Abstract
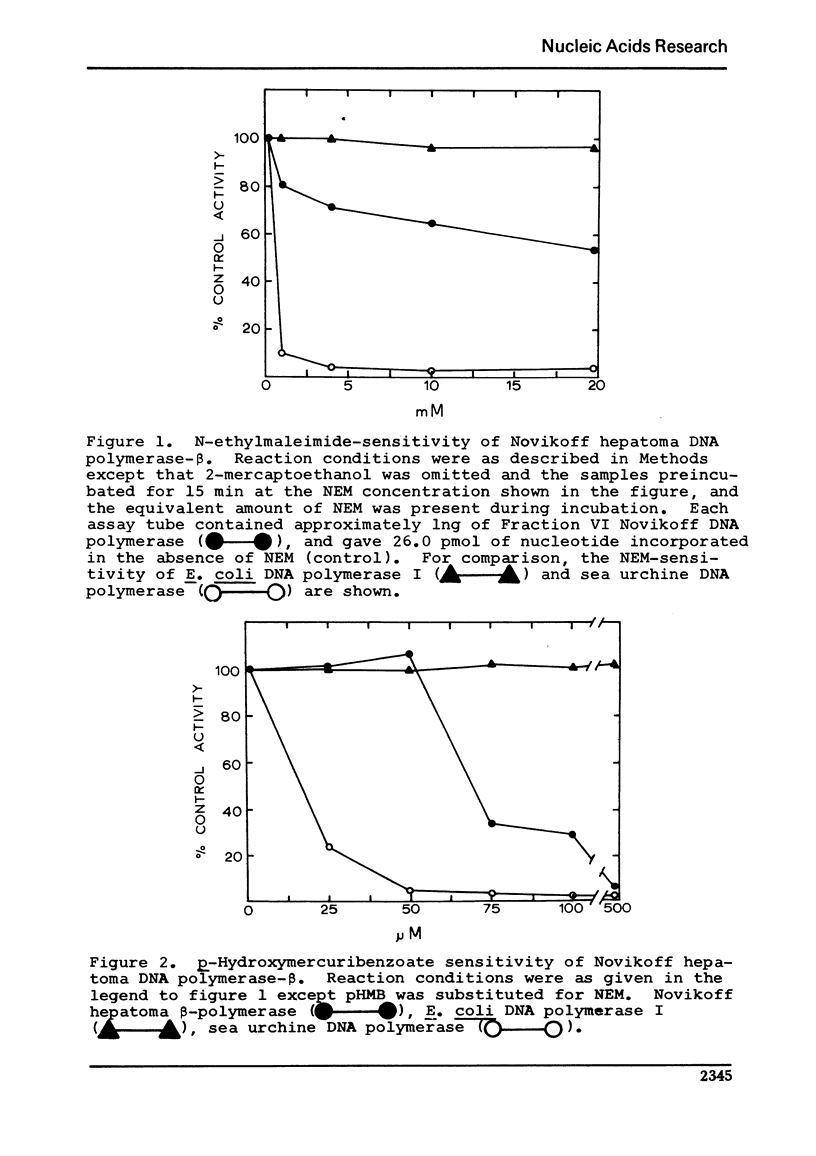
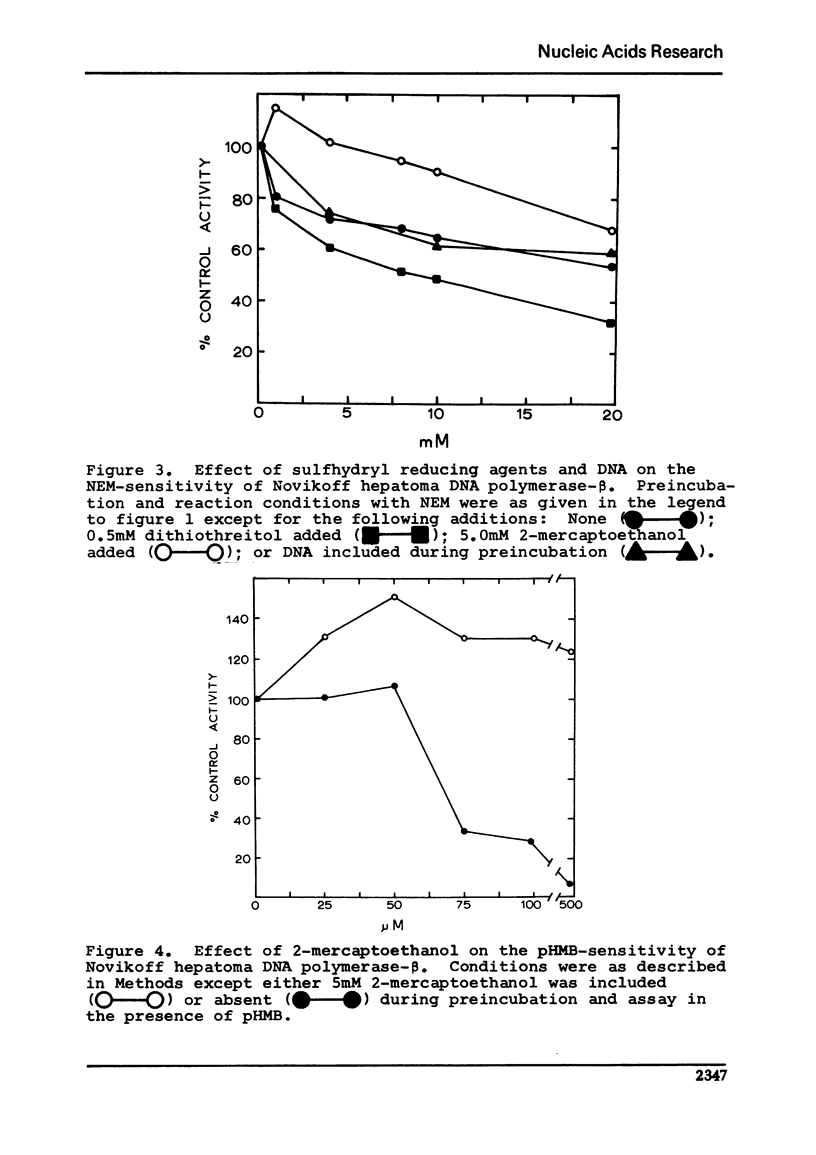
Unlike other beta-class eukaryotic DNA polymerases, the enzyme purified from the Novikoff hepatoma is inhibited by both sulfhydryl blocking agents N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) and p-hydroxymercuribenzoate (pHMB). The degree of sensitivity varies depending on the enzyme purity, pH of the reaction, and the presence of sulfhydryl reducing agents. Novikoff beta-polymerase activity is unaffected by the presence of 2-mercaptoethanol (2-Me) or dithiothreitol (DTT); however, the combination of 2-mercaptoethanol and NEM or pHMB acts to reverse the inhibition of the sulfhydryl blocking agent. The reversal of inhibition involves more than just a titration of NEM with 2-mercaptoethanol since a) the combination of these two reagents actually stimulates the DNA polymerase, and b) dithiothreitol did not reverse the inhibition. Binding of the polymerase to DNA did not affect the enzyme sensitivity to NEM.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baril E. F., Jenkins M. D., Brown O. E., Laszlo J., Morris H. P. DNA polymerases I and II in regenerating rat liver and Morris hepatomas. Cancer Res. 1973 Jun;33(6):1187–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn E. W., Matsukage A., Wilson S. H. Stimulation of DNA polymerase activity by the combination of p-hydroxymercuribenzoate and dithiothreitol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 10;59(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollum F. J. Mammalian DNA polymerases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1975;15(0):109–144. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan A. T. Adenosine triphosphate-dependent synthesis of biologically active DNA by azide-poisoned bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1296–1300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines M. E., Holmes A. M., Johnston I. R. Distinct cytoplasmic and nuclear DNA polymerases from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 15;17(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80564-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Englund P. T., Bertsch L. L. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXVI. Physical and chemical studies of a homogeneous deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):2996–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Englund P. T., Kornberg A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXVII. Chemical modifications of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):3009–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knippers R. DNA polymerase II. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1050–1053. doi: 10.1038/2281050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A. Purification and properties of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from nuclei of sea urchin embryos. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 10;244(7):1672–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukage A., Bohn E. W., Wilson S. H. Differential sensitivity of low molecular weight DNA polymerase to sulfhydryl-blocking reagents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 21;383(3):338–343. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. R., Keller S. J. DNA polymerase activity: Factors affecting counting efficiency of radioactive DNA on filter paper discs. Anal Biochem. 1972 Mar;46(1):332–337. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90424-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses R. E., Richardson C. C. A new DNA polymerase activity of Escherichia coli. I. Purification and properties of the activity present in E. coli polA1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 24;41(6):1557–1564. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90565-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst G. S., Stalker D. M., Mosbaugh D. W., Meyer R. R. Stimulation of DNA polymerase by factors isolated from Novikoff hepatoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1171–1174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. P., Tamir I., Loeb L. A., Mildvan A. S. The mechanism of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase I. Magnetic resonance and kinetic studies of the role of metals. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6784–6794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. G., Gallo R. C. DNA-dependent DNA polymerases I and II from normal human-blood lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2879–2884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava B. I. Deoxynucleotide-polymerizing enzymes in normal and malignant human cells. Cancer Res. 1974 May;34(5):1015–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A., Baltimore D., Bollum F., Gallo R., Korn D. Nomenclature of eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Science. 1975 Oct 24;190(4212):401–402. doi: 10.1126/science.1179222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A. Vertebrate DNA polymerases. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


