Abstract
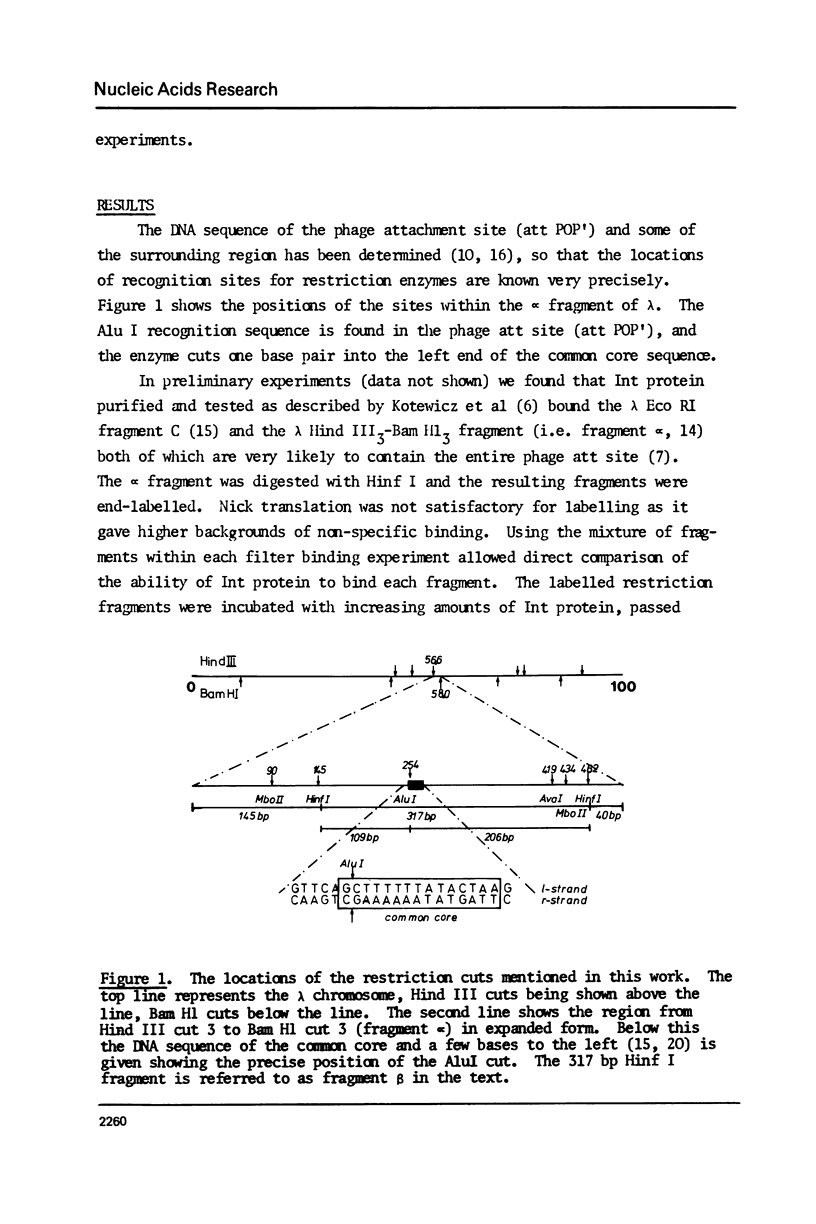
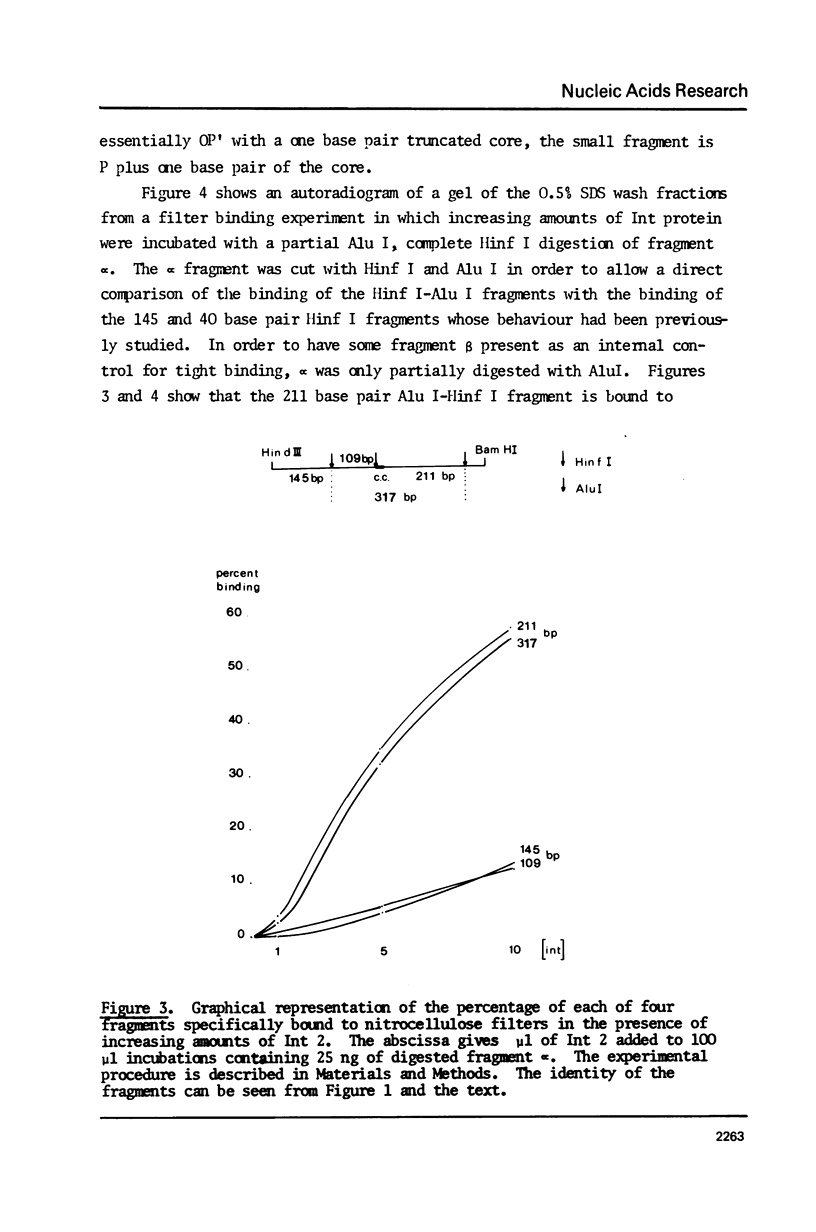
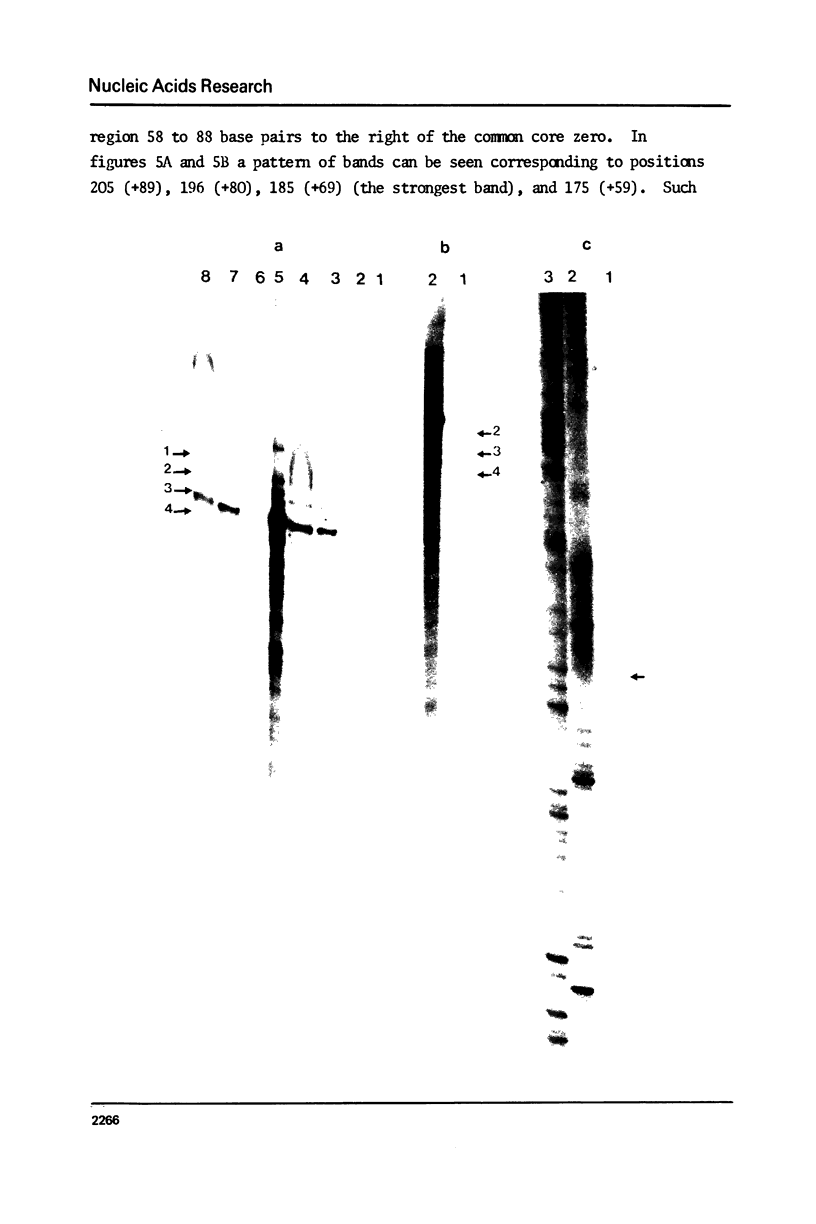
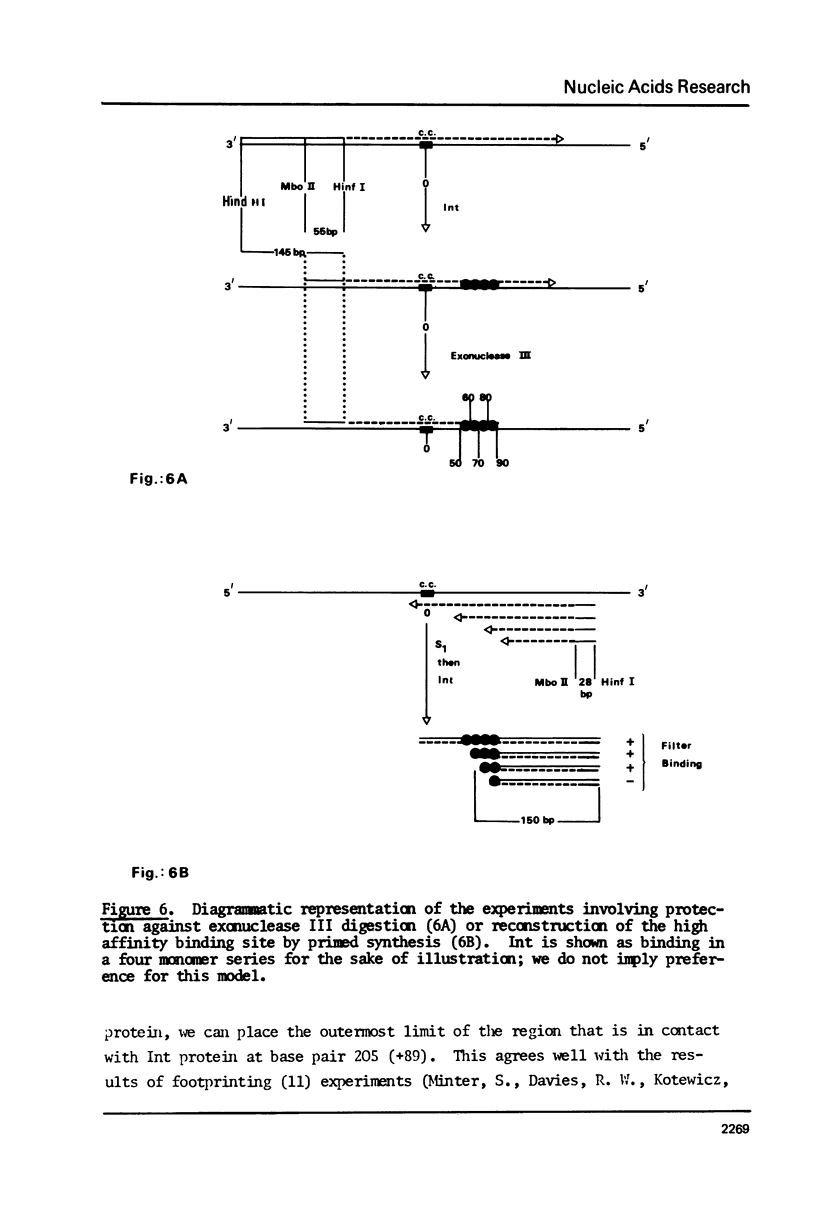
We have used three approaches to studying the interaction of lambda Int protein with bacteriophage attachment site DNA, POP': location of binding sites by retention of DNA fragments in a filter binding assay, reconstruction of a binding site by DNA synthesis and protection of a binding site from an exonuclease. Retention of restriction fragments on nitrocellulose filters in the presence of Int protein was used to locate binding sites. A high affinity binding site lies in P' between base pairs -6 and +173 from the center of the common core sequence, and low affinity sites are found in the 200 base pair region left of position -6. Reconstruction of the high affinity binding site region from the right using primed DNA synthesis and testing for filter binding in the presence of Int protein shows that sequences sufficient for tight binding of Int protein lie to the right of position +66. When attachment site DNA is protected by bound Int protein against digestion by exonuclease III, four Int dependent protection bands are seen in positions +58, +68, +79 and +88. This can be interpreted either as showing that four Int protein monomers bind to the high affinity region in series, or as evidence for wrapping of the DNA around Int protein, leading to structural changes resembling those occurring to DNA in nucleosomes.
