Abstract
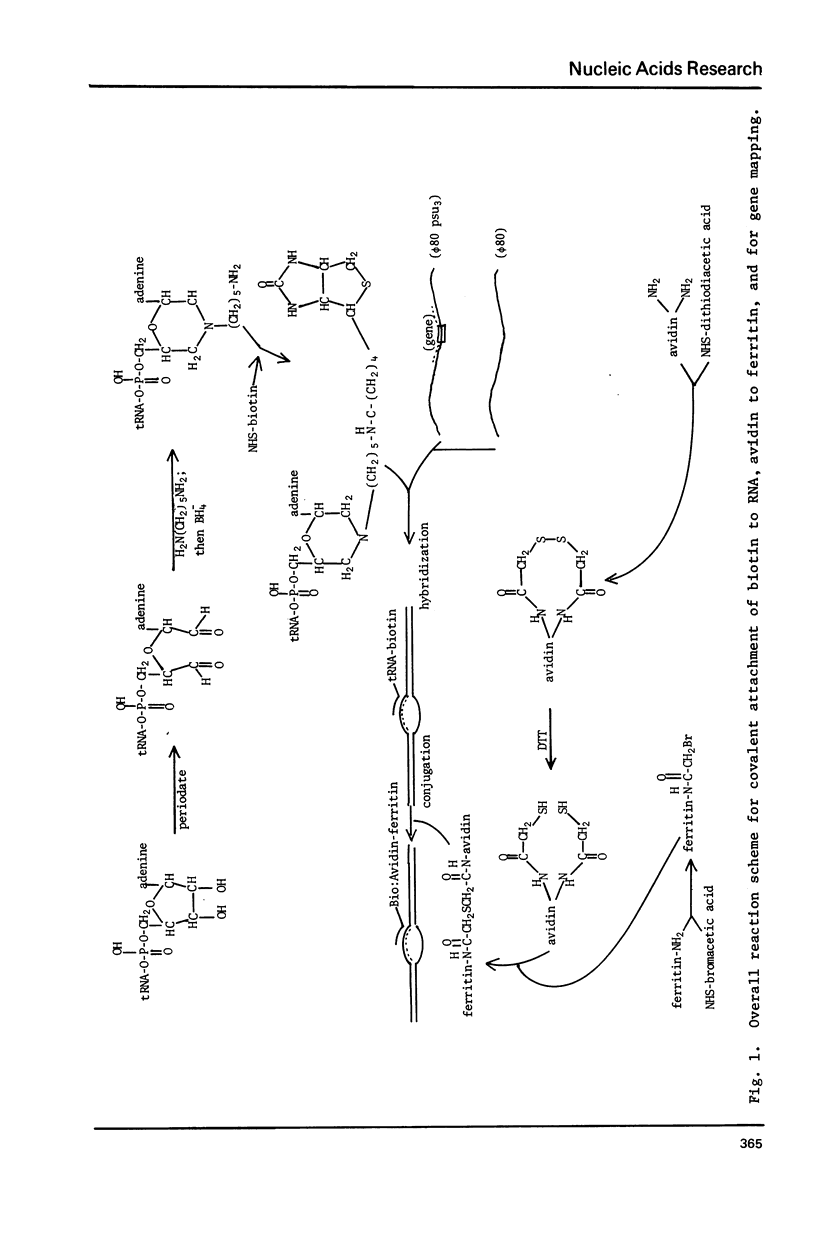
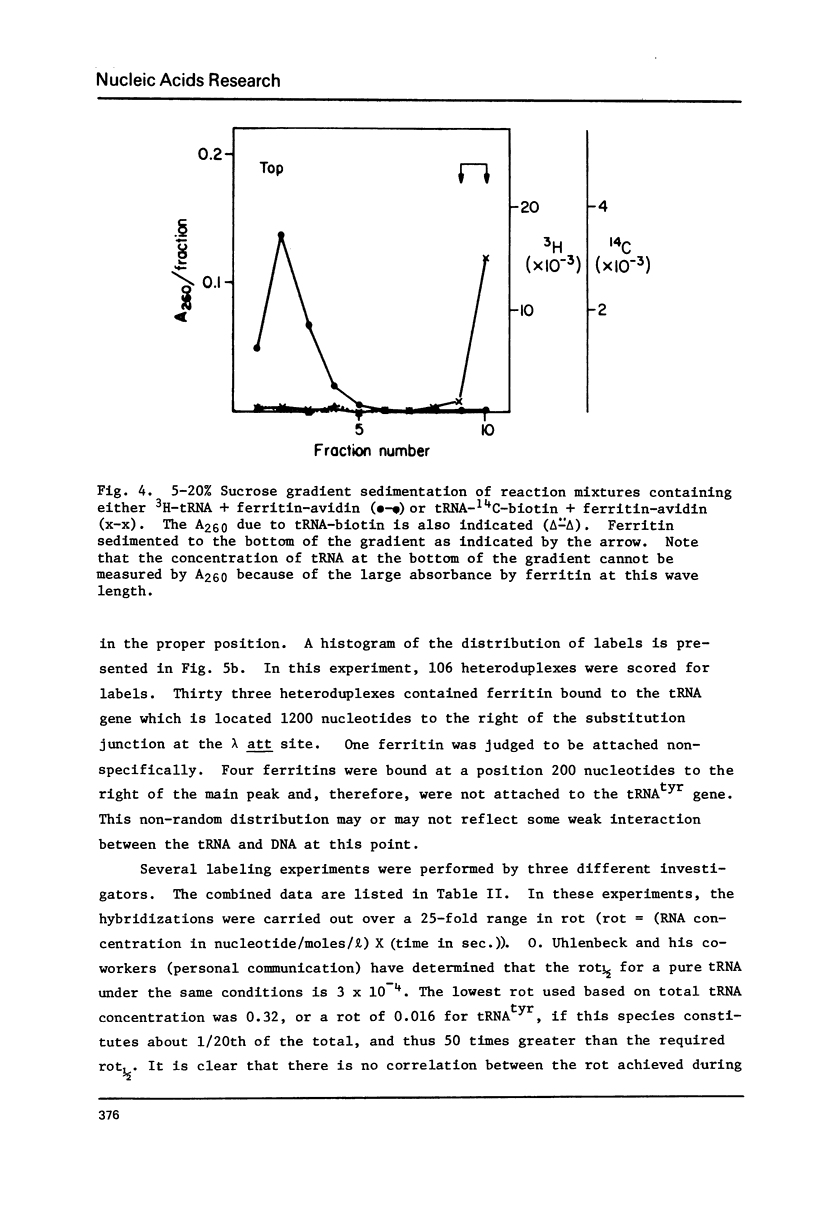
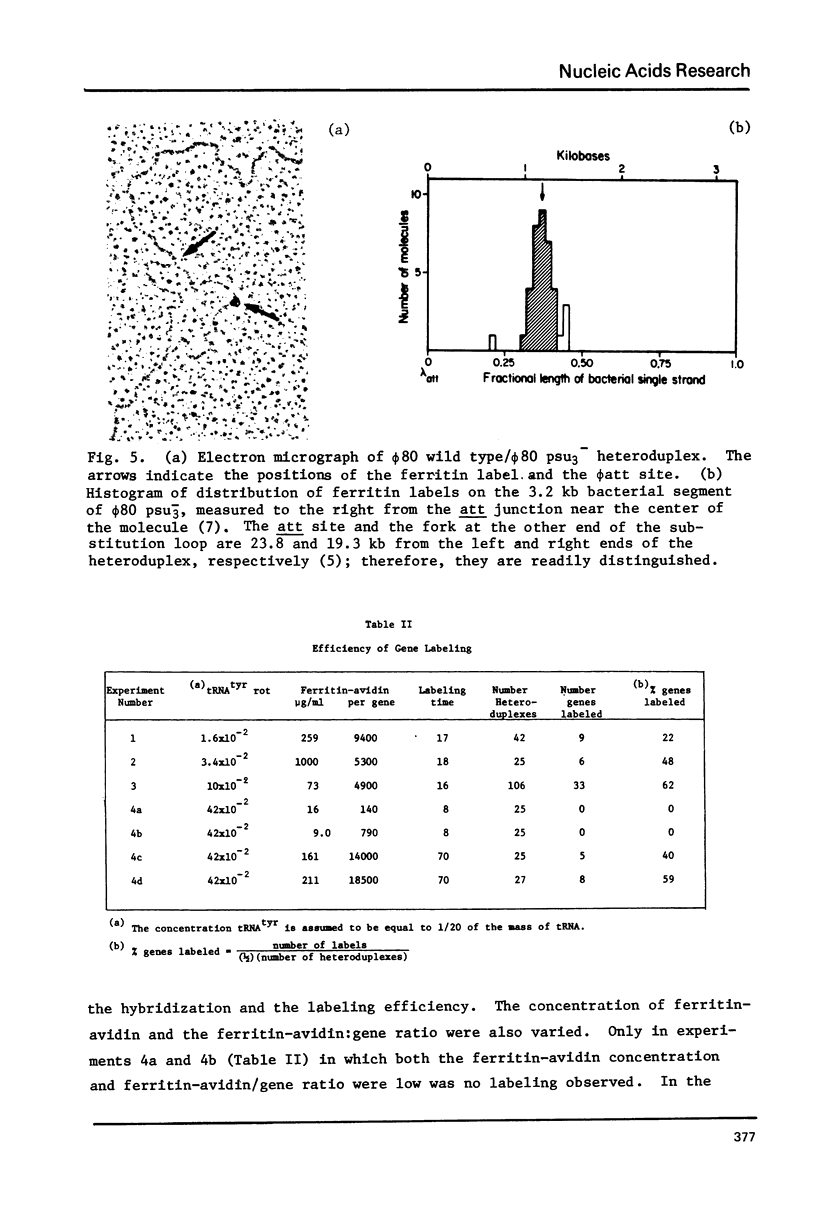
A method is described for indirect electron microscopic visualization and mapping of tRNA and other short transcripts hybridized to DNA. This method depends upon the attachment of the electron-dense protein ferritin to the RNA, the binding being mediated by the remarkably strong association of the egg white protein avidin with biotin. Biotin is covalently attached to the 3' end of tRNA using an NH2(CH2)5NH2 bridge. The tRNA-biotin adduct is hybridized to complementary DNA sequences present in a single stranded non-homology loop of a DNA:DNA heteroduplex. Avidin, covalently crosslinked to ferritin, is mixed with the heteroduplex and becomes bound to the hybridized tRNA-biotin. Observation of the DNA:RNA-biotin:avidin-ferritin complex by electron microscopy specifically and accurately reveals the position of the tRNA gene, with a frequency of labeling of approximately 50%.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angerer L., Davidson N., Murphy W., Lynch D., Attardi G. An electron microscope study of the relative positions of the 4S and ribosomal RNA genes in HeLa cells mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J. M., Wilchek M., Katchalski E. Irreversible inhibition of biotin transport in yeast by biotinyl-p-nitrophenyl ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2604–2607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodanszky A., Bodanszky M. Sepharose-avidin column for the binding of biotin or biotin-containing peptides. Experientia. 1970 Mar 15;26(3):327–327. doi: 10.1007/BF01900128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti P., Miller N. Selective reduction of yeast transfer ribonucleic acid with sodium borohydride. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90260-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Wilchek M. Single-step purification of avidine from egg white by affinity chromatography on biocytin-Sepharose columns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 24;33(2):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90774-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., SNELL N. S., DUCAY E. D. Avidin. I. Isolation and characterization of the protein and nucleic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Jul;39(1):80–96. