Abstract
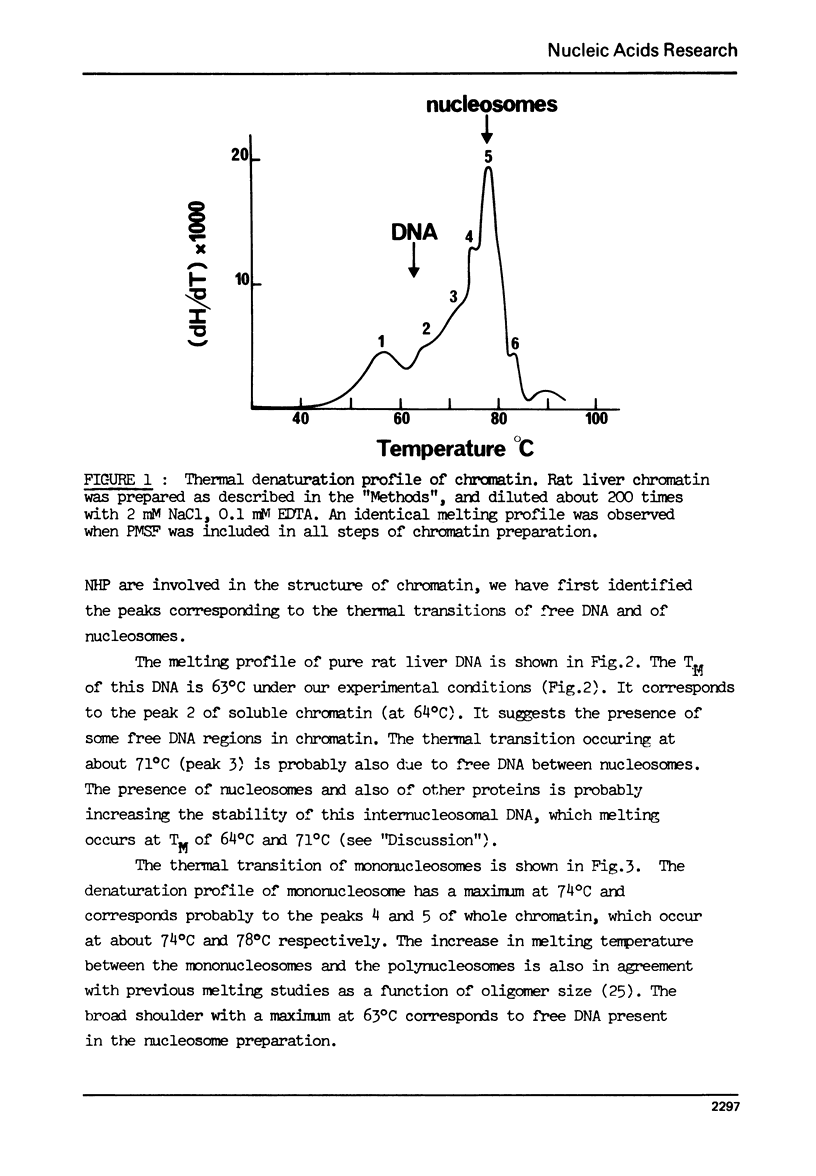
The effect of chromatin non-histone protein on DNA and chromatin stability is investigated by differential thermal denaturation method. 1) Chromatin (rat liver) yields a multiphasic melting profile. The major part of the melting curve of this chromatin is situated at temperatures higher than pure DNA, with a distinct contribution due to nucleosomes melting. A minor part melts at temperatures lower than DNA which may be assigned to chromatin non-histone protein-DNA complex which destabilized DNA structure. 2) Heparin which extracts histones lowers the melting profile of chromatin and one observes also a contribution with a Tm lower that of pure DNA. In contrast, extraction on non-histone proteins by urea supresses the low Tm peak. 3) Reconstitution of chromatin non-histone protein-DNA complexes confirms the existence of a fraction of chromatin non-histone protein which lowers the melting temperature when compared to pure DNA. It is concluded that chromatin non-histone proteins contain different fractions of proteins which are causing stabilizing and destabilizing effect on DNA structure.
