Abstract
Sustained Ca2+ entry into CD4+CD8+ double-positive thymocytes is required for positive selection. We identified a voltage-gated Na+ channel (VGSC), essential for positive selection of CD4+ T cells. Pharmacological inhibition of VGSC activity inhibitedsustained Ca2+ influx induced by positive-selecting ligands and in vitro positive selection of CD4+ but not CD8+ T cells. In vivo shRNA knockdown of Scn5a specifically inhibited positive selection of CD4+ T cells. Ectopic expression of VGSC in peripheral AND CD4+ T cells bestowed the ability to respond to a positively selecting ligand, directly demonstrating VGSC expression was responsible for increased sensitivity. Thus active VGSCs in thymocytes provide a mechanism by which a weak positive selecting signal can induce sustained Ca2+ signals required for CD4+ T cell development.
Introduction
Generation of the adaptive immune response requires production of a diverse T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire that recognizes a wide range of foreign pathogens, while concurrently eliminating self-reactive T cells1–3. The stringent processes of positive and negative selection establish this anticipatory TCR repertoire during thymocyte development. In positive selection, a weak yet productive TCR-self-peptide–major histocompatibility complex (MHC) interaction rescues CD4+CD8+ double-positive (DP) thymocytes expressing TCRs capable of peptide–self-MHC recognition from death by neglect. In negative selection, a strong TCR-self-peptide–MHC interaction results in thymocyte death, thus deleting potentially self-reactive DP thymocytes1-3. Discrimination between “weak” and “strong” TCR-pMHC interactions is currently thought to depend upon the duration of activation of the critical signaling molecules Ca2+ 4-8and Erk9,10. However, the mechanism by which a weak TCR-self-peptide–MHC interaction induces and maintains sustained Ca2+ and Erk signals during successful positive selection has been unknown. While the Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) pathway is crucial for peripheral T cell functions8,11,12, genetic depletion of its two key components (ORAI and STIM) has no effect on positive selection of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells8,13-15, suggesting that Ca2+ signals of DP thymocytes during selection is complicated and may involve undefined ion channels in regulating a sustained Ca2+ signal during positive selection.
Here we report a previously unknown role for a voltage-gated Na+ channel (VGSC) in the sustained Ca2+ entry in non-excitable DP thymocytes that is necessary for positive selection of CD4+ T cells. We have previously identified the peptide gp250 as a naturally occurring self-peptide that positively selects thymocytes from the TCR transgenic mouse, AND, specific for moth cytochrome c (MCC)–I-Ek 16. Despite the apparent weak affinity of the AND TCR for gp250–I-Ek in solution, gp250–I-Ek induced a sustained Ca2+ signal and in vitro positive selection of AND thymocytes, whereas the MCC agonist induced a transient Ca2+ signal and negative selection. Comparison of transcripts of AND DP thymocytes stimulated with gp250–I-Ek with those stimulated with MCC–I-Ek identified several candidate genes that might function specifically in positive selection. Through analysis of these candidates, we observed that a VGSC (composed of a pore-forming SCN5A subunit and a regulatory SCN4B subunit) induced sustained Ca2+ influx during positive selection of AND T cells. Specific pharmacological blockade of the VGSC with tetrodotoxin (TTX) inhibited gp250-stimulated sustained Ca2+ signal, and importantly abolished positive selection of AND thymocytes in reaggregate thymic cultures. Animmunoglobulin (Ig) fusion protein of SCN4B extracelluar Ig domain inhibited the gp250-stimulated Ca2+ signal and the positive selection of AND DP thymocytes, highlighting a critical role for this region of the SCN4B subunit during thymocyte selection. In non-transgenic, chimeric C57BL/6 mice reconstituted with bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells expressing shRNA that silenced expression of SCN5A, reduced positive selection of CD4SP thymocytes confirmed a requirement for VGSC during positive selection in vivo. To substantiate our model, we explored the role of VGSC in antigen sensitivity of peripheral T cells by conducting a gain-of-function assay. We reconstituted peripheral AND TCR transgenic CD4+ T cells, which normally do not express VGSC, with human SCN5A and SCN4B. The human VGSC-reconstituted AND CD4+ T cells acquired the ability to respond to positively selecting ligand gp250, to which they normally do not respond. Thus, the expression of a VGSC in DP thymocytes provides a mechanism through which a weak positive selection signal is amplified and sustained, resulting in the developmental process of positive selection.
Results
gp250 induces sustained Ca2+ flux
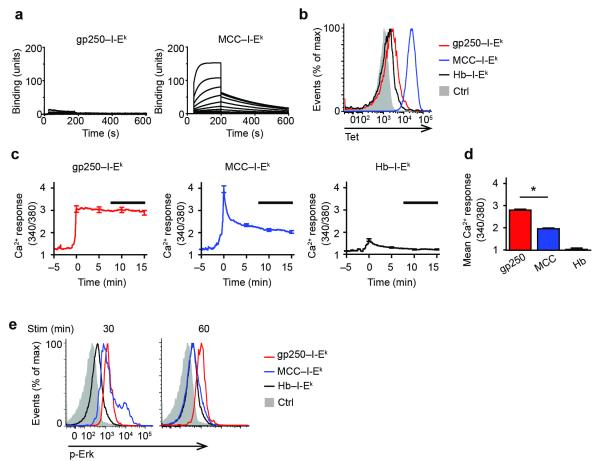
The endogenous positively selecting peptide gp250 for AND TCR has no homology with the agonist MCC ligand, but is recognized with a high degree of specificity. Surface plasmon resonance analysis showed that the binding affinity for AND TCR with gp250– I-Ek is very weak (>500 μM), in comparison to MCC–I-Ek (~13μM) (Fig. 1a). Staining AND DP thymocytes with gp250–I-Ek tetramers confirmed this weak affinity (Fig. 1b). To examine early signaling events, we investigated Ca2+ influx in pre-selected AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes stimulated with plate-bound gp250–I-Ek Ig dimers. AND thymocytes are not selected on an H-2d background and are therefore arrested as pre-selection DP thymocytes, while expression of the transgenic TCR on the Rag1−/− background prevents expression of other TCR specificities. Thus, essentially all thymocytes from AND.Rag1−/−H-2d mice are resting, pre-selected DP thymocytes. Using Fura-2 AM based ratiometric imaging, we compared the pattern of Ca2+ influx in pre-selected AND DP thymocytes stimulated with the positively-selecting peptide gp250–I-Ek, the negatively-selecting agonist peptide MCC–I-Ek or a non-selecting control peptide hemoglobin (Hb)–I-Ek. gp250–I-Ek stimulated a strong and sustained Ca2+ influx (Fig. 1c; Supplementary Fig. 1a), which was maintained at the peak level for more than 15 minutes, consistent with Ca2+ responses observed during positive selection. In contrast, MCC–I-Ek stimulated a transient Ca2+ influx with a strong initial peak but rapid diminution, similar to Ca2+ fluxes observed in negative selection (Fig. 1c; Supplementary Fig. 1b). The difference in sustained Ca2+ influx from 7.5 to 15 minutes induced by gp250–I-Ek and MCC–I-Ek was highly significant (Fig. 1d). Phosphorylation of Erk was also sustained by stimulation with gp250–I-Ek, but not by stimulation with MCC–I-Ek (Fig. 1e). Thus, the positively selecting ligand gp250, despite its weak interaction with the AND TCR, induces sustained Ca2+ signaling and Erk phosphorylation in DP thymocytes, whereas the agonist MCC induces a strong yet transient signal.