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., SNELL N. S., DUCAY E. D. Avidin. II. Composition and mode of action of avidin A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Jul;39(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach F. A., Anderegg J. W. An x-ray scattering study of ferritin and apoferritin. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):458–473. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsheit A. B., Davidson N., Brown D. D. An electron microscope heteroduplex study of the ribosomal DNAs of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN N. M. AVIDIN. 1. THE USE OF (14-C)BIOTIN FOR KINETIC STUDIES AND FOR ASSAY. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:585–591. doi: 10.1042/bj0890585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN N. M. AVIDIN. 3. THE NATURE OF THE BIOTIN-BINDING SITE. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:599–609. doi: 10.1042/bj0890599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN N. M. AVIDIN. 4. STABILITY AT EXTREMES OF PH AND DISSOCIATION INTO SUB-UNITS BY GUANIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:609–620. doi: 10.1042/bj0890609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., Konieczny L., Toms E. J., Valentine R. C. The use of bifunctional biotinyl compounds to determine the arrangement of subunits in avidin. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(3):781–791. doi: 10.1042/bj1250781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., Ross M. E. The effect of N-bromosuccinimide on the sub-unit structure of acidin and its complexes with biotin. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(1):59–66. doi: 10.1042/bj1100059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., Toms E. J. Purification and crystallization of avidin. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):67–70. doi: 10.1042/bj1180067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., Toms E. J. The properties of subunits of avidin coupled to sepharose. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):687–700. doi: 10.1042/bj1330687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitzmann H., Richards F. M. Use of the avidin-biotin complex for specific staining of biological membranes in electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3537–3541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann K., Finn F. M., Friesen H. J., Diaconescu C., Zahn H. Biotinylinsulins as potential tools for receptor studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2697–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasiewicz M. L., Schoenberg D. R., Mueller G. C. Selective retrieval of biotin-labeled cells using immobilized avidin. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jun;100(1):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. E., Hershey N. D., Broker T. R., Pellegrini M., Mitchell H. K., Davidson N. A new method of in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 24;53(2):107–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00333039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J., Pellegrini M., Davidson N. A method for gene enrichment based on the avidin-biotin interaction. Application to the Drosophila ribosomal RNA genes. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1364–1370. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsubo E., Lee H. J., Deonier R. C., Davidson N. Electron microscope heteroduplex studies of sequence relations among plasmids of Escherichia coli. VI. Mapping of F14 sequences homologous to phi 80dmetBJF and phi 80dargECBH bacteriophages. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 15;89(4):599–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENSWICK J. R., HOLLEY R. W. SPECIFIC CLEAVAGE OF THE YEAST ALANINE RNA INTO TWO LARGE FRAGMENTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Mar;53:543–548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini M., Holmes D. S., Manning J. Application of the avidin-biotin method of gene enrichment to the isolation of long double-stranded DNA containing specific gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):2961–2973. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.2961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini M., Oen H., Cantor C. R. Covalent attachment of a peptidyl-transfer RNA analog to the 50S subunit of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):837–841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Alwine J. C. An analysis by electron microscopy of early simian virus 40 RNA from a tsA mutant. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):523–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARIN P. S., ZAMECNIK P. C. ON THE STABILITY OF AMINOACYL-S-RNA TO NUCLEOPHILIC CATALYSIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 16;91:653–655. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwer P. Buoyant density sedimentation of macromolecules in sodium iothalamate density gradients. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 5;92(3):433–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., White R. L., Davis R. W. Hybridization of RNA to double-stranded DNA: formation of R-loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintermeyer W., Zachau H. G. Tertiary structure interactions of 7-methylguanosine in yeast tRNA Phe as studied by borohydride reduction. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):306–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Davidson N. A technique for mapping transfer RNA genes by electron microscopy of hybrids of ferritin-labeled transfer RNA and DNA: the phi-80hpsu+3-system. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;78(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90424-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Davidson N. Use of gene 32 protein staining of single-strand polynucleotides for gene mapping by electron microscopy: application to the phi80d3ilvsu+7 system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4506–4510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Sodja A., Cohen M., Jr, Conrad S. E., Wu M., Davidson N. Sequence arrangement of tRNA genes on a fragment of Drosophila melanogaster DNA cloned in E. coli. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):763–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



