Abstract
The terminal 220 base pairs (bp) of the gene for 18S rRNA and 18 bp of the adjoining spacer rDNA of the silkworm Bombyx mori have been sequenced. Comparison with the sequence of the 16S rRNA gene of Escherichia coli has shown that a region including 45 bp of the B. mori sequence at the 3' end is remarkably homologous with the 3' terminal E. coli sequence. Other homologies occur in the terminal regions of the 18S and 16S rRNAs, including a perfectly conserved stretch of 13 bp within a longer homology located 150--200 bp from the 3' termini. These homologies are the most extensive so far reported between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomic DNA.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberty H., Raba M., Gross H. J. Isolation from rat liver and sequence of a RNA fragment containing 32 nucleotides from position 5 to 36 from the 3' end of ribosomal 18S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):425–434. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baralle F. E., Brownlee G. G. AUG is the only recognisable signal sequence in the 5' non-coding regions of eukaryotic mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):84–87. doi: 10.1038/274084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulik M., Hellmann W. Comparison of Artemia salina and Escherichia coli ribosome structure by electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman N. M., Noller H. F. Protection of specific sites in 16 S RNA from chemical modification by association of 30 S and 50 S ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 5;109(1):131–149. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonge P., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Sequence of the 3'-terminal 21 nucleotides of yeast 17S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Oct;4(10):3655–3663. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.10.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonge P., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Terminal nucleotide sequences of 17-S ribosomal RNA and its immediate precursor 18-S RNA in yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):361–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage L. P., Manning R. F. Determination of the multiplicity of the silk fibroin gene and detection of fibroin gene-related DNA in the genome of Bombyx mori. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 5;101(3):327–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren-Zur M., Boublik M., Ofengand J. Localization of the decoding region on the 30S Escherichia coli ribosomal subunit by affinity immunoelectron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1054–1058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. S., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequences within the ribosomal ribonucleic acids of HeLa cells, Xenopus laevis and chick embryo fibroblasts. J Mol Biol. 1976 Feb 25;101(2):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. H., Nolan C., Lazar J. M., Clark J. M., Jr Translation of satellite tobacco necrosis virus ribonucleic acid. I. Characterization of in vitro procaryotic and eucaryotic translation products. Biochemistry. 1972 May 23;11(11):2009–2014. doi: 10.1021/bi00761a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. How do eucaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1109–1123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A. Ribosome structure determined by electron microscopy of Escherichia coli small subunits, large subunits and monomeric ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughrea M., Moore P. B. On the relationship between the binding of ribosomal protein S1 to the 30 S subunit of Escherichia coli and 3' terminus of 16 S RNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jun 5;121(4):411–430. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
