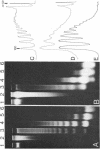
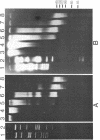
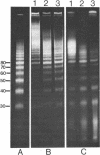
Abstract
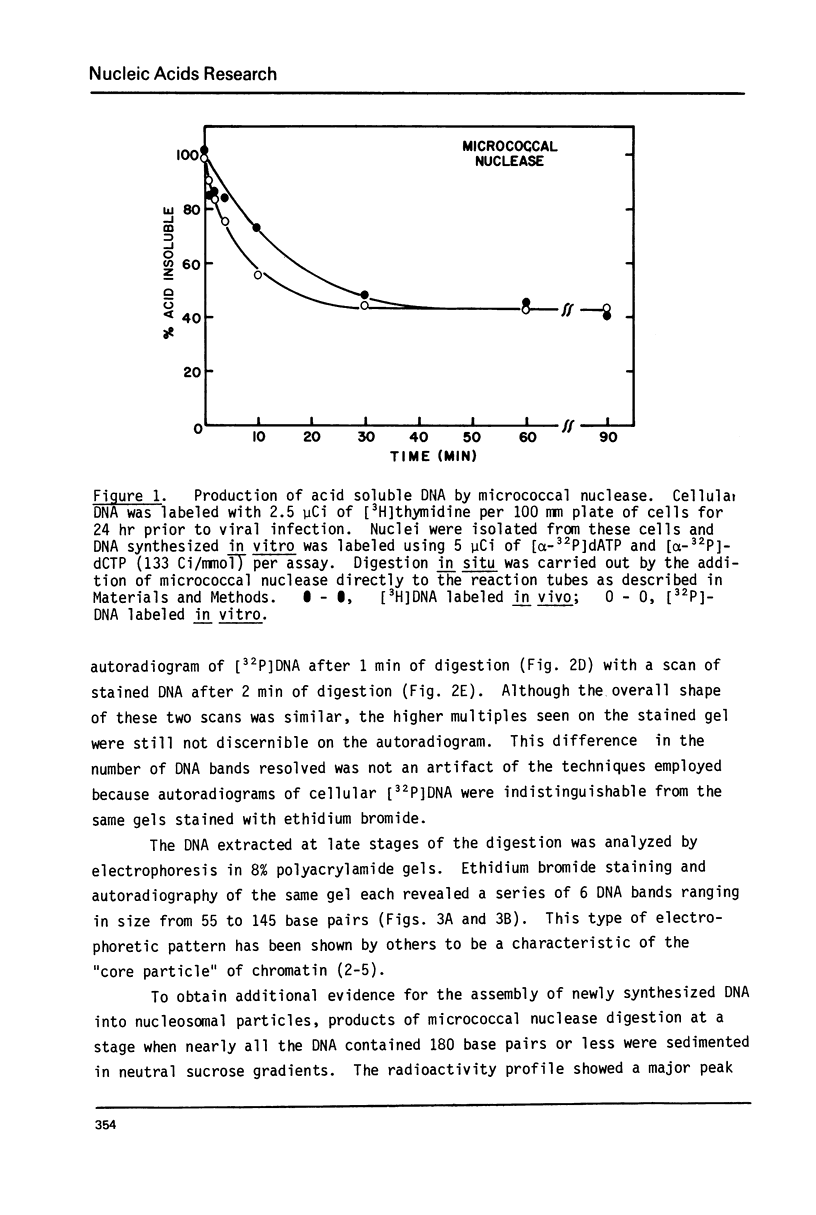
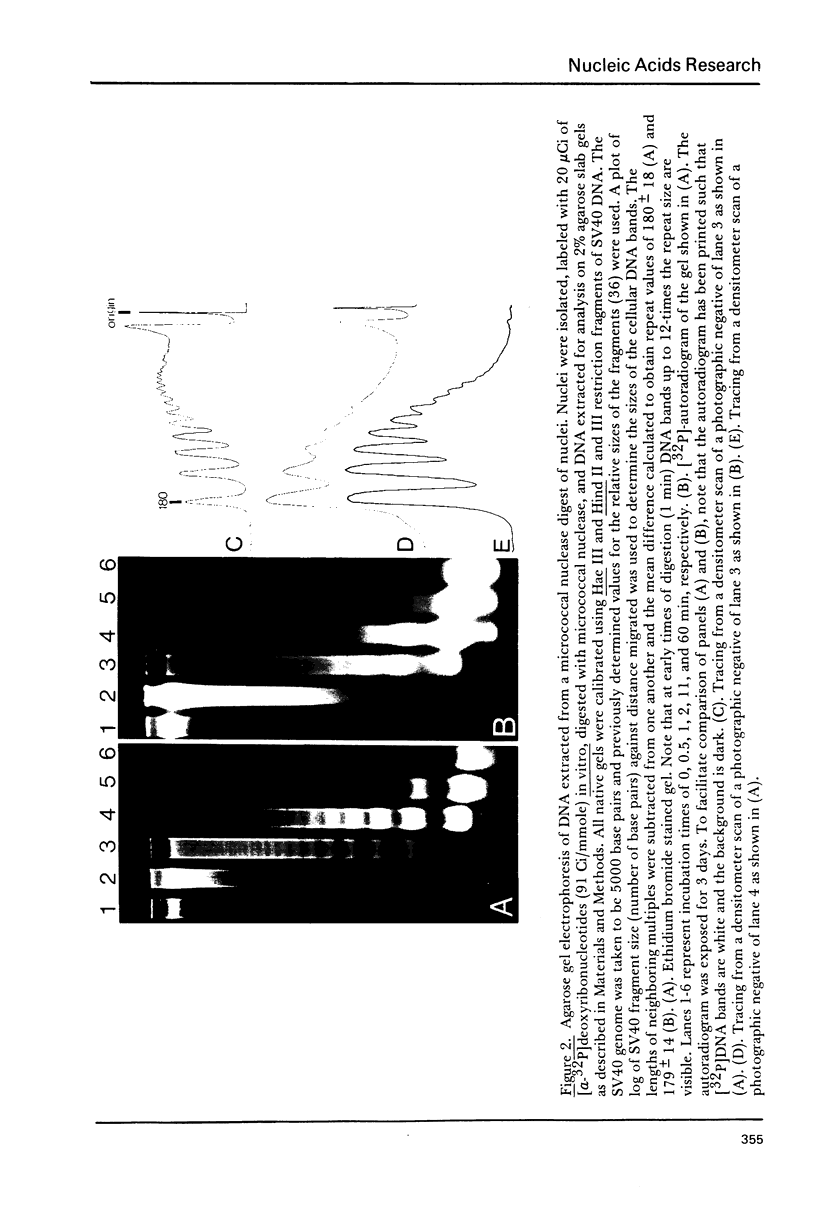
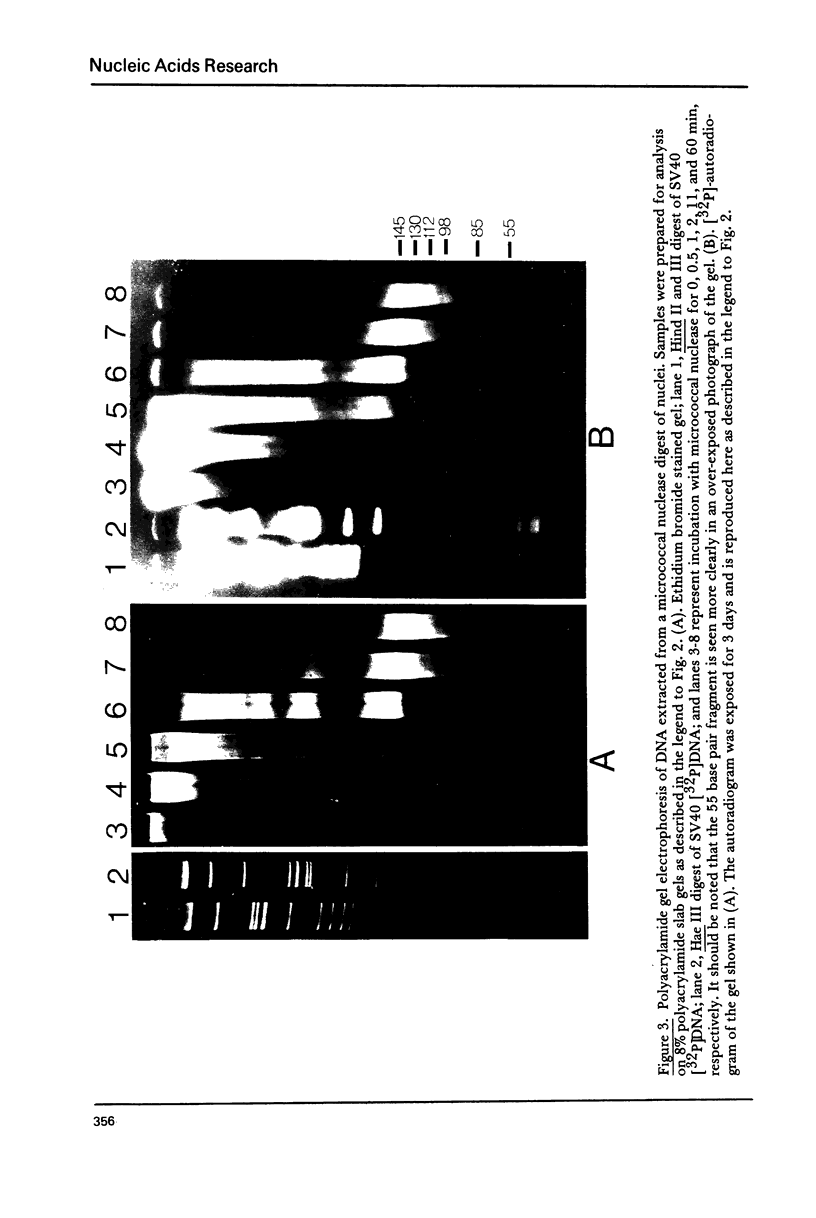
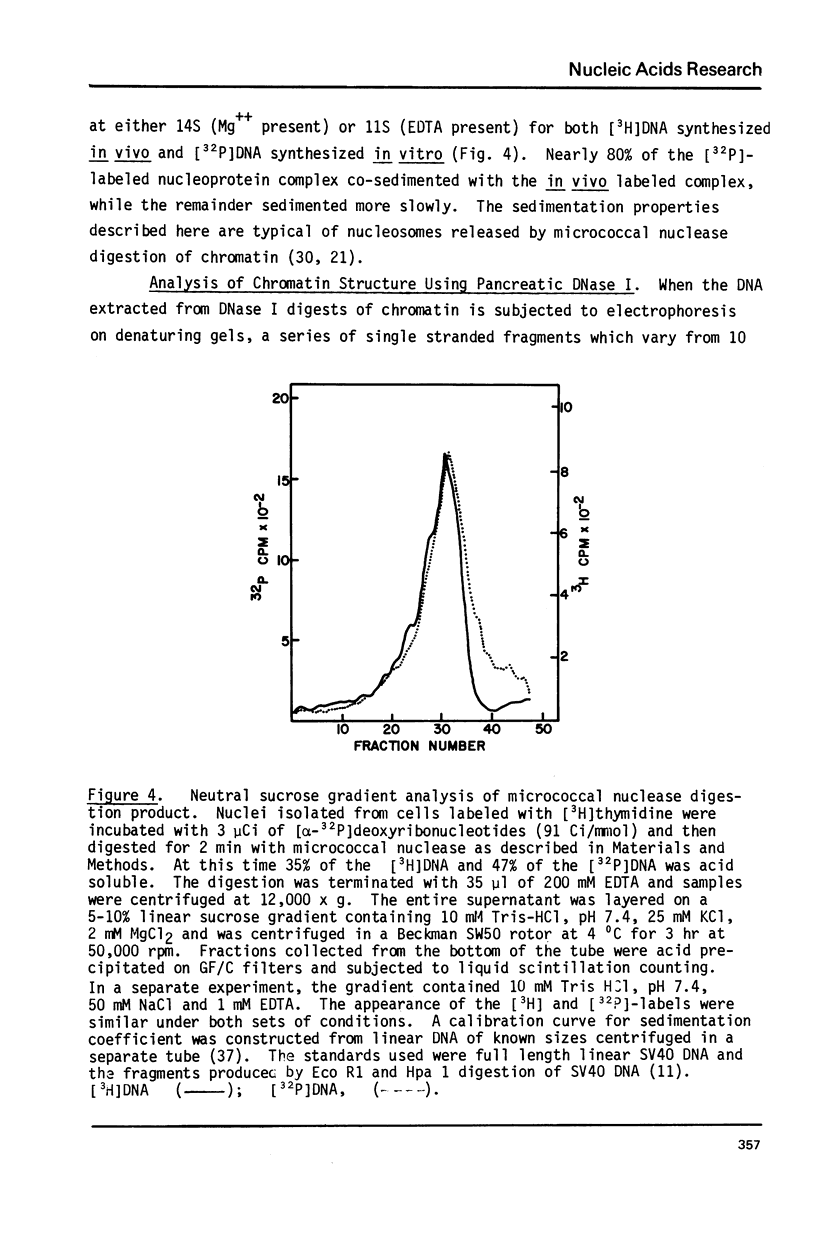
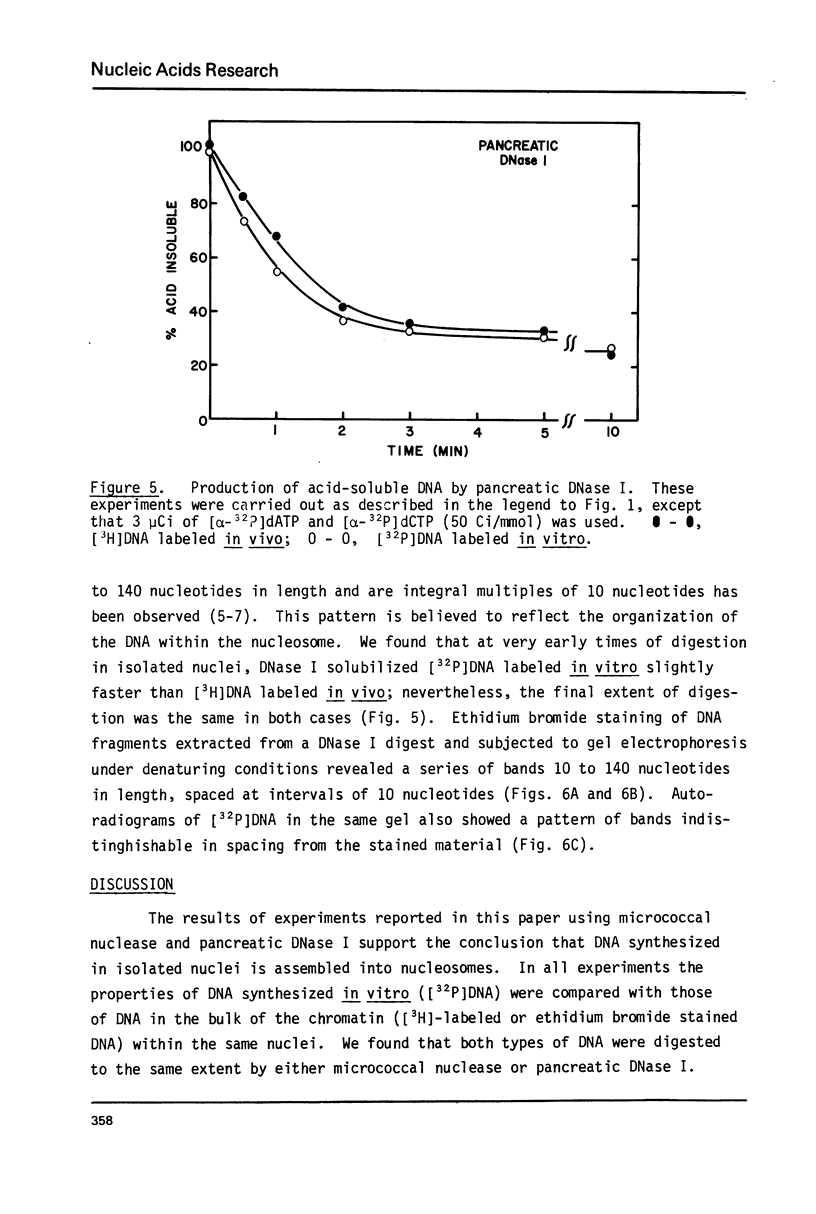
Cellular DNA replication was stimulated in confluent monolayers of CV-1 monkey kidney cells following infection with SV40. Nuclei were isolated from CV-1 cells labeled with [3H]thymidine and then incubated in the presence of [alpha-32P]deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates under conditions that support DNA replication. To determine whether or not the cellular DNA synthesized in vitro was assembled into nucleosomes the DNA was digested in situ with either micrococcal nuclease or pancreatic DNase I, and the products were examined by electrophoretic and sedimentation analysis. The distribution of DNA fragment lengths on agarose gels following micrococcal nuclease digestion was more heterogeneous for newly replicated than for the bulk of the DNA. Nonetheless, the state of cellular DNA synthesized in vitro (32P-labeled) was found to be identical with that of the DNA in the bulk of the chromatin (3H-labeled) by the following criteria: (i) The extent of protection against digestion by micrococcal nuclease of DNase I. (ii) The size of the nucleosomes (180 base pairs) and core particles (145 base pairs). (iii) The number and sizes of DNA fragments produced by micrococcal nuclease in a limit digest. (iv) The sedimentation behavior on neutral sucrose gradients of nucleoprotein particles released by micrococcal nuclease. (v) The number and sizes of DNA