Full text
PDF



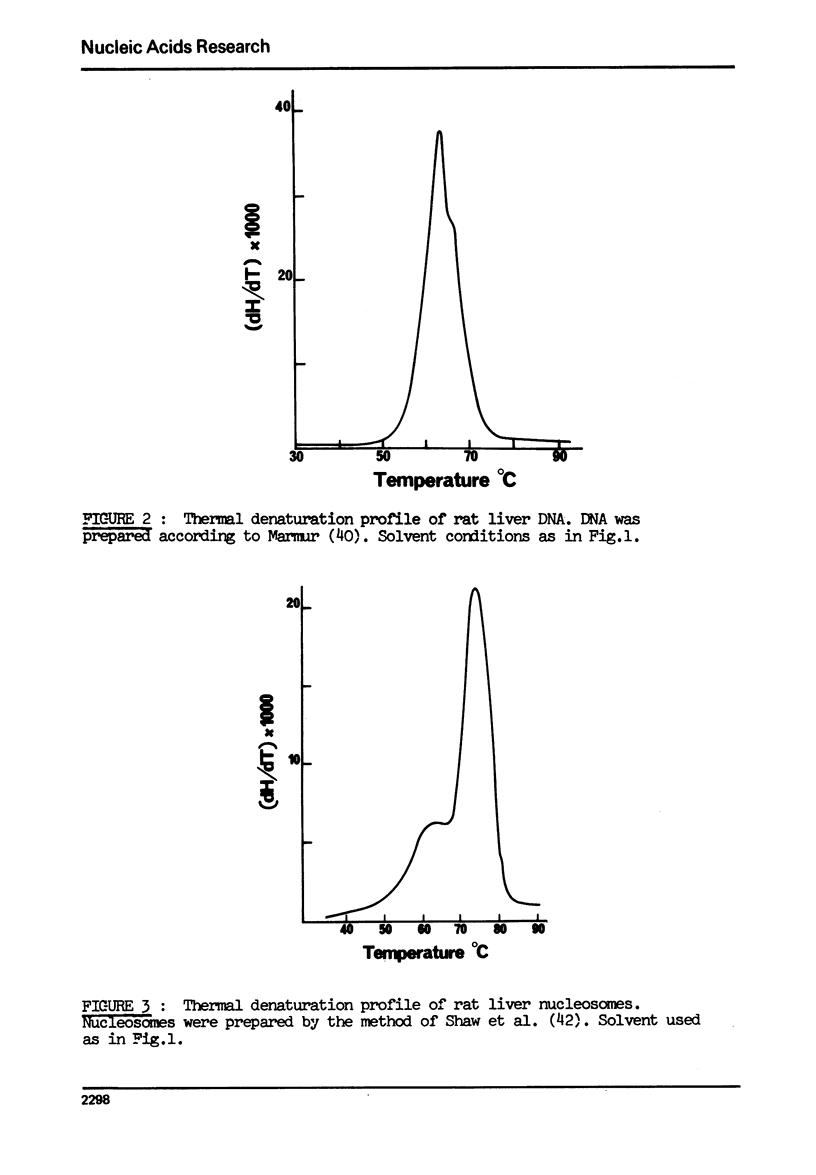




Images in this article
Selected References
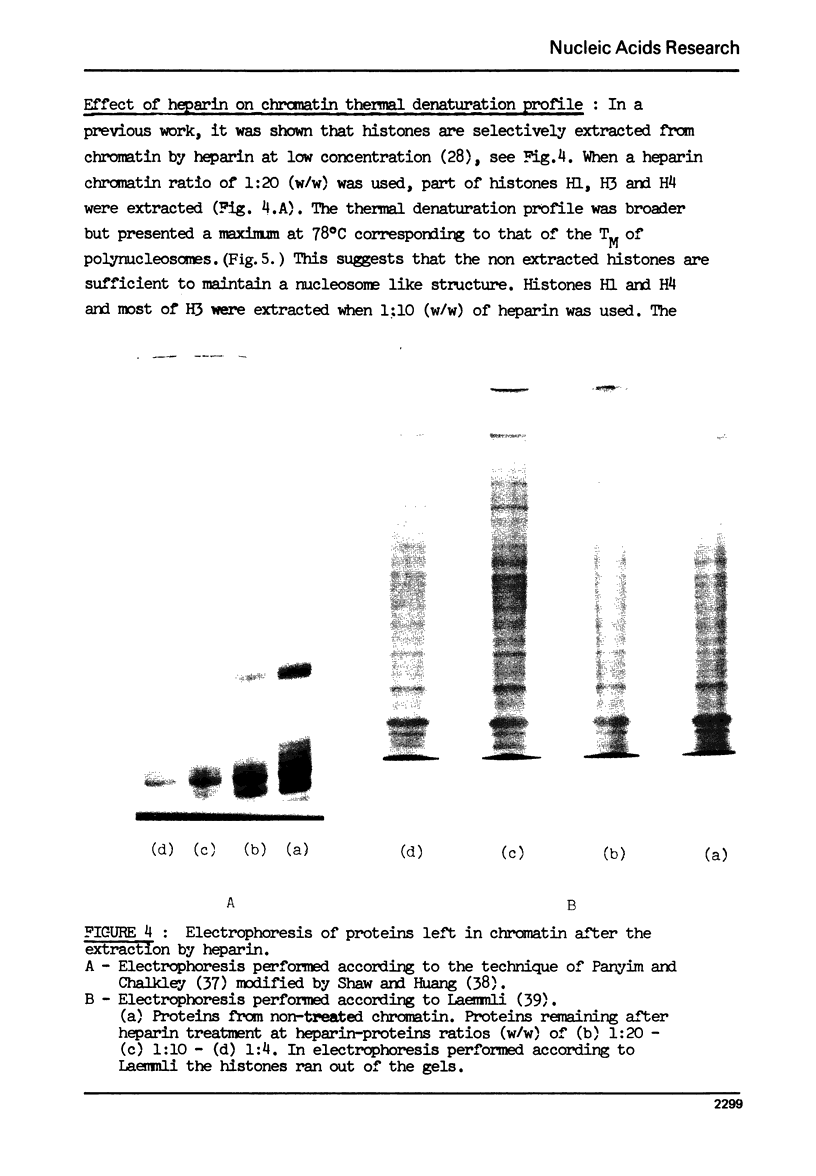
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansevin A. T., Hnilica L. S., Spelsberg T. C., Kehm S. L. Structure studies on chromatin and nucleohistones. Thermal denaturation profiles recorded in the presence of urea. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 7;10(25):4793–4803. doi: 10.1021/bi00801a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansevin A. T., Macdonald K. K., Smith C. E., Hnilica L. S. Mechanics of chromatin template activation. Physical evidence for destabilization of nucleoproteins by polyanions. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):281–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T., Maryanka D., Hamlyn P. H., Gould H. J. Nonhistone proteins control gene expression in reconstituted chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5057–5061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekhor I., Feldman B. Assembly of DNA with histones and nonhistone chromosomal proteins in vitro. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4771–4777. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlowitz L., Kitchin R., Pallotta D. Histones and RNA synthesis: selective binding of histones by a synthetic polyanion in calf thymus nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):160–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUVEAU J., MOULE Y., ROUILLER C. Isolation of pure and unaltered liver nuclei morphology and biochemical composition. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Aug;11(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. The organization of histones and DNA in chromatin: evidence for an arginine-rich histone kernel. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):333–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. D., Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Urea denaturation of chromatin periodic structure. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3122–3125. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois Y., Dastugue B., Kamiyama M., Kruh J. Binding of chromosomal non histone proteins to DNA and to nucleohistones. Effect of in vitro phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80501-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadski R. A., Chae C. B. Mode of reconstitution of chicken erythrocyte and reticulocyte chromatin. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3812–3817. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner Y., Monroy G., Jacquet M., Hurwitz J. Chromatin as a template for RNA synthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):194–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Oba Y. Selective removal of histones from calf-thymus nucleohistone with sodium dodecylsulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2419–2422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick G., Alberts B. Purification and physical characterization of nucleic acid helix-unwinding proteins from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2124–2132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide T., Nakane M., Anzai K., Ando T. Supercoiled DNA folded by non-histone proteins in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 1975 Dec 4;258(5534):445–447. doi: 10.1038/258445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiyama M., Dastugue B., Defer N., Kruh J. Liver chromatin non-histone proteins. Partial fractionation and mechanism of action on RNA synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 14;277(3):576–583. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiyama M., Wang T. Y. Activated transcription from rat liver chromatin by non-histone proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 28;228(2):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
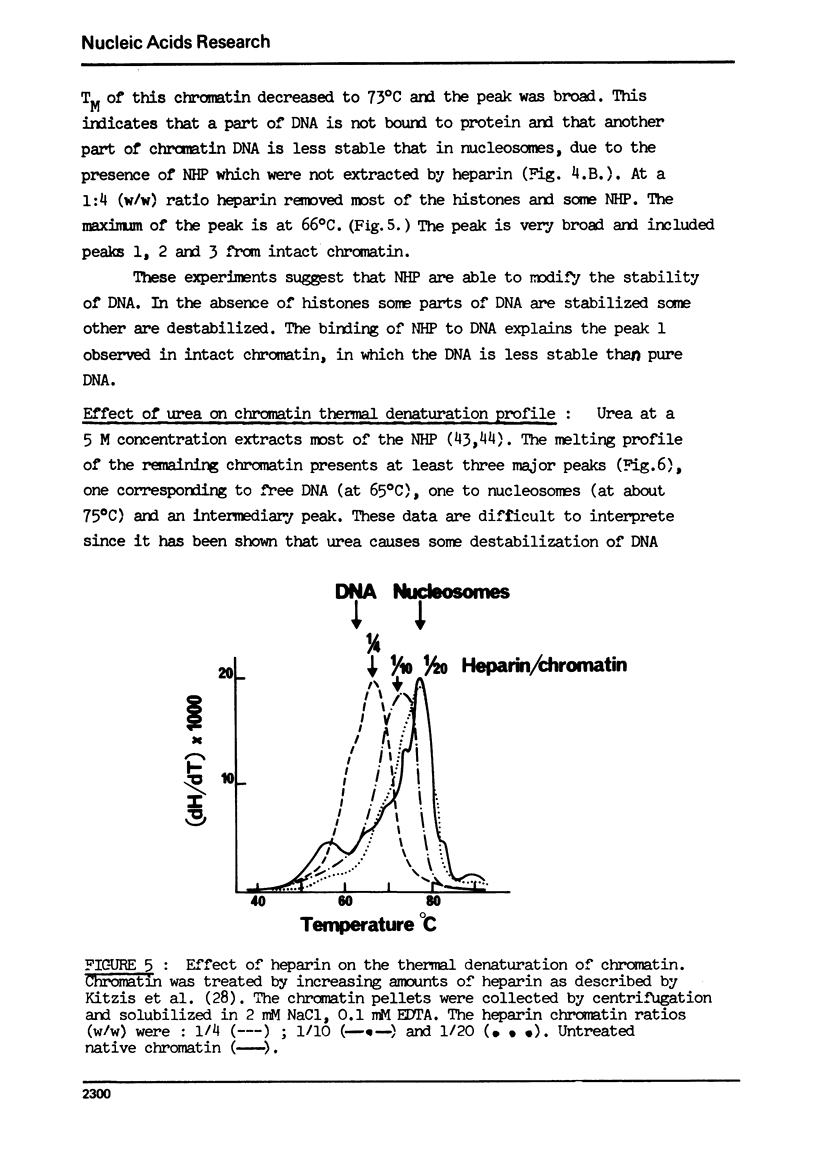