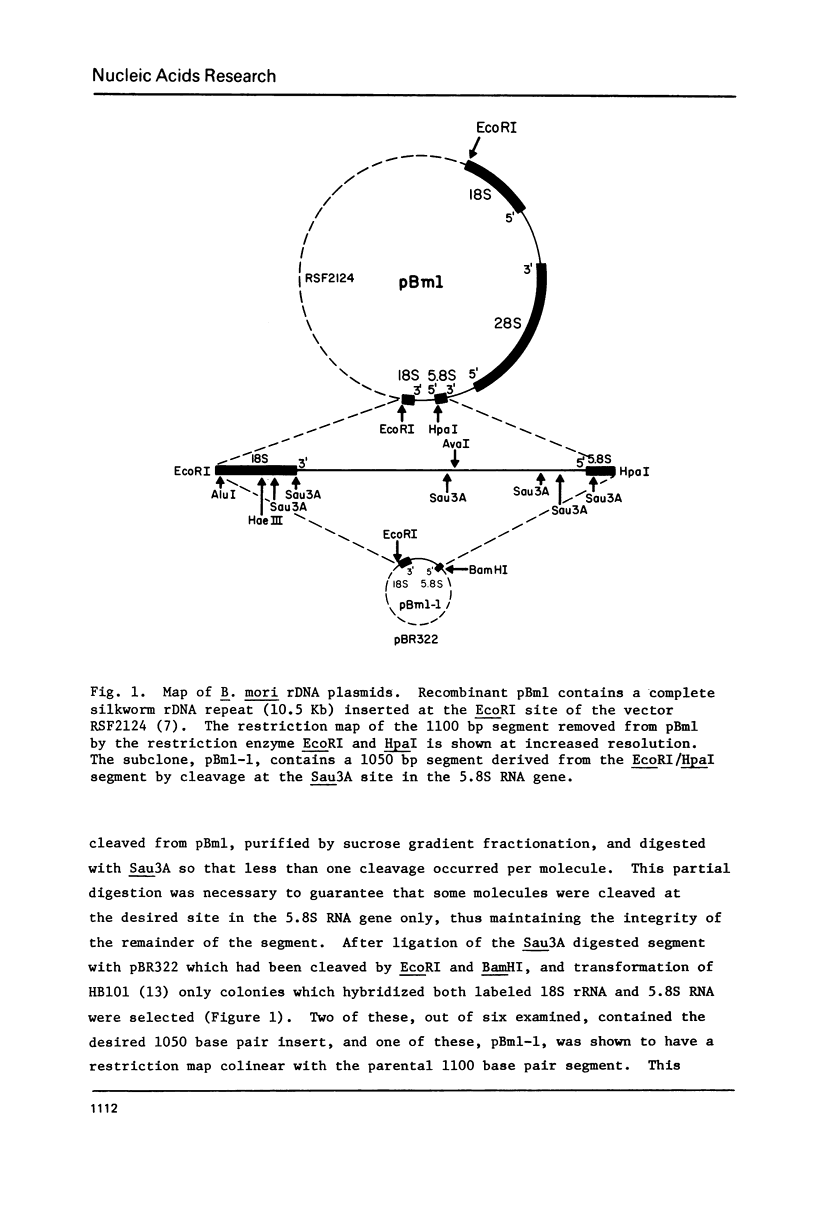
- Manning R. F., Samols D. R., Gage L. P. The genes for 18S, 5.8S and 28S ribosomal RNA of Bombyx mori are organized into tandem repeats of uniform length. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):153–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson H. M., Glitz D. G. Ribosome structure: localization of 3' end of RNA in small subunit by immunoelectronmicroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3769–3773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Rosenberg M. Efficient translation of prokaryotic mRNAs in a eukaryotic cell-free system requires addition of a cap structure. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):692–696. doi: 10.1038/279692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phang-Cheng-Tai, Davis B. D. Activity of colicin E3-treated ribosomes in initiation and in chain elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1021–1025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Jakes K. S. Intact 3' end of 16S rRNA is not required for specific mRNA binding. Nature. 1976 Jul 8;262(5564):150–153. doi: 10.1038/262150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Ross A., Brimacombe R. Characterisation of RNA fragments obtained by mild nuclease digestion of 30-S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Paterson B. M. Efficient cap-dependent translation of polycistronic prokaryotic mRNAs is restricted to the first gene in the operon. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):696–701. doi: 10.1038/279696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santer M., Shane S. Area of 16S ribonucleic acid at or near the interface between 30S and 50S ribosomes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):900–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.900-910.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Identical 3'-terminal octanucleotide sequence in 18S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from different eukaryotes. A proposed role for this sequence in the recognition of terminator codons. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):609–615. doi: 10.1042/bj1410609a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Gill R., Falkow S. The generation of a ColE1-Apr cloning vehicle which allows detection of inserted DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 30;142(3):239–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00425649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Steege D. A. Characterization of two mRNA-rRNA complexes implicated in the initiation of protein biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 25;114(4):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnowsky F., Högenauer G. Colicin E 3, an inactivating agent of the ribosomal A-site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 19;55(4):1246–1254. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Complementary sequences 1700 nucleotides apart form a ribonuclease III cleavage site in Escherichia coli ribosomal precursor RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3593–3597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B., Evans R. M. Coincidence of the promoter and capped 5' terminus of RNA from the adenovirus 2 major late transcription unit. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1463–1475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]