Abstract
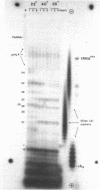
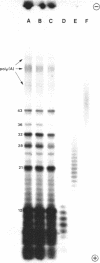
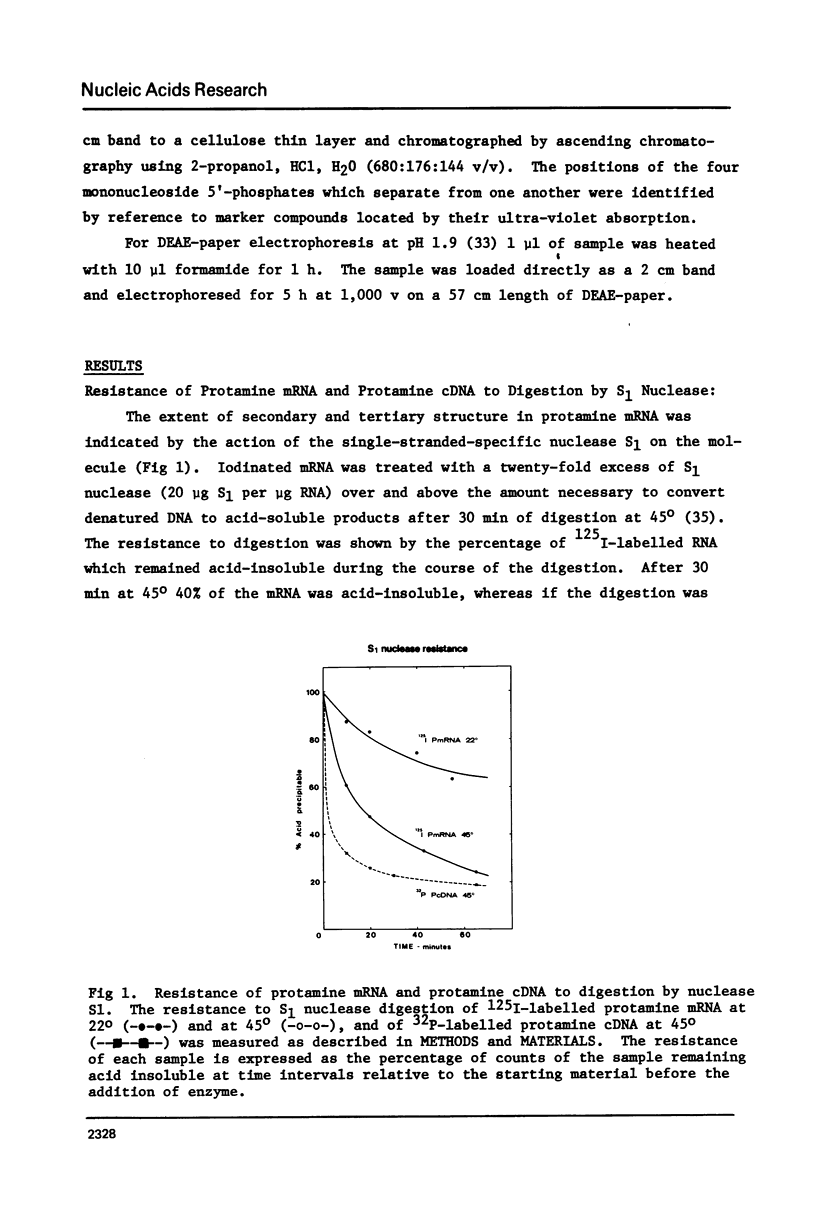
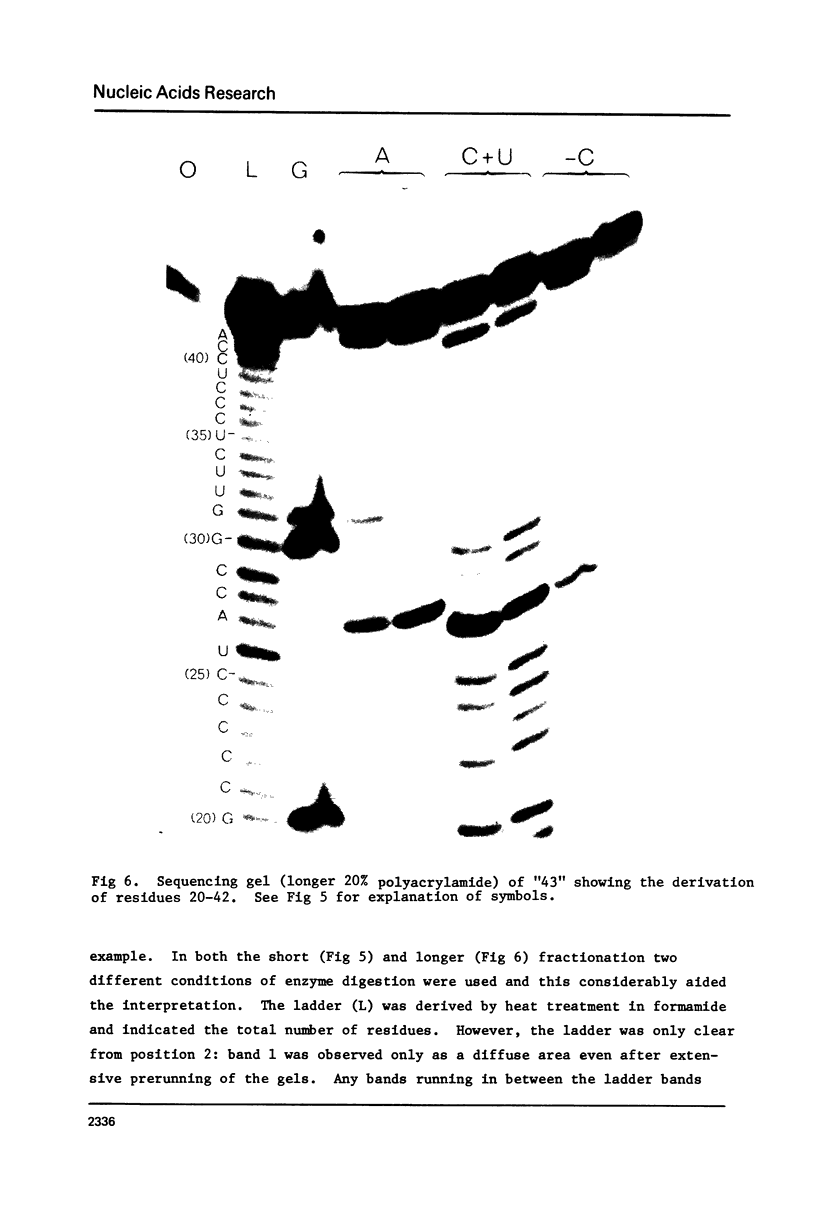
Limited T1 ribonuclease digestion of the family of protamine mRNA's purified from rainbow trout testis yields several large oligoribonucleotide fragments ranging in size from 12--54 nucleotides in length. Several of these fragments purified by two dimensional gel electrophoresis contain several G residues and must represent nuclease-resistant, base-paired regions of the mRNA. Sequence analysis of these oligonucleotides by the method of Simoncsits, A., Brownlee, G.G., Brown, R.S., Rubin, J.R. and Guilley, H. (1977) Nature 269: 833-836, shows that these oligoribonucleotides arise from the 5'- and 3'-non-coding regions of the mRNA. Comparisons of the sequences of the large RNA fragment with DNA sequences obtained after cloning double-stranded protamine cDNA in the plasmids pBr322 and pmB9 show precise correspondence of a 54 nucleotide RNA fragment with positions 49--100 from the 3'-poly(A) tract and extending to within 5 nucleotides of the termination codon. Two other RNA fragments of 21 and 25 nucleotides in length arise from the 5'-non-coding region of the message and possess an AUG-sequence at their 3'-termini which is the initiation codon. The presence of distinct by homologous sequences in several sets of large RNA fragments is consistent with the presence of several closely related protamine mRNA's.
