Abstract
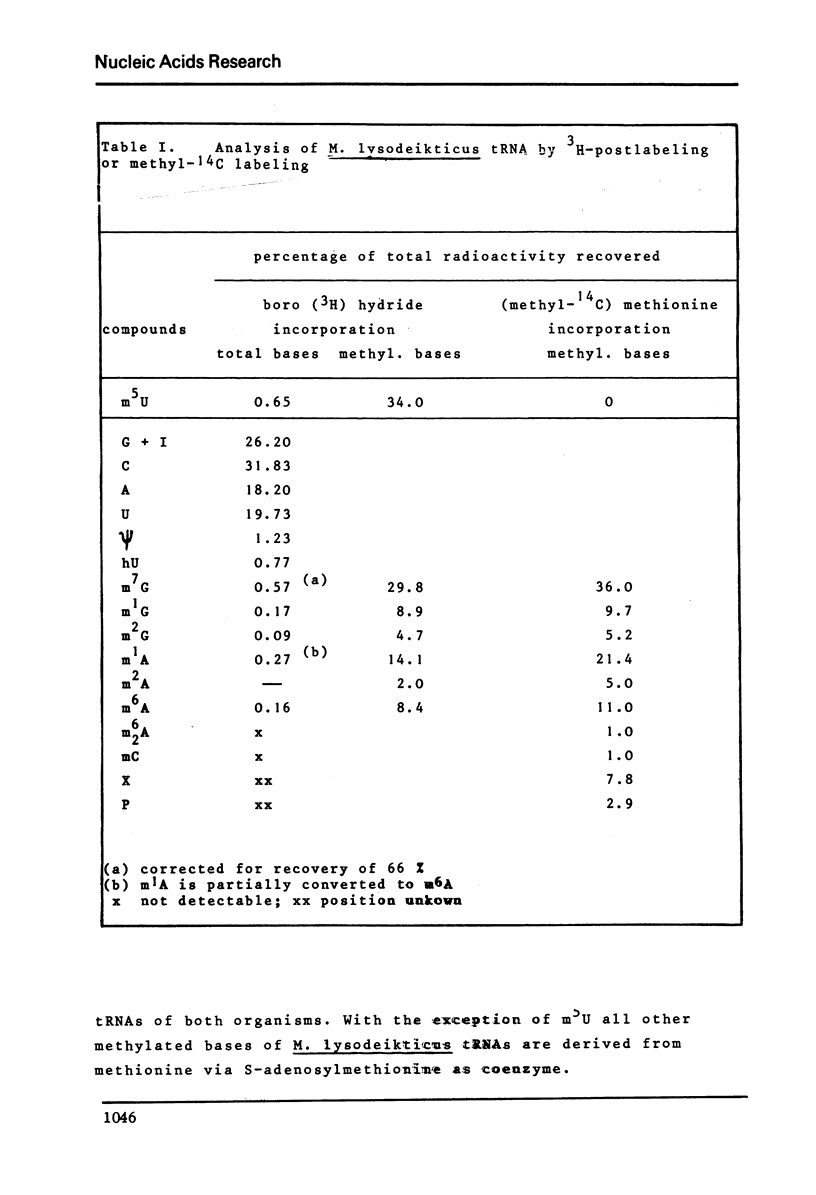
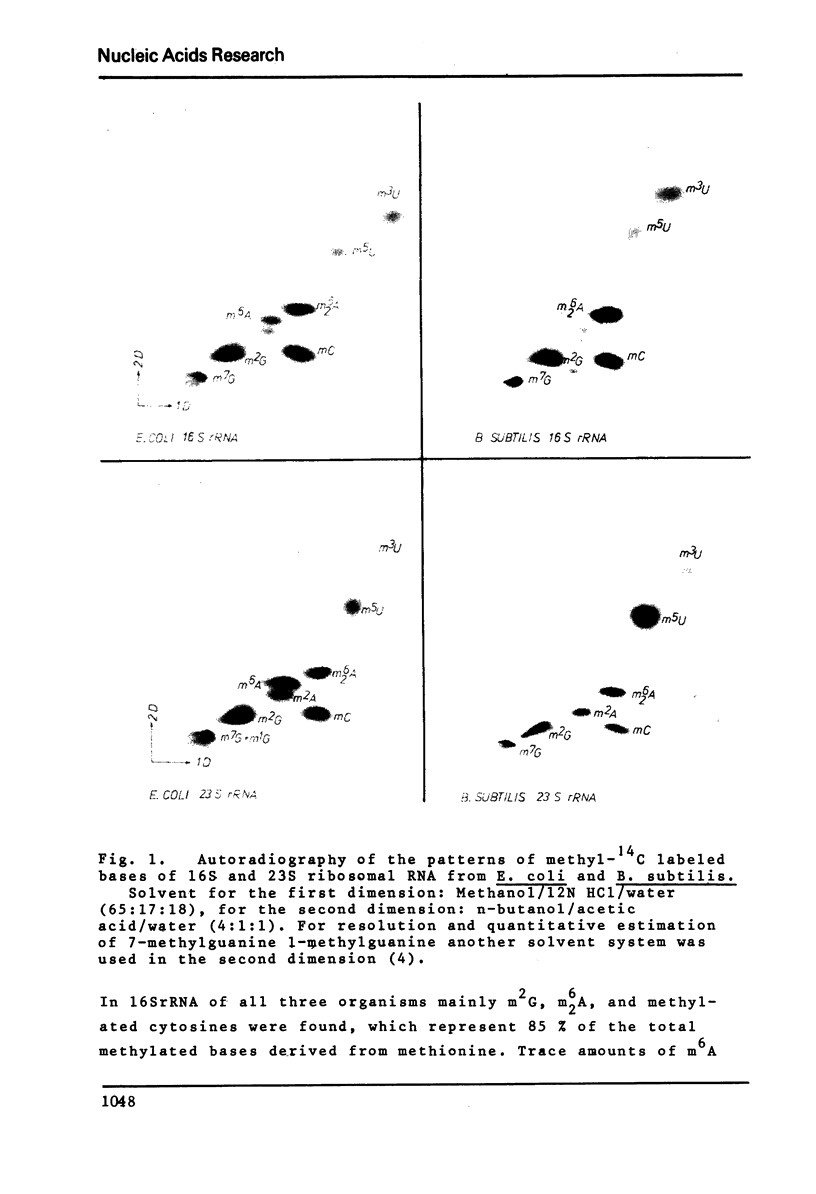
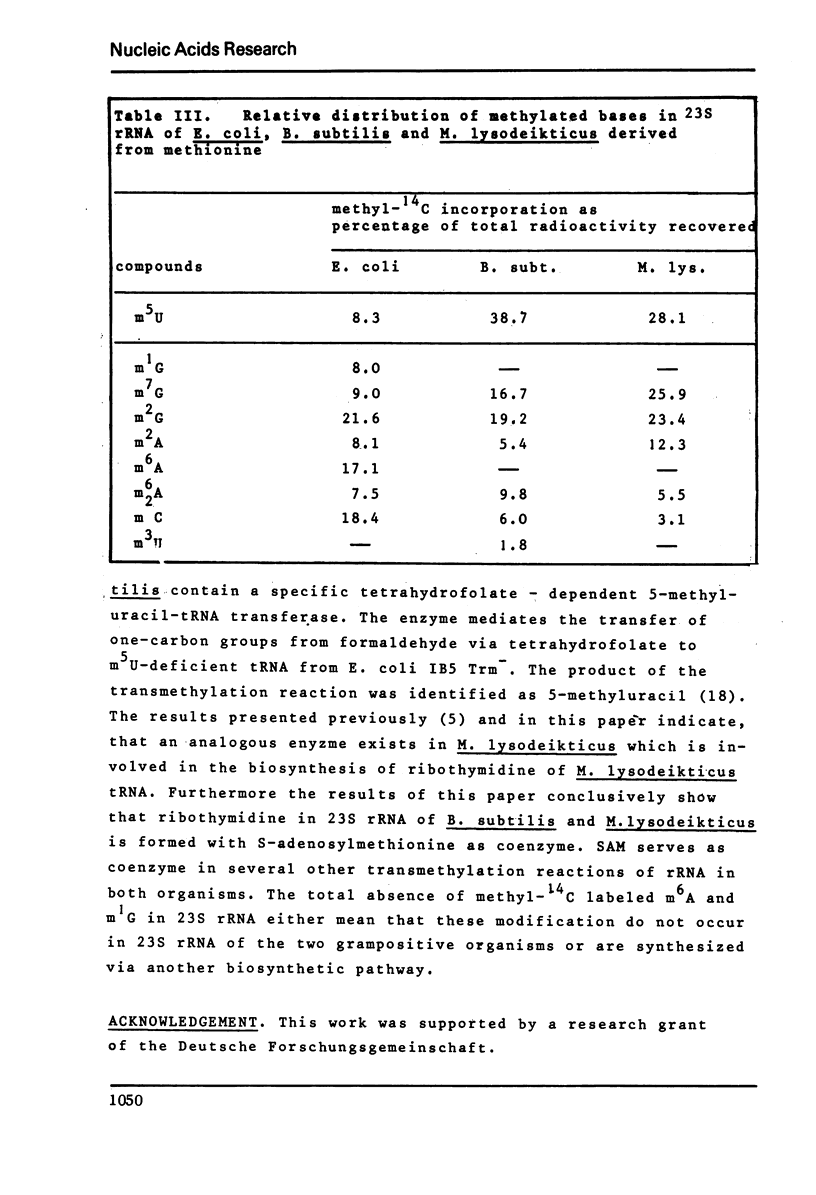
Ribothymidine (m5u) in tRNAs of M. lysodeikticus is not derived from methionine. The results indicate that as in tRNAs of B. subtilis a tetrahydrofolate derivative is involved in the formation of m5U, whereas methionine serves as precursor in the biosynthesis of m7G, m1A and m6A. Ribothymidine also occurs in 23S rRNA of B. subtilis and M. lysodeikticus. Approximately 2-3 moles of m5U residues were found per mole of 23S rRNA. In contrast to m5U residues present in tRNAs of B. subtilis and M. lysodeikticus, ribothymidine in 23S rRNA of these organisms and of E. coli is synthesized via S-adenosylmethionine. m6A and m1G, present in E. coli rRNAs, were not detected in rRNAs of (methyl-14C) methionine labeled B. subtilis and M. lysodeikticus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agris P. F., Koh H., Söll D. The effect of growth temperatures on the in vivo ribose methylation of Bacillus stearothermophilus transfer RNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H. H., Kersten H. Inhibition of the tetrahydrofolate-dependent biosynthesis of ribothymidine in tRNAs of B. subtilis and M. lysodeikticus by trimethoprim. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 1;53(2):258–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H. H., Schmidt W., Kersten H. Occurrence and biosynthesis of ribothymidine in tRNAs of B. subtilis. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 15;52(1):62–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80638-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H., Kersten H. The occurrence of ribothymidine, 1-methyladenosine, methylated guanosines and the corresponding methyltransferases in E. coli and Bacillus subtilis. FEBS Lett. 1973 Oct 1;36(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delk A. S., Rabinowitz J. C. Biosynthesis of ribosylthymine in the transfer RNA of Streptococcus faecalis: a folate-dependent methylation not involving S-adenosylmethionine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):528–530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Stiegler P., Mackie G. A., Zimmermann R. A., Ebel J. P., Fellner P. Primary sequence of the 16S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Feb;2(2):265–278. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellner P. Nucleotide sequences from specific areas of the 16S and 23S ribosomal RNAs of E. coli. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Nov;11(1):12–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ J., GOLD M., ANDERS M. THE ENZYMATIC METHYLATION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. 3. PURIFICATION OF SOLUBLE RIBONUCLEIC ACID-METHYLATING ENZYMES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3462–3473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M. An evolutionary study of the methylation of transfer and ribosomal ribonucleic acid in prokaryote and eukaryote organisms. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2612–2620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath E., Chia L. L., Morris H. P., Randerath K. Base analysis of RNA by 3H postlabeling--a study of ribothymidine content and degree of base methylation of 4 S RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 11;366(2):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo J. M., Delk A. S., Rabinowitz J. C. The occurrence of a transmethylation reaction not involving S-adenosylmethionine in the formation of ribothymidine in Bacillus subtilis transfer-RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1256–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80419-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]