Figure 1.
gp250 ligand induces sustained Ca2+ signals in AND DP thymocytes. (a) Equilibrium binding of soluble AND TCR to biotinylated gp250–I-Ek and MCC–I-Ek ligand at various concentrations of soluble AND TCR. Sample SPR sensorgrams were used to determine binding affinity of soluble AND TCR to gp250–I-Ek (KD > 500 μM) or MCC–I-Ek (KD = 13.03 μM). n = 2. (b) Tetramerized biotinylated gp250–I-Ek or MCC–I-Ek staining of AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes. Hb–I-Ek and hCLIP/I-Ab tetramer (Ctrl) were used as negative controls. n = 3. (c) Fura-2 AM ratios for AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes stimulated with gp250–I-Ek, MCC–I-Ek, or Hb–I-Ek. Traces represent Fura-2 AM ratio mean ± s.e.m (n = 50) as a function of time. Curves for each cell (Supplementary Fig. 1) were adjusted to time 0 being when the Ca2+ influx started. Black bar indicates the time from 7.5 to 15 min used for the summary of mean ratios in (d) of 250 cells in five experiments. *P < 0.0001 by two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. (e) Erk phosphorylation of AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes induced by gp250–I-Ek, MCC– I-Ek, Hb–I-Ek at 30 min and 60 min of stimulation time.
Pre-selected DP thymocytes express VGSC components
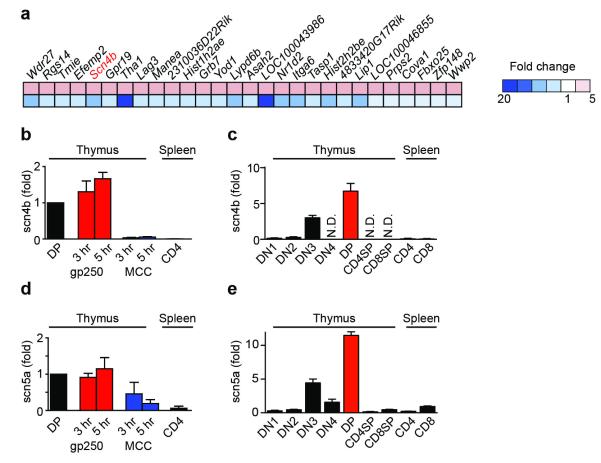
To identify genes critical for the gp250-induced sustained Ca2+ influx, we performed transcriptional profiling of DP thymocytes. Pre-selected AND DP thymocytes were stimulated for seven hours with I-Ek Ig dimers loaded with the positively-selecting peptide gp250, the negatively-selecting agonist peptide MCC, or the non-selecting control peptide Hb. We identified 28 genes upregulated by positive selection and downregulated in response to negative selection (Fig. 2a). Only one of these 28 genes, Scn4b, encoded an ion channel-related protein17–19. Scn4b encodes a regulatory β subunit of VGSCs. We first confirmed by qRT-PCR that gp250 stimulation of AND DP thymocytes maintained the expression of Scn4b transcripts, while MCC stimulation downregulated Scn4b expression (Fig. 2b). Next, we confirmed that Scn4b was highly expressed in normal C57BL/6 DP thymocytes, but not in mature single-positive thymocytes or peripheral T cells (Fig. 2c). Thus, expression of Scn4b transcripts precisely correlated with positive selection both in vivo and in vitro, indicating that SCN4B may participate in signaling during positive selection.
Figure 2.
Expression of Scn5a-Scn4b VGSC during the course of positive selection. (a) Transcriptional profiling analysis of 28 differentially expressed genes upregulated by gp250–I-Ek and simultaneously downregulated by MCC–I-Ek in AND Rag1−/− H-2d DP thymocytes after 7 h stimulation. (b, c) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Scn4b mRNA expression in pre-selected AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes stimulated with gp250–I-Ek and MCC–I-Ek for various times of incubation (b) or in various cell subsets sorted by flow cytometry (c). (d, e) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Scn5a mRNA expression in pre-selected AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes stimulated with gp250–I-Ek and MCC–I-Ek for various times of incubation (d) or in various cell subsets sorted by flow cytometry (e). Results (mean ± s.d.; n = 2) are presented relative to Actb expression.
The functions of VGSCs have been extensively characterized in excitable cells, such as neurons and muscle cells, but have not been studied previously in T cell development20. VGSCs are composed of a pore-forming α subunit along with one or two auxiliary regulatory β subunits20,21. SCN4B, a VGSC β subunit, could potentially interact with ten different VGSC α subunits20. To identify the pore-forming α subunit in DP thymocytes that pairs with SCN4B, we assessed which of ten potential VGSC α subunits are expressed in pre-selected DP T cells. SCN5A was the VGSC α subunit most highly expressed in pre-selected DP thymocytes, as assessed by qRT-PCR, and is thus the strongest candidate to form the pore of VGSCs in pre-selected DP thymocytes (Supplementary Fig. 2). Expression of Scn5a transcripts, like those of Scn4b, correlated with positive selection (DP) and β-selection (DN3) checkpoints in thymocyte development (Fig. 2e). The expression of Scn5a mRNA was maintained during gp250–I-Ek stimulation but decreased during MCC–I-Ek stimulation (Fig. 2d). Thus, DP thymocytes express both pore-forming (SCN5A) and regulatory (SCN4B) subunits of a VGSC, and expression of both subunits was specifically maintained by a positive selection signal.
