Abstract
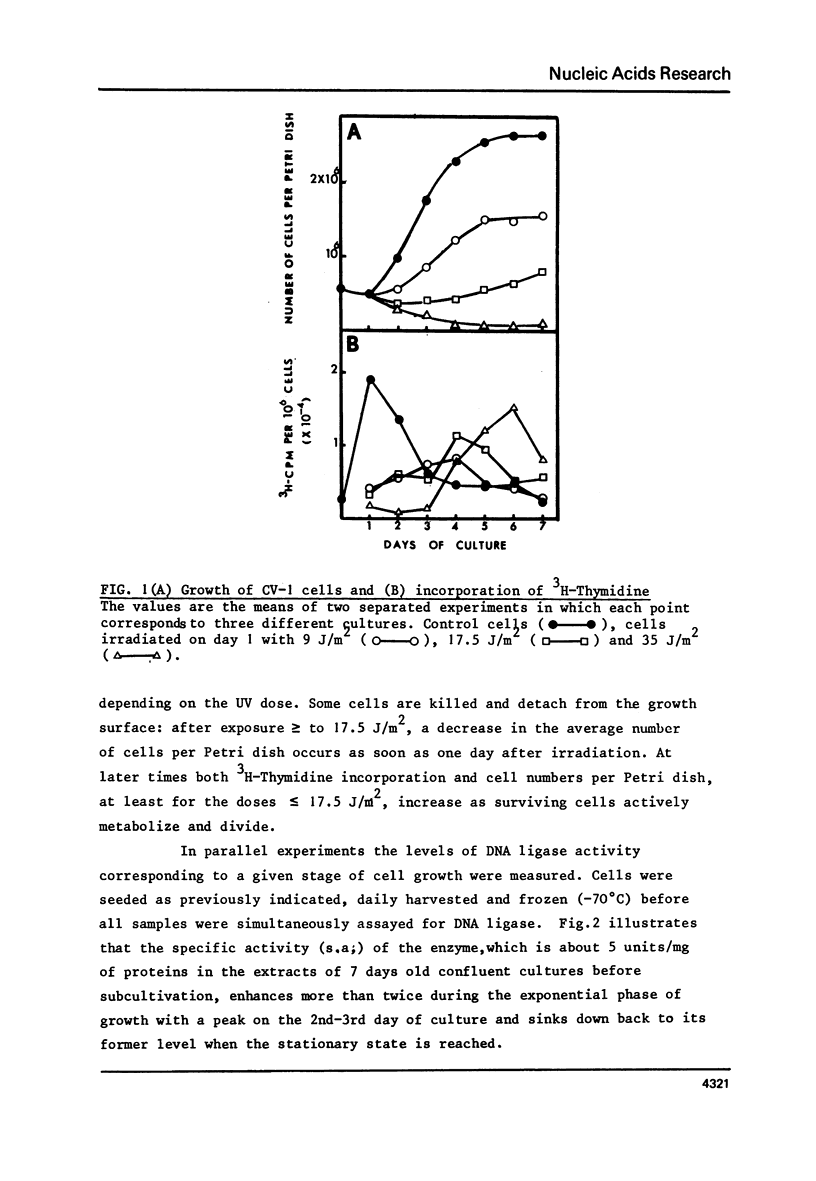
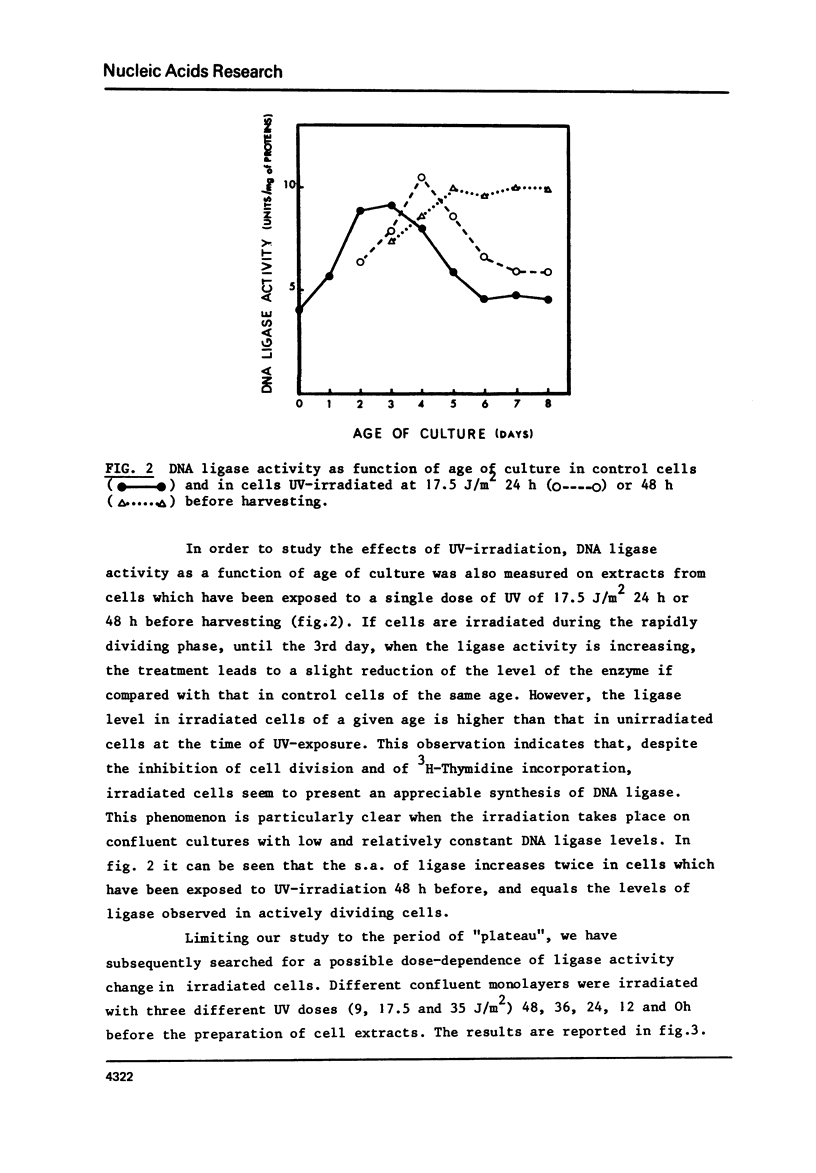
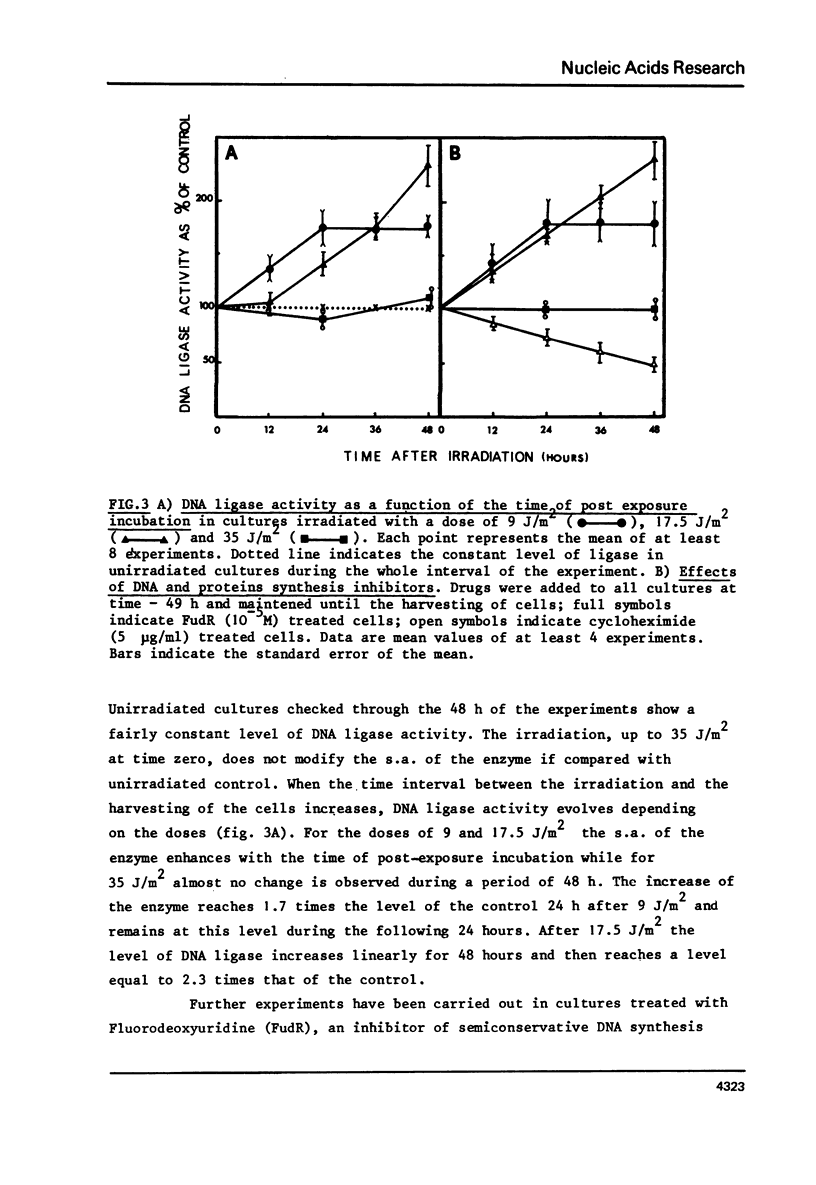
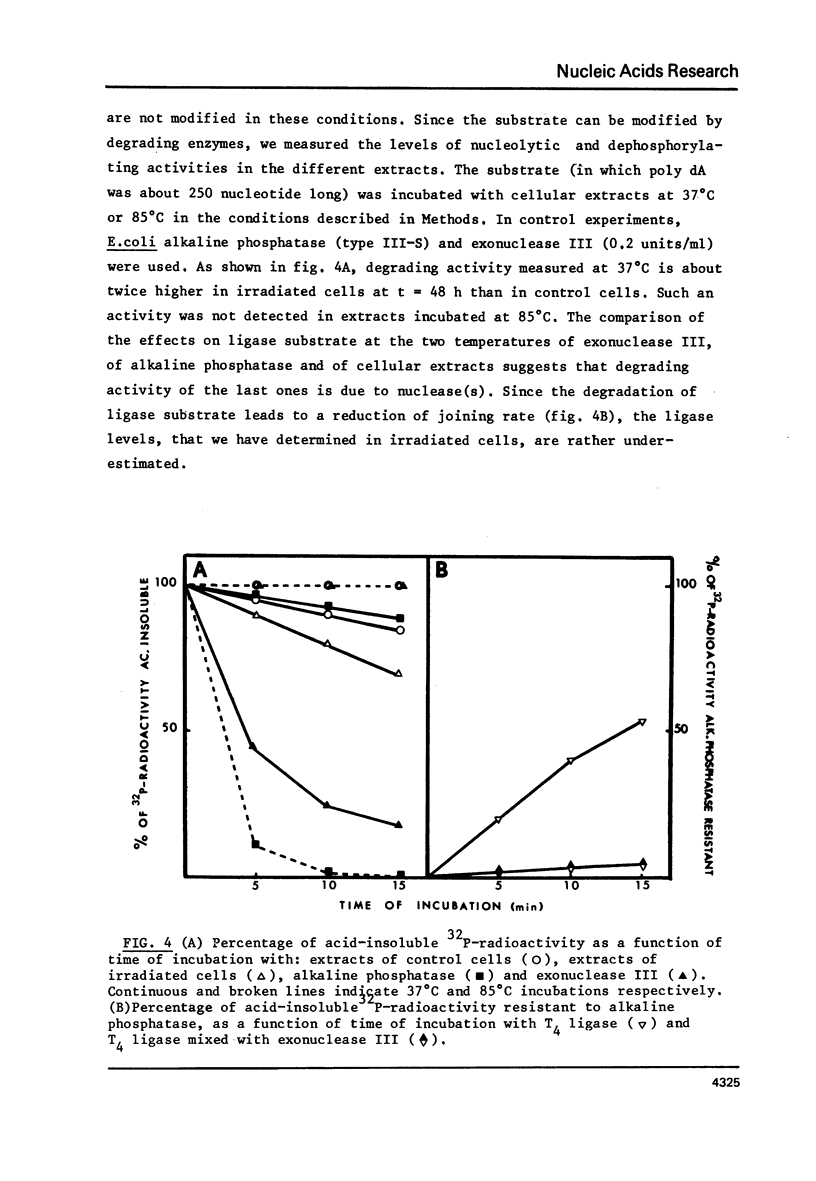
The DNA ligase activity of monkey kidney CV-1 cells has been measured at different stages of culture growth and after different time intervals following ultraviolet irradiation. Results indicate that: - The level of enzyme activity is about twice higher in non synchronous, rapidly dividing cells than in confluent cultures. - UV-irradiation of cells induces a "de novo" synthesis of DNA ligase. - This induction is dose dependent in its extent and kinetics, and may lead to a DNA ligase level in UV-irradiated stationary cultures of the same order as observed in unirradiated exponentially growing cells. - This induction seems to be independent of semiconservative DNA synthesis since it is not affected by fluorodeoxyuridine.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. The relation between the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid and the synthesis of protein in the multiplication of bacteriophage T2. Biochem J. 1955 Nov;61(3):473–483. doi: 10.1042/bj0610473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P. Polynucleotide