Abstract
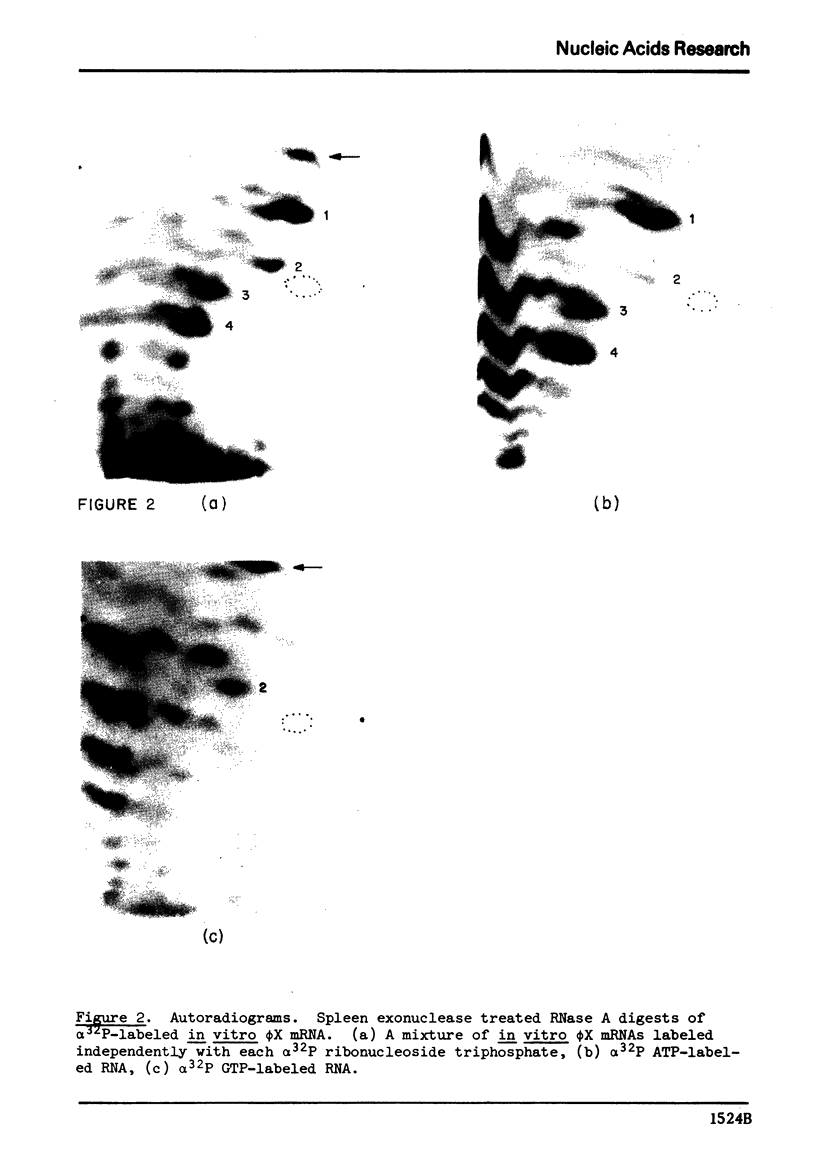
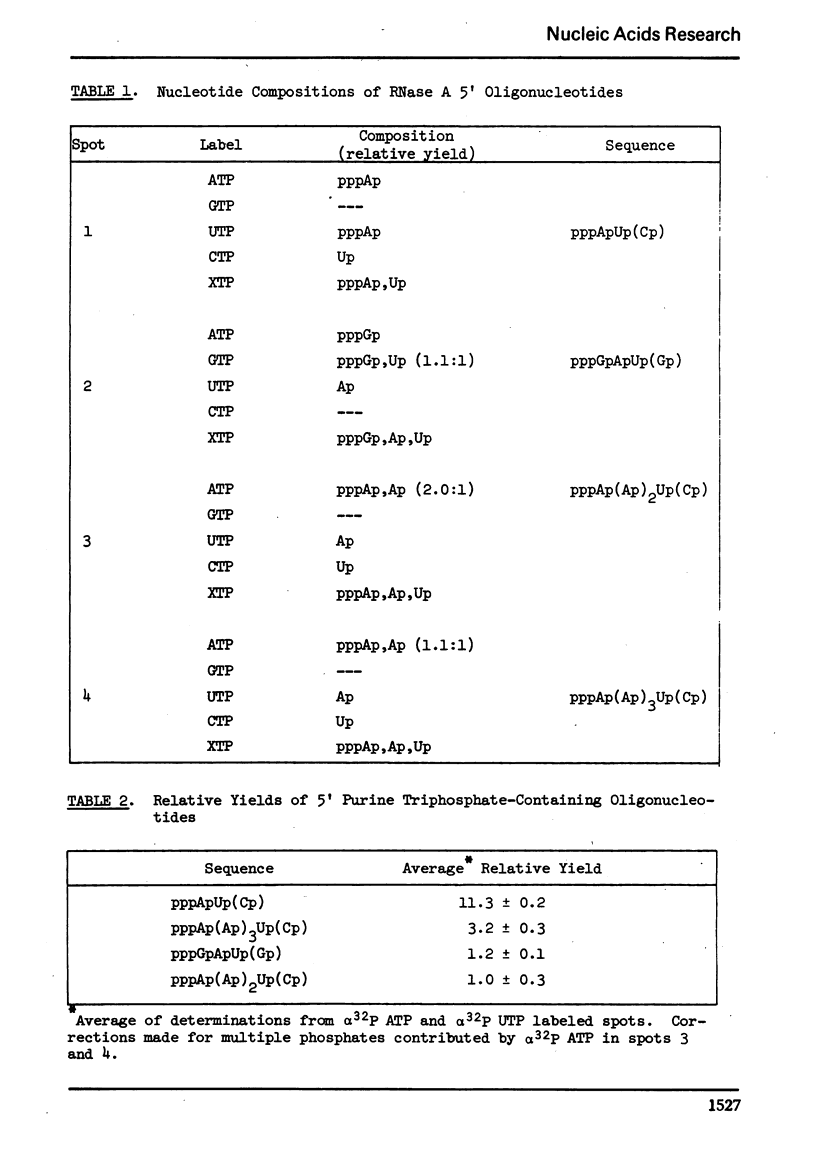
When using φX174 RFI DNA as a template, in vitro, E. coli RNA polymerase synthesizes four major purine triphosphate-containing 5′ end sequences. RNase A digests of α32P labeled RNA were further digested with spleen exonuclease to remove the bulk of the oligonucleotides with 5′ hydroxyls and then chromatographed on DEAE cellulose to resolve the remaining 5′ terminal oligonucleotides. By application of standard separation and sequence techniques, the major 5′ end sequences were shown to be: pppApUp(Cp), pppApApApUp(Cp), pppApApApApUp(Cp), and pppGpApUp(Gp).
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernardi A., Bernardi G. Studies on acid hydrolases. IV. Isolation and characterization of spleen exonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):360–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi A., Cantoni G. L. Action of spleen exonuclease on transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1468–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Dahlberg J. E. RNA synthesis startpoints in bacteriophage lambda: are the promoter and operator transcribed? Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):227–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio237227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F. Chromatography of 32P-labelled oligonucleotides on thin layers of DEAE-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Isolation and genetic localization of three phi-X174 promoter regions. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):233–236. doi: 10.1038/newbio243233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. T7 early RNAs are generated by site-specific cleavages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1559–1563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M. N., Hayashi M. Isolation of phi X174 specific messenger ribonucleic acids in vivo and identification of their 5' terminal nucleotides. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):207–215. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.207-215.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano T., Sinsheimer R. L. Preparation and purification of phi X-RF component I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 29;155(1):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Webster R. E., Zinder N. D. Purification and properties of ribonuclease III from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M., Okamoto T., Takanami M. Starting nucleotide sequences of RNA synthesized on the replicative form DNA of coliphage fd. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 28;43(2):299–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]