Full text
PDF




















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F. Chromatography of 32P-labelled oligonucleotides on thin layers of DEAE-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. L., Dixon G. H., Dugaiczyk A. Double-stranded protamine cDNA: synthesis and characterization. Can J Biochem. 1979 Mar;57(3):259–266. doi: 10.1139/o79-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. L., Dixon G. H., Ferrier L. N., Gedamu L., Iatrou K. The structure and function of protamine mRNA from developing trout testis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;19:135–155. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60915-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. L., Ferrier L. N., Dixon G. H. Sequence analysis of protamine mRNA from the rainbow trout. Depurination and nearest neighbor analysis of protamine cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1386–1393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favre A., Morel C., Scherrer K. The secondary structure and poly(A) content of globin messenger RNA as a pure RNA and in polyribosome-derived ribonucleoprotein complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):147–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier L. N., Davies P. L., Dixon G. H. Protamine messenger RNA from rainbow trout testis contains the nucleotide sequence A-A-U-A-A-A in an untranslated region. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 14;479(4):460–470. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flashner M. S., Vournakis J. N. Specific hydrolysis of rabbit globin messenger RNA by S1 nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jul;4(7):2307–2319. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.7.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Dixon G. H. Effect of enzymatic "decapping" on protamine mRNA translation in wheat germ S-30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):114–124. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Dixon G. H. Purification and properties of biologically active rainbow trout testis protamine mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1455–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Iatrou K., Dixon G. H. A simple procedure for the isolation and purification of protamine messenger ribonucleic acid from trout testis. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):589–599. doi: 10.1042/bj1710589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Iatrou K., Dixon G. H. Translation of partially purified poly(A)+ protamine messenger RNA components in wheat germ and rabbit reticulocyte cell-free systems. Evidence for translational control mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 24;562(3):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heindell H. C., Liu A., Paddock G. V., Studnicka G. M., Salser W. A. The primary sequence of rabbit alpha-globin mRNA. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder J. W., Lingrel J. B. Determination of secondary structure in rabbit globin messenger RNA by thermal denaturation. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4209–4215. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou K., Dixon G. H. The distribution of poly(A)+ and poly(A)- protamine messenger RNA sequences in the developing trout testis. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou K., Gedamu L., Dixon G. H. Protamine messenger RNA: partial purification and characterization of a heterogeneous family of polyadenylated messenger components. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):945–956. doi: 10.1139/o79-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R. Sequence divergence of rainbow trout protamine mRNAs; comparison of coding and non-coding nucleotide sequences in three protamine cDNA plasmids. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):809–811. doi: 10.1038/279809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Cawthon M. L., Kabat D. Improved methods for purification and assay of eukaryotic messenger ribonucleic acids and ribosomes. Quantitative analysis of their interaction in a fractionated reticulocyte cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6077–6084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. "Fingerprinting" high molecular weight RNA by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: application to poliovirus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jul;3(7):1647–1658. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.7.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling V. Fractionation and sequences of the large pyrimidine oligonucleotides from bacteriophage fd DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):87–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90322-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L., O'Malley B. W., Nisbet A. D., Fothergill J. E., Givol D., Fields S., Robertson M., Brownlee G. G. Sequence of chicken ovalbumin mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):723–728. doi: 10.1038/273723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilly D., Niemeyer A., Schmidt M., Bargetzi J. P. Enzymes for RNA sequence analysis. Preparation and specificity of exoplasmodial ribonucleases I and II from Physarum polycephalum. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):437–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Rich A. Structural domains of transfer RNA molecules. Science. 1976 Nov 19;194(4267):796–806. doi: 10.1126/science.790568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A., Brimacombe R. Application of a rapid gel method to the sequencing of fragments of 16S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):241–256. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Brownlee G. G., Barrell B. G. A two-dimensional fractionation procedure for radioactive nucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):373–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. G., Brown R. S., Rubin J. R., Guilley H. New rapid gel sequencing method for RNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):833–836. doi: 10.1038/269833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van N. T., Monahan J. J., Woo S. L., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Comparative studies on the secondary structure of ovalbumin messenger RNA and its complementary DNA transcript. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 6;16(18):4090–4100. doi: 10.1021/bi00637a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]