Abstract
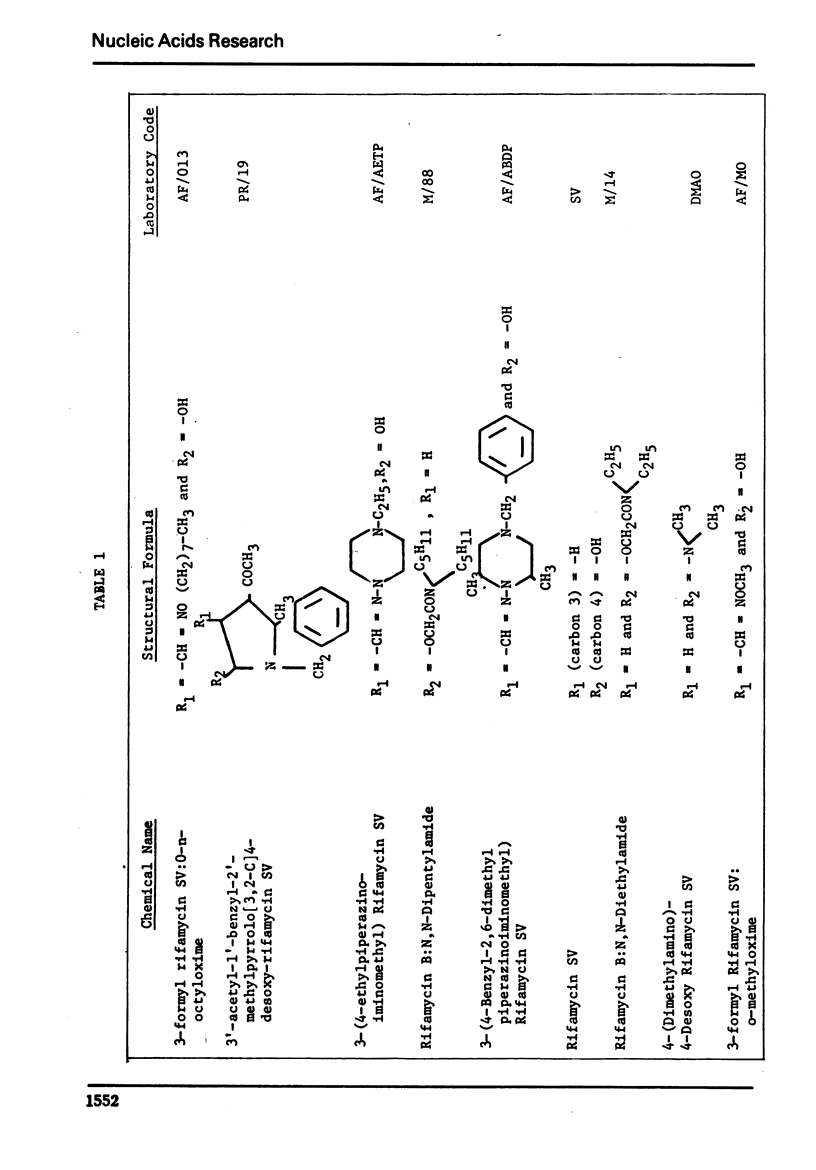
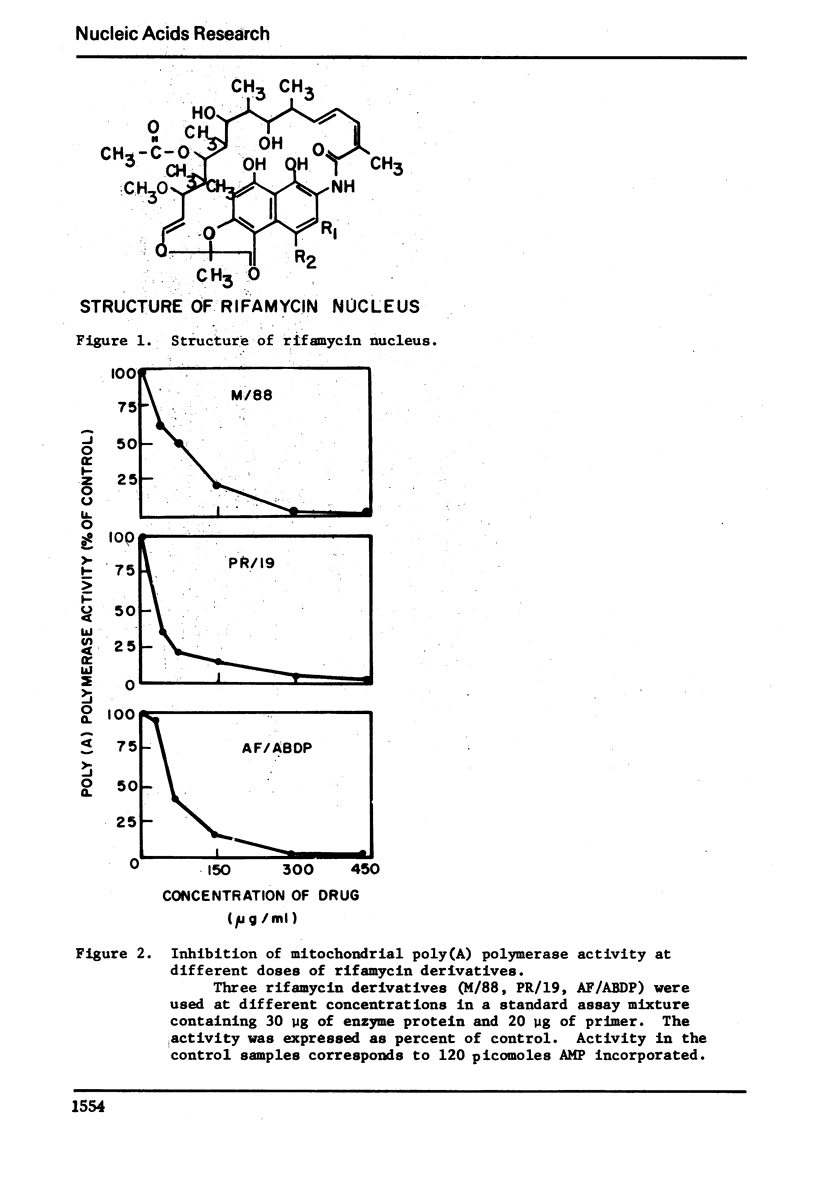
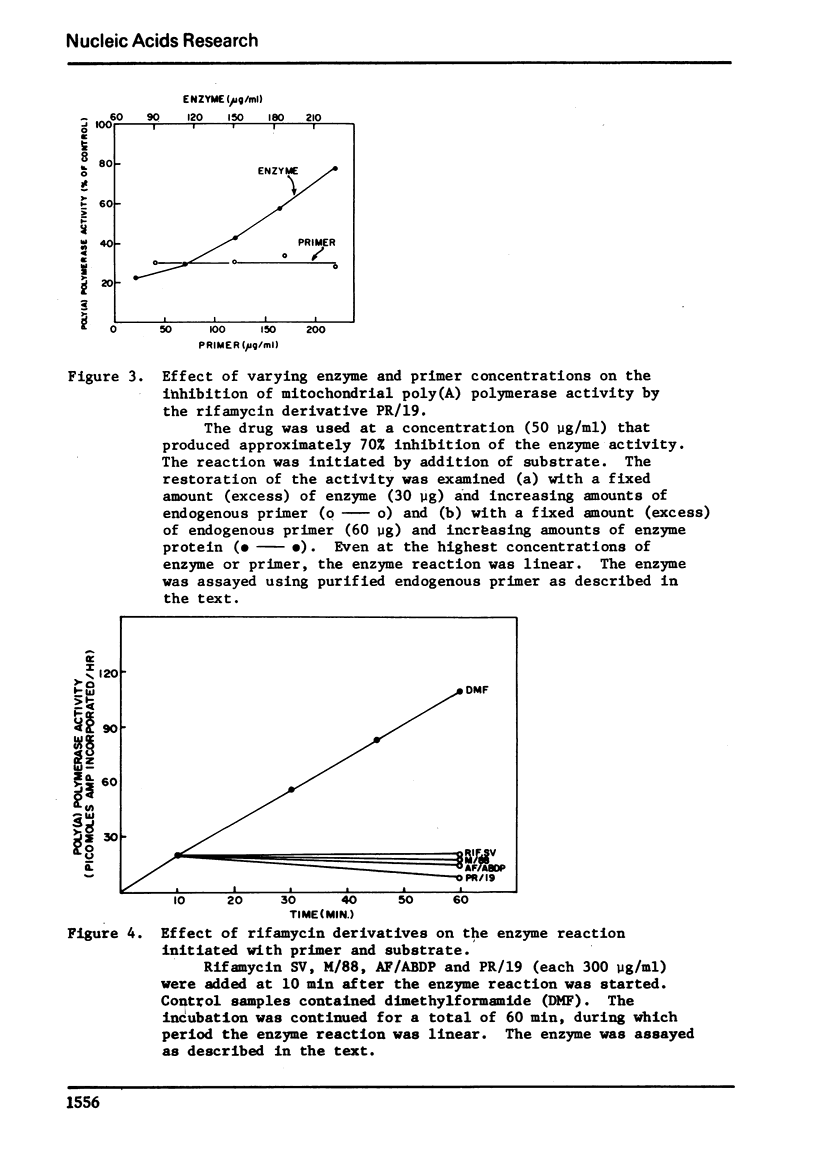
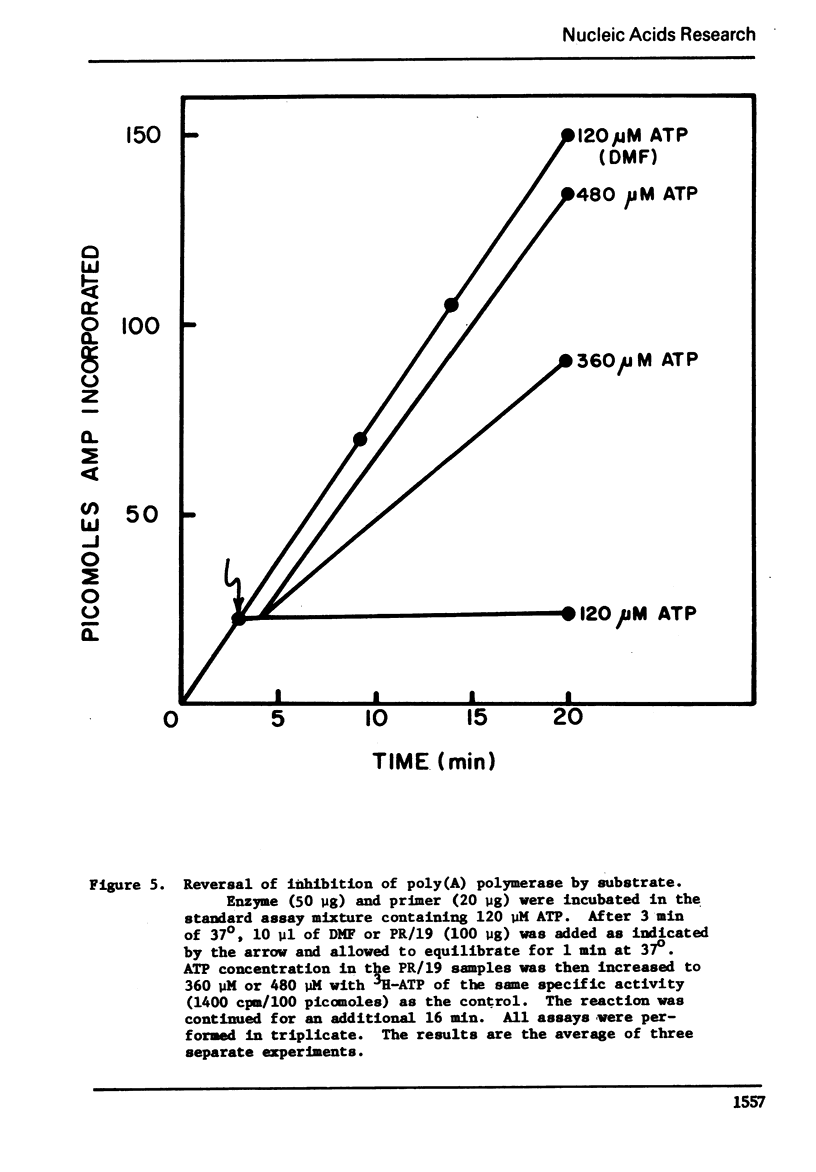
The effect of several rifamycin derivatives on poly(A) synthesis in vitro was tested using purified rat liver mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase assayed with an exogenous primer. When used at a concentration of 300 μg/ml, derivatives AF/013, PR/19, AF/AETP, M/88 and AF/ABDP completely inhibited activity corresponding to 50 μg of enzyme protein. Under similar conditions, derivatives DMAO and AF/MO failed to inhibit enzyme activity. Studies with PR/19 showed that the drug interacted directly with the enzyme molecule and did not affect the enzyme-primer complex formation. The inhibition by the drug could be reversed by increasing the substrate (ATP) concentration. It is concluded that some rifamycin derivatives can specifically inhibit template-independent nucleotide chain elongation reactions.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark R. J. Antiviral action of rifampin. N Engl J Med. 1971 Mar 25;284(12):675–675. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197103252841219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Altered characteristics of mammalian RNA polymerase following solubilization from nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Sep 6;32(5):831–838. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Schindler D. G. Polyriboadenylate polymerase solubilized from rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):126–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhasz P. P., Benecke B. J., Seifart K. H. Inhibition of RNA polymerases from rat liver by the semi-synthetic rifampicin derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 15;27(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80402-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein J., Scholte H. R., Wit-Peeters E. M. A rapid and simple procedure to deplete rat-liver mitochondria of lysosomal activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 8;223(2):432–436. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin L. I. Minor species of ribonucleic acid associated with rat liver mitochondria. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 7;10(25):4752–4756. doi: 10.1021/bi00801a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meilhac M., Tysper Z., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 4. Studies on inhibition by rifamycin derivatives. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):291–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi T., Muramatsu M. Inhibition by derivatives of rifamycin of soluble ribonucleic acid polymerase from rat liver. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1361–1364. doi: 10.1042/bj1281361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C., Greenawalt J. W. Enzymatic properties of the inner and outer membranes of rat liver mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):158–175. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A., Hartmann G. Mode of action of rafamycin on the RNA polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):218–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So A. G., Downey K. M. Studies on the mechanism of ribonucleic acid synthesis. II. Stabilization of the deoxyribonucleic acid-ribonucleic acid polymerase complex by the formation of a single phosphodiester bond. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 24;9(24):4788–4793. doi: 10.1021/bi00826a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Mizuno S., Yamazaki H., Nitta K. Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis by rifamycins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Mar;21(3):234–236. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Nüesch J., Knüsel F., Staehelin M. Action of rifamycins on RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Mauro E., Synder L., Marino P., Lamberti A., Coppo A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Rifampicin sensitivity of the components of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):533–537. doi: 10.1038/222533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