Blocking VGSC pore activity impairs positive selection
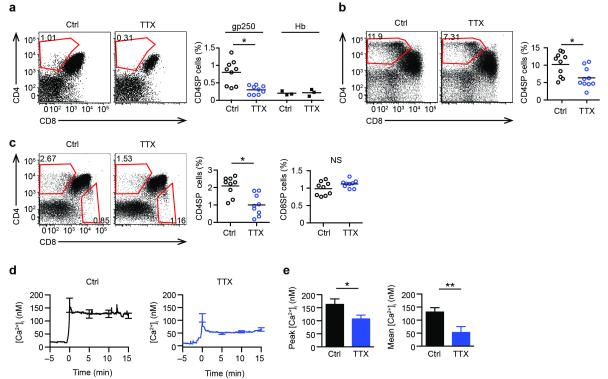
To ascertain if a VGSC was required in positive selection, pre-selected AND DP thymocytes were treated with tetrodotoxin (TTX), a specific inhibitor of VGSCs22, in gp250-induced reaggregate culture. TTX blocks Na+ entry into cells through VGSC α subunits, with SCN5A being in the subset which requires higher TTX concentrations to inhibit20,21. Blockade of VGSCs abolished gp250-mediated positive selection of AND CD4+ T cells in reaggregate culture (Fig. 3a). Furthermore, TTX treatment inhibited the upregulation of the positive selection markers, TCR and CD69 on DP thymocytes stimulated with gp250 (Supplementary Fig. 3). In the reaggregate cultures, we have utilized the unstimulated ANV41.2 cortical thymic epithelial cell line transfected with I-Ek under a viral promoter, to minimize the number of endogenous positive-selecting ligands, allowing us to add known self-peptides, such as gp250. ANV41.2 cells, after treatment with interferon-γ (IFN-γ), upregulate MHC class I and II molecules and the antigen processing components, thereby presenting large numbers of endogenous peptides capable of inducing efficient positive selection, including AND and polyclonal T cells. With a wide range of positively selecting self-peptides induced by IFN-γ, TTX treatment also repressed the positive selection of AND CD4+ T cells in reaggregate culture (Fig. 3b). When polyclonal DP thymocytes from B6.K (H-2k) mice were added to the reaggregate cultures, a significant CD4+ population developed which was inhibited by TTX treatment (Fig. 3c), whereas the CD8SP T cell population that developed was not inhibited by TTX (Fig. 3c). This finding suggests that the VGSC is more critical for positive selection of CD4+ T cells than CD8+ T cells. Finally, TTX-mediated inhibition of VGSC pore activity greatly diminished the sustained Ca2+ flux induced by gp250 stimulation from 131 nM to 52 nM (Fig. 3d,e), but did not alter the Ca2+ flux induced by MCC agonist stimulation, a negative selection condition (Supplementary Fig. 4a). In high-dose MCC reaggregrate cultures, there was a disappearance of DP thymocytes regardless of the presence or absence of TTX, indicating the dispensable role of VGSC in negative selection (Supplementary Fig. 4b). Together, these observations demonstrate that VGSC pore activity is critical to modulate sustained Ca2+ signaling and is thus essential for positive selection.
Figure 3.
Pore-forming SCN5A subunit is critical in positive selection. (a, b, c) Left: Flow cytometry of thymocyte differentiation induced in reaggregate culture with or without TTX (1 μM). Right: Quantification of percent subpopulation; each symbol represents a reaggregate culture. All P values were calculated by two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. (a) Pre-selected AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes were cultured for 96 h with I-Ek transfected ANV41.2 cells along with 30 μM gp250 peptide with vehicle or TTX (mean ± s.d.; n = 9 in three experiments; *P = 0.007). (b) ANV41.2 cells were treated with IFN-γ for 24 h (100 units/ml), and cultured with pre-selected AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes for four days with vehicle or TTX (mean ± s.d.; n = 10 in three experiments; *P = 0.0068). (c) Pre-selected CD53− B6.K DP thymocytes were cultured with IFN-γ treated ANV41.2 cells with or without TTX (mean ± s.d.; n = 9 in three experiments; *P = 0.0027). (d) Fura-2 AM Ca2+ ratios of AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes stimulated with gp250–I-Ek with vehicle or TTX. (e) Summary of peak and average of intracellular Ca2+ concentration from 7.5 to 15 min of two experiments each involving 50 cells (*P = 0.0099; **P < 0.0001).
SCN4B extracellular domain regulates pore activity
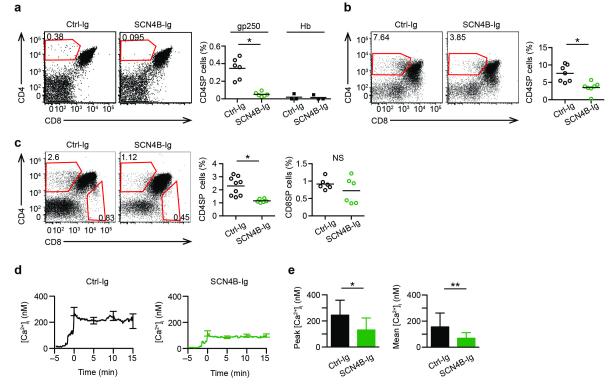
The SCN4B protein contains one extracellular Ig domain, a single transmembrane segment, and a short intracellular tail. In excitable cells, the regulatory β subunits of the VGSCs have been shown to facilitate cell-cell interactions through the extracellular Ig domain and modulate VGSC channel gating through either the extracellular Ig domain or the intracellular tail, which may favor an open VGSC at depolarized potentials17–19. Thus, the SCN4B extracellular Ig domain may interact with Ig domains of other adhesion molecules on cortical thymic epithelial cells to facilitate cell-cell interaction, or may act in cis with the extracellular portion of SCN5A pore subunit regulating the pore activity23,24. To study the importance of the extracellular Ig domain of SCN4B, we generated SCN4B-Ig fusion protein that would saturate potential ligands of SCN4B and thus disrupt the cis- or trans-interaction mediated by SCN4B. The SCN4B-Ig fusion protein inhibited in vitro positive selection of AND thymocytes in gp250-mediated (Fig. 4a) or IFN-γ stimulated (Fig. 4b) reaggregate culture, while an unrelated Ig fusion protein did not. The SCN4B-Ig fusion protein also inhibited the positive selection of CD4+ polyclonal B6.K thymocytes, but not the selection of CD8+ T cells (Fig. 4c). These findings demonstrate that SCN4B is essential for positive selection of CD4+ T cells in vitro.
Figure 4.
A regulatory subunit SCN4B is critical in positive selection. (a, b, c) Left: Flow cytometry of thymocyte differentiation induced in reaggregate culture. The reaggregate cultures in a,b,c were set up as described in Fig. 3a,b,c respectively, with treatment of SCN4B-Ig or unrelated Ctrl-Ig (Ceacam4-Ig) fusion protein. Right: Quantification of percent subpopulation; each symbol represents a reaggregate culture. All P values were calculated by two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. (a) gp250 induced AND CD4SP positive selection with SCN4B-Ig or Ctrl-Ig (10 μg; mean ± s.d.; n = 6 in three experiments; *P = 0.0022). (b) Positive selection of AND CD4SP T cells induced by IFN-γ–treated ANV41.2 cells with 10 μg SCN4B-Ig or Ctrl-Ig (mean ± s.d.; n = 7 in three experiments; *P = 0.0041). (c) Positive selection of polyclonal pre-selected B6.K DP thymocytes with 1 μg SCN4B-Ig or Ctrl-Ig (mean ± s.d.; n = 9 in three experiments; *P = 0.0018). (d) Fura-2 Ca2+ flux of pre-selected AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes stimulated with gp250–I-Ek with SCN4B-Ig or Ctrl-Ig (1 μg). (e) Summary of peak and mean value of intracellular Ca2+ concentration from 7.5 to 15 min of two experiments each involving 50 cells (*P < 0.0001; **P < 0.0001)
To determine if the SCN4B Ig domain was acting in cis or trans, we assessed the effect of SCN4B-Ig fusion protein on the Ca2+ response, in which the DP thymocytes are the only cells present in the assay. In vitro, SCN4B-Ig fusion protein inhibited the gp250-induced Ca2+ responses of AND pre-selected DP thymocytes to the pattern similar to TTX treatment (Fig. 4d,e). This finding supports the concept that the SCN4B extracellular domain is essential for positive selection by its regulation of the SCN5a pore in cis.
