Abstract
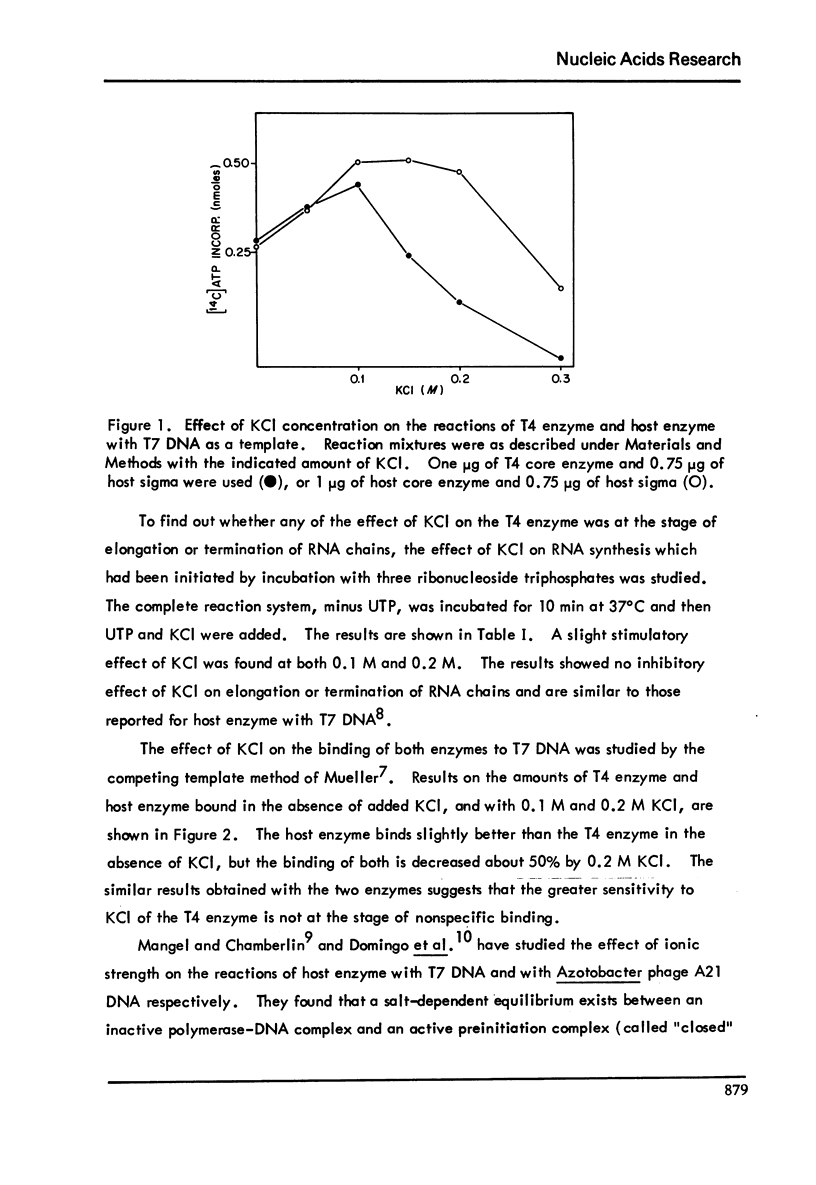
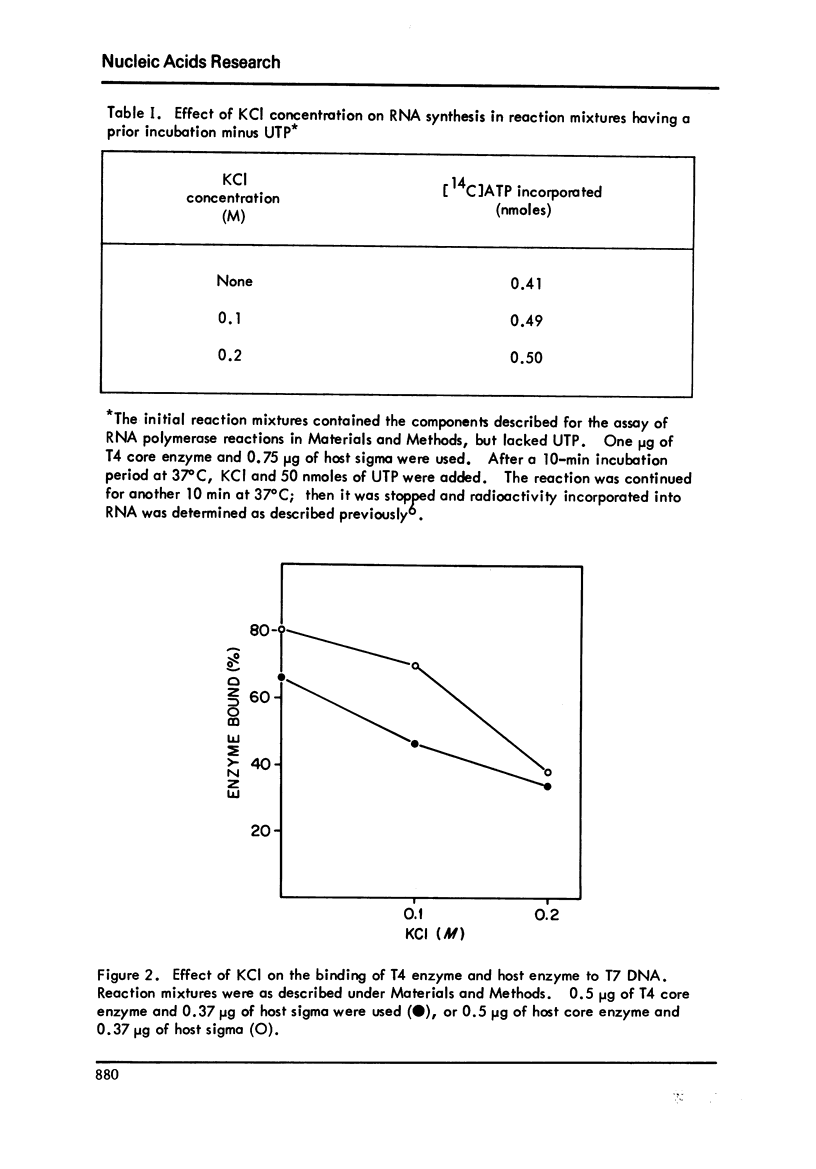
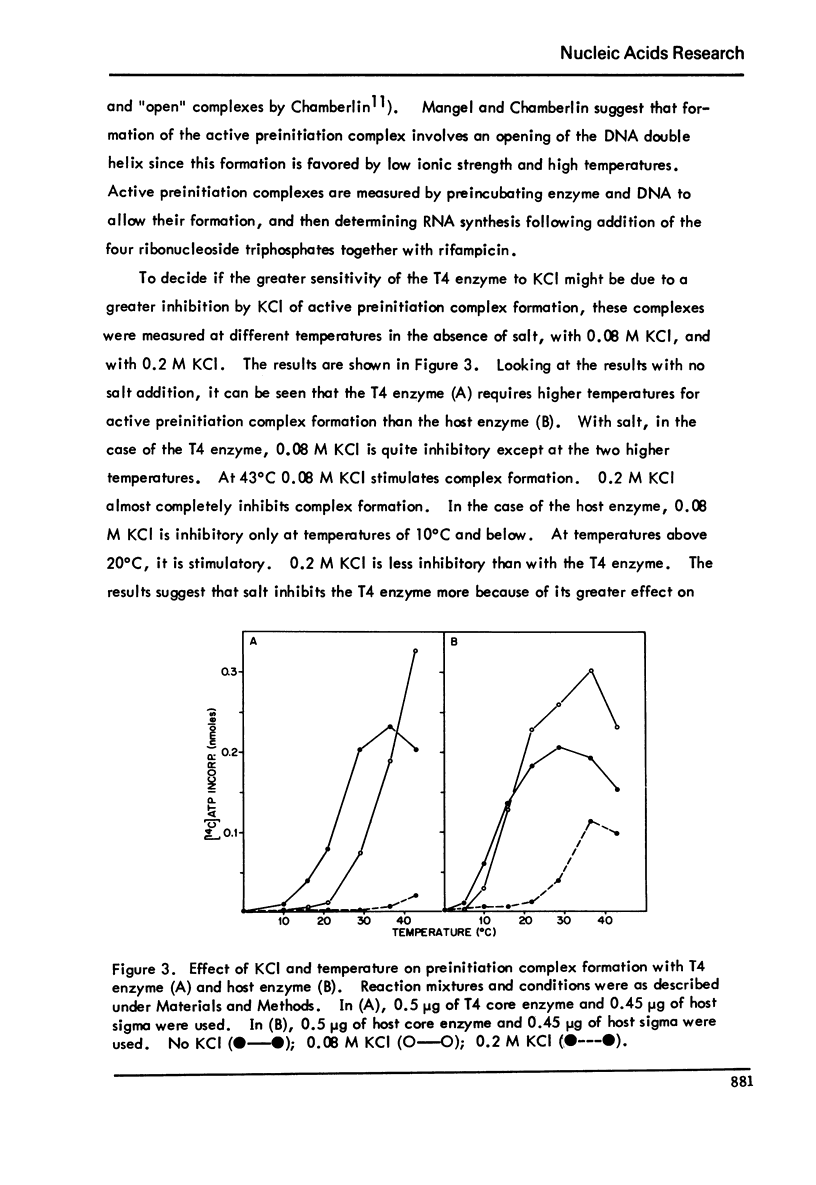
Transcription of T7 DNA by T4 core enzyme with host sigma is more sensitive to KCI than that by host core enzyme with host sigma. When salt is added after initiation of RNA chains has occurred, it is not inhibitory. Salt affects the binding of T4 enzyme to T7 DNA to the same degree as the binding of host enzyme. Active preinitiation complex formation is inhibited more by salt with the T4 enzyme and the inhibition is temperature-dependent.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamberlin M. J. The selectivity of transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):721–775. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Escarmis C., Warner R. C. Transcription of Azotobacter phage deoxyribonucleic acid. Salt-dependent equilibrium between steps in initiation. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2872–2877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff C. G. Chemical structure of a modification of the Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase alpha polypeptides induced by bacteriophage T4 infection. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6181–6190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleppe R. K. Influence of salt on transcription by T4 core RNA polymerase. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 1;51(1):237–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80895-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangel W. F., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of ribonucleic acid chain initiation by Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase bound to T7 deoxyribonucleic acid. II. The effect of alterations in ionic strength of chain initiation and on the conformation of binary complexes. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3002–3006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukage A. The effects of KC1 concentration on the transcription by E. coli RNA polymerase. I. Specific effect of the combination of nucleoside triphosphates. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;118(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02428328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller K. The function of the -factor of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in template site selection. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(3):273–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00433112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVENS A., HENRY J. STUDIES ON THE RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. PURIFICATION OF THE ENZYME AND STUDIES OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID FORMATION. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:196–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert W., Rabussay D., Zillig W. On the chemical nature of alteration and modification of DNA dependent RNA polymerase of E. coli after T4 infection. FEBS Lett. 1971 Aug 15;16(3):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Deoxyribonucleic acid dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases from two T4 phage-infected systems. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):493–503. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A., Rhoton J. C. Characterization of an inhibitor causing potassium chloride sensitivity of an RNA polymerase from T4 phage-infected Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5074–5079. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