Full text
PDF














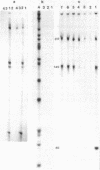
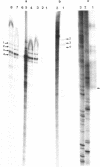
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Frey L. T4 bacteriophage gene 32: a structural protein in the replication and recombination of DNA. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1313–1318. doi: 10.1038/2271313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Schreier P. H., Buchel D. E. Nucleotide sequence of the attachment site of coliphage lambda. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):757–760. doi: 10.1038/270757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Schreier P. H., Büchel D. E. Determination of the endpoints of partial deletion mutants of the attachment site of bacteriophage lambda by DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3209–3218. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humayun Z., Kleid D., Ptashne M. Sites of contact between lambda operators and lambda repressor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1595–1607. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Nash H. A. The bacteriophage lambda int gene product. A filter assay for genetic recombination, purification of int, and specific binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7149–7157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. DNA sequence analysis of Tn10 insertions: origin and role of 9 bp flanking repetitions during Tn10 translocation. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):711–720. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotewicz M., Chung S., Takeda Y., Echols H. Characterization of the integration protein of bacteriophage lambda as a site-specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1511–1515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Ross W. Viral integration and excision: structure of the lambda att sites. Science. 1977 Sep 16;197(4309):1147–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.331474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D., Rich A. Asymmetric lateral distribution of unshielded phosphate groups in nucleosomal DNA and its role in DNA bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1118–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;78:171–199. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66800-5_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Subunit structure of chromatin. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):249–251. doi: 10.1038/251249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Backman K., Humayun M. Z., Jeffrey A., Maurer R., Meyer B., Sauer R. T. Autoregulation and function of a repressor in bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):156–161. doi: 10.1126/science.959843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D., Weintraub H. Nucleosomal DNA is digested to repeats of 10 bases by exonuclease III. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A., Kikuchi Y., Nash H. Interaction of int protein with specific sites on lambda att DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90049-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Davies R. W., Buchell D. E., Gronenborn B., Fanning T. G., von Wilcken B., Messing J. Precise location of the crossover region in the lambda attachment sequence. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):555–557. doi: 10.1038/267555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. Pancreatic DNAase cleavage sites in nuclei. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Rushizky G. W., Simpson R. T. DNase-sensitive sites in nucleosomes. Their relative suspectibilities depend on nuclease used. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):3003–3006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]