Scn5a shRNA knockdown impairs CD4SP positive selection
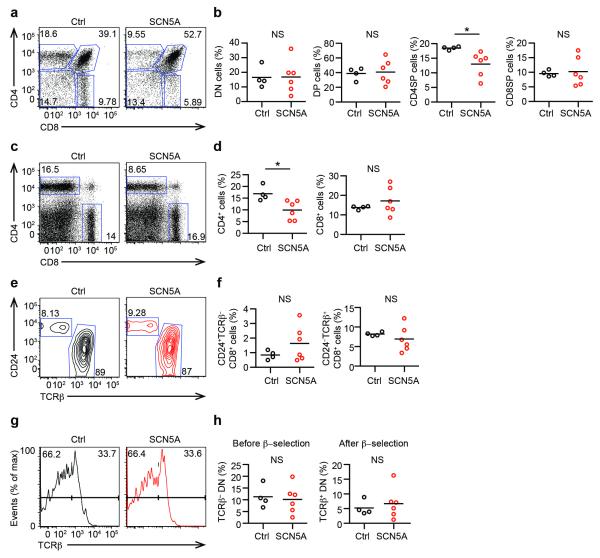
We obtained in vivo genetic evidence of the requirement for VGSCs in positive selection, using bone marrow chimeras that expressed shRNAs that silenced Scn5a expression in hematopoietic stem cells. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) was used as a marker of transduction. Because of the lability of non-proliferating DP thymocytes, we could not lentivirally transduce DP thymocytes in sufficient numbers to allow for immunoblot analyses. Through in vitro single cell-based Ca2+ flux experiments, we successfully identified a pool of two shRNA-GFP lentiviruses that targeted Scn5a and reduced the sustained Ca2+ flux in gp250–I-Ek stimulated GFP+ AND DP thymocytes (Supplementary Fig. 5a,b). Control cells were transfected with a “non-target” scramble-GFP shRNA that targets no mouse transcripts, with which all on-target effects were compared. The GFP+ cells transduced with scramble-GFP shRNA showed no known reduction in the gp250-induced sustained Ca2+ flux. Ly5.1+B6 Sca-1+c-kit+ hematopoietic stem cells were then infected with lentiviruses expressing a pool of two SCN5A-GFP shRNAs or control scramble-GFP shRNA, and intravenously injected into lethally irradiated B6 donors. After 12 weeks, SCN5A-shRNA knockdown revealed a significant reduction of the CD4SP thymocyte populations from 18.5% to 13.2%, compared to the control groups (Fig. 5a,b; Supplementary Fig. 5c,d). A similar loss of mature CD4+ T cells was also observed in the periphery (Fig. 5c,d; Supplementary Fig. 5d). In contrast, there was no decrease in the DN or DP populations, and a slight increase in the CD8SP thymocyte population (9.58% versus 10.02%; Fig. 5b). Separation of the CD8SP population into mature CD8SP and immature CD8SP, revealed that the slight increase (Fig. 5b) resulted from the accumulation of immature CD8SP T cells (Fig. 5e,f), whereas the TCRβ+CD24− mature CD8SP population was not significantly increased (Fig. 5e,f). No apparent difference in TCRβ upregulation in DN cells was observed (Fig. 5g,h), suggesting a dispensable or less critical role of SCN5A in β-selection. The inhibition of CD4SP selection, but not CD8SP, is consistent with what we observed with TTX inhibition of in vitro positive selection of B6.K thymocytes (Fig. 3c). This differential effect on CD4SP cells is consistent with current linage commitment models in which CD4SP cells require a sustained strong signal, compared to CD8SP T cells2,3. Thus, shRNA knockdown of Scn5a significantly decreased development of CD4+ T cells in B6 mice, establishing the importance of a VGSC in positive selection in vivo.
Figure 5.
shRNA knockdown of Scn5a impairs the positive selection of CD4SP cells in vivo. Flow cytometry analysis of thymocytes and splenocytes from lethally-irradiated bone marrow B6 chimeras reconstituted with Ly5.1+ B6 HSC transduced with lentiviruses expressing scramble-GFP or SCN5A-GFP shRNA. Recipient mice were analyzed after 12 weeks and summarized in scatter plots (scramble-GFP, n = 4, SCN5A-GFP, n = 6 in two experiments; two-tailed Mann-Whitney test was used for statistic analysis). Each symbol presents an individual mouse. (a) Flow cytometry of thymocytes gated on Ly5.1+GFP+ cells from recipient mice. (b) Quantification of percent DN, DP, CD4SP and CD8SP thymus population out of Ly5.1+GFP+ cells (*P = 0.0095) . (c) Flow cytometry of CD4+ and CD8+ splenocytes. Gated on Ly5.1+GFP+ cells. (d) Percent of splenotcytes of the recipient mice (*P = 0.0095). (e) Flow cytometry of immature CD8SP (CD24+TCRβ−) and mature CD8SP (CD24−TCRβ+). Gated on Ly5.1+GFP+ CD8SP thymocytes. (f) Summary of percent of immature and mature CD8SP. (g) Representative histogram of TCRβ expression on DN cells in the presence of scramble-GFP or SCN5A-GFP. Gated on Ly5.1+GFP+ DN thymocytes. (h) Percent of TCRβ−DN and TCRβ+DN recovered from recipient mice. Gated on Ly5.1+GFP+DN cells.
VGSC reconstitution enhances sensitivity to gp250
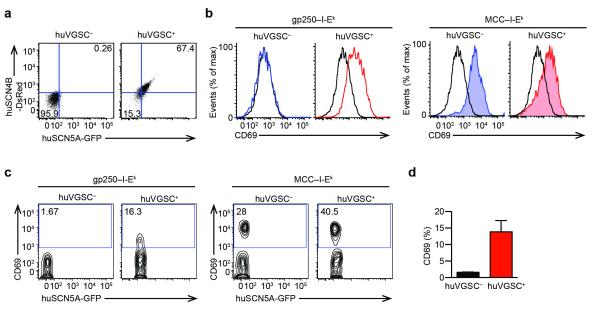
Pre-selected thymocytes are known to be more sensitive to TCR stimulation than mature T cells25. VGSCs were specifically expressed in pre-selected thymocytes, and immediately down-regulated after thymocytes complete positive selection (Fig. 2c,e), correlating with the change in sensitivity. To examine potential contribution of VGSCs to make pre-selected thymocytes more sensitive, we generated a stable cell line from AND T cell hybridomas, which expressed human SCN5A and SCN4B proteins. Human SCN5A and SCN4B cDNA were cloned into plasmids that also encode fluorescence protein GFP and DsRed respectively. We electrophorated AND T cell hybridomas, and sorted for AND huVGSC+ hybridomas to obtain a stable cell line and test for the gain-of-function (Fig. 6a). AND huVGSC+ T cells hybridomas upregulated CD69 expression when stimulated with gp250–I-Ek, whereas the VGSC− AND cells did not (Fig. 6b). The expression of huVGSC allowed AND hybridomas to respond to positively selecting ligand stimulation, suggesting the presence of huVGSC may make T cells more sensitive. Given only pre-selected DP thymocytes express VGSC, whereas peripheral T cells do not, we then expressed human SCN5A and SCN4B in murine AND peripheral CD4+ T cells, to see if the expression of huVGSC may likely make peripheral CD4+ T cells as sensitive as pre-selected DP thymocytes. Human SCN5A and SCN4B cDNA were electroporated into peripheral AND CD4+ T cells. The huVGSC+ population of AND peripheral CD4+ T cells was stimulated by positively selecting ligand gp250, assessed by CD69 upregulation (Fig. 6c,d). Both populations responded to agonist peptide MCC stimulation (Fig. 6c). This gain-of-function study strongly supports our hypothesis that the VGSC is essential for positive selection of CD4+ T cells, by increasing the sensitivity of DP thymocytes to weak positively selecting ligand.
