394, 1047–1052 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.121 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X., Su S., Long J., Mei B., Chen Y. (2011). microRNA-191 targets N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 and promotes cell growth in human gastric carcinoma cell line MGC803. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1093/abbs/gmr084 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin V. Y., Jin H., Ng E. K., Cheng A. S., Chong W. W., Wong C. Y., Leung W. K., Sung J. J., Chu K. M. (2011). NF-kappaB targets miR-16 and miR-21 in gastric cancer: involvement of prostaglandin E receptors. Carcinogenesis 32, 240–245 10.1093/carcin/bgq240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Y. X., Yue Z. Y., Wang Z. N., Xu Y. Y., Luo Y., Xu H. M., Zhang X., Jiang L., Xing C. Z., Zhang Y. (2011). microRNA-148b is frequently down-regulated in gastric cancer and acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation. Mol. Cancer 10, 1–13 10.1186/1476-4598-10-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Q., Gu H., Zeng Y., Xia Y., Wang Y., Jing Y., Yang L., Wang B. (2010). Hsa-mir-27a genetic variant contributes to gastric cancer susceptibility through affecting miR-27a and target gene expression. Cancer Sci. 101, 2241–2247 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01608.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Yamamoto E., Nojima M., Kai M., Yamano H. O., Yoshikawa K., Kimura T., Kudo T., Harada E., Sugai T., Takamaru H., Niinuma T., Maruyama R., Yamamoto H., Tokino T., Imai K., Toyota M., Shinomura Y. (2010). Methylation-associated silencing of microRNA-34b/c in gastric cancer and its involvement in an epigenetic field defect. Carcinogenesis 31, 2066–2073 10.1093/carcin/bgp179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi T., Iio A., Nakagawa Y., Naoe T., Tanigawa N., Akao Y. (2009). Decreased expression of microRNA-143 and -145 in human gastric cancers. Oncology 77, 12–21 10.1159/000218166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang B., Xiao B., Liu Z., Li N., Zhu E. D., Li B. S., Xie Q. H., Zhuang Y., Zou Q. M., Mao X. H. (2010). Identification of MyD88 as a novel target of miR-155, involved in negative regulation of Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. FEBS Lett. 584, 1481–1486 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.02.063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchernitsa O., Kasajima A., Schafer R., Kuban R. J., Ungethum U., Gyorffy B., Neumann U., Simon E., Weichert W., Ebert M. P., Rocken C. (2010). Systematic evaluation of the miRNA-ome and its downstream effects on mRNA expression identifies gastric cancer progression. J. Pathol. 222, 310–319 10.1002/path.2759 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thai T. H., Calado D. P., Casola S., Ansel K. M., Xiao C., Xue Y., Murphy A., Frendewey D., Valenzuela D., Kutok J. L., Schmidt-Supprian M., Rajewsky N., Yancopoulos G., Rao A., Rajewsky K. (2007). Regulation of the germinal center response by microRNA-155. Science 316, 604–608 10.1126/science.1141229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tie J., Pan Y., Zhao L., Wu K., Liu J., Sun S., Guo X., Wang B., Gang Y., Zhang Y., Li Q., Qiao T., Zhao Q., Nie Y., Fan D. (2010). miR-218 inhibits invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting the Robo1 receptor. PLoS Genet. 6, e1000879. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000879 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai K. W., Liao Y. L., Wu C. W., Hu L. Y., Li S. C., Chan W. C., Ho M. R., Lai C. H., Kao H. W., Fang W. L., Huang K. H., Lin W. C. (2011a). Aberrant hypermethylation of miR-9 genes in gastric cancer. Epigenetics 6, 1189–1197 10.4161/epi.6.10.16535 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai K. W., Wu C. W., Hu L. Y., Li S. C., Liao Y. L., Lai C. H., Kao H. W., Fang W. L., Huang K. H., Chan W. C., Lin W. C. (2011b). Epigenetic regulation of miR-34b and miR-129 expression in gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 129, 2600–2610 10.1002/ijc.25919 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujiura M., Ichikawa D., Komatsu S., Shiozaki A., Takeshita H., Kosuga T., Konishi H., Morimura R., Deguchi K., Fujiwara H., Okamoto K., Otsuji E. (2010). Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with gastric cancers. Br. J. Cancer 102, 1174–1179 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605608 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto Y., Nakada C., Noguchi T., Tanigawa M., Nguyen L. T., Uchida T., Hijiya N., Matsuura K., Fujioka T., Seto M., Moriyama M. (2010). microRNA-375 is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta. Cancer Res. 70, 2339–2349 10.1158/1538-7445.AM10-2339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda R., Kohanbash G., Sasaki K., Fujita M., Zhu X., Kastenhuber E. R., McDonald H. A., Potter D. M., Hamilton R. L., Lotze M. T., Khan S. A., Sobol R. W., Okada H. (2009). Dicer-regulated microRNAs 222 and 339 promote resistance of cancer cells to cytotoxic T-lymphocytes by down-regulation of ICAM-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 10746–10751 10.1073/pnas.0811817106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Volinia S., Okumura H., Shimizu M., Taccioli C., Rossi S., Alder H., Liu C. G., Oue N., Yasui W., Yoshida K., Sasaki H., Nomura S., Seto Y., Kaminishi M., Calin G. A., Croce C. M. (2010). Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis of gastric cancer: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 11, 136–146 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70343-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varambally S., Cao Q., Mani R. S., Shankar S., Wang X., Ateeq B., Laxman B., Cao X., Jing X., Ramnarayanan K., Brenner J. C., Yu J., Kim J. H., Han B., Tan P., Kumar-Sinha C., Lonigro R. J., Palanisamy N., Maher C. A., Chinnaiyan A. M. (2008). Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science 322, 1695–1699 10.1126/science.1165395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volinia S., Calin G. A., Liu C. G., Ambs S., Cimmino A., Petrocca F., Visone R., Iorio M., Roldo C., Ferracin M., Prueitt R. L., Yanaihara N., Lanza G., Scarpa A., Vecchione A., Negrini M., Harris C. C., Croce C. M. (2006). A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 2257–2261 10.1073/pnas.0510565103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada R., Akiyama Y., Hashimoto Y., Fukamachi H., Yuasa Y. (2010). miR-212 is downregulated and suppresses methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 in human gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 127, 1106–1114 10.1002/ijc.25126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan H. Y., Guo L. M., Liu T., Liu M., Li X., Tang H. (2010). Regulation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB1 by microRNA-9 in human gastric adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer 9, 16–26 10.1186/1476-4598-9-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. J., Ruan H. J., He X. J., Ma Y. Y., Jiang X. T., Xia Y. J., Ye Z. Y., Tao H. Q. (2010). microRNA-101 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and involved in cell migration and invasion. Eur. J. Cancer 46, 2295–2303 10.1016/j.ejca.2009.12.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Qian J., Li C., Kwok L., Cheng F., Liu P., Perdomo C., Kotton D., Vaziri C., Anderlind C., Spira A., Cardoso W. V., Lu J. (2010a). miR-129 regulates cell proliferation by downregulating Cdk6 expression. Cell Cycle 9, 1809–1818 10.4161/cc.9.9.11535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Zhang Y. C., Suo W. H., Liu X. B., Shen W. W., Tian H., Fu G. H. (2010b). Induction of anion exchanger-1 translation and its opposite roles in the carcinogenesis of gastric cancer cells and differentiation of K562 cells. Oncogene 29, 1987–1996 10.1038/onc.2009.504 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Q., Jin H., Yang Z., Luo G., Lu Y., Li K., Ren G., Su T., Pan Y., Feng B., Xue Z., Wang X., Fan D. (2010c). miR-150 promotes gastric cancer proliferation by negatively regulating the pro-apoptotic gene EGR2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 392, 340–345 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.054 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. Y., Xue X. Y., Chen Z. J., Han S. L., Huang Y. P., Zhang L. F., Zhu G. B., Shen X. (2011a). Potentially predictive microRNAs of gastric cancer with metastasis to lymph node. World J. Gastroenterol. 17, 3645–3651 10.3748/wjg.v17.i36.4143 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X. M., Shao X. Q., Meng X. X., Zhang X. N., Zhu L., Liu S. X., Lin J., Xiao H. S. (2011b). Genome-wide analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression signatures in hydroxycamptothecin-resistant gastric cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 32, 259–269 10.1038/aps.2011.2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia L., Zhang D., Du R., Pan Y., Zhao L., Sun S., Hong L., Liu J., Fan D. (2008). miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 123, 372–379 10.1002/ijc.23501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao B., Guo J., Miao Y., Jiang Z., Huan R., Zhang Y., Li D., Zhong J. (2009a). Detection of miR-106a in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Clin. Chim. Acta 400, 97–102 10.1016/j.cca.2008.10.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao B., Liu Z., Li B. S., Tang B., Li W., Guo G., Shi Y., Wang F., Wu Y., Tong W. D., Guo H., Mao X. H., Zou Q. M. (2009b). Induction of microRNA-155 during Helicobacter pylori infection and its negative regulatory role in the inflammatory response. J. Infect. Dis. 200, 916–925 10.1086/605443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao B., Zhu E. D., Li N., Lu D. S., Li W., Li B. S., Zhao Y. L., Mao X. H., Guo G., Yu P. W., Zou Q. M. (2011). Increased miR-146a in gastric cancer directly targets SMAD4 and is involved in modulating cell proliferation and apoptosis. Oncol. Rep. