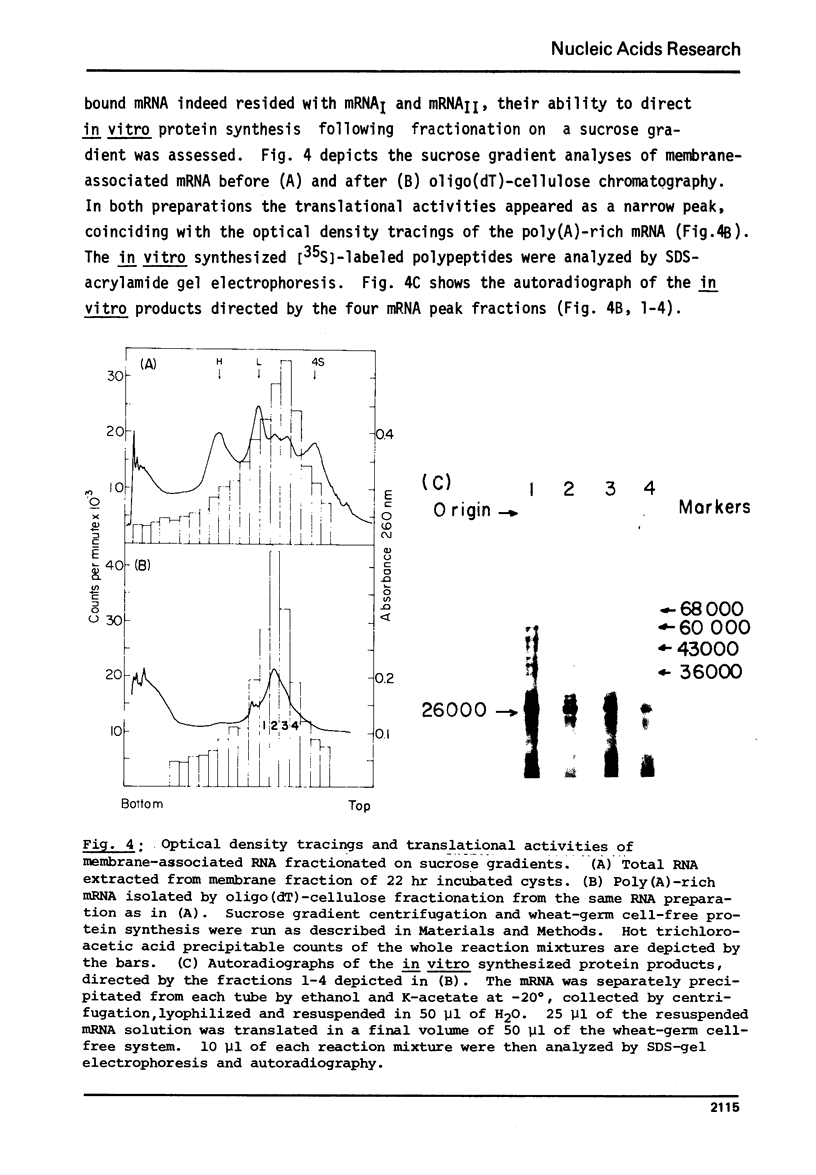
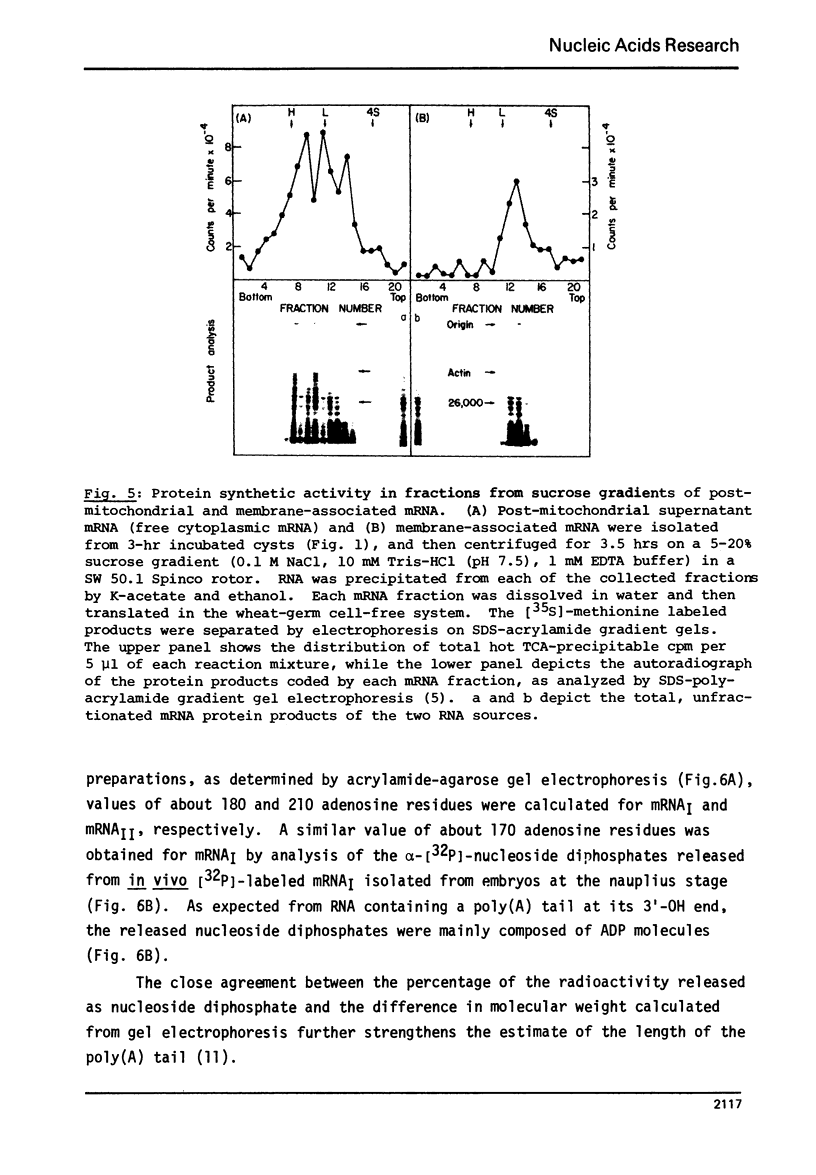
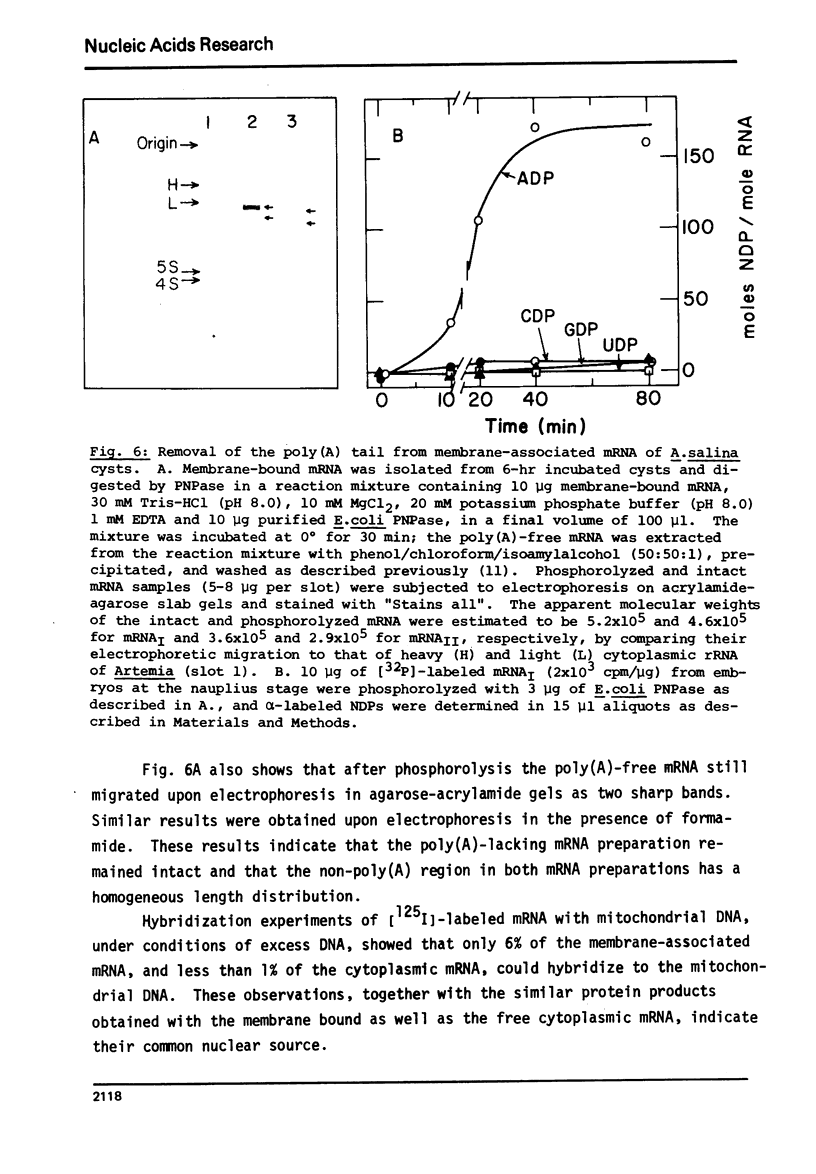
Abstract
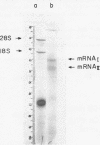
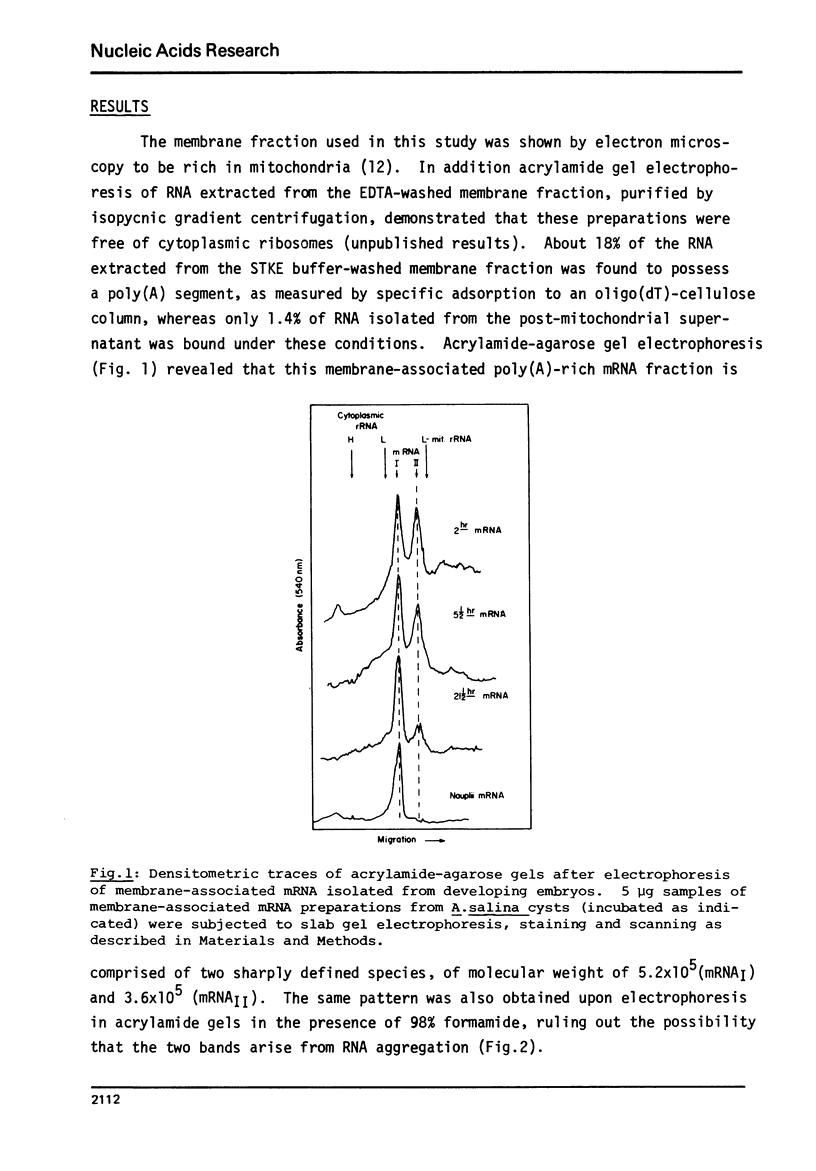
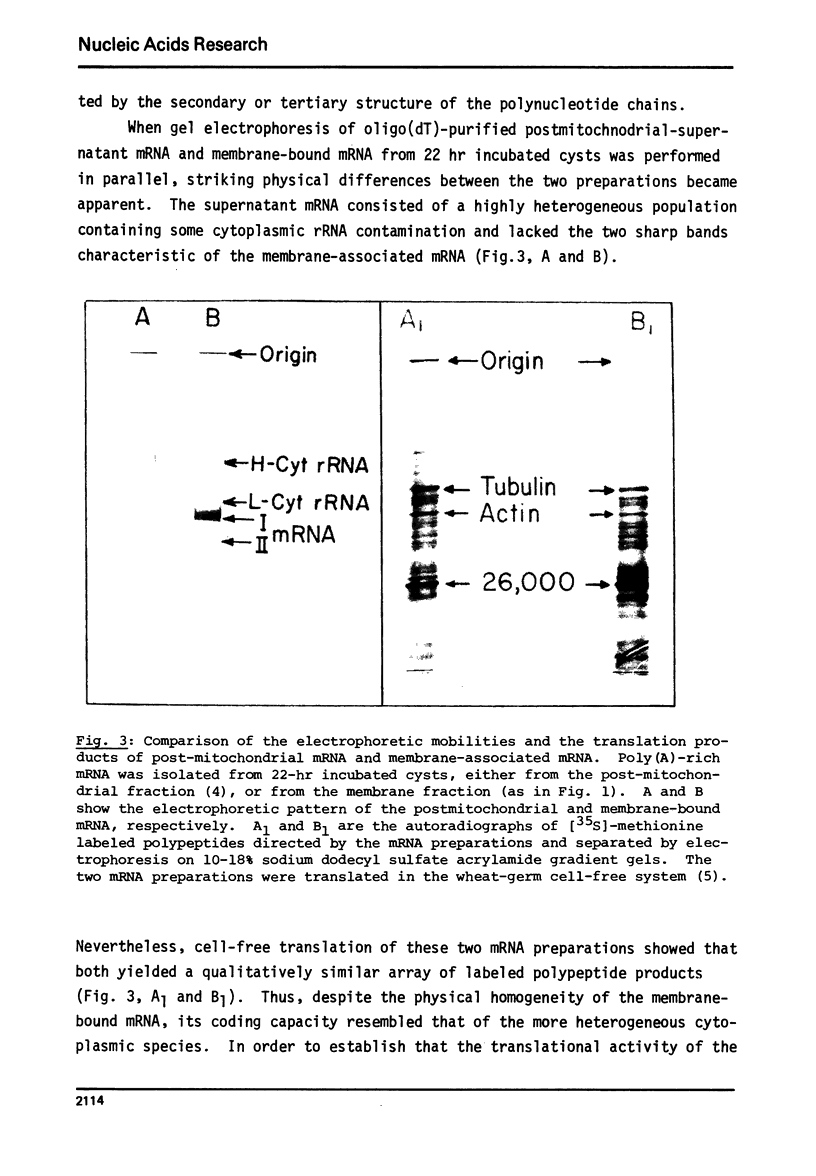
The physical and functional properties of the mRNA population from developing embryos of the brine shrimp Artemia salina were characterized. About 20% of the total poly(A)-rich mRNA in these embryos appears to be specifically associated with the membrane fraction throughout early development, and physically differs markedly from the free cytoplasmic mRNA. The membrane-associated mRNA fraction consists of two well-defined populations of molecular weight of 5.2x10(5) and 3.6x10(5), whose relative amount changes during the various stages of embryo development. The size of the poly(A) tail at the 3'-end of the mRNA molecules, as estimated by processive phosphorolysis, was found to consist of 180 and 210 adenosine residues for the two respective mRNA species. The in vitro translation products of the membrane-bound mRNA molecules are apparently similar to those of the free mRNA molecules.