fragments produced by DNase I digestion. These results demonstrate that cellular DNA replicated in isolated nuclei is organized into typical nucleosomes. Consequently, subcellular systems can be used to study the relationship between DNA replication and the assembly of chromatin under physiological conditions.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Kaufman G., DePamphilis M. L. RNA primers in SV40 DNA replication: identification of transient RNA-DNA covalent linkages in replicating DNA. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):4990–4998. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axel R. Cleavage of DNA in nuclei and chromatin with staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2921–2925. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. J., Felsenfeld G. Structure of chromatin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 27;229(4):101–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio229101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., Bellard M., Chambon P. Biochemical evidence of variability in the DNA repeat length in the chromatin of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4382–4386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Zimm B. H. Viscosity and sedimentation of the DNA from bacteriophages T2 and T7 and the relation to molecular weight. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):525–536. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Beard P., Berg P. Synthesis of Superhelical Simian Virus 40 Deoxyribonucleic Acid in Cell Lysates*. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4340–4347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Berg P. Requirement of a Cytoplasmic Fraction for Synthesis of SV40 Deoxyribonucleic Acid in Isolated Nuclei*. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4348–4354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenberg H. J., Huberman J. A. Eukaryotic chromosome replication. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:245–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Granner D., Chalkley R. Deposition of histone onto the replicating chromosome: newly synthesized histone is not found near the replication fork. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2266–2269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G., Anderson S., DePamphilis M. L. RNA primers in Simian virus 40 DNA replication. II. Distribution of 5' terminal oligoribonucleotides in nascent DNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 5;116(3):549–567. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keichline L. D., Wassarman P. M. Developmental study of the structure of sea urchin embryo and sperm chromatin using micrococcal nuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 2;475(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D., Morris N. R. Assembly of SV40 chromatin in a cell-free system from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Corden J., Tatchell K., Kovacic R. T., Van Holde K. E. Comparative subunit structure of HeLa, yeast, and chicken erythrocyte chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Kovacic R. T., Van Holde K. E. Quantitative analysis of the digestion of yeast chromatin by staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 8;16(3):463–471. doi: 10.1021/bi00622a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Engel J. D. Subunit structure of chromatin is the same in plants and animals. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):449–450. doi: 10.1038/254449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Differences and similarities in chromatin structure of Neurospora crassa and higher eucaryotes. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Internal structure of the chromatin subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1573–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Subunit structure of chromatin. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):249–251. doi: 10.1038/251249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Resolution of multiple ribonucleic acid species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1818–1827. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rill R., Van Holde K. E. Properties of nuclease-resistant fragments of calf thymus chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):1080–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzi E., Levine A. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid replication in simian virus 40-infected cells. 3. Comparison of simian virus 40 lytic infection in three different monkey kidney cell lines. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):686–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.686-692.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Baserga R., Defendi V. Early increase in nuclear acidic protein synthesis after SV40 infection. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):240–241. doi: 10.1038/newbio237240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale R. L. Temporal relationships of chromatin protein synthesis, DNA synthesis, and assembly of deoxyribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2270–2274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw B. R., Herman T. M., Kovacic R. T., Beaudreau G. S., Van Holde K. E. Analysis of subunit organization in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Wilcox K. W. A restriction enzyme from Hemophilus influenzae. I. Purification and general properties. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. A comparison of the digestion of nuclei and chromatin by staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2915–2920. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. Pancreatic DNAase cleavage sites in nuclei. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su R. T., DePamphilis M. L. In vitro replication of simian virus 40 DNA in a nucleoprotein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3466–3470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Synthesis of (alpha-32P) ribo- and deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphates. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:102–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Cooperative alignment of nu bodies during chromosome replication in the presence of cycloheximide. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):419–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Robbins E. Histone synthesis in polyoma- and SV40-infected cells. Virology. 1970 Feb;40(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R. C., Van de Voorde A., Fiers W. Cleavage map of the simian-virus-40 genome by the restriction endonuclease III of Haemopholus aegyptius. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 2;61(1):101–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]