Abstract
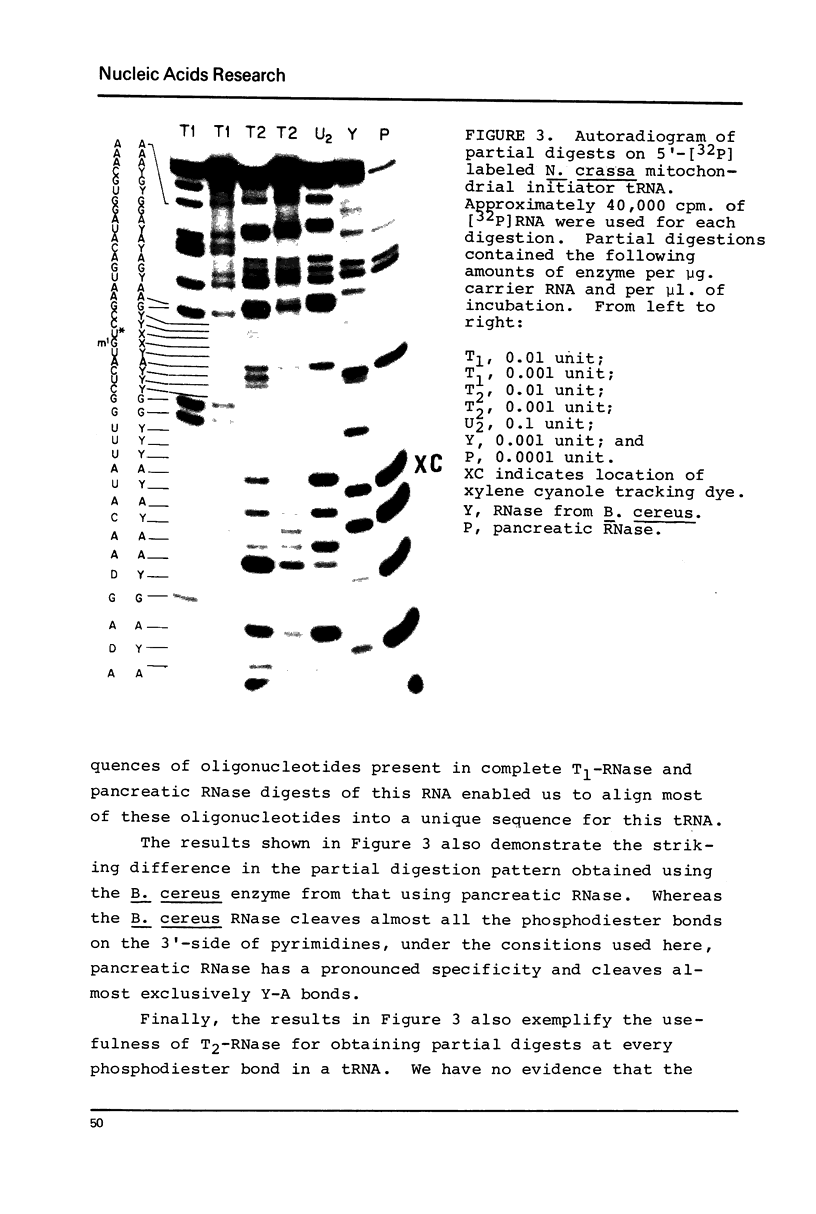
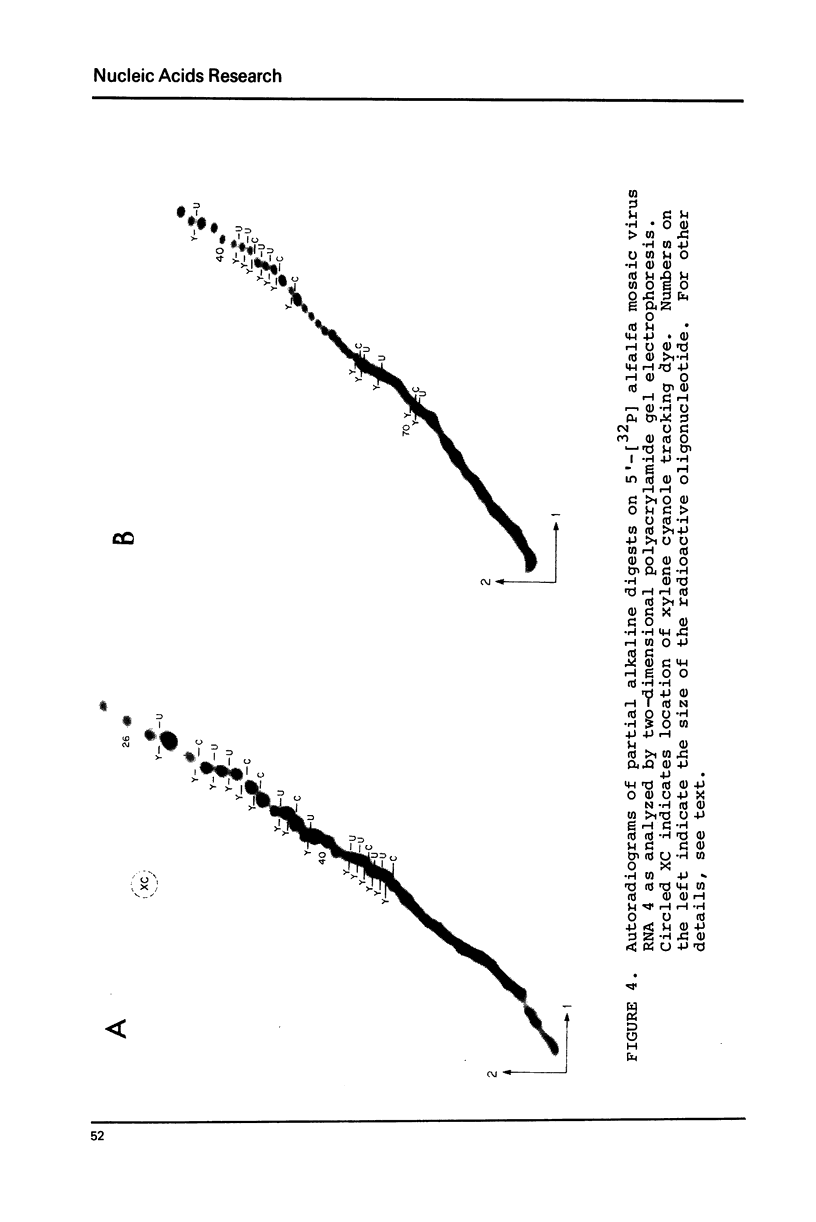
Sequence analysis of 5'-[32P] labeled tRNA and eukaryotic mRNA using an adaptation of a method recently described by Donis-Keller, Maxam and Gilbert for mapping guanines, adenines and pyrimidines from the 5'-end of an RNA is described. In addition, a technique utilizing two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for identification of pyrimidines within a sequence is described. 5'-[32P] Labeled rabbit beta-globin mRNA and N. crassa mitochondrial initiator tRNA were partially digested with T1- RNase for cleavage at G residues, with U2-RNase for cleavage at A residues, with an extracellular RNase from B. cereus for cleavage at pyrimidine residues and with T2-RNase or with alkali for cleavage at all four residues. The 5'-[32P] labeled partial digestion products were separated according to their size, by electrophoresis in adjacent lanes of a polyacrylamide slab gel and the location of G's, A's and of pyrimidines extending 60-80 nucleotides from the 5'-end of the RNA determined. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was used to separate the 5'-[32P] labeled fragments present in partial alkali digests of a 5'-[32P] labeled mRNA. The mobility shifts corresponding to the difference of a C residue were distinct from those corresponding to a U residue and this formed the basis of a method for distinguishing between the pyrimidines.
Full text
PDF

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baralle F. E. Complete nucleotide sequence of the 5' noncoding region of rabbit beta-globin mRNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. H., Brum C. K., Siberklang M., RajBhandary U. L., Hecker L. I., Barnett W. E. The first nucleotide sequence of an organelle transfer RNA: chloroplastic tRNAphe. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):717–723. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Urquhart N., Smith M., RajBhandary U. L. Nucleotide sequence of salmon testes and salmon liver cytoplasmic initiator tRNA. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90189-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. C., Randerath K. Use of specific endonuclease cleavage in RNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):1957–1978. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay E., Bambara R., Padmanabhan R., Wu R. DNA sequence analysis: a general, simple and rapid method for sequencing large oligodeoxyribonucleotide fragments by mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Mar;1(3):331–353. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockhard R. E., Rajbhandary U. L. Nucleotide sequences at the 5'termini of rabbit alpha and beta globin mRNA. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):747–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panet A., van de Sande J. H., Loewen P. C., Khorana H. G., Raae A. J., Lillehaug J. R., Kleppe K. Physical characterization and simultaneous purification of bacteriophage T4 induced polynucleotide kinase, polynucleotide ligase, and deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5045–5050. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Donelson J. E., Coulson A. R., Kössel H., Fischer D. Use of DNA polymerase I primed by a synthetic oligonucleotide to determine a nucleotide sequence in phage fl DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1209–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Prochiantz A., Haenni A. L., Rajbhandary U. L. Studies on the sequence of the 3'-terminal region of turnip-yellow-mosaic-virus RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb;72(3):465–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simsek M., RajBhandary U. L., Boisnard M., Petrissant G. Nucleotide sequence of rabbit liver and sheep mammary gland cytoplasmic initiatory transfer RNAs. Nature. 1974 Feb 22;247(5442):518–520. doi: 10.1038/247518a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]