Figure 6.
Peripheral AND CD4+ T cells acquire the ability to respond to positively selecting ligands by expression of human VGSCs. (a) Flow cytometry of AND hybridoma transduced with huSCN5A and huSCN4B plasmids containing IRES expression of GFP and DsRED fluorescence proteins respectively. (b) CD69 upregulation on huVGSC+ AND hybridomas in response to gp250–I-Ek stimulation. huVGSC+ AND hybridomas and untransduced AND hybridomas were stimulated with plate bound gp250–I-Ek or MCC–I-Ek overnight. (c) CD69 upregulation on AND peripheral CD4+ T cells with or without the expression of huVGSC in respond to plate bound gp250–I-Ek or MCC–I-Ek stimulation. CD4+ peripheral T cells from AND.Rag1−/− H-2k mice were electroporated with human SCN5A-GFP and human SCN4B-DsRed plasmids. The post-electroporation cells were rested for 12 h, and stimulated with plate bound gp250–I-Ek or MCC–I-Ek for 10 h. (d) The bar graphs summarize the percent CD69-expressing cells in respond to gp250–I-Ek stimulation (n = 3 in two experiments; *P = 0.0139 by paired t test).
Discussion
Positive selection is an exacting process during which DP thymocytes translate a spectrum of TCR-self-peptide–MHC interactions into the physiological outcome of lineage commitment into CD4SP or CD8SP T cells or death1,2. The molecules exclusively required for positive selection or specific lineage commitments are still poorly understood. Here we identify a previously unknown role for a VGSC in the positive selection of CD4+ T cells. The specific expression of a SCN5A-SCN4B VGSC in DP thymocytes endows these cells at a crucial developmental stage to respond to positively selecting signals, thereby translating weak signals into a sustained one. After maturing into CD4+ or CD8+ T cells and emigrating to the periphery, T cells are poised to recognize foreign antigens. Furthermore, SCN5A is not expressed in mature CD4+ T cells. Thus, stage specific expression of a VGSC empowers a DP thymocyte to respond to a peptide-MHC ligand, whereas no expression in peripheral T cells avoids autoreactivity. Interestingly, in the B cell lineage, Scn4b is only expressed at the pre-B and pro-B stages26, where weak receptor signals are critically involved in B cell development.
How do VGSCs increase the sensitivity of DP thymocytes to weak positively selecting ligand; how are they activated by downstream of the TCR signal, how are they regulated, and how are they involved in activating sustained Ca2+ signal? In neurons and muscle cells, VGSC-mediated Na+ fluxes may lead to Ca2+ elevation through the activation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (CaV)27–30; the regulatory subunit SCN4B may mediate high frequency firing19; the activity of pore SCN5A may be modulated by phosphorylation through several protein kinases, including Fyn, PKC, PKA, CaMKII and calmodulin31. In lymphocytes, essentially nothing is known about how a VGSC functions, but it is possible that activation of a protein kinase downstream of the TCR is important for activation of VGSC. In peripheral T cells, store-operated Ca2+ entry through CRAC channels is the main pathway to increase intracellular Ca2+ concentration8,11,12, but T cell development and positive selection is normal in multiple separate knockouts of STIM and ORAI13–15. One possibility is that there is/are undefined channel(s) involved, which might function independently of STIM and ORAI, and might control the Ca2+ influx into DP thymocytes during positive selection8. Or alternatively, CRAC channels play an important but redundant role. An intriguing possibility is that DP thymocytes may dominantly use a non-store-operated Ca2+ channels during positive selection. In a recent study, L-type CaV-mediated voltage-gated Ca2+ current was recorded in T cells, and shown to be involved in peripheral T cell maintenance and CD4+ T cell lineage commitment32. It would be informative to see if VGSCs may serve as a linkage, followed by receiving positive selection TCR signal, to activate L-type CaV channel or other channels which may carry Ca2+ to allow sustained Ca2+ influx into DP thymocytes.
In our studies, negative selection induced a stronger Ca2+ flux, and such a higher Ca2+ peak might play a key role in inhibiting channel activity and decreasing transcript expression. On the other hand, a weaker yet more sustained Ca2+ flux may activate calcineurin- and Erk-dependent pathways, leading to survival and maturation. We believe it is the function of sustained kinetics of Ca2+ flux that is key to support positive selection, as recently suggested2,3, rather than a function of the magnitude of Ca2+ flux. Along with our observation, a previous study examined Ca2+ response in MHCII-restricted positive selection in thymic slices, and found that the naturally occurring positive selection on H-2k thymic slices induced a positive selection signal specific sustained oscillation6. Notably, in this model using thymic slices, pre-selected thymocytes may freely move around and sample multiple positively selecting ligands to result in the sustained Ca2+ oscillation. However, in our system, the pre-selected thymocytes in vitro were forced to receive repetitive stimulation from the same positively selecting ligands leading to sustained signaling. The Ca2+ kinetics in MHC class I-restricted positive selection was described by others5,7. Stimulated by a positively selecting altered peptide ligand tetramers, pre-selected OT1 thymocytes induced a Ca2+ influx at a slower rate than being stimulated by agonist OVA tetramer7. Also, macrophages pulsed with p33 altered peptide ligand induced quantitatively different and weaker Ca2+ elevation than negative selection, and approaches a steady state and remained elevated for at least one hour5. The usage of altered peptide ligand of agonist peptides and the thymocytes expressing MHCI restricted TCR might account for some of the observed differences5,7,33 compared to our study.
Another important question raised by our study is whether VGSCs control the selection of only CD4+ T cells, or the selection of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. We showed that inhibition of VGSCs by TTX did not affect the positive selection of polyclonal CD8+ T cells. Given the starting point for the MHCI-mediated selection is the same DP population, which expresses VGSC components, we wonder if a low-affinity antigen stimulating through MHCI-restricted TCR might fail to sustain VGSC expression. There is no direct evidence for this; however, it has been suggested that naturally occurring positively selecting MHCI ligands can sustain Erk activation for the positive selection of CD8+ T cells10, which might suggest MHCI ligand can sustain the VGSC surface expression and function for a certain period of time to allow Ca2+ entry and activate Erk. Thus it remains to be determined the VGSC surface expression induced by MHCI and MHCII.
