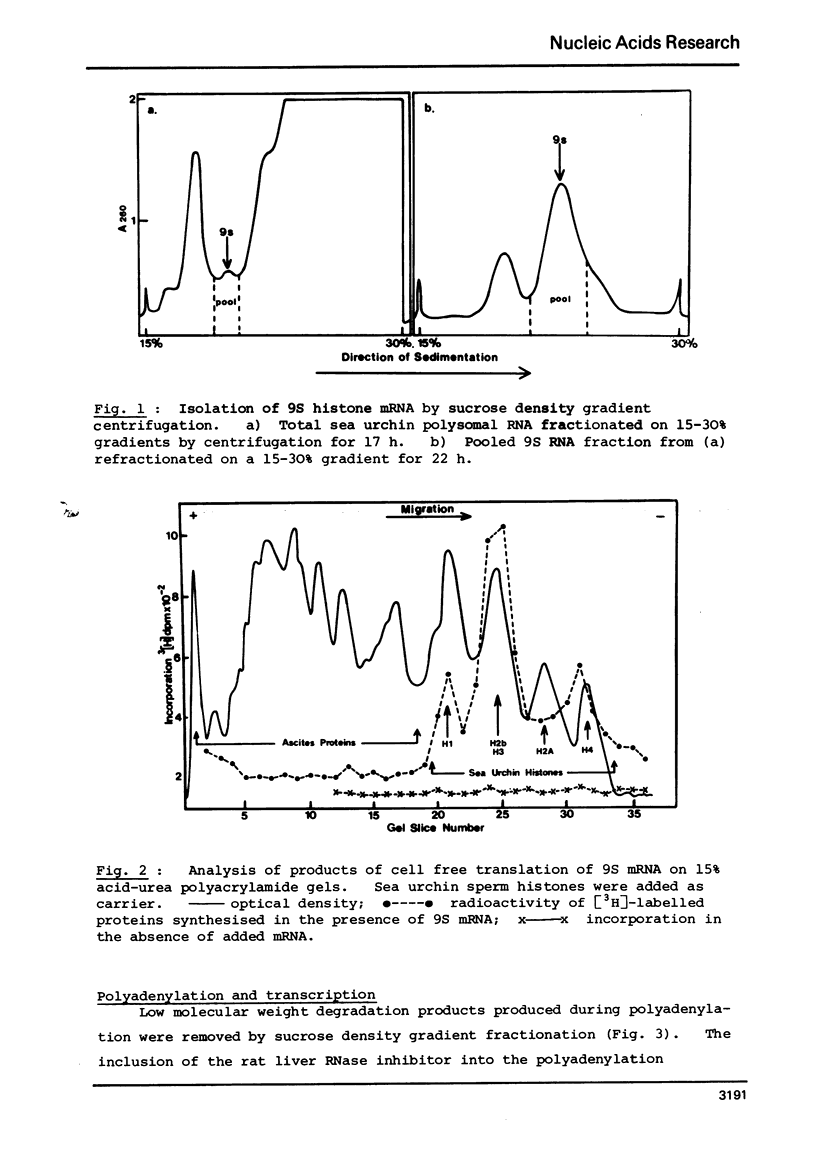
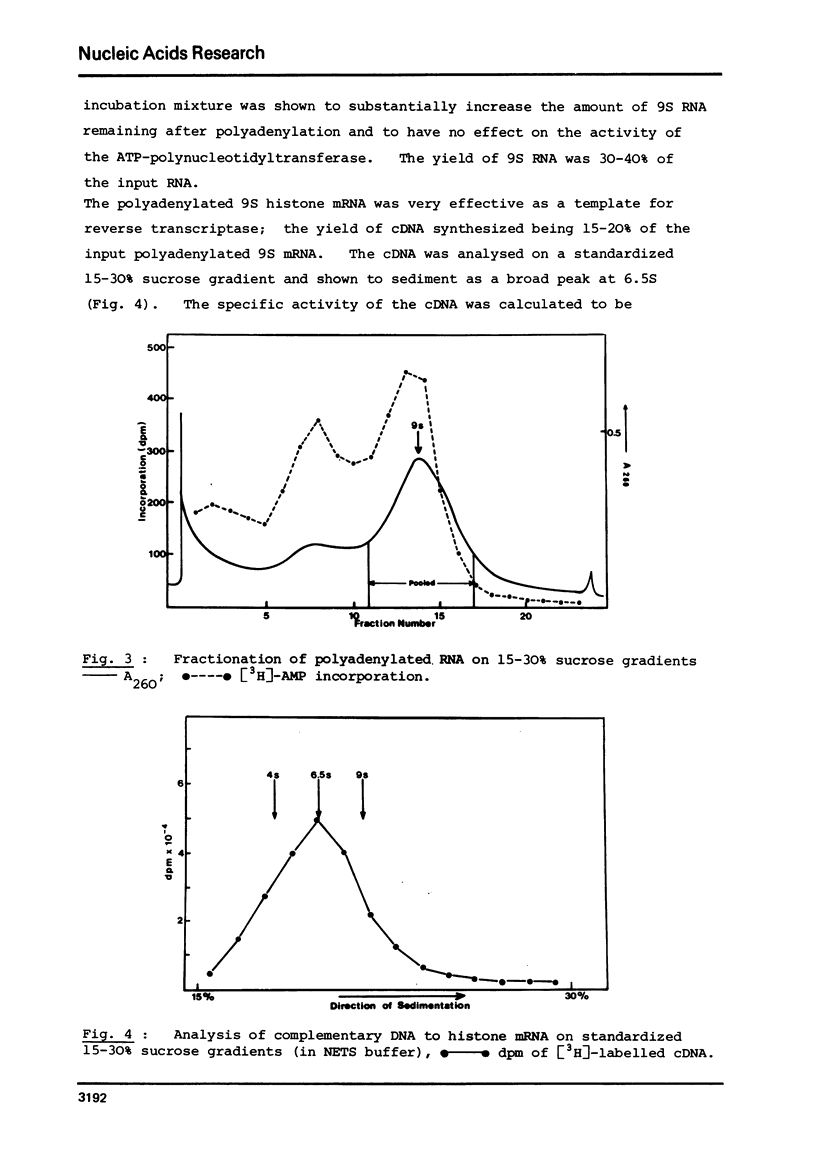
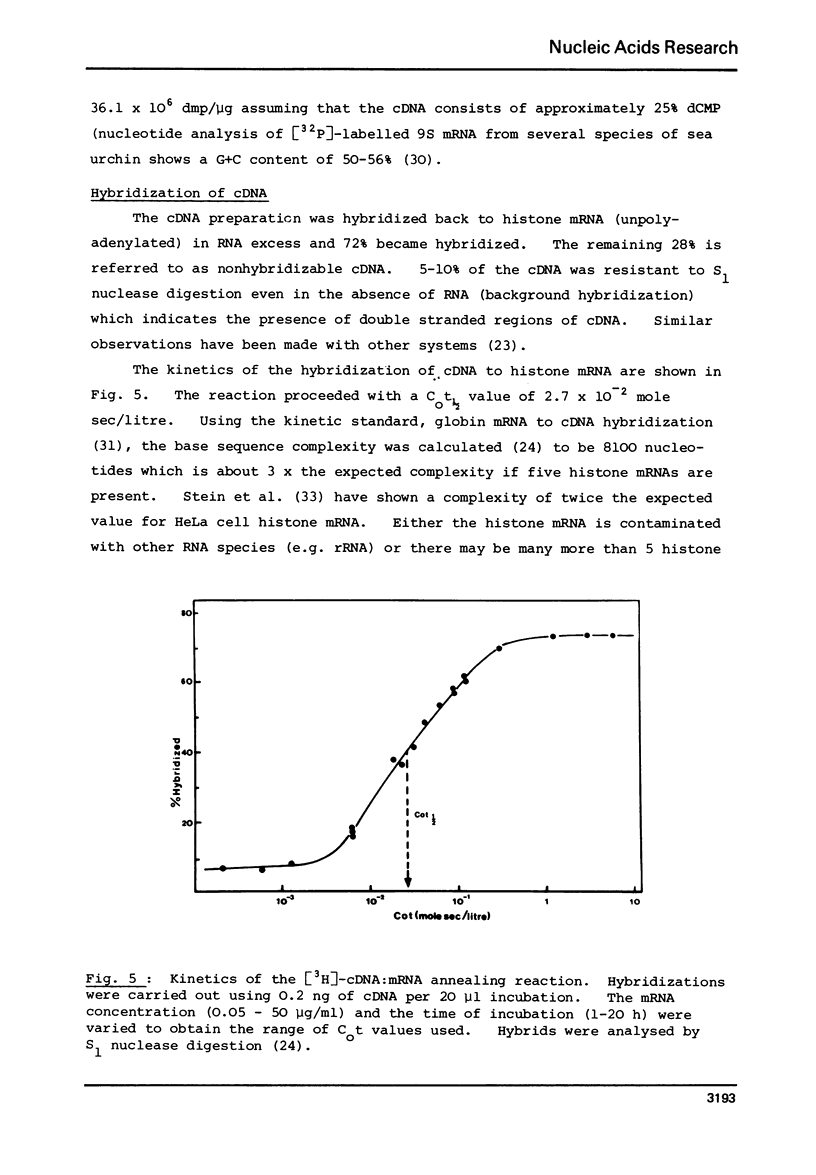
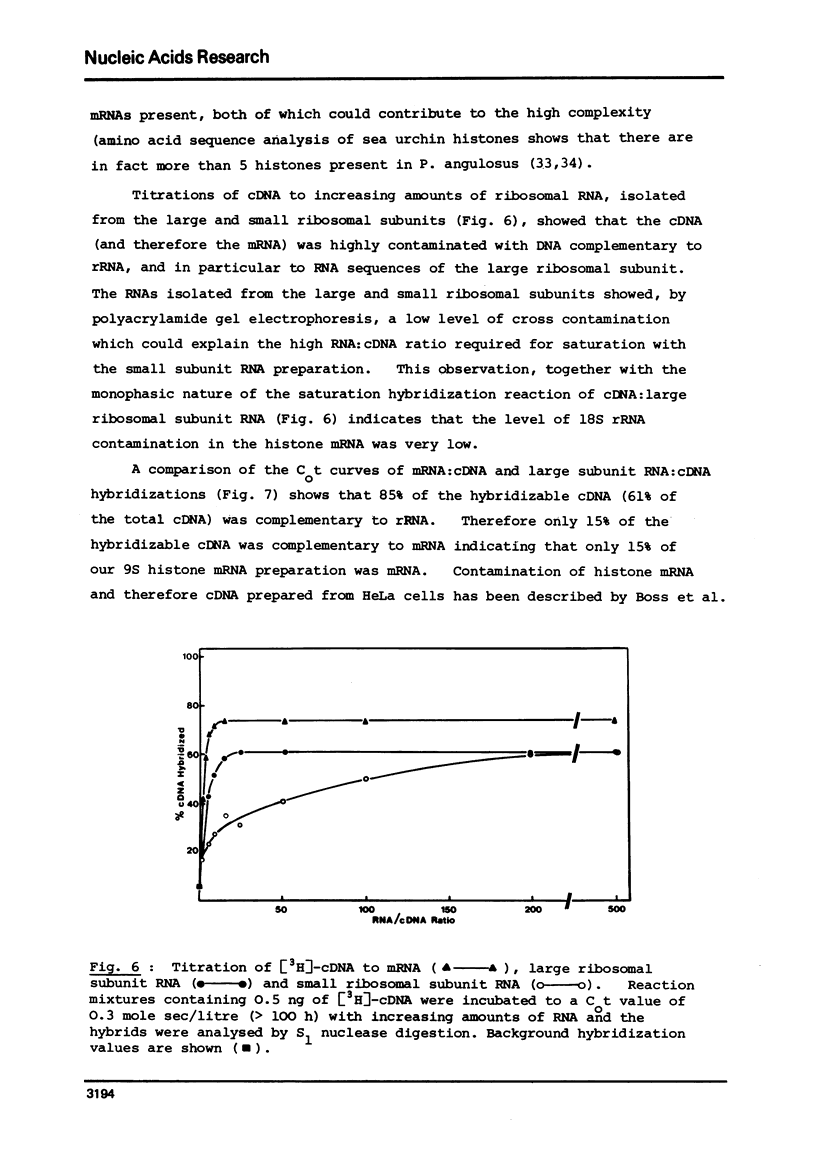
Abstract
Complementary DNA (cDNA) was transcribed from a polyadenylated sea urchin histone mRNA preparation isolated by density gradient centrifugation. By hybridization, this cDNA was shown to be extensively contaminated (85% of hybridizable cDNA) with DNA complementary to RNA derived from the large ribosomal subunit. Purification of a mRNA specific cDNA fraction was achieved by hybridization of purified rRNA to cDNA followed by fractionation on hydroxyapatite. After further purification to remove nonhybridizable cDNA our purified cDNA showed only 8% hybirdization to rRNA.