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.3892/or.2011.1514 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu L., Wang F., Xu X. F., Mo W. H., Xia Y. J., Wan R., Wang X. P., Guo C. Y. (2010). Down-regulation of miR-212 expression by DNA hypermethylation in human gastric cancer cells. Med. Oncol. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1007/s12032-010-9691-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Deng Y., Yan X., Zhou T. (2011). Targeting miR-375 in gastric cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 15, 961–972 10.1517/14728222.2011.581232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakuchi M., Lowenstein C. J. (2009). miR-34, SIRT1 and p53: the feedback loop. Cell Cycle 8, 712–715 10.4161/cc.8.5.7753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Jie Z., Cao H., Greenlee A. R., Yang C., Zou F., Jiang Y. (2011). Low-level expression of let-7a in gastric cancer and its involvement in tumorigenesis by targeting RAB40C. Carcinogenesis 32, 713–722 10.1093/carcin/bgr035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao R., Ma Y., Du Y., Liao M., Li H., Liang W., Yuan J., Zhijunma, Yu X., Xiao H., Liao Y. (2011). The altered expression of inflammation-related microRNAs with microRNA-155 expression correlates with Th17 differentiation in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Cell. Mol. Immunol. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1038/cmi.2011.22 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Y., Suo A. L., Li Z. F., Liu L. Y., Tian T., Ni L., Zhang W. G., Nan K. J., Song T. S., Huang C. (2009). microRNA profiling of human gastric cancer. Mol. Med. Report 2, 963–970 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H. H., Wang X. J., Li G. X., Yang E., Yang N. M. (2007). Detection of let-7a microRNA by real-time PCR in gastric carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 13, 2883–2888 10.3748/wjg.13.6385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Zhu W., Zhang J., Huo S., Zhou L., Gu Z., Zhang M. (2010a). microRNA-650 targets ING4 to promote gastric cancer tumorigenicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 395, 275–280 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Guo J., Li D., Xiao B., Miao Y., Jiang Z., Zhuo H. (2010b). Down-regulation of miR-31 expression in gastric cancer tissues and its clinical significance. Med. Oncol. 27, 685–689 10.1007/s12032-009-9377-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Li Z., Gao C., Chen P., Chen J., Liu W., Xiao S., Lu H. (2008). miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab. Invest. 88, 1358–1366 10.1038/labinvest.2008.94 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Liu S., Shi R., Zhao G. (2011). miR-27 promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Genet. 204, 486–491 10.1016/j.cancergen.2011.07.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X., Yang L., Hu J. (2011). Down-regulation of miR-27a might inhibit proliferation and drug resistance of gastric cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 30, 55–60 10.1186/1756-9966-30-22 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng B., Liang L., Wang C., Huang S., Cao X., Zha R., Liu L., Jia D., Tian Q., Wu J., Ye Y. W., Wang Q., Long Z., Zhou Y., Du C., He X., Shi Y. (2011). microRNA-148a suppresses tumor cell invasion and metastasis by downregulating ROCK1 in gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H., Guo J. M., Lou Y. R., Zhang X. J., Zhong F. D., Jiang Z., Cheng J., Xiao B. X. (2010). Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood from patients with gastric cancer using microRNA as a marker. J. Mol. Med. 88, 709–717 10.1007/s00109-010-0617-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L. H., Liu T., Tang H., Tian R. Q., Su C., Liu M., Li X. (2010a). microRNA-23a promotes the growth of gastric adenocarcinoma cell line MGC803 and downregulates interleukin-6 receptor. FEBS J. 277, 3726–3734 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07773.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W., Shan X., Wang T., Shu Y., Liu P. (2010b). miR-181b modulates multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 127, 2520–2529 10.1002/ijc.25260 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y. M., Zhong Z. X., Liu Z. M. (2010c). Relationship between let-7a and gastric mucosa cancerization and its significance. World J. Gastroenterol. 16, 3325–3329 10.3748/wjg.v16.i26.3325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W., Xu H., Zhu D., Zhi H., Wang T., Wang J., Jiang B., Shu Y., Liu P. (2011a). miR-200bc/429 cluster modulates multidrug resistance of human cancer cell lines by targeting BCL2 and XIAP. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1007/s00280-011-1752-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W., Zhu D., Lu S., Wang T., Wang J., Jiang B., Shu Y., Liu P. (2011b). miR-497 modulates multidrug resistance of human cancer cell lines by targeting BCL2. Med. Oncol. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1007/s12032-010-9797-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]