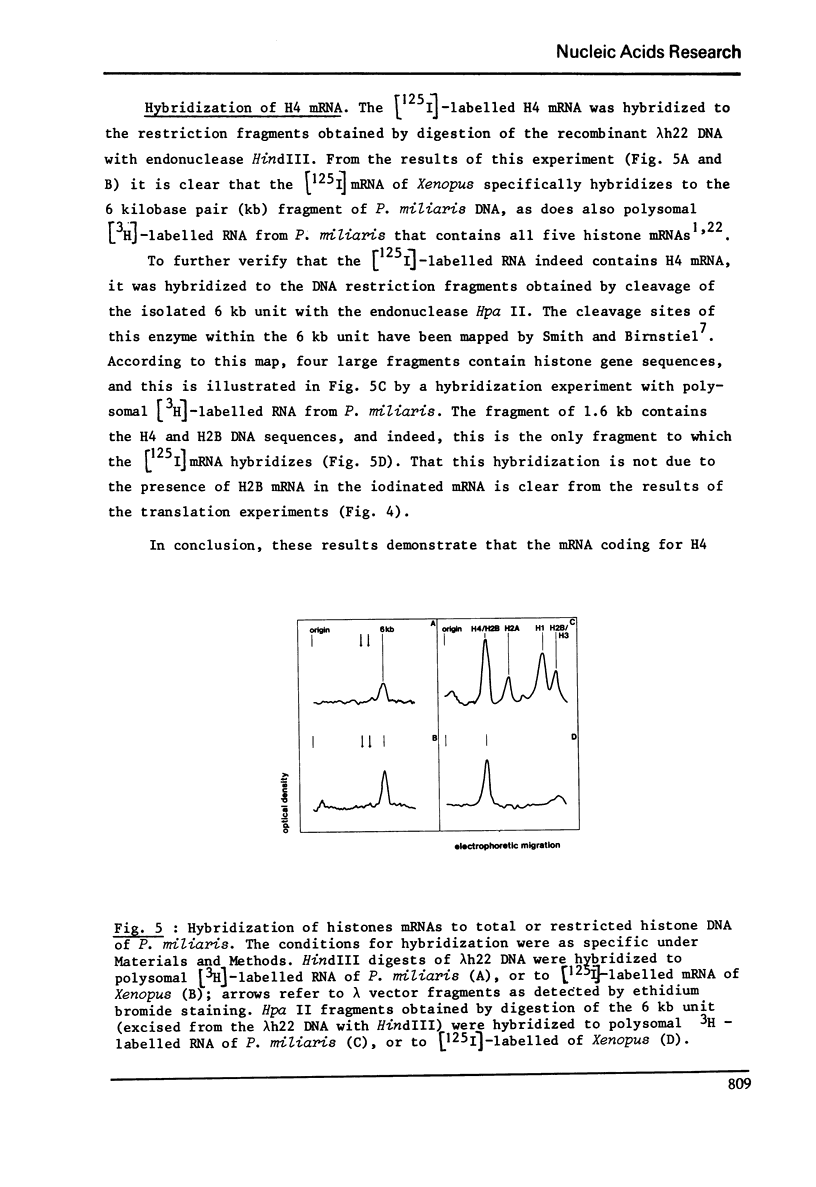
Abstract
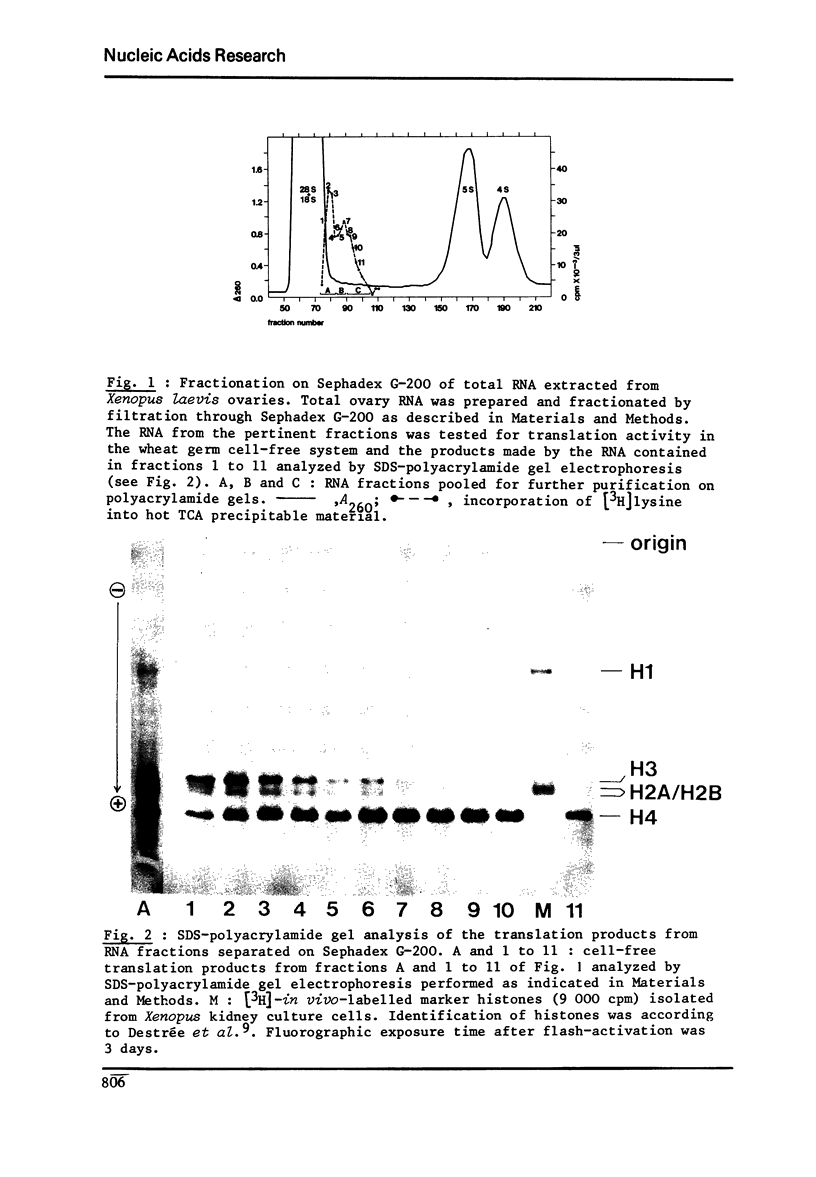
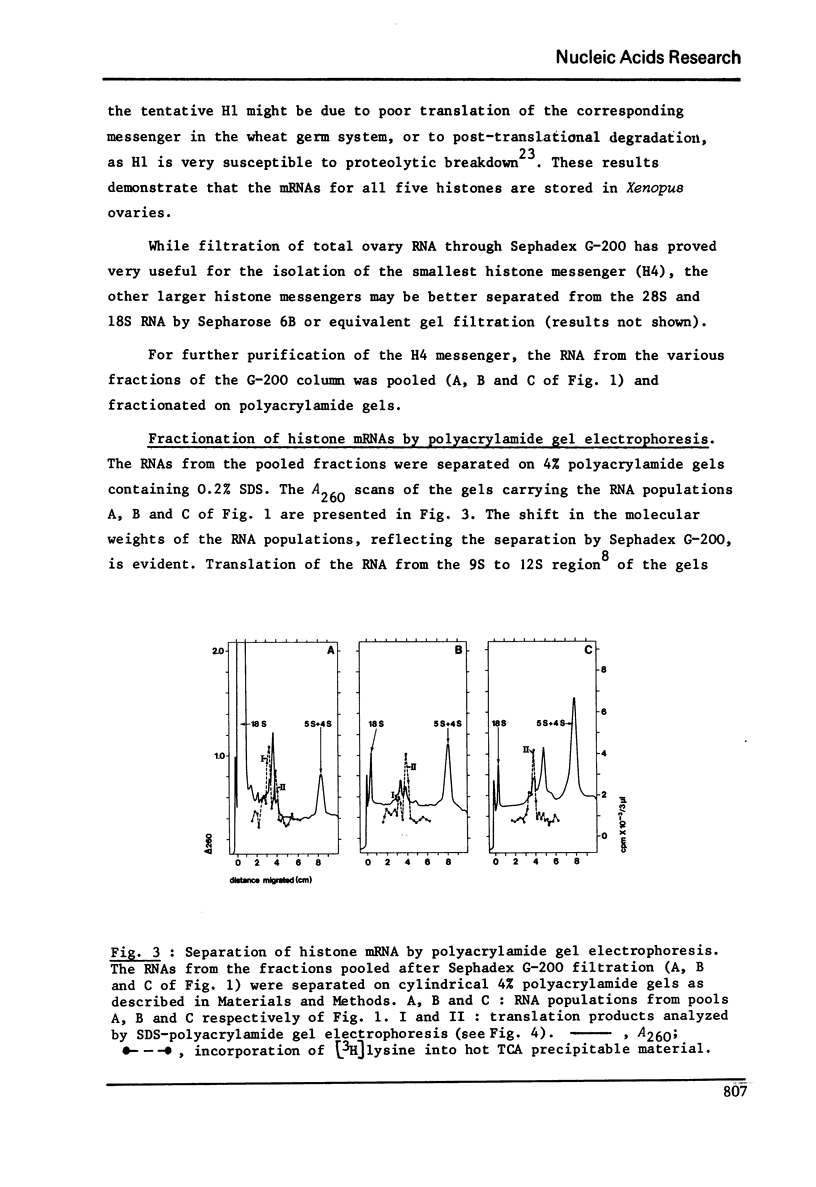
RNA extracted from ovaries of adult Xenopus laevis and introduced into a wheat germ cell-free system, directs the synthesis of polypeptides co-electrophoresing with all five histones. By frationation of total ovary RNA through Sephadex G-200 and polyacrylamide gel, RNA was isolated that is translated into histones 4 (H4) only. In addition, this RNA labelled in vitro with [I125] hybridizes to a restriction fragment of cloned sea urchin DNA known to contain the H4 gene.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson E. D., Woodland H. R. Histone synthesis in early amphibian development: histone and DNA syntheses are not co-ordinated. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):263–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90481-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd E. W., Jr, Kasinsky H. E. Histone synthesis during early embryogenesis in Xenopus laevis (South African clawed toad). Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):246–253. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Smith H. O., Schaffner W., Gross K. W., Birnstiel M. L. Integration of eukaryotic genes for 5S RNA and histone proteins into a phage lambda receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2617–2632. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Destree O. H., D'Adelhart-Toorop H. A., Charles R. Cytoplasmic origin of the so-called nuclear neutral histone protease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 10;378(3):450–458. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Destrée O. H., d' Adelhart Toorop H. A., Charles R. Analysis of histones from different tissues and embryos of Xenopus laevis (Daudin). II. Qualitative and quantitative aspects of nuclear histones during early stages of development. Cell Differ. 1973 Oct;2(4):229–242. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(73)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getz M. J., Altenburg L. C., Saunders G. F. The use of RNA labeled in vitro with iodine-125 in molecular hybridization experiments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 22;287(3):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K., Probst E., Schaffner W., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of Psammechinus miliaris: I. Fractionation and identification of five individual histone mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):455–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K., Schaffner W., Telford J., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of Psammechinus miliaris: III. Polarity and asymmetry of the histone-coding sequences. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90215-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E., Malacinski G., Birnstiel M. L. Reiteration frequency of the histone genes in the genome of the amphibian, Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone messengers and histone genes. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The determination of the molecular weight of ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophresis. The effects of changes in conformation. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):131–138. doi: 10.1042/bj1130131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mairy M., Denis H. Recherches biochimiques sur l'oogenèse. I. Synthèse et accumulation du RNA pendant l'oogenèse du crapaud sud-africain Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1971 Feb;24(2):143–165. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish J. H., Kirby K. S. Reagents which reduce interactions between ribosomal RNA and rapidly labelled RNA from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 21;129(3):554–562. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portmann R., Schaffner W., Birnstiel M. Partial denaturation mapping of cloned histone DNA from the sea urchin Psammechinus miliaris. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):31–34. doi: 10.1038/264031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K. An evaluation of film detection methods for weak beta-emitters, particularly tritium. Anal Biochem. 1970 Mar;34:188–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Gross K., Telford J., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of psammechinus miliaris: II. The arrangement of the five histone-coding and spacer sequences. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]