In the SCN5A knockdown experiments, we observed an inhibition in the positive selection of CD4+, but not CD8+ T cells, and we noticed the variability of the percent CD8+ T cells in the bone marrow chimeras. There are two possible explanations for this result. The first is that there is a differential sensitivity of CD4 and CD8 positive selection for SCN5A and we only achieved a partial knockdown of the Scn5a mRNA. As the asymmetric model suggests34, the CD4+ T cell commitment requires stronger and more sustained positive selection signals compared to the CD8+ T cell commitment, and our data support this model. The second hypothesis is that SCN5A controls only selection of CD4+ T cells. The variability of the percent CD8+ population might also be the consequence caused by both. If positive selection of CD8+ T cells requires less involvement of SCN5A, variable efficiency of VGSC depletion would present variable possibility for DP thymocytes to complete CD8+ T cell development. On the contrary, if CD4SP selection critically require absolute participation of SCN5A, we shall find a significant development defect in CD4SP selection with less variability from mouse to mouse, which was consistent with our observation. The knockout of SCN5A is embryonic lethal35, and therefore, a conditional knockout would be required to conclude whether the SCN5A-SCN4B VGSC controls the selection of only CD4+ T cells (such as Themis36 and Thpok/cKrox37,38), or the selection of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (such as Calcineurin39 and Bcl11b40).
A similar rationale may be applied to our other observation that SCN5A knockdown only showed the defects in CD4SP positive selection but not on β-selection of DN3 cells. A first possibility is the concern of incomplete knockdown of Scn5a mRNA. The second possibility is that only positive selection requires the participation of SCN5A, because pre-TCR selection does not involve pMHC ligand recognition, but dimerization. In the future, it would worthwhile to pursue and define the precise role of SCN5A, if any, in early T cell development. A conditional allele of SCN5A crossed to Lck-Cre mice to delete at the DN stage would be most definitive way to assess the role of VGSC in TCRβ selection.
Methods
Mice and cells
MCC–I-Ek–specific AND TCR–transgenic mice, B6.D (H-2d) mice, B6.K (H-2k), and B6 mice were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory. All mice were bred and housed in specific pathogen–free conditions of the animal facility at the Washington University Medical Center. All the use of laboratory animals was approved and done in accordance with the Washington University Division of Comparative Medicine guidelines. The ANV41.2 cortical epithelial cell line transfected with I-Ek (provided by A.G. Farr) was cultured in Iscove’s DMEM containing 10% FCS, 1x nonessential amino acids, 2 mM GlutaMax, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 0.05% gentamicin, 50 μM 2-mercaptoethanol and 0.5 mg/ml of the aminoglycoside G418.
Flow cytometry
Fluorescence-conjugated antibodies from commercial sources were as follows: fluorescein isothiocyanate–, allophycocyanin– or allophycocyanin-indodicarbocyanine– conjugated anti-CD4 (GK1.5; BioLegend); phycoerythrin-indodicarbocyanine– conjugated anti-CD8 (53-6.7; BioLegend); phycoerythrin-cy7-conjugated anti-Ly5.1 (Biolegend); phycoerythrin–, allophycocyanin– or phycoerythrin–cy7-conjugated anti-CD69 (1-11.2F3; BioLegend); LIVE/DEAD Fixable Blue Dead Cell Stain (Invitrogen); or fluorescein isothiocyanate–conjugated or biotinylated anti-Vα11 (RR8-1; BD Pharmingen). All samples were analyzed on a FACSCalibur, FACSLSRII, or FACSAria (BD) and data were analyzed with FlowJo software (TreeStar).
SPR analysis
Soluble AND TCR was generated in Escherichia coli using the chimeric expression system41. The variable regions of murine AND TCR were fused with the constant regions of human T cell clone LC13, to create pLC13-ANDα and pLC13-ANDβ constructs as AND TCR α and β chains. AND α and β chains were expressed in inclusion bodies, refolded in an oxidized/reduced glutathione redox buffer, and purified by fast protein liquid chromatography. The gp250–I-Ek-biotin, MCC–I-Ek-biotin, Hb–I-Ek-biotin ligands were refolded from inclusion bodies. The pMHC ligands were attached to the SPR chip via streptavidin, and soluble AND TCRs were injected over the chip surface at a flow rate of 30 μl/min at 25 °C. The injected soluble AND TCR will be tested over various concentration ranges (by using 2-fold dilution) up to 500 μM. All measurements were baseline corrected by subtracting results of TCR injected over Hb–I-Ek-biotin ligands.
Tetramer binding decays
PE-labeled I-Ek tetramers in complex with MCC, gp250, or Hb were generated. Irrelevant MHC tetramers (hCLIP/I-Ab from NIH) were used as negative control. For tetramer staining, 106 T cells were stained with PE-conjugated tetramer (50 μg/ml), FITC-Vα11, and PE/Cy5 B220 (RA3-6B2) on ice for 3 h. Cells positive for PI and B220 were gated out of the analysis.
Gene expression analysis
Pre-selected AND.Rag1−/−H-2d DP thymocytes were MACS-beads positively selected and stimulated with plate bound gp250–I-Ek, MCC–I-Ek or Hb–I-Ek Ig dimers for 7 h. For microarray analysis, as previously published40, RNA was isolated using RNeasy kits (Qiagen), and gene expression analysis was performed using Illumina’s MouseRef-8 mouse Expression BeadChip. DNA-Chip Analyzer (www.dchip.org) was used to normalize the data and model expression values. The baseline levels were established using stimulation by the control Hb–I-Ek dimers. The microarray data presented in this article have been submitted to the National Center for Biotechnology Information Gene Expression Omnibus Web site under accession number xxxxxxx.
Quantitative RT-PCR
cDNA was synthesized from 25 ng DNase-treated RNA from MACS-beads sorted pre-selected AND.Rag1−/−H-2d or FACS-purified B6 thymocytes at various developmental stages using random hexamer primer (SuperScript II kit; Invitrogen). qRT-PCR was conducted with the SYBR Green PCR master mix and an ABI7000 machine (Applied Biosystems)40. Cycling conditions were 50 °C for 2 min, followed by 95 °C for 10 min, 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 sec, and a dissociation stage (95 °C for 15 sec, 60 °C for 20 sec, and 95 °C for 15 sec). β-actin was included for internal control for all samples. Fold changes were quantified by ΔCt (Fig. 2c,e) using standard curves, or calculated using the ΔΔCt method with nonselection Hb–I-Ek samples as the baseline sample, and β-actin as the reference gene (Fig. 2b,d). The following primers (5′ to 3′; forward then reverse) were used:
Scn4b: GGGCTTTTGGGTCTCTTC, GAGGTTCTCAAAGCCATAACA;
Scn5a: ATGGCAAACTTCCTGTTACCTC, CCACGGGCTTGTTTTTCAGC;
β-actin: CTAAGGCCAACCGTGAAAAG, ACCAGAGGCATACAGGGACA.
