Abstract
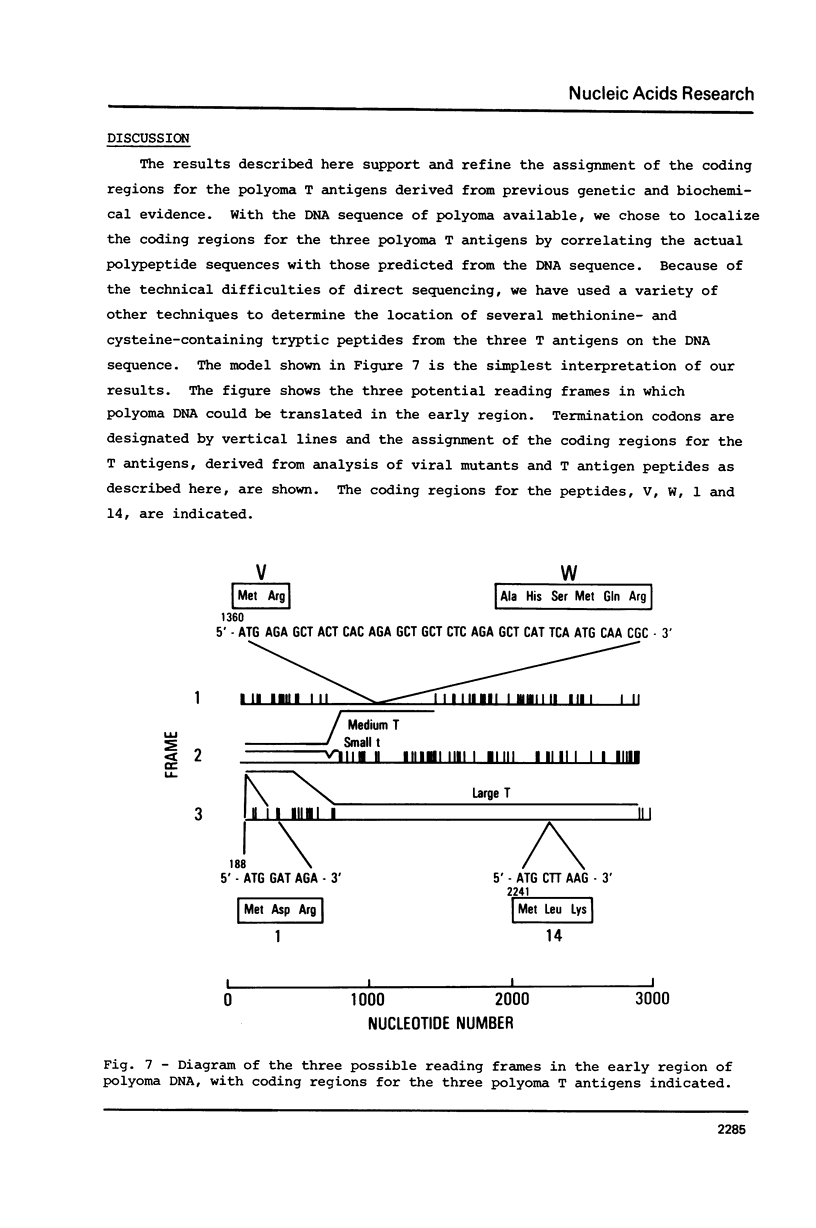
The early region of the polyoma genome encodes three T antigens. We have analyzed the organization of the coding regions for the T antigens, using the nucleotide sequence of polyoma DNA and peptides derived from purified, radio-labeled T antigens, separated by two-dimensional electrophoresis and chromatography. We compared the peptides, predicted from the nucleotide sequence of the DNA, with those derived from the purified T antigens. We also compared chemically synthesized peptides, predicted from the DNA sequence, with observed peptides. The results show that the three polyoma T antigens are encoded in overlapping regions of the viral DNA, translated, in part, in two different reading frames.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eckhart W. Complementation between temperature-sensitive (ts) and host range nontransforming (hr-t) mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90484-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluck M. M., Staneloni R. J., Benjamin T. L. Hr-t and ts-a: two early gene functions of polyoma virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):610–624. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90486-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T., Doolittle R. F., Walter G. Amino acid sequence homology between polyoma and SV40 tumour antigens deduced from nucleotide sequences. Nature. 1978 Jul 20;274(5668):291–293. doi: 10.1038/274291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T., Esty A., LaPorte P., Deininger P. The nucleotide sequence and genome organization of the polyoma early region: extensive nucleotide and amino acid homology with SV40. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Hutchinson M. A., Eckhart W. Translation of polyoma virus T antigens in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5917–5921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M. A., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Characterization of T antigens in polyoma-infected and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Brocklehurst J. R., Dulbecco R. Virus-specific proteins in the plasma membrane of cells lytically infected or transformed by pol-oma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4666–4670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Spurr N., Dulbecco R. Characterization of polyoma virus T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1259–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Piatak M., Weissman S. M. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's. I. Genomic localization of 3' and 5' termini and two major splices in mRNA from transformed and lytically infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):279–296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.279-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Silver J. E., Benjamin T. L. Tumor antigen(s) in cell productively infected by wild-type polyoma virus and mutant NG-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. C., Walker J. E., Northrop F. D., Barrell B. G., Godson G. N., Fiddes J. C. Gene K, a new overlapping gene in bacteriophage G4. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):510–515. doi: 10.1038/272510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Ito Y. Three species of polyoma virus tumor antigens share common peptides probably near the amino termini of the proteins. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1427–1437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J. The use of exonuclease III for preparing single stranded DNA for use as a template in the chain terminator sequencing method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):831–848. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Griffin B. E. Sequence from early region of polyoma virus DNA containing viral replication origin and encoding small, middle and (part of) large T antigens. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):357–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Sequence data handling by computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):4037–4051. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]