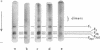Abstract
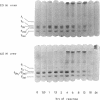
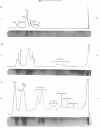
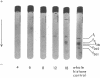
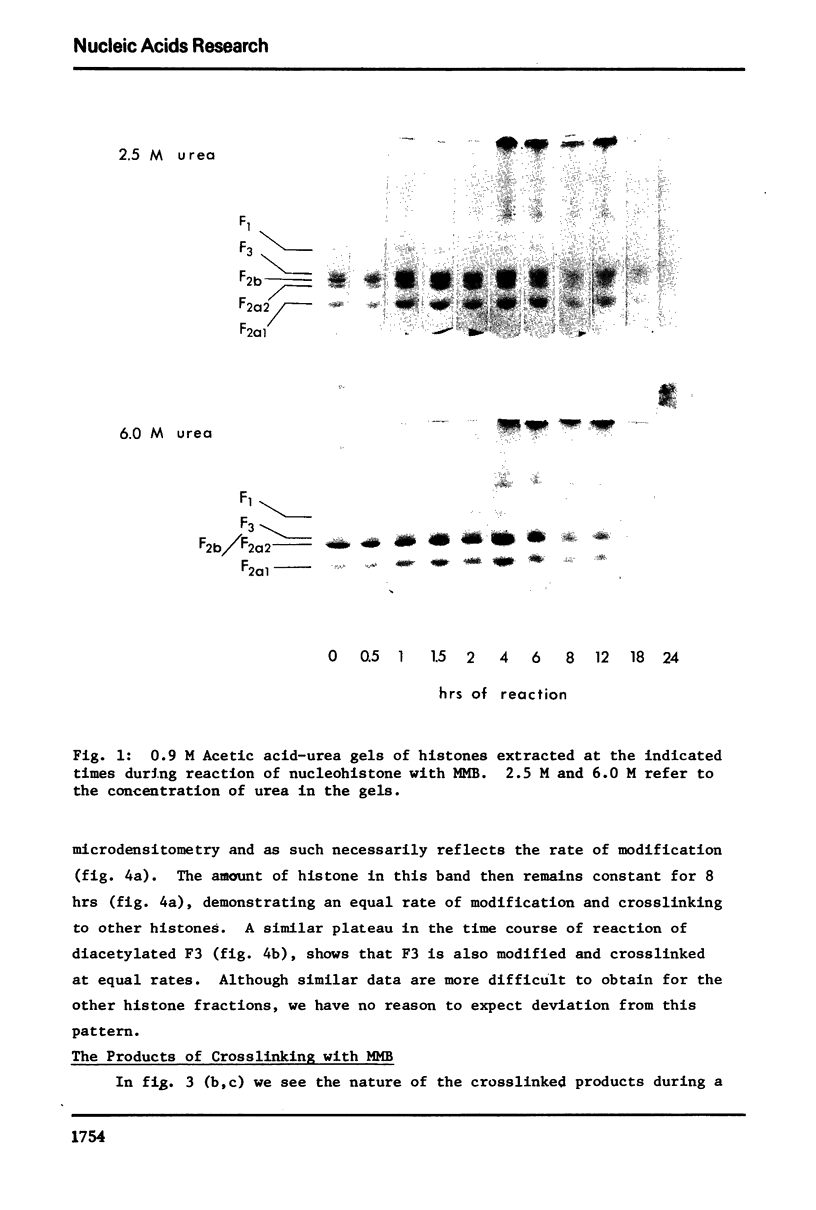
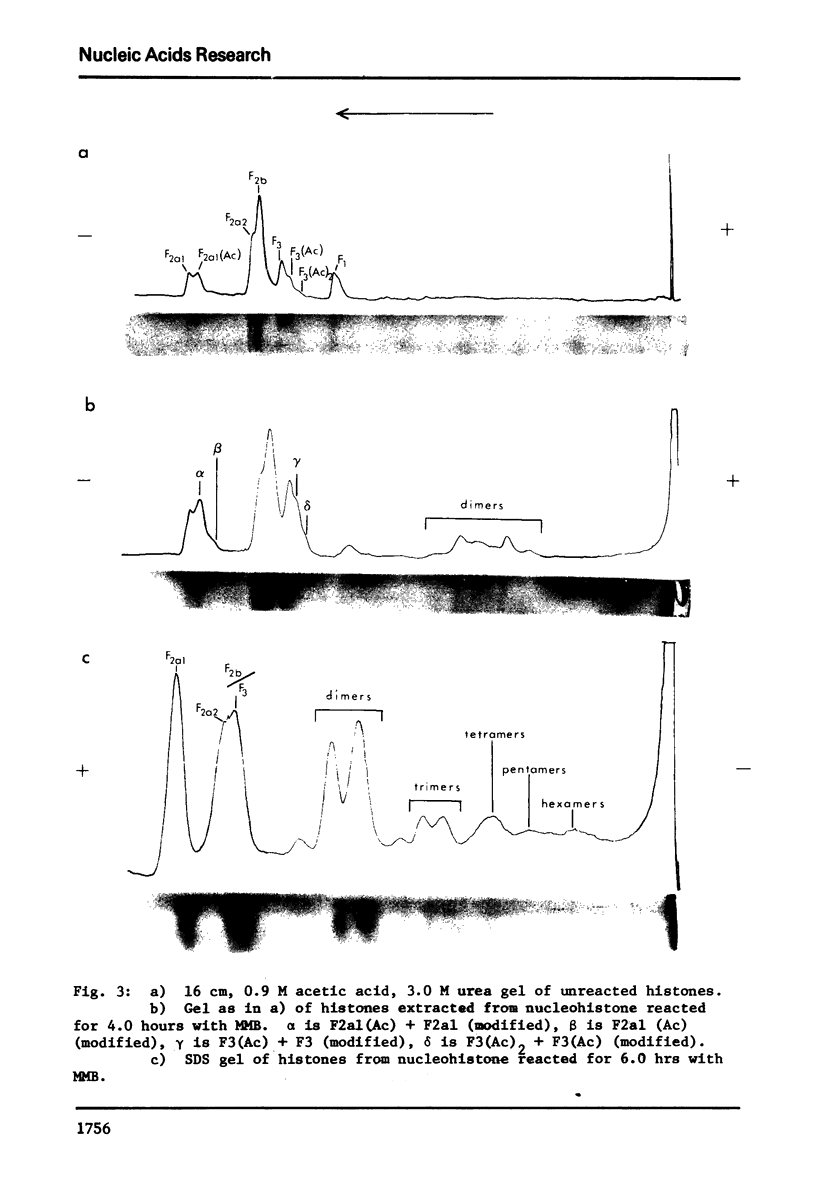
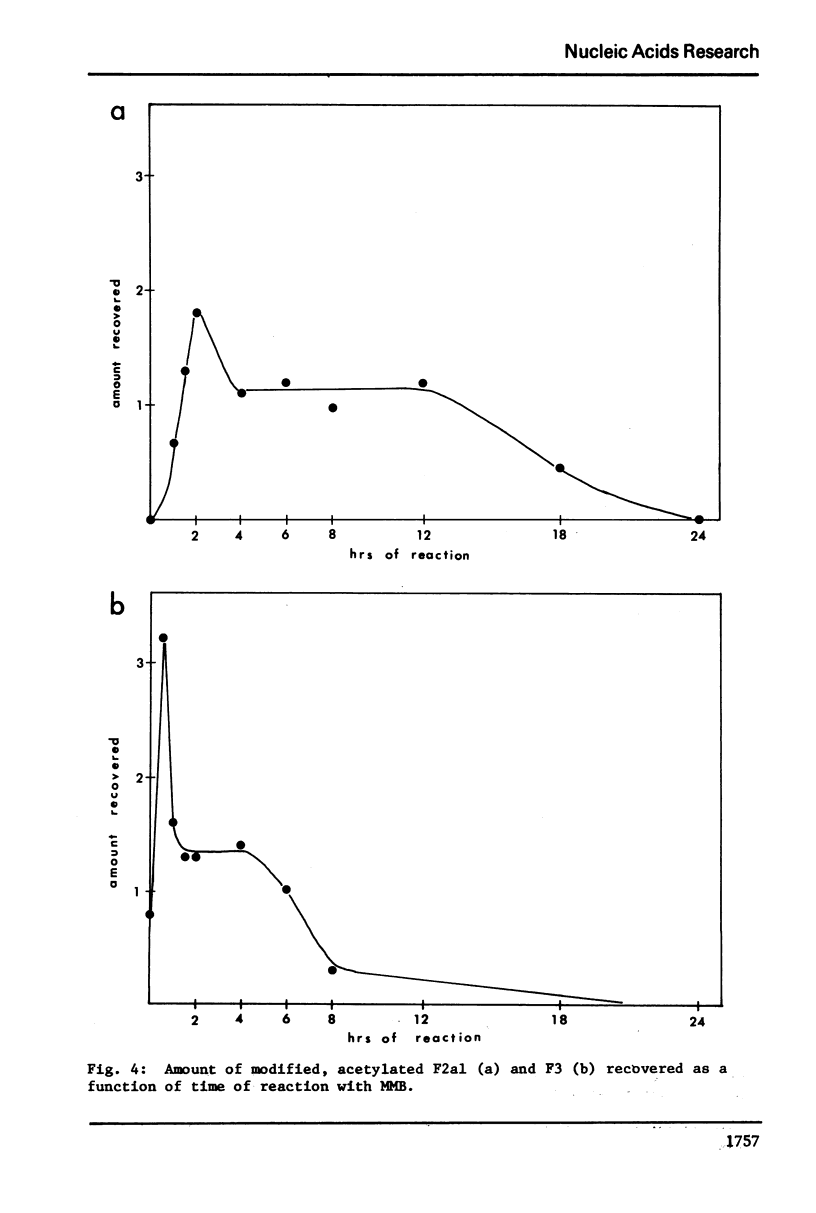
