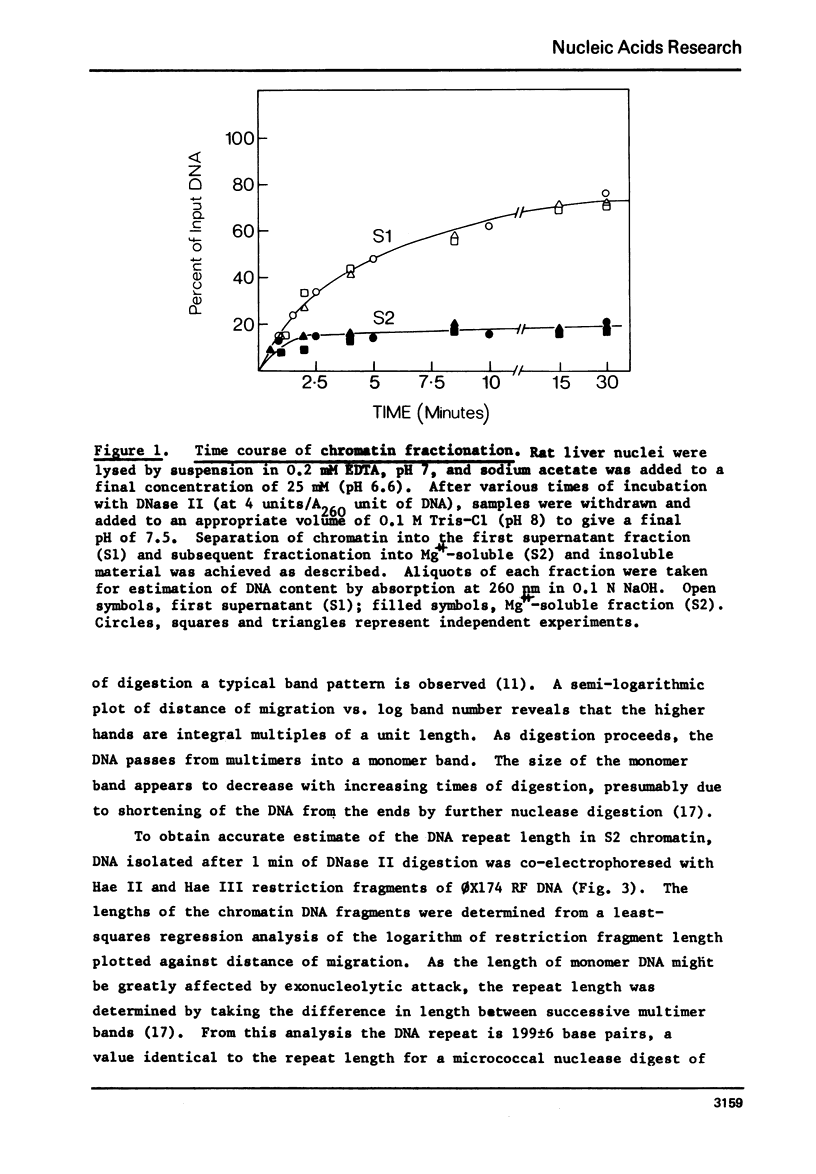
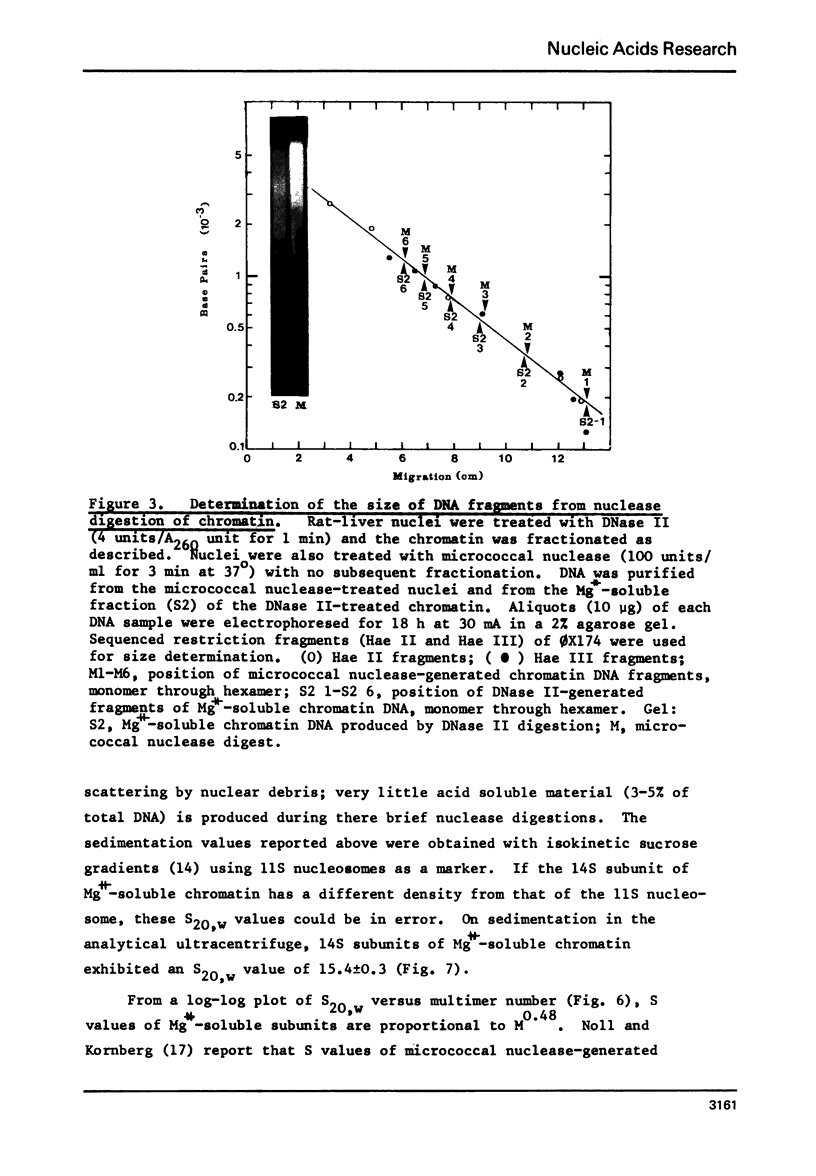
Abstract
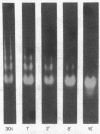
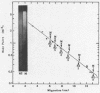
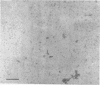
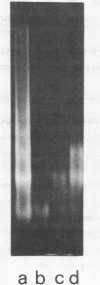
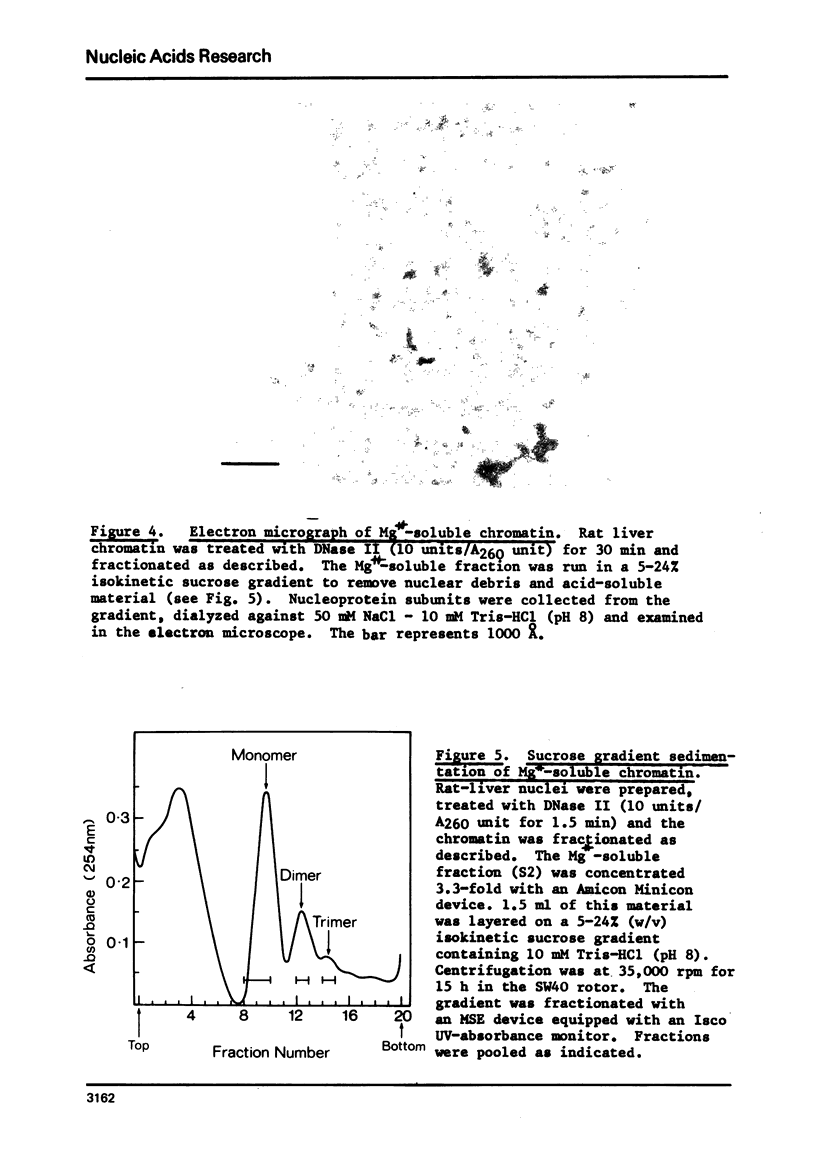
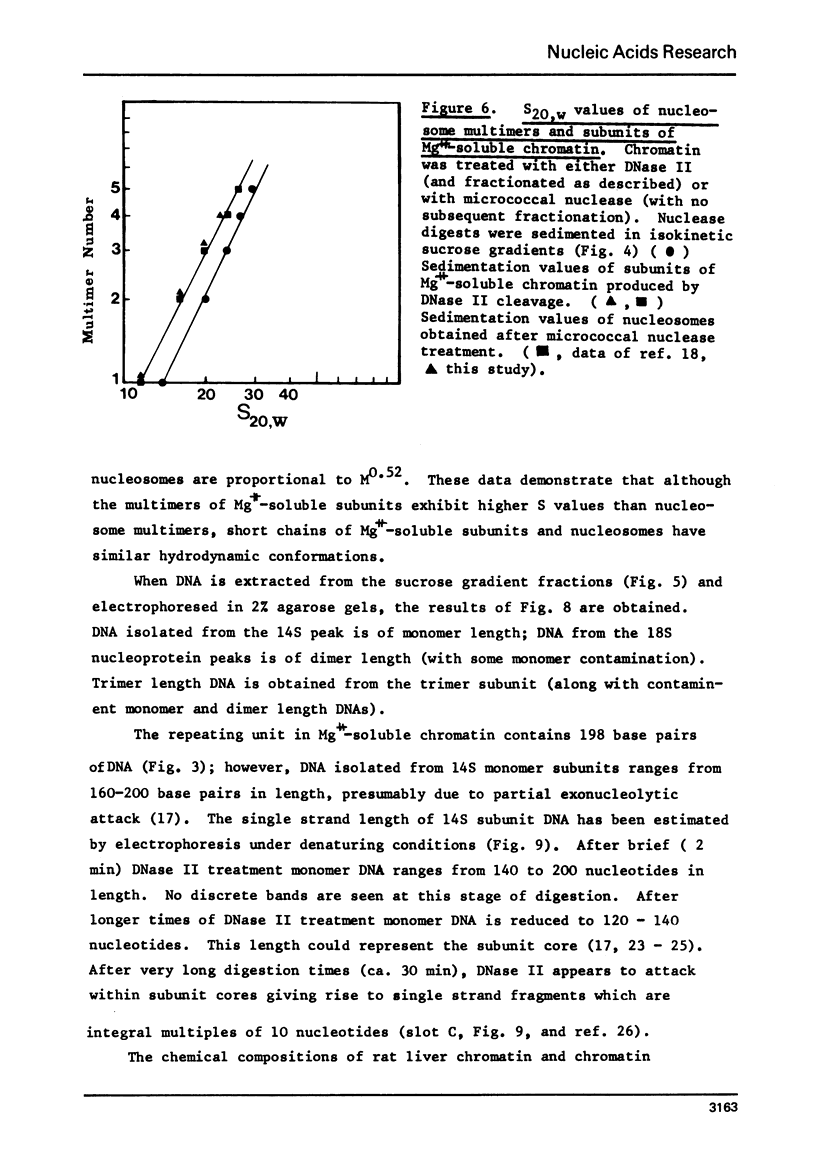
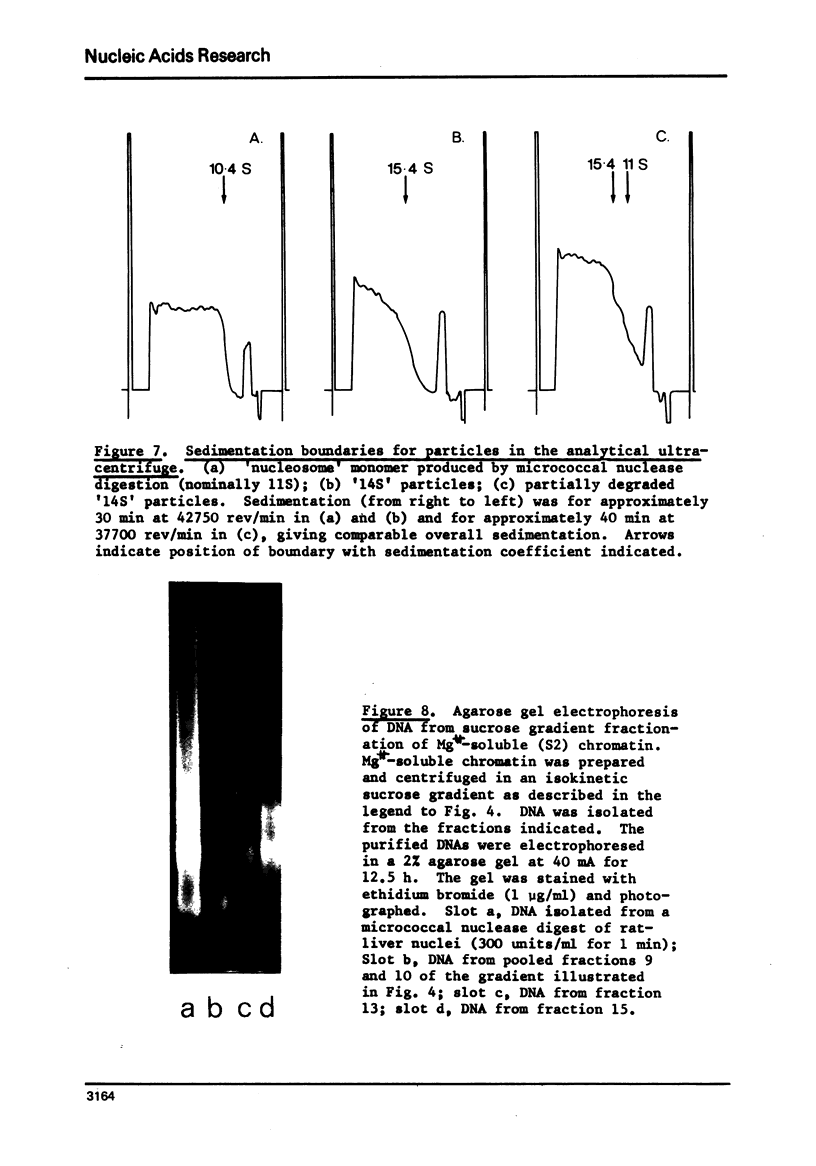
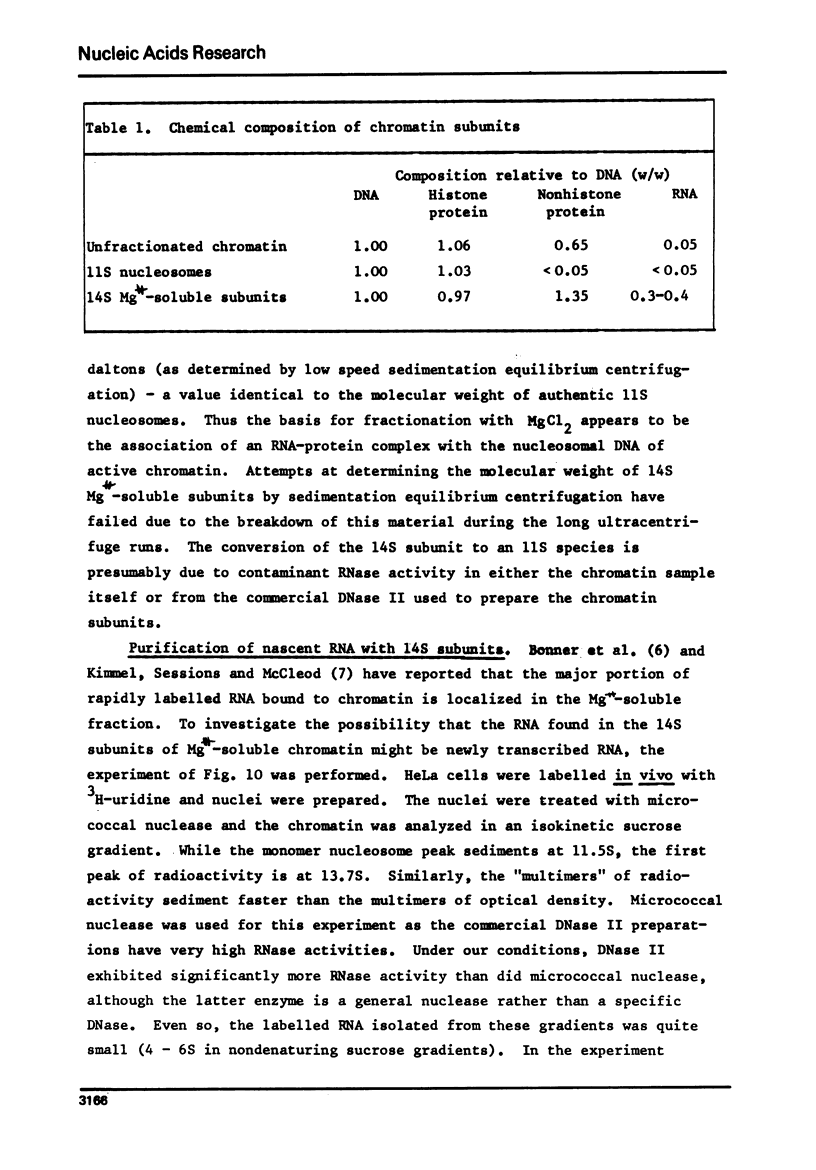
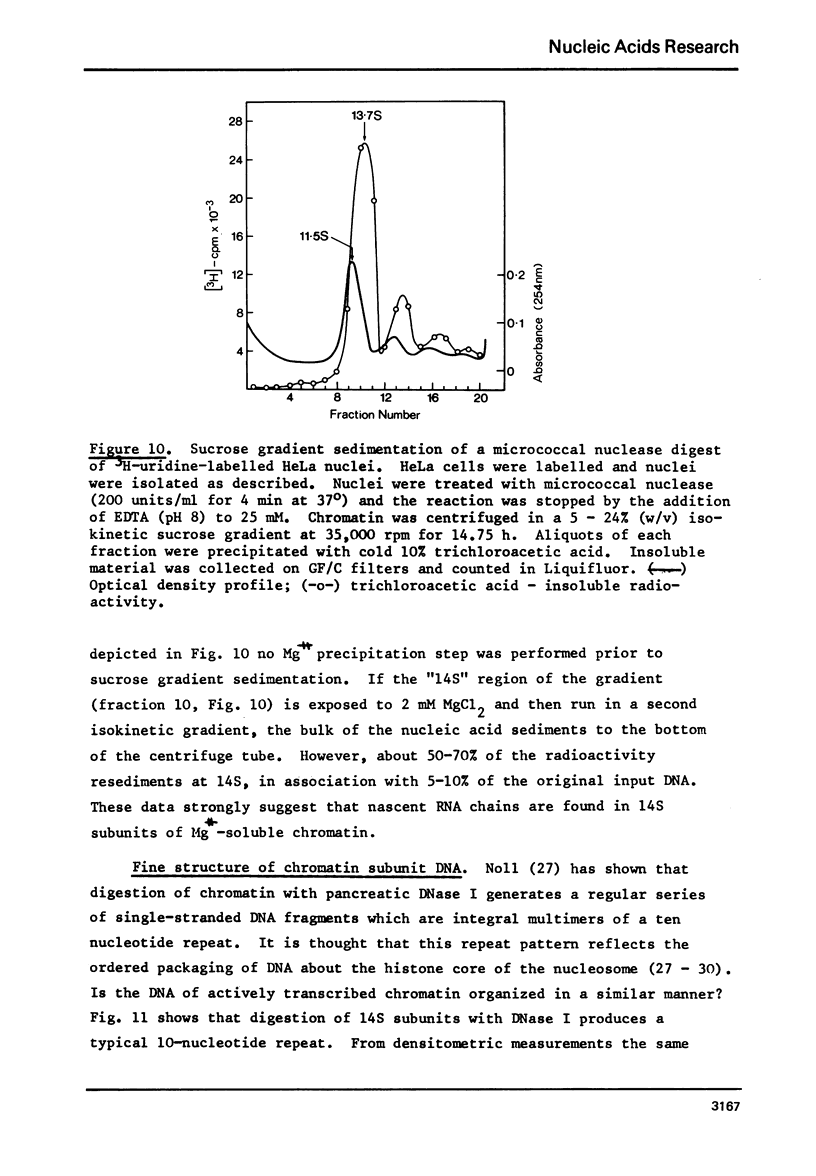
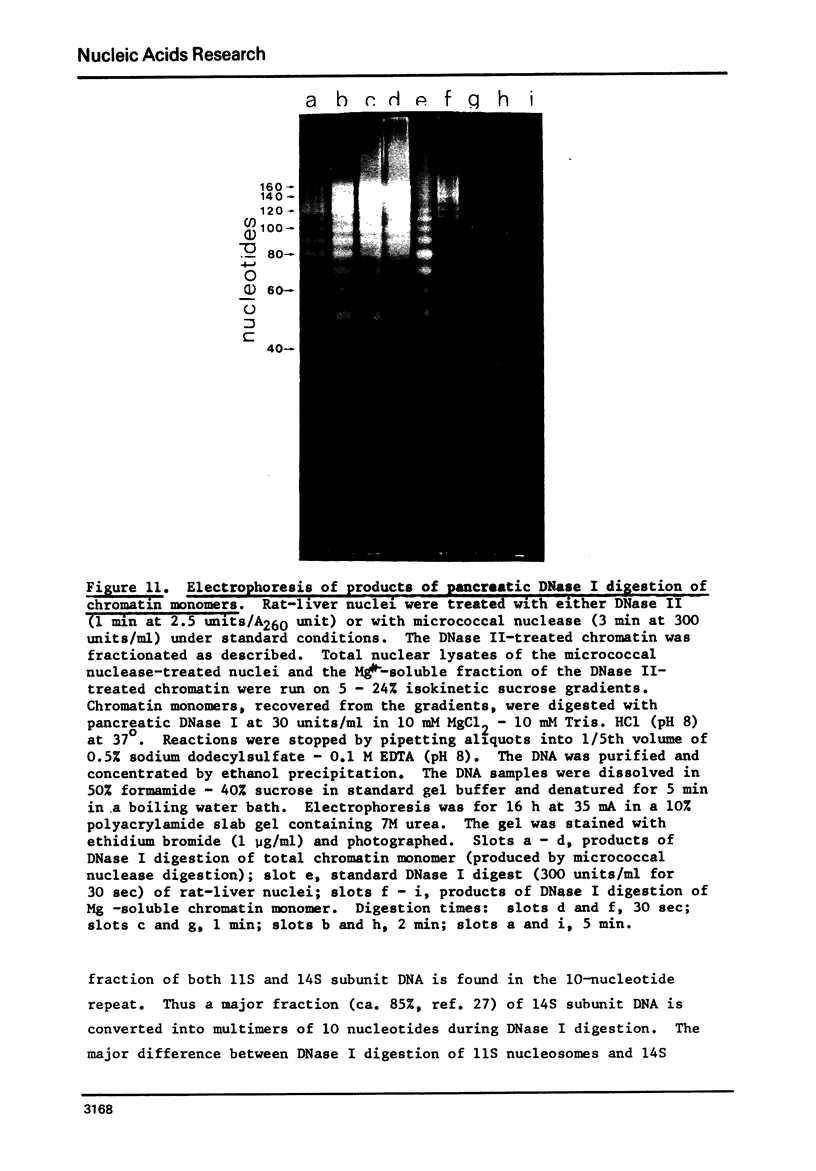
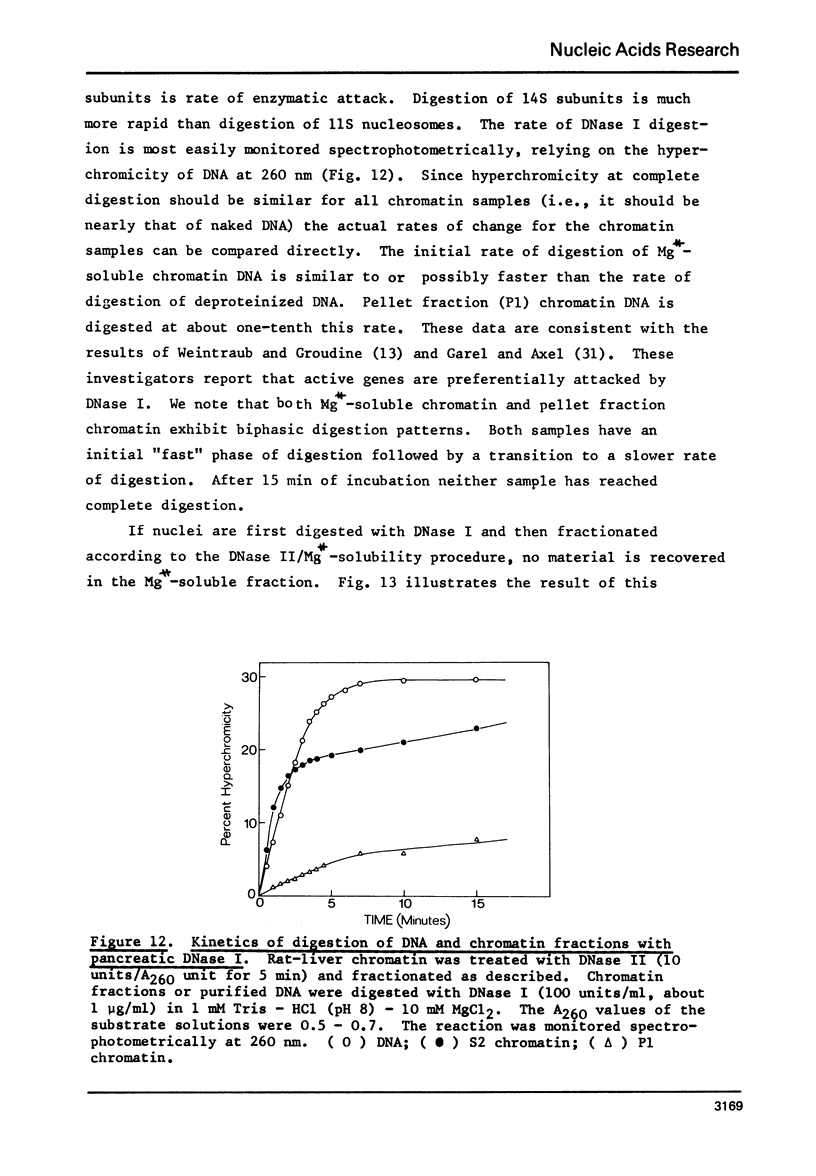
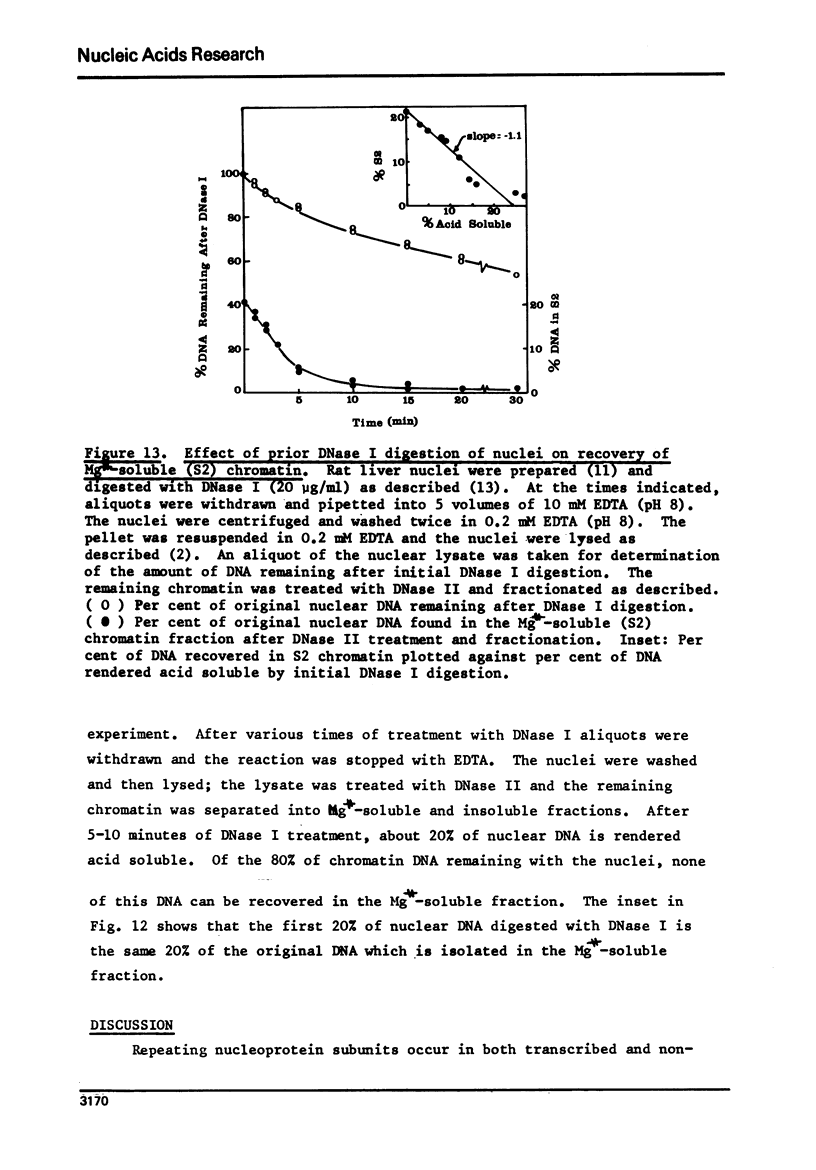
Rat liver chromatin is organized into regions of DNA which differ in degree of susceptibility to attack by the endonucleases DNase I and DNase II. The most nuclease-sensitive portion of chromatin DNA is enriched in transcribed sequences. This fraction may be separated