- Kitzis A., Defer N., Dastugue B., Sabatier M. M., Kruh J. Effect of heparin on chromatin. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 15;66(2):336–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80534-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Thomas J. O. Chromatin structure; oligomers of the histones. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):865–868. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. J., Bonner J. Interaction of histone half-molecules with deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1461–1470. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel R., Fasman G. D. Chromatin and nucleosome structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Aug;3(8):1839–1855. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.8.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
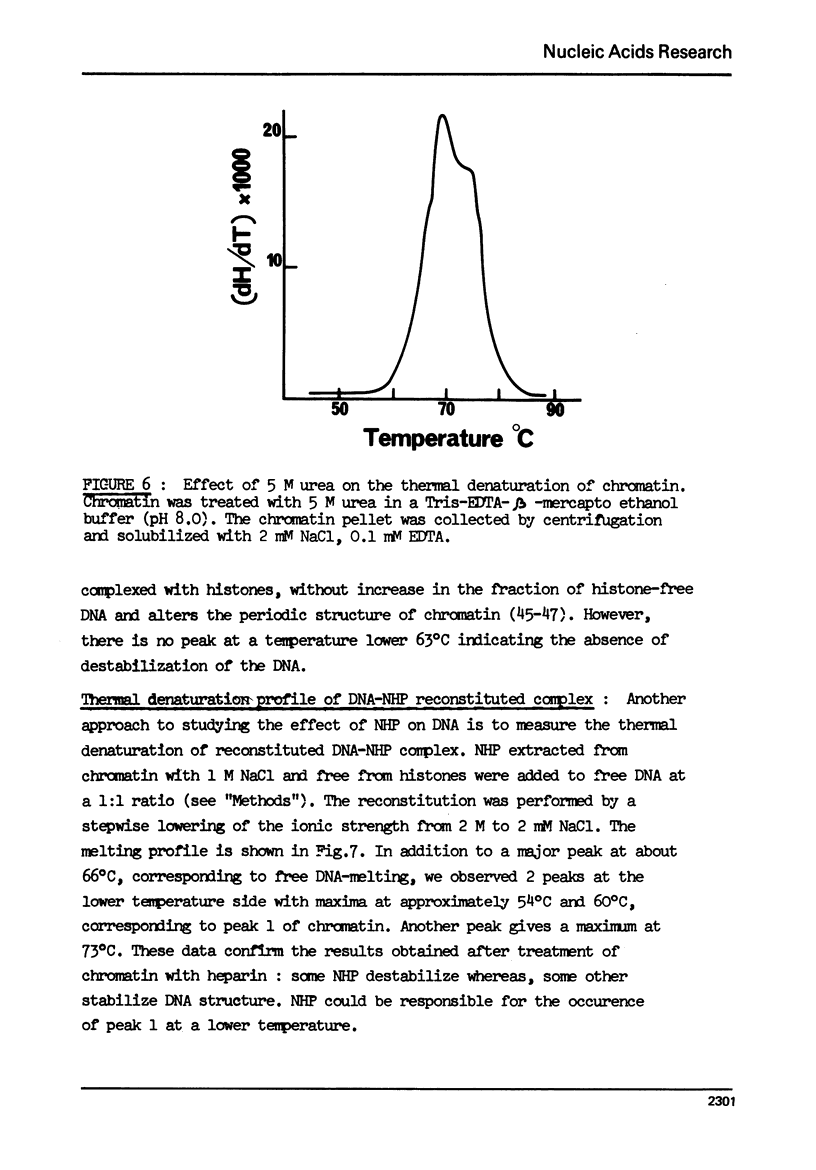
- Noll M. Subunit structure of chromatin. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):249–251. doi: 10.1038/251249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlenbusch H. H., Olivera B. M., Tuan D., Davidson N. Selective dissociation of histones from calf thymus nucleoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):299–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Spheroid chromatin units (v bodies). Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
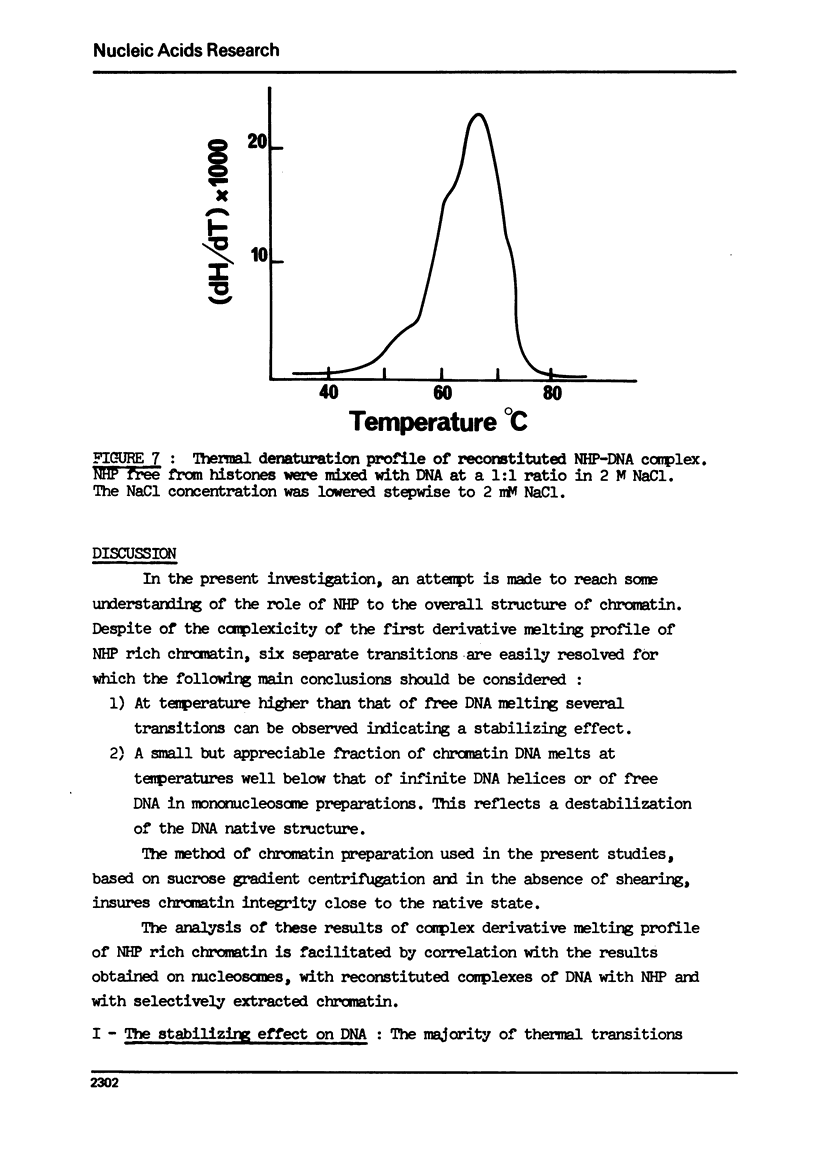
- Olins D. E., Olins A. L., Von Hippel P. H. Model nucleoprotein complexes: studies on the interaction of cationic homopolypeptides with DNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Mar 14;24(2):157–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J., Gilmour R. S. Organ-specific restriction of transcription in mammalian chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90255-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Transcription of chromatin by bacterial RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 25;80(2):229–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rill