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman M. R., Sabatini D. D., Blobel G. Ribosome-membrane interaction. Nondestructive disassembly of rat liver rough microsomes into ribosomal and membranous components. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jan;56(1):206–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. S., Golub A. L. Protein synthesis in Artemia salina embryos. II. Resumption of RNA and protein synthesis upon cessation of dormancy in the encysted gastrula. Dev Biol. 1969 Feb;19(2):178–200. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingman C. W., Peacock A. C. Analytical studies on nuclear ribonucleic acid using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):659–668. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub A., Clegg J. S. Protein synthesis in Artemia salina embryos. I. Studies on polyribosomes. Dev Biol. 1968 Jun;17(6):644–656. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner Y., Grosfeld H., Littauer U. Z. 5'-Capping structures of Artemia salina mRNA and the translational inhibition by cap analogs. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec;71(1):281–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosfeld H., Littauer U. Z. Cryptic form of mRNA in dormant Artemia salina cysts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):176–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90299-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosfeld H., Littauer U. Z. Proceedings: In vitro translation of mRNA from developing cysts of Artemia salina. Isr J Med Sci. 1975 Nov;11(11):1203–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosfeld H., Littauer U. Z. The translation in vitro of mRNA from developing cysts of Artemia salina. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):589–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lande M. A., Adesnik M., Sumida M., Tashiro Y., Sabatini D. D. Direct association of messenger RNA with microsomal membranes in human diploid fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jun;65(3):513–528. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milcarek C., Penman S. Membrane-bound polyribosomes in HeLa cells: association of polyadenylic acid with membranes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90522-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson M. O., Hultin T. Poly(A)-containing cytoplasmic RNA in dormant cysts of Artemia salina. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 1;52(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80822-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosbash M., Penman S. Membrane-associated protein synthesis of mammalian cells. I. The two classes of membrane-associated ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 28;59(2):227–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H., Grossfeld H., Littauer U. Z. Mitochondrial biogenesis during differentiation of Artemia salina cysts. J Cell Biol. 1973 Sep;58(3):643–649. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Nudel U., Salomon R., Revel M., Littauer U. Z. In vitro translation of polyadenylic acid-free rabbit globin messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90307-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staynov D. Z., Pinder J. C., Gratzer W. B. Molecular weight determination of nucleic acids by gel electrophoresis in non-aqueous solution. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 26;235(56):108–110. doi: 10.1038/newbio235108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]