from the bulk of chromatin by virtue of its solubility in solutions containing 2 mM MgCl2. Both transcribed and nontranscribed regions of chromatin are organized into repeating units of DNA and histone, which appear as 100 A beads in the electron microscope. The length of DNA in the repeat unit is the same for these two classes of chromatin (198 +/- 6 base pairs in rat liver); however, the subunits of active, Mg++-soluble chromatin differ from the nucleosomes of inactive regions of chromatin in several respects. Active subunits are enriched in nascent RNA and nonhistone protein and exhibit higher sedimentation values than the corresponding subunits of inactive chromatin.
Full text
PDF








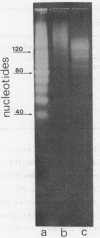
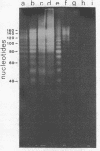
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axel R. Cleavage of DNA in nuclei and chromatin with staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2921–2925. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billing R. J., Bonner J. The structure of chromatin as revealed by deoxyribonuclease digestion studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 27;281(3):453–462. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J., Garrard W. T., Gottesfeld J., Holmes D. S. Functional organization of the mammalian genome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:303–310. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. H., Klug A. Kinky helix. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):530–533. doi: 10.1038/255530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Noll M., Kornberg R. D. Electron microscopy of defined lengths of chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3320–3322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Axel R. Selective digestion of transcriptionally active ovalbumin genes from oviduct nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Bagi G., Berg B., Bonner J. Sequence composition of the template-active fraction of rat liver chromatin. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2472–2483. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Garrard W. T., Bagi G., Wilson R. F., Bonner J. Partial purification of the template-active fraction of chromatin: a preliminary report. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2193–2197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Murphy R. F., Bonner J. Structure of transcriptionally active chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4404–4408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewish D. R., Burgoyne L. A. Chromatin sub-structure. The digestion of chromatin DNA at regularly spaced sites by a nuclear deoxyribonuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel C. B., Sessions S. K., MacLeod M. C. Evidence for an association of most nuclear RNA with chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 5;102(2):177–191. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Lindberg U. Characterization of messenger ribonucleoprotein and messenger RNA from KB cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):681–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Axel R. Analysis of DNA of isolated chromatin subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipchitz L., Axel R. Restriction endonuclease cleavage of satellite DNA in intact bovine nuclei. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marushige K., Bonner J. Fractionation of liver chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2941–2944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConaughy B. L., McCarthy B. J. Fractionation of chromatin by thermal chromatography. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 14;11(6):998–1003. doi: 10.1021/bi00756a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris N. R. A comparison of the structure of chicken erythrocyte and chicken liver chromatin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):627–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll H. Characterization of macromolecules by constant velocity sedimentation. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):360–363. doi: 10.1038/215360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Internal structure of the chromatin subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1573–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Kornberg R. D. Action of micrococcal nuclease on chromatin and the location of histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):393–404. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Subunit structure of chromatin. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):249–251. doi: 10.1038/251249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. Preparation of native chromatin and damage caused by shearing. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Spheroid chromatin units (v bodies). Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T., Bhorjee J. S. A special class of non-histone protein tightly complexed with template-inactive DNA in chromatin. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3238–3242. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Whitlock J. P. Mapping DNAase l-susceptible sites in nucleosomes labeled at the 5' ends. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Chromatin structure as probed by nucleases and proteases: evidence for the central role of histones H3 and H4. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. A comparison of the digestion of nuclei and chromatin by staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2915–2920. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien Kuo M., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Saunders G. F. Presence of messenger specifying sequences in the DNA of chromatin subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1572–1575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]