ligase in mouse cells infected by polyoma virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 29;269(3):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppey J. Common precursor pathways of Herpes DNA and of repair synthesis in ultraviolet irradiated cells. Nature. 1977 Jan 20;265(5591):260–261. doi: 10.1038/265260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppey J., Nocentini S. Herpes virus and viral DNA synthesis in ultraviolet light-irradiated cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jul;32(1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNIS H. L., LUBIN M. CYCLOHEXIMIDE: ASPECTS OF INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN MAMMALIAN CELLS. Science. 1964 Dec 11;146(3650):1474–1476. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3650.1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTMANN K. U., HEIDELBERGER C. Studies on fluorinated pyrimidines. XIII. Inhibition of thymidylate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J., Hanawalt P. Role of polynucleotide ligase in T4 DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 14;35(3):639–642. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocentini S. Inhibition and recovery of ribosomal RNA synthesis in ultraviolet-irradiation mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 12;454(1):114–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Lehman I. R. Enzymic joining of polynucleotides. 3. The polydeoxyadenylate-polydeoxythymidylate homopolymer pair. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 14;36(2):261–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrali Noy G. C., Spadari S., Ciarrocchi G., Pedrini A. M., Falaschi A. Two forms of the DNA ligase of human cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):343–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrini A. M., Nuzzo F., Ciarrocchi G., Dalprà L., Falaschi A. Induction of polynucleotide ligase in human lymphocytes stimulated by phytohemoagglutinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 9;47(5):1221–1227. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90965-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Shatkin A. J. Polynucleotide ligase activity in cells infected with simian virus 40, polyoma virus, or vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):719–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.719-726.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai Y., Tsukada K. Change of ribonuclease H activity in developing and regenerating rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 2;479(1):126–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S. Properties of DNA ligase from uninfected and virus-infected HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Aug;3(8):2155–2167. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.8.2155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderhäll S. DNA ligases during rat liver regeneration. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):640–642. doi: 10.1038/260640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Shimoyachi M., Tsukada K. Two distinct polynucleotide ligases from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jun 15;54(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada K., Hokari S., Hayasaki N., Ito N. Increased activity of polynucleotide ligase from rat hepatoma induced by N-2-fluorenylacetamide. Cancer Res. 1972 May;32(5):886–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada K., Ichimura M. Polynucleotide ligase from rat liver after partial hepatectomy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Mar 19;42(6):1156–1161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