Full text
PDF



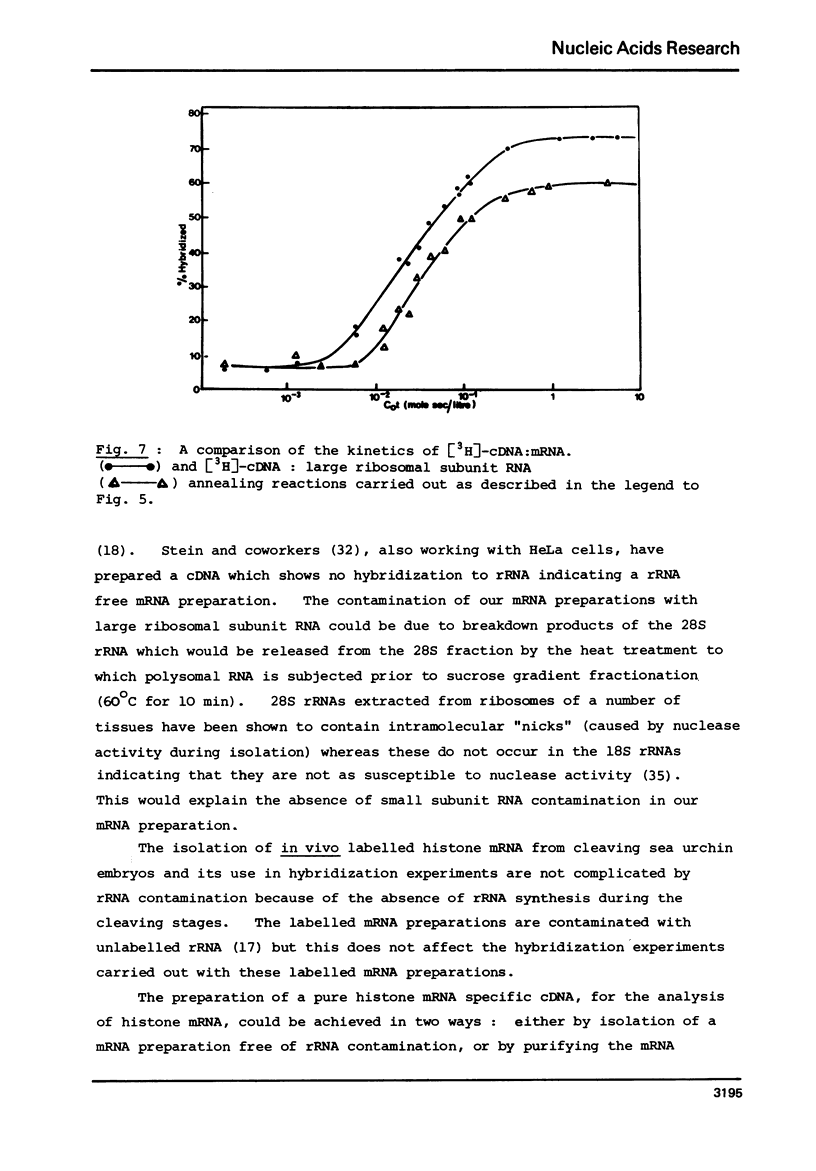

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Darnell J. E. Biogenesis and characterization of histone messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M., Telford J., Weinberg E., Stafford D. Isolation and some properties of the genes coding for histone proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2900–2904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos E., Roskam W., Gallwitz D. Partial purification and characterization of individual histone messenger RNAs from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Nov 22;73(2):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90722-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G., Mendecki J., Lee S. Y. A procedure for the isolation of mammalian messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):637–641. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn R. H., Lowry J. C., Kedes L. H. Histone genes of the sea urchin (S. purpuratus) cloned in E coli: order, polarity, and strandedness of the five histone-coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):147–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromson D., Duchastel A. Poly (A)-containing polyribosomal RNA in sea urchin embryos: changes in proportion during development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 10;378(3):394–404. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getz M. J., Birnie G. D., Young B. D., MacPhail E., Paul J. A kinetic estimation of base sequence complexity of nuclear poly(A)-containing RNA in mouse Friend cells. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K., Probst E., Schaffner W., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of Psammechinus miliaris: I. Fractionation and identification of five individual histone mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):455–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K., Ruderman J., Jacobs-Lorena M., Baglioni C., Gross P. R. Cell-free synthesis of histones directed by messenger RNA from sea urchin embryos. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):272–274. doi: 10.1038/newbio241272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Levy S., Schedl P., Kedes L. Messenger RNAs for individual histone proteins: fingerprint analysis and in vitro translation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:717–724. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. R., Birnie G. D., Hell A., Humphries S., Young B. D., Paul J. Kinetic studies of gene frequency. I. Use of a DNA copy of reticulocyte 9 S RNA to estimate globin gene dosage in mouse tissues. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 25;84(4):539–554. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hell A., Young B. D., Birnie G. D. Synthesis of DNAs complementary to human ribosomal RNAs polyadenylated in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 2;442(1):37–49. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs-Lorena M., Baglioni C. Characterization of a mouse ascites cell-free system. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4970–4974. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Birnstiel M. L. Reiteration and clustering of DNA sequences complementary to histone messenger RNA. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 7;230(14):165–169. doi: 10.1038/newbio230165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Cohn R. H., Lowry J. C., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. The organization of sea urchin histone genes. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90185-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Gross P. R., Cognetti G., Hunter A. L. Synthesis of nuclear and chromosomal proteins on light polyribosomes during cleavage in the sea urchin embryo. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):337–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Gross P. R. Identification in cleaving embryos of three RNA species serving as templates for the synthesis of nuclear proteins. Nature. 1969 Sep 27;223(5213):1335–1339. doi: 10.1038/2231335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Gross P. R. Synthesis and function of messenger RNA during early embryonic development. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 28;42(3):559–575. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S., Wood P., Grunstein M., Kedes L. Individual histone messenger RNAs: identification by template activity. Cell. 1975 Mar;4(3):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mans R. J., Huff N. J. Utilization of ribonucleic acid and deoxyoligomer primers for polyadenylic acid synthesis by adenosine triphosphate: polynucleotidylexotransferase from maize. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3672–3678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Schimke R. T. Ovalbumin messenger RNA: evidence that the initial product of transcription is the same size as polysomal ovalbumin messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4327–4331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moav B., Nemer M. Histone synthesis. Assignment to a special class of polyribosomes in sea urchin embryos. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 2;10(5):881–888. doi: 10.1021/bi00781a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M. Preparation of RNA from animal cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;7:23–51. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61770-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old J., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Ottolenghi S., Comi P., Giglioni B., Mitchell J., Tolstoshev P., Williamson R. A direct estimate of the number of human gamma-globin genes. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. S., Park W. D., Thrall C. L., Mans R. J., Stein J. L. Cell cycle stage-specific transcription of histone genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):945–949. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90660-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G., Park W., Thrall C., Mans R., Stein J. Regulation of cell cycle stage-specific transcription of histone genes from chromatin by non-histone chromosomal proteins. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):764–767. doi: 10.1038/257764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrall C. L., Park W. D., Rashba H. W., Stein J. L., Mans R. J., Stein G. S. In vitro synthesis of DNA complementary to polyadenylated histone messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1443–1449. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. S., Birnstiel M. L., Purdom I. F., Williamson R. Genes coding for polysomal 9S RNA of sea urchins: conservation and divergence. Nature. 1972 Nov 24;240(5378):225–228. doi: 10.1038/240225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Holmes D. S., Davidson N., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H. The relative positions of sea urchin histone genes on the chimeric plasmids pSp2 and pSp17 as studied by electronmicroscopy. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. D., Harrison P. R., Gilmour R. S., Birnie G. D., Hell A., Humphries S., Paul J. Kinetic studies of gene frequency. II. Complexity of globin complementary DNA and its hybridization characteristics. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 25;84(4):555–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