Analysis of intercellular Ca2+
Fura-2 AM Ca2+ imaging was performed as previously published40. Pre-selected AND.Rag-1−/−H-2d thymocytes were isolated by CD8a MicroBeads (Miltenyi Biotech #130-049-401) loaded with 5 μM Fura-2 AM (Invitrogen F-1221) for 20 min at 37 °C. 105 cells were loaded onto 8-chamber coverglass slides (Lab-Tek cat#177-402) which had been coated with peptide-loaded I-Ek Ig dimers (0.3 μg/well) of 4 °C overnight. Ca2+ imaging was performed at 37 °C on a Zeiss Axiovert 200M microscope equipped with a xenon arc lamp, and fluorescence was monitored in ratio mode. We quantified the number of cells, which were being activated, and the reactive cell percentage was about 10%, similar between gp250 and MCC stimulation. Collected data were analyzed with MetaMorph on randomly selected Ca2+ reactive cells. The curve for each cells were adjusted to time zero being when the Ca2+ started. The values of Rmin and Rmax were determined by exposing cells to Ca2+ free solution containing 1 μM ionomycin to obtain Rmin, and 10 mM Ca2+ solution with 1 μM ionomycin to obtain Rmax43. [Ca2+]i was calculated using an effective K value for Fura-2 AM of 260 nM16. For pharmacological inhibitor treatment, cells were treated with 1μM TTX or vehicle (1 μM citric acid pH 4.8) acutely before start of imaging. For Ig fusion protein treatment, cells were treated with 1 μg SCN4B-Ig fusion protein or 1 μg unrelated Ceacam4-Ig fusion protein right before the start of imaging.
Reaggregate culture
In vitro positive selection reaggregate cultures were performed as previously described27. Preselection DP thymocytes were used AND.Rag1−/−H-2d or B6.K (H-2k) CD53− preselection thymocytes. AND thymocytes are not selected on an H-2d background and are essentially all DP DP thymocytes. Pre-selection AND thymocytes were selected by CD8 MicroBeads (Miltenyi Biotech #130-049-401). Pre-selection B6K thymocytes were obtained by CD53 depletion. Cortical thymic epithelia cells ANV41.2 were pulsed with gp250 ligand (30 μM) or control peptide Hb (30 μM) in peptide-mediated positive selection. In IFN-γ induced positive selection, ANV41-2 cells were treated with IFN-γ (100 units/ml) overnight on the previous day, washed twice, and used for reaggregate culture. For pharmacological inhibitor treatment, cells were treated with 1 μM TTX or vehicle (1 μM citric acid pH 4.8). For Ig fusion protein treatment, cells were treated with 1 μg SCN4B-Ig fusion protein or 1 μg unrelated Ceacam4-Ig fusion protein
Production of lentiviruses expressing shRNA
Five clones of shRNA targeting SCN5A genes (TRCN0000069003 - TRCN0000069007, Sigma), and one non-target control (SHC002, Sigma) were cloned into pLKO-puro-CMV-tGFP vector (Sigma). SCN5A-GFP or Scramble-GFP shRNA plasimds, and each packaging vector (delta 8.2, VSV-g) were cotransfected into HEK293 T cells. Supernatants containing virus particles were collected 48 h after transfection, filtered and concentrated by PEG 8000 precipitation. Two pairs of shRNA (TRCN0000069004 + TRCN0000069007) were found to substantially reduce the sustained phase of Ca2+ influx (Supplementary Fig. 5a,b), and thus were selected for use in the bone marrow chimeras experiments.
Bone marrow chimeras
Ly5.1+ B6 hematopoietic stem cells were enriched by c-kit MicroBeads (Miltenyi Biotech #130-091-224), stained for c-kit and Sca-1, and sorted out c-kit+Sca-1+ population on an AriaII. Hematopoietic stem cells were resuspended at 104 cells per 200 μl DMEM-F12, containing 10% FCS, 1x nonessential amino acids, 2 mM GlutaMax, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 0.05% gentamicin, 50 M 2-mercaptoethanol, 50 ng/ml stem cell factor and 50 ng/ml thrombopoietin per well of a 96-well round bottom plate. After 18-24 h of culture, 5 μl of lentiviruses stock was added to each well. 24 h afterwards, the cells were adoptively transferred into lethally irradiated B6 mice by retroorbital injection on day 0 (at least 104 hematopoietic stem cells per mouse). After 12 weeks of reconstitution, cells were recovered from thymus and spleen of each recipient mouse, and analyzed by flow cytometry.
Expression of human VGSC in peripheral CD4+ T cells and AND hybridomas
The human SCN5A-GFP construct was obtained from C. Nichols (Washington University in St. Louis) as a gift. The human SCN4B cDNA was purchased from Origene (RC223951). The SCN4B cDNA was amplified by PCR, and cloned into pcDNA3.1. IRES/DsRed cassette (Clontech #6921-1) was ligated into the pcDNA3.1-huSCN4B construct through BamH1 and Not1 restriction site. CD4+ peripheral T cells which were isolated by CD4 MACS beads, or AND hybridomas were electrophoresed with human SCN5A-GFP and SCN4B-DsRed constructs (Amaxa Nucleofector kit for primary mouse T cells). After electroporation, primary peripheral AND CD4+ cells were rested for 12 h, and stimulated with plate bound gp250–I-Ek (10 μg), or MCC–I-Ek (1 μg) along with 1 μg CD28 mAb for 10 h, and subjected to flow cytometry analysis of CD69 expression. As for AND hybridomas, after electrophoration, cells were stimulated with plate bound gp250–I-Ek (3 μg) or MCC/I-Ek (1 μg) for 24 h along with CD28 (1 μg). Cells were stained with Live/Dead Blue Dead Cell Stain (Invitrogen cat# L23105), CD4 and CD69.
Generation of AND hybridoma
CD4+ T cells from AND.Rag1−/−H-2k mice were stimulated with MCC in vitro for three days and T cell hybridomas were generated by using established protocol44 and the BW5147α−β− fusion partner.
Statistics
All data were analyzed nonparametrically by the Mann-Whitney U-test or paired t test with Prism 4 or Prism 5 software (Graph Pad). p values of less than 0.05 were considered significant.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank A. Farr (University of Washington) for providing the ANV41.2, the cortical epithelial cell line; D. Kreamalmeyer for maintaining the mouse colony; S. Horvath for peptide synthesis and purification; M. Cella for advice on SCN4B-Ig fusion protein production; M. Colonna for providing Ceacam4 Ig fusion protein; S. Chan, S. Srivatsan and D. Bhattacharya for helpful advice on shRNA knockdown experiments; R. Schreiber for providing murine IFN-γ; J. Silva, C. Nichols and S. Goldstein (University of Chicago) for providing the huSCN5A-GFP construct; J. Nerbonne for helpful discussions; N. Felix for initiating the gp250 project; G. Morris for critical data analysis and assistance with the manuscript; K. Weber, C. Morley, A. Shaw, M. Vig, Y. Huang, K. Murphy, and T. Egawa for critical reading of the manuscript and comments. Supported by the National Institutes of Health grant: AI-24157 (P.M.A.).
Footnotes
Author contributions W.-L.L., and P.M.A. designed the study and wrote the manuscript; W.-L.L. performed the experimental work. D.L.D. generated the AND hybridoma cell lines.
