Abstract
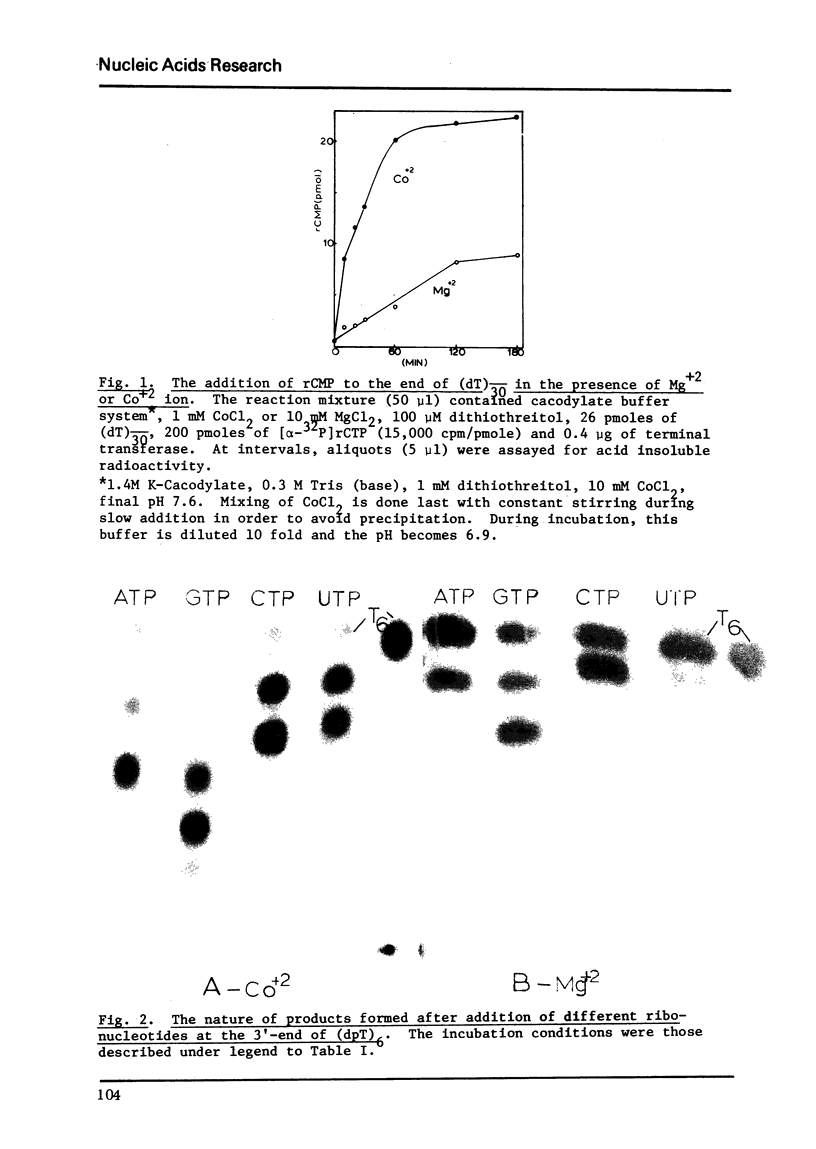
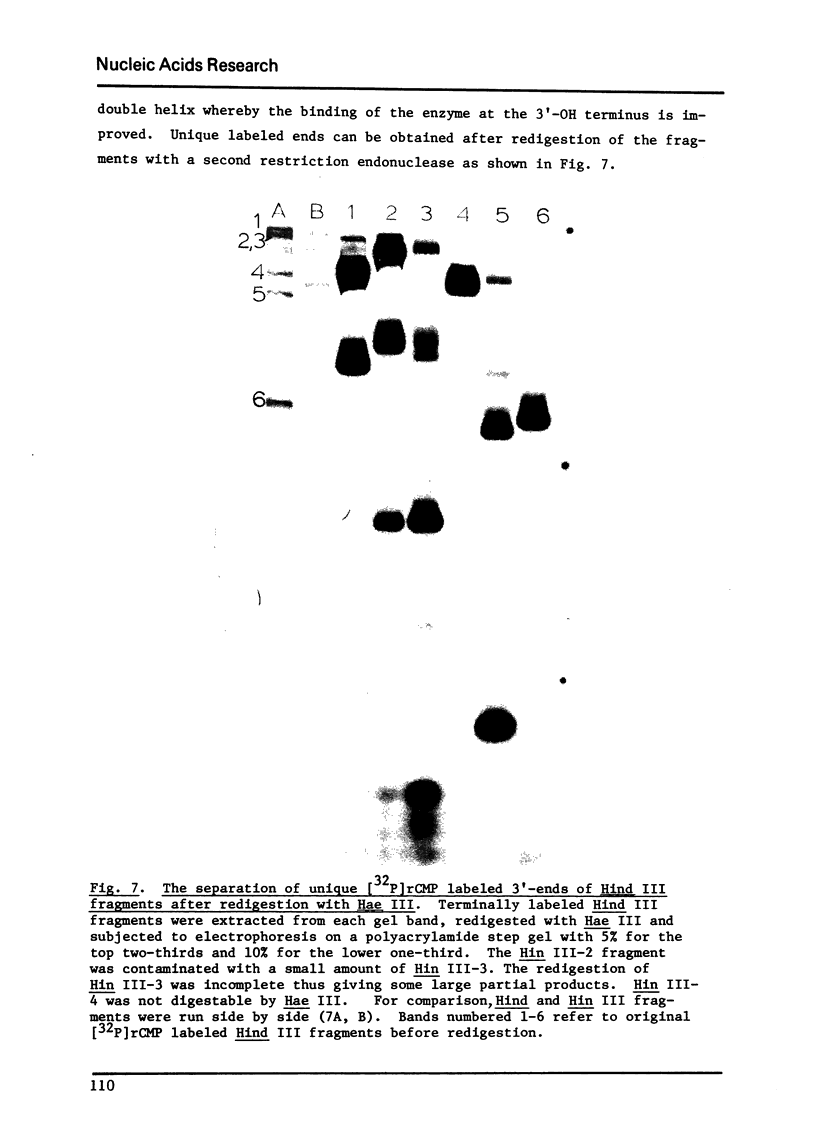
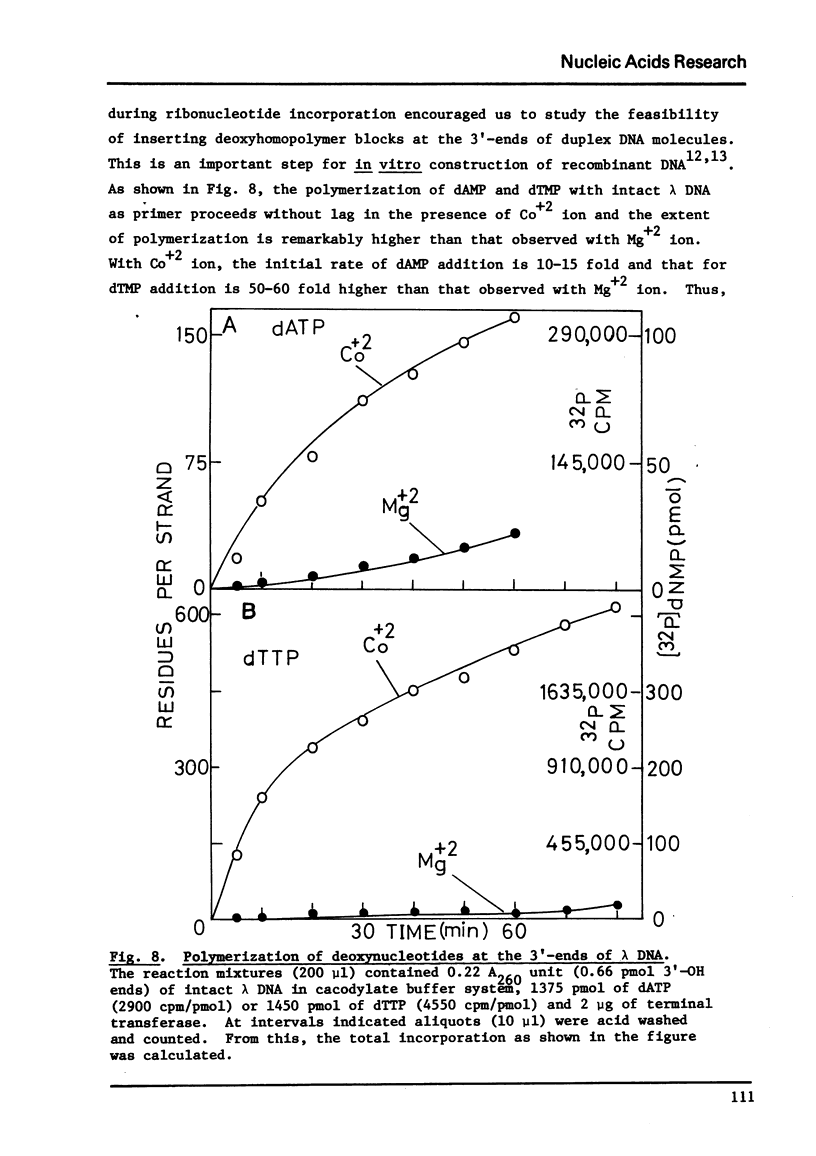
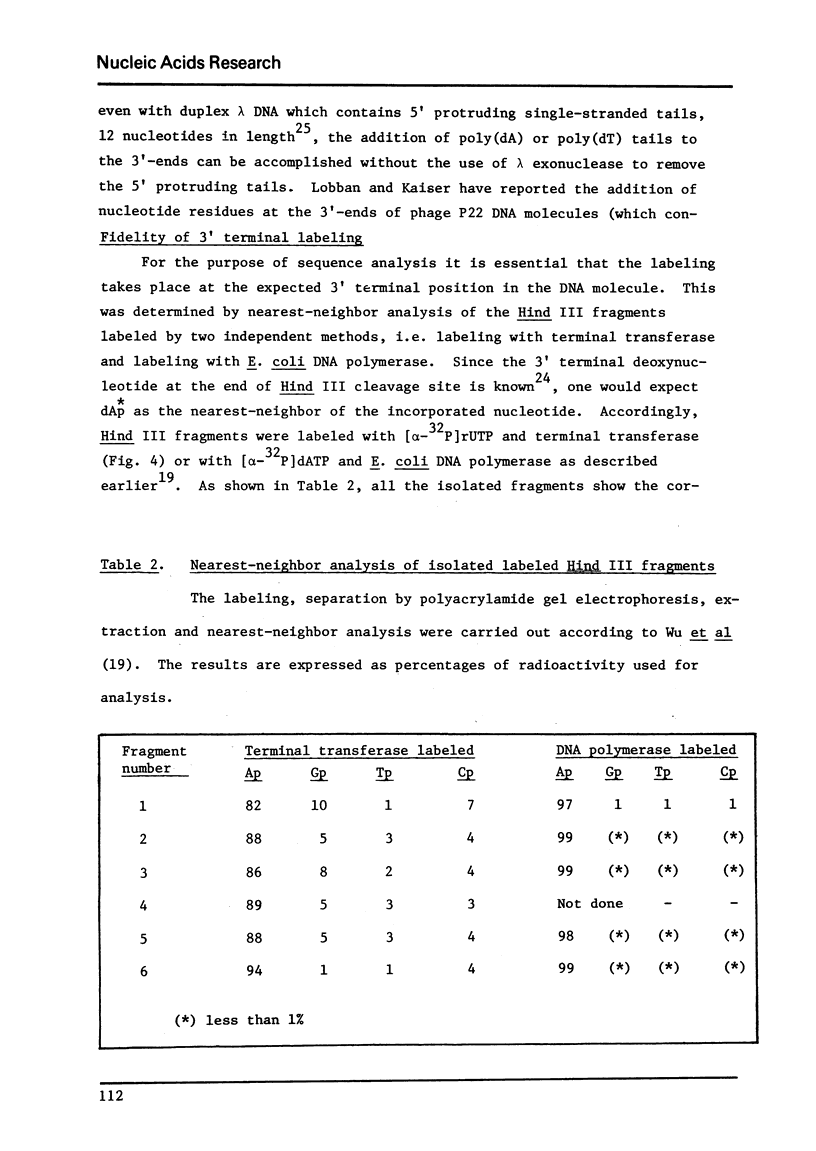
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, which requires a single-stranded DNA primer under the usual assay conditions, can be made to accept double-stranded DNA as primer for the addition of either rNMP or dNMP, if Mg+2 ion is replaced by Co+2 ion. The priming efficiency in the presence of (C leads to) CO+2 ion with respect to initial rate tested with 2 single-stranded primer, is 5-6 fols higher than that observed with Mg+2 ion. In the presence of Co+2 ion, the primer specificity is altered so that all forms of duplex DNA molecules can be labeled at their unique 3' -ends regardless of whether such ends are staggered or even. Thus, using ribonucleotide incorporation, we have for the first time employed this reaction for sequence analysis of duplex DNA fragments generated by restriction endonuclease cleavages. Furthermore, by using Co+2 ion, it is possible to add a long homopolymer tract of deoxyribonucleotides to the 3'-terminus of double-stranded DNA. Therefore, without prior treatment with lambda exonuclease to expose the 3' terminus as single-stranded primer, this reaction now permits insertion of homopolymer tails at the 3'-ends of all types of DNA molecules for the purpose of in vitro construction of recombinant DNA.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOLLUM F. J. Thermal conversion of nonpriming deoxyribonucleic acid to primer. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2733–2734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertazzoni U., Ehrlich S. D., Bernardi G. Analysis of labeled 3' terminal nucleotides of DNA fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:355–359. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F., Barrell B. G. The sequence of 5 s ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):379–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Symons R. H., Berg P. Biochemical method for inserting new genetic information into DNA of Simian Virus 40: circular SV40 DNA molecules containing lambda phage genes and the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2904–2909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay E., Bambara R., Padmanabhan R., Wu R. DNA sequence analysis: a general, simple and rapid method for sequencing large oligodeoxyribonucleotide fragments by mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Mar;1(3):331–353. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Englund P. T., Bertsch L. L. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXVI. Physical and chemical studies of a homogeneous deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):2996–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kössel H., Roychoudhury R., Fischer D., Otto A. 3' End-group labeling and partial sequence determination of oligodeoxynucleotides. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:322–341. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kössel H., Roychoudhury R. Proofreading function of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase I from Escherichia coli. Nature of excision of ribonucleotides from the 3' termini of oligodeoxynucleotide primers. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4094–4099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kössel H., Roychoudhury R. Synthetic polynucleotides. Ther terminal addition of riboadenylic acid to deoxyoligonucleotides by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase as a tool for the specific labelling of deoxyoligonucleotides at the 3'-ends. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Sep 24;22(2):271–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobban P. E., Kaiser A. D. Enzymatic end-to end joining of DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 15;78(3):453–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90468-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old R., Murray K., Boizes G. Recognition sequence of restriction endonuclease III from Hemophilus influenzae. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):331–339. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson K., Harvey C. Determination of the 3' terminal nucleotide of DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Mar;2(3):319–325. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan R., Wu R., Calendar R. Complete nucleotide sequence of the cohesive ends of bacteriophage P2 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6197–6207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Breitmeyer J. B., Tabachnik N. F., Myers P. A. A second specific endonuclease from Haemophilus aegyptius. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 5;91(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R. Enzymic synthesis of polynucleotides. Oligodeoxynucleotides with one 3'-terminal ribonucleotide as primers for polydeoxynucleotide synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3910–3917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Fischer D., Kössel H. A new method for the sequence analysis of oligodeoxynucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):430–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90837-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Kössel H. Synthetic polynucleotides. Enzymic synthesis of ribonucleotide terminated oligodeoxynucleotides and their use as primers for the enzymic synthesis of polydeoxynucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Oct 14;22(3):310–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiua T., Ormondt H. V., Khorana H. G. The nucleotide sequence in the promoter region of the fene for an Escherichia coli tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):1087–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Wilcox K. W. A restriction enzyme from Hemophilus influenzae. I. Purification and general properties. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink P. C., Finnegan D. J., Donelson J. E., Hogness D. S. A system for mapping DNA sequences in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Padmanabhan R., Bambara R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of bacteriophage DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:231–253. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Taylor E. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. II. Complete nucleotide sequence of the cohesive ends of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):491–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Tu C. D., Padmanabhan R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. XII. The chemical synthesis and sequence analysis of a dodecadeoxynucleotide which binds to the endolysin gene of bacteriophage lambda. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 19;55(4):1092–1099. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]