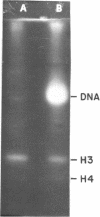
Abstract
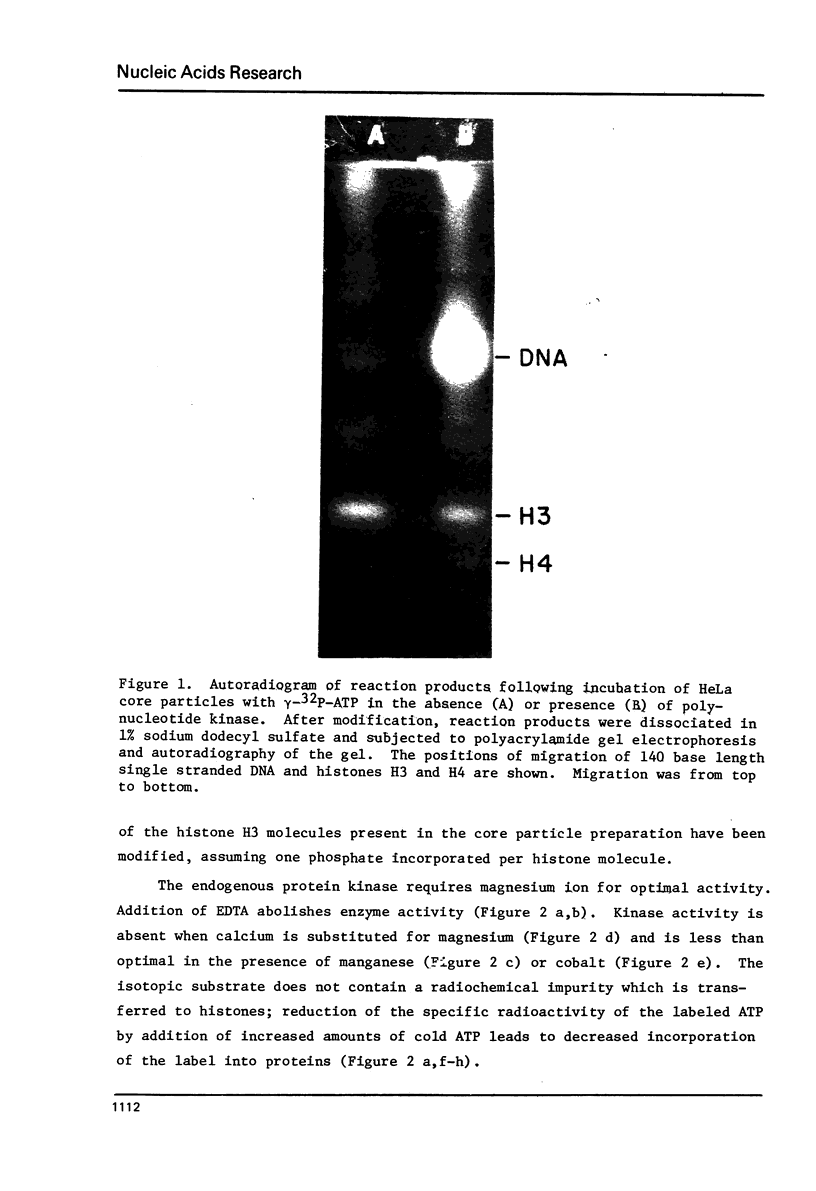
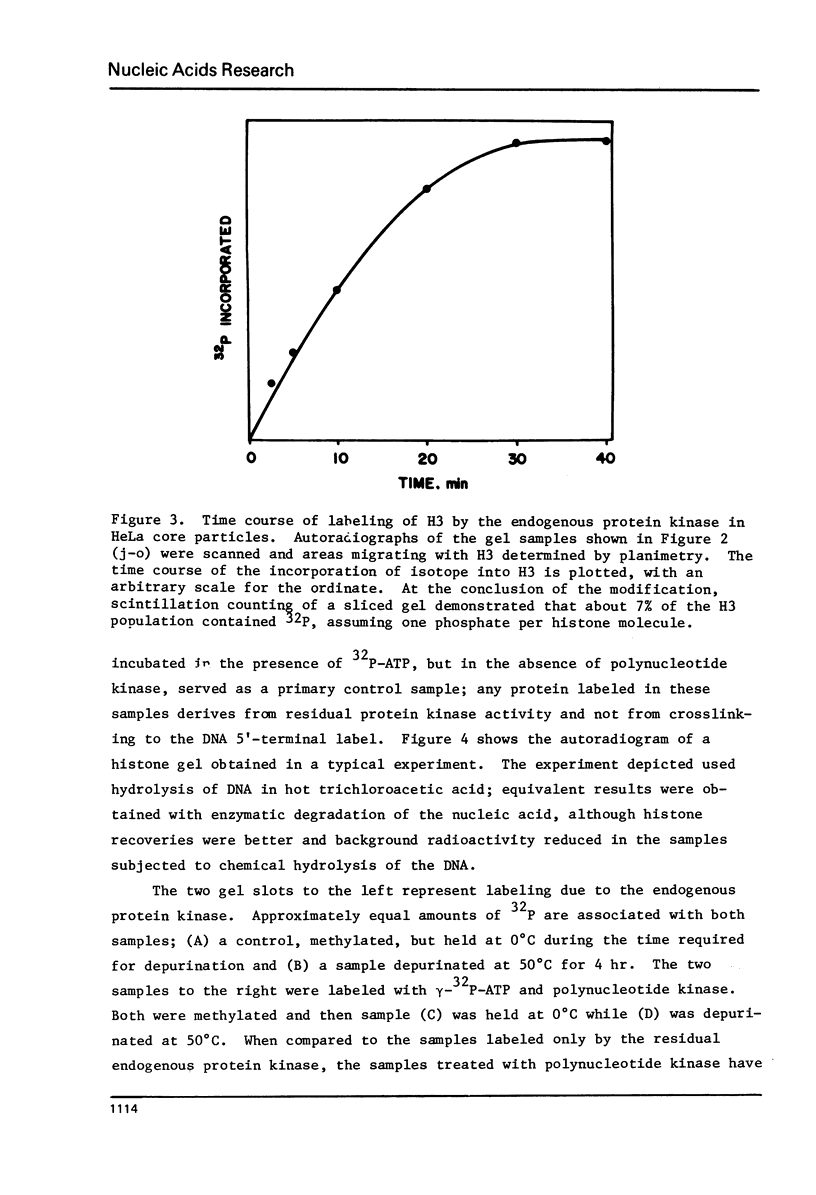
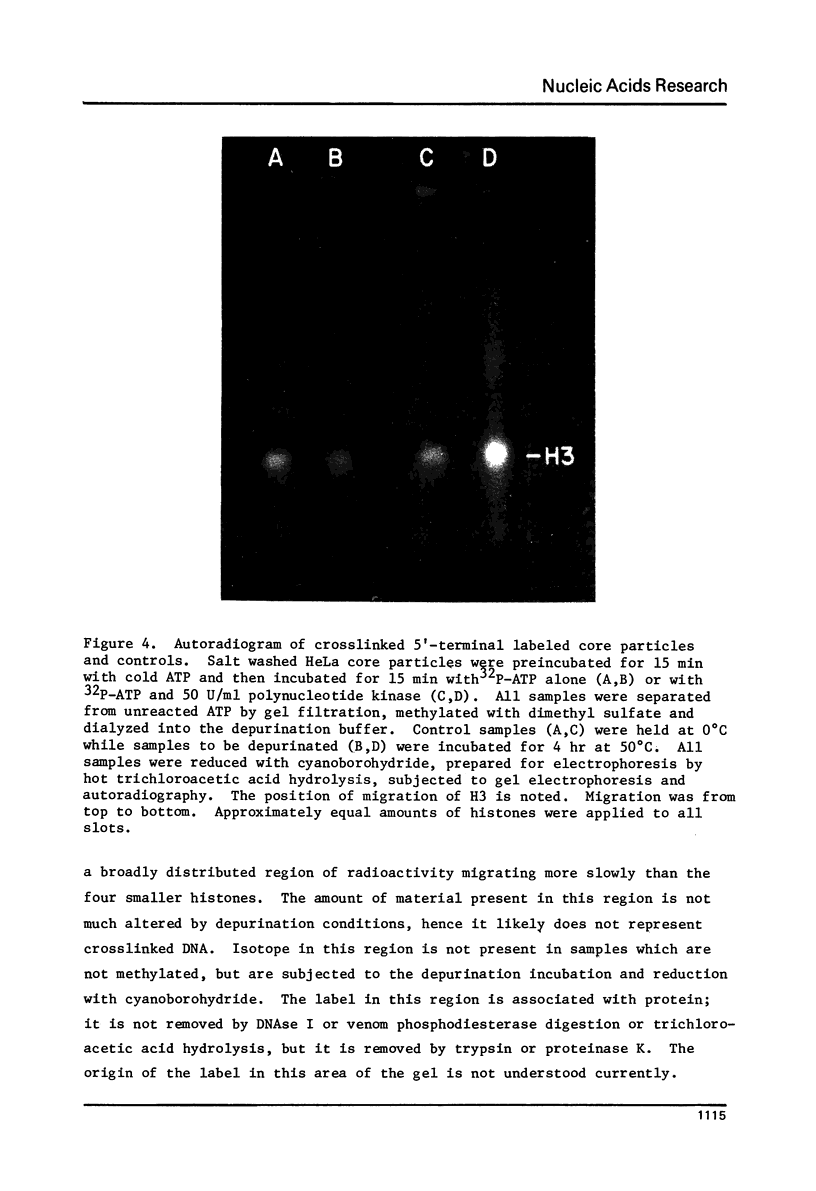
HeLa chromatin core particles contain a protein kinase which transfers phosphate from ATP to both nonhistone proteins and histones. The enzyme preferentially modifies H3 among the histones; about 7% of the H3 molecules in the nucleoprotein are modified at saturation. Activity of this kinase likely contributed to earlier results using crosslinking methodology to study which histones interact with the ends of core particle DNA. When the kinase is largely removed by sedimentation of core particles through sucrose gradients containing 0.45 M NaCl, crosslinking of the 5'-terminal label on DNA is observed only to histone H3. The overall efficiency of the crosslinking reaction is about 15%. The origin of the 5'-terminal 32P previously assigned as crosslinked to H4 is not explained by the current experiments.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bina-Stein M., Simpson R. T. Specific folding and contraction of DNA by histones H3 and H4. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P. G., Bradbury E. M., Butler-Browne G. S., Carpenter B. G., Stephens R. M. Physical studies of chromatin. The recombination of histones with DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 2;62(1):21–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. The organization of histones and DNA in chromatin: evidence for an arginine-rich histone kernel. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):333–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Lutter L. C., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Rushton B., Levitt M., Klug A. Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):29–36. doi: 10.1038/269029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Axel R. Analysis of DNA of isolated chromatin subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levina E. S., Mirzabekov A. D. Kovalentnoe sviazyvanie belkov s DNK v sostave khromatina. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1975 Apr 11;(5):1222–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Histones H3 and H4 interact with the ends of nucleosome DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4400–4404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Whitlock J. P., Jr Chemical evidence that chromatin DNA exists as 160 base pair beads interspersed with 40 base pair bridges. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jan;3(1):117–127. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Whitlock J. P. Mapping DNAase l-susceptible sites in nucleosomes labeled at the 5' ends. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Worcel A., Alberts B. A model for chromatin based upon two symmetrically paired half-nucleosomes. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):409–417. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]