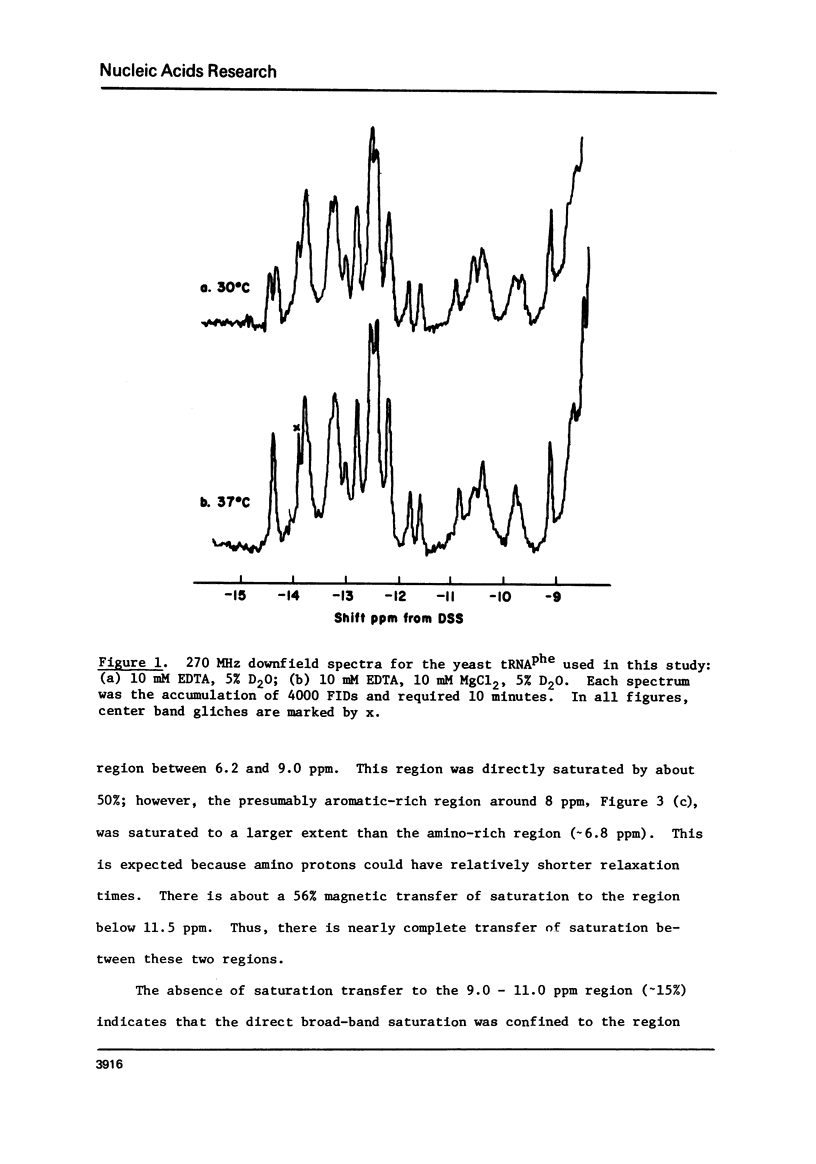
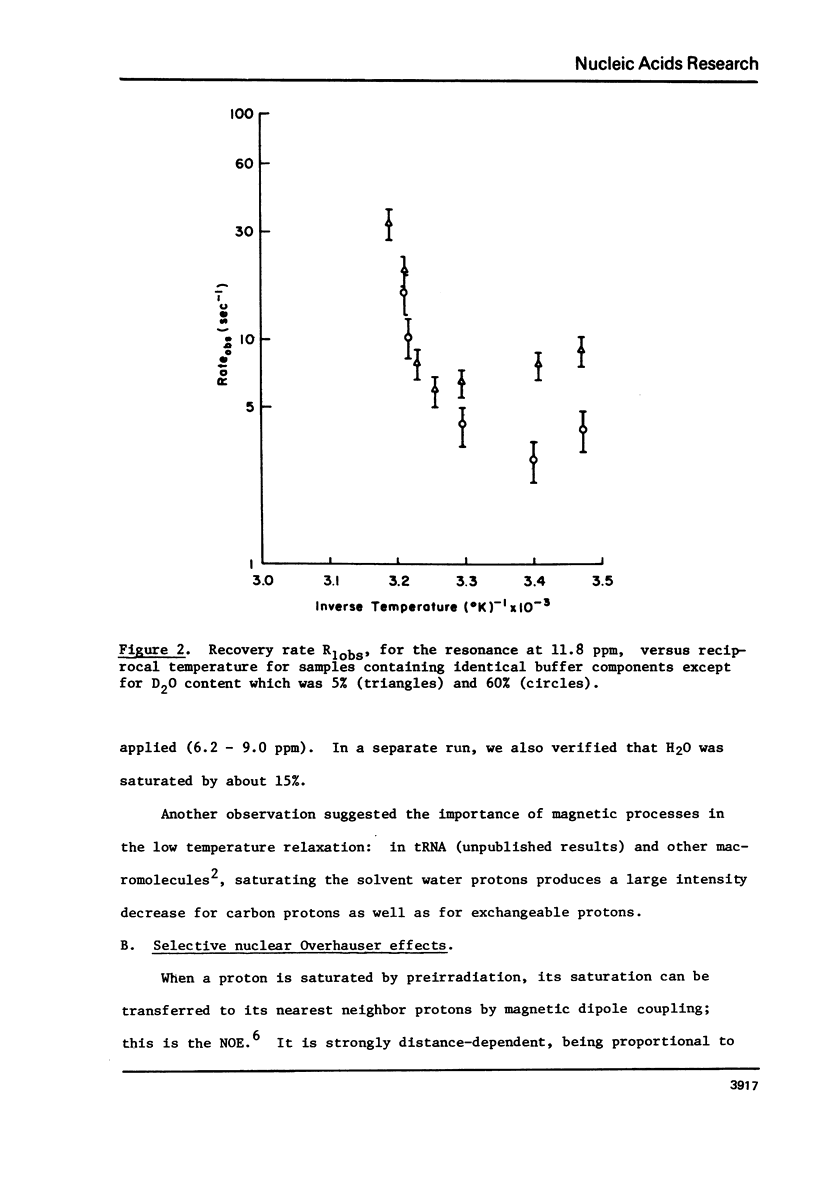
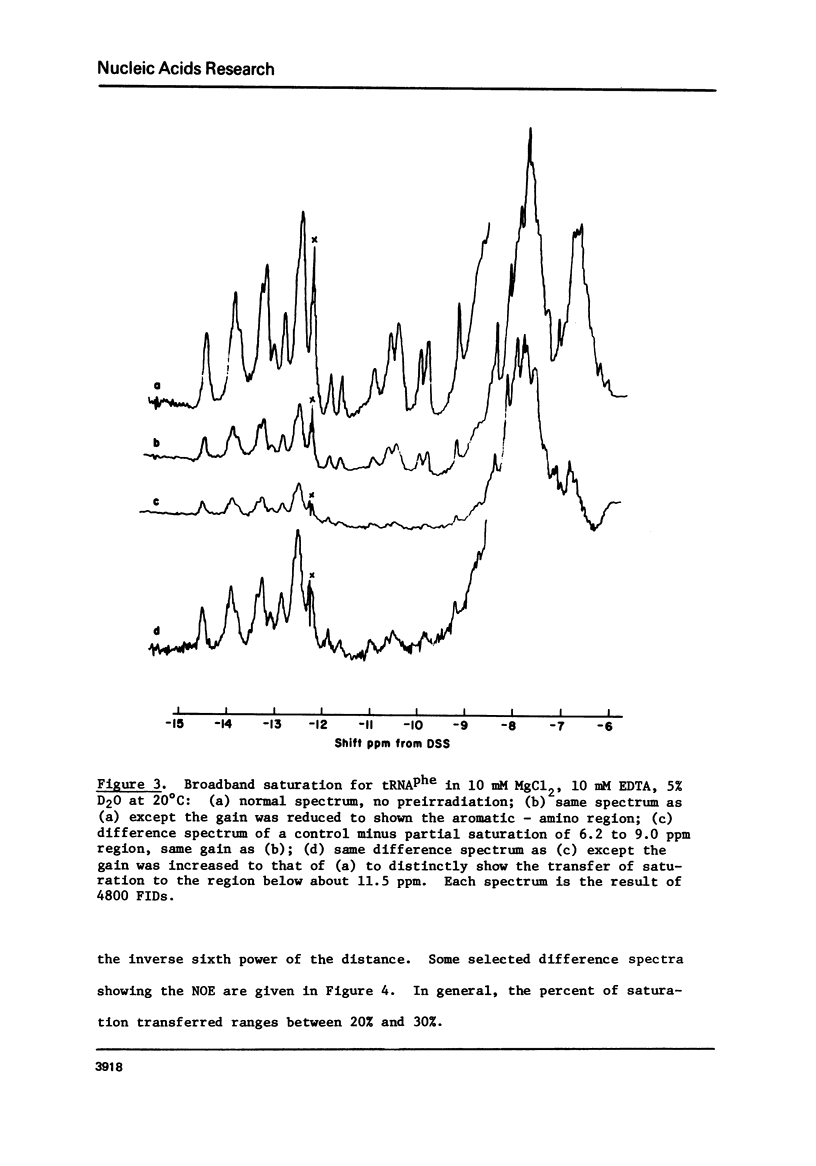
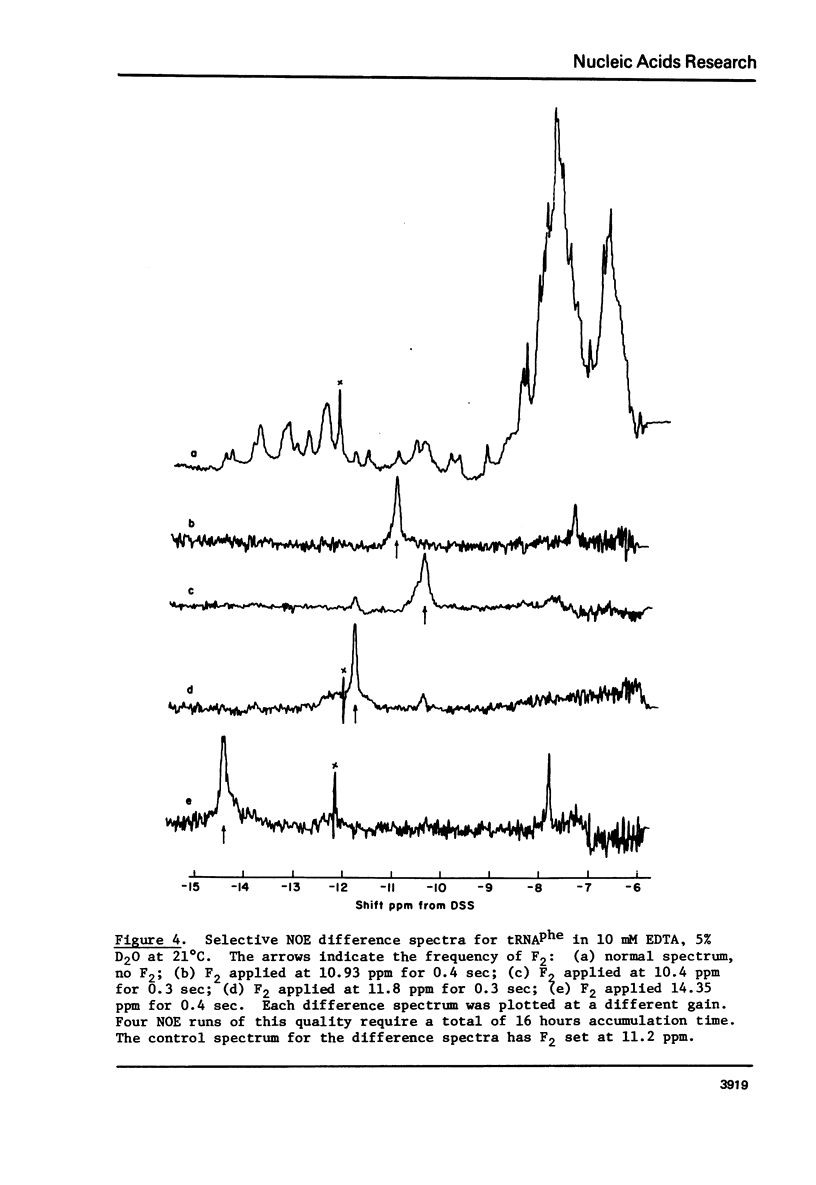
Abstract
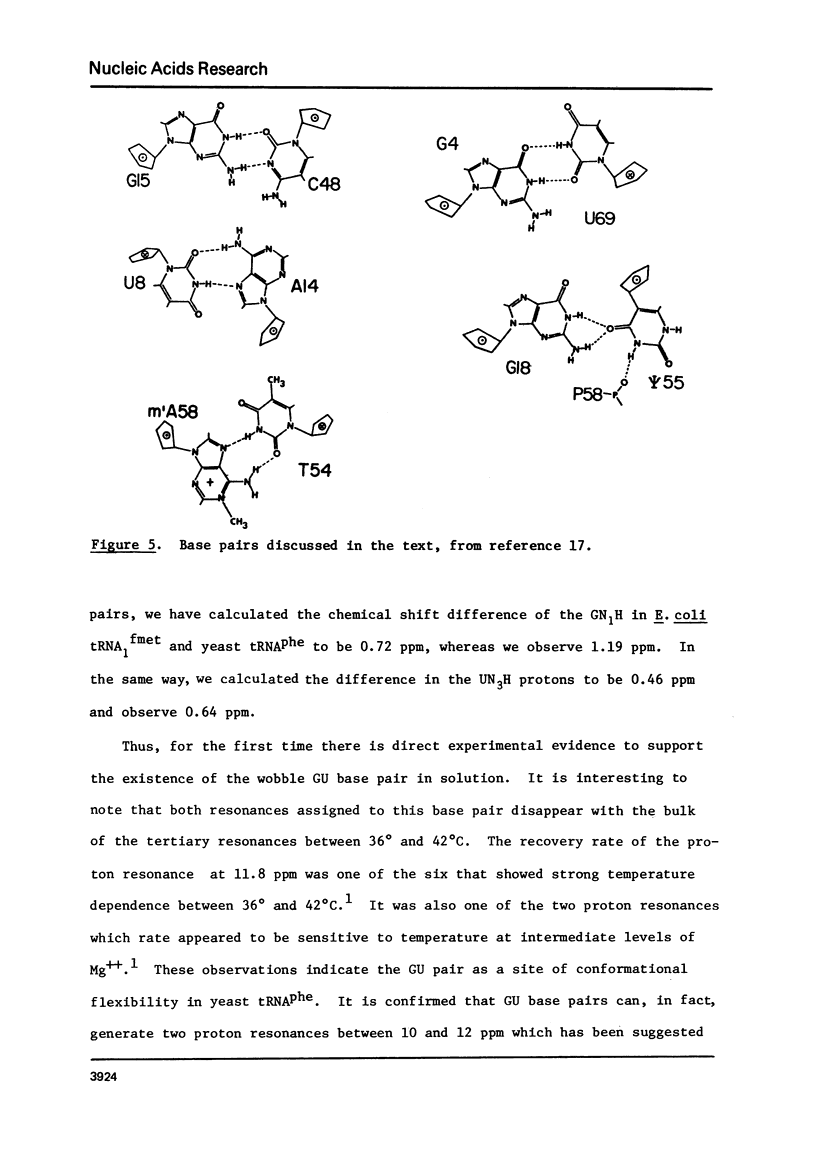
Cross-relaxation effects are demonstrated between the imino protons and other protons in yeast tRNAPhe and H2O. A detailed examination has been made of the observed relaxation rate of the proton resonance at 11.8 ppm from DSS as a function of the D2O content in the solvent. This result, as well as the size and number of observed nuclear Overhauser effects, suggests that dipolar magnetization transfer between solvent H2O, amino, imino, and other tRNA protons may dominate the relaxation processes of the imino protons at low temperature. At higher temperatures the observed relaxation rate is dominated by chemical exchange. The selective nuclear Overhauser effects are shown to be an important aid in resonance assignments. By these means we were able to identify tow protons from the wobble base pair GU4 at 11.8 ppm and 10.4 ppm.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arter D. B., Schmidt P. G. Ring current shielding effects in nucleic acid double helices. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jun;3(6):1437–1447. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.6.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A., Ladner J. E., Klug A. Crystallographic refinement of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA at 2-5A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec 25;108(4):619–649. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. D., Redfield A. G. An NMR study of the exchange rates for protons involved in the secondary and tertiary structure of yeast tRNA Phe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Oct;4(10):3599–3615. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.10.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallenbach N. R., Daniel W. E., Jr, Kaminker M. A. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of hydrogen-bonded ring protons in oligonucleotide helices involving classical and nonclassical base pairs. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1218–1224. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearns D. R. High-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance investigations of the structure of tRNA in solution. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;18:91–149. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60587-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komoroski R. A., Allerhand A. Observation of resonances from some minor bases in the natural-abundance carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of unfractionated yeast transfer ribonucleic acid. Evidence for fast internal motion of the dihydrouracil rings. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):369–372. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Rich A. Structural domains of transfer RNA molecules. Science. 1976 Nov 19;194(4267):796–806. doi: 10.1126/science.790568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. R., Ribeiro N. S., Gould G., Robillard G., Hilbers C. W., Shulman R. G. Tertiary hydrogen bonds in the solution structure of transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2049–2053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., RajBhandary U. L. Transfer RNA: molecular structure, sequence, and properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:805–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard G. T., Hilbers C. W., Reid B. R., Gangloff J., Dirheimer G., Shulman R. G. A study of secondary and tertiary solution structure of yeast tRNA(Asp) by nuclear magnetic resonance. Assignment of G.U ring NH and hydrogen-bonded base pair proton resonances. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1883–1888. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoesz J. D., Redfield A. G. Cross relaxation and spin diffusion effects on the proton NMR of biopolymers in H2O. Solvent saturation and chemical exchange in superoxide dismutase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jul 15;91(2):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelder S. F., Redfield A. G. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of exchangeable protons. II. The solvent exchange rate of the indole nitrogen proton of tryptophan derivatives. Biopolymers. 1977 Mar;16(3):623–629. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelder S., Lee L., Redfield A. G. Letter: Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of exchangeable protons. I. Fourier transform saturation-recovery and transfer of saturation of the tryptophan indole nitrogen proton. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 May 14;97(10):2927–2928. doi: 10.1021/ja00843a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. L., Bolton P. H., Kearns D. R. Tertiary structure in E. coli tRNA Arg and tRNA Val. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 2;383(4):446–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