R., Van Holde K. E. Properties of nuclease-resistant fragments of calf thymus chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):1080–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw B. R., Corden J. L., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Van Holde K. E. Chromatographic separation of chromatin subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Lake R. S. Studies on the structure of metaphase and interphase chromatin of Chinese hamster cells by circular dichroism and thermal denaturation. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 5;11(25):4811–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00775a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staynov D. Z. Thermal denaturation profiles and the structure of chromatin. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):522–525. doi: 10.1038/264522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subirana J. A. Studies on the thermal denaturation of nucleohistones. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 5;74(3):363–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro T., Kurokawa M. A contribution of nonhistone proteins to the conformation of chromatin. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 15;60(2):569–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb21035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng C. S., Teng C. T., Allfrey V. G. Studies of nuclear acidic proteins. Evidence for their phosphorylation, tissue specificity, selective binding to deoxyribonucleic acid, and stimulation effects on transcription. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3597–3609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. H., Ansevin A. T., Hnilica L. S. Association of tissue-specific histones with deoxyribonucleic acid. Thermal denaturation of native, partially dehistonized, and reconstituted chromatins. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 25;14(6):1257–1265. doi: 10.1021/bi00677a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hippel P. H., McGhee J. D. DNA-protein interactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41(10):231–300. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S., Chiu J. F., Klyszejko-Stefanowicz L., Fujitani H., Hnilica L. S. Tissue-specific chromosomal non-histone protein interactions with DNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1471–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein B. I., Li H. Stimulation of chromatin template activity by the physiological macromolecule polyphosphate: a possible mechanism for eukaryotic gene derepression. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm F. X., de Murcia G. M., Daune M. P. The premelting of nucleoprotein: role of non-histone proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Aug;1(8):1043–1057. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.8.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. S., Li H. J., Shih T. Y. Interactions between arginine-rich histones and deoxyribonucleic acids. I. Thermal denaturation. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2027–2034. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pomerai D. I., Chesterton C. J., Butterworth P. H. Preparation of chromatin. Variation in the template properties of chromatin dependent on the method of perparation. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 1;46(3):461–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pomerai D. I., Chesterton C. J., Butterworth P. H. The effect of heparin on the structure and template properties of chromatin. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 1;42(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80773-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek H. W., Noodén L. D., Sevall J. S., Bonner J. Isolation, purification, and fractionation of nonhistone chromosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):229–236. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]