Competing financial interests The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Accession codes GEO: GSE38909
References
- 1.Starr TK, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Positive and negative selection of T cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003;21:139–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moran AE, Hogquist KA. T-cell receptor affinity in thymic development. Immunology. 2012;135:261–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Morris GP, Allen PM. How the TCR balances sensitivity and specificity for the recognition of self and pathogens. Nat. Immunol. 2012;13:121–128. doi: 10.1038/ni.2190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kane LP, Hedrick SM. A role for calcium influx in setting the threshold for CD4+CD8+ thymocyte negative selection. J. Immunol. 1996;156:4594–4601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mariathasan S, et al. Duration and strength of extracellular signal-regulated kinase signals are altered during positive versus negative thymocyte selection. J. Immunol. 2001;167:4966–4973. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.9.4966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bhakta NR, Oh DY, Lewis RS. Calcium oscillations regulate thymocyte motility during positive selection in the three-dimensional thymic environment. Nat. Immunol. 2005;6:143–151. doi: 10.1038/ni1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Daniels MA, et al. Thymic selection threshold defined by compartmentalization of Ras/MAPK signalling. Nature. 2006;444:724–729. doi: 10.1038/nature05269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Oh-hora M. Calcium signaling in the development and function of T-lineage cells. Immunol. Rev. 2009;231:210–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Werlen G, Hausmann B, Palmer E. A motif in the alphabeta T-cell receptor controls positive selection by modulating ERK activity. Nature. 2000;406:422–426. doi: 10.1038/35019094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.McNeil LK, Starr TK, Hogquist KA. A requirement for sustained ERK signaling during thymocyte positive selection in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:13574–13579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505110102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cahalan MD, Chandy KG. The functional network of ion channels in T lymphocytes. Immunol. Rev. 2009;231:59–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00816.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Feske S. ORAI1 and STIM1 deficiency in human and mice: roles of store-operated Ca2+ entry in the immune system and beyond. Immunol. Rev. 2009;231:189–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00818.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gwack Y, et al. Hair loss and defective T- and B-cell function in mice lacking ORAI1. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008;28:5209–5222. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00360-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vig M, et al. Defective mast cell effector functions in mice lacking the CRACM1 pore subunit of store-operated calcium release-activated calcium channels. Nat. Immunol. 2008;9:89–96. doi: 10.1038/ni1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Beyersdorf N, et al. STIM1-independent T cell development and effector function in vivo. J. Immunol. 2009;182:3390–3397. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lo WL, et al. An endogenous peptide positively selects and augments the activation and survival of peripheral CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2009;10:1155–1161. doi: 10.1038/ni.1796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yu FH, et al. Sodium channel beta4, a new disulfide-linked auxiliary subunit with similarity to beta2. J. Neurosci. 2003;23:7577–7585. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-20-07577.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Grieco TM, Malhotra JD, Chen C, Isom LL, Raman IM. Open-channel block by the cytoplasmic tail of sodium channel beta4 as a mechanism for resurgent sodium current. Neuron. 2005;45:233–244. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.12.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bant JS, Raman IM. Control of transient, resurgent, and persistent current by open-channel block by Na channel beta4 in cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:12357–12362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005633107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Catterall WA. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 2000;26:13–25. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)81133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Goldin AL, et al. Nomenclature of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 2000;28:365–368. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Fozzard HA, Lipkind GM. The tetrodotoxin binding site is within the outer vestibule of the sodium channel. Mar. Drugs. 2010;8:219–234. doi: 10.3390/md8020219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kaczmarek LK. Non-conducting functions of voltage-gated ion channels. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006;7:761–771. doi: 10.1038/nrn1988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brackenbury WJ, Djamgoz MB, Isom LL. An emerging role for voltage-gated Na+ channels in cellular migration: regulation of central nervous system development and potentiation of invasive cancers. Neuroscientist. 2008;14:571–583. doi: 10.1177/1073858408320293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Davey GM, et al. Preselection thymocytes are more sensitive to T cell receptor stimulation than mature T cells. J. Exp. Med. 1998;188:1867–1874. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.10.1867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Painter MW, Davis S, Hardy RR, Mathis D, Benoist C. Transcriptomes of the B and T lineages compared by multiplatform microarray profiling. J. Immunol. 2011;186:3047–3057. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Catterall WA. Structure and regulation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000;16:521–555. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dravid SM, Baden DG, Murray TF. Brevetoxin activation of voltage-gated sodium channels regulates Ca dynamics and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in murine neocortical neurons. J. Neurochem. 2004;89:739–749. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fekete A, et al. Mechanism of the persistent sodium current activator veratridine-evoked Ca elevation: implication for epilepsy. J. Neurochem. 2009;111:745–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Catterall WA. Signaling complexes of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels. Neurosci. Lett. 2010;486:107–116. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rook MB, Evers MM, Vos MA, Bierhuizen MF. Biology of cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5 expression. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012;93:12–23. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Omilusik K, et al. The Ca(v)1.4 calcium channel is a critical regulator of T cell receptor signaling and naive T cell homeostasis. Immunity. 2011;35:349–360. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Juang J, et al. Peptide-MHC heterodimers show that thymic positive selection requires a more restricted set of self-peptides than negative selection. J. Exp. Med. 2010;207:1223–1234. doi: 10.1084/jem.20092170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Singer A. Molecular and cellular basis of T cell lineage commitment: An overview. Semin. Immunol. 2010;22:253. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2010.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Papadatos GA, et al. Slowed conduction and ventricular tachycardia after targeted disruption of the cardiac sodium channel gene Scn5a. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:6210–6215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.082121299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Allen PM. Themis imposes new law and order on positive selection. Nat. Immunol. 2009;10:805–806. doi: 10.1038/ni0809-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sun G, et al. The zinc finger protein cKrox directs CD4 lineage differentiation during intrathymic T cell positive selection. Nat. Immunol. 2005;6:373–381. doi: 10.1038/ni1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.He X, et al. The zinc finger transcription factor Th-POK regulates CD4 versus CD8 T-cell lineage commitment. Nature. 2005;433:826–833. doi: 10.1038/nature03338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gallo EM, et al. Calcineurin sets the bandwidth for discrimination of signals during thymocyte development. Nature. 2007;450:731–735. doi: 10.1038/nature06305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Albu DI, et al. BCL11B is required for positive selection and survival of double-positive thymocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2007;204:3003–3015. doi: 10.1084/jem.20070863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Clements CS, et al. The production, purification and crystallization of a soluble heterodimeric form of a highly selected T-cell receptor in its unliganded and liganded state. Acta. Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2002;58:2131–2134. doi: 10.1107/s0907444902015482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Weber KS, Hildner K, Murphy KM, Allen PM. Trpm4 differentially regulates Th1 and Th2 function by altering calcium signaling and NFAT localization. J. Immunol. 2010;185:2836–2846. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fanger CM, Neben AL, Cahalan MD. Differential Ca2+ influx, KCa channel activity, and Ca2+ clearance distinguish Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2000;164:1153–1160. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.3.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Allen PM. Monoclonal antibody productton techniques and applications. Marcel Dekker Inc.; New York: 1987. Construction of murine T-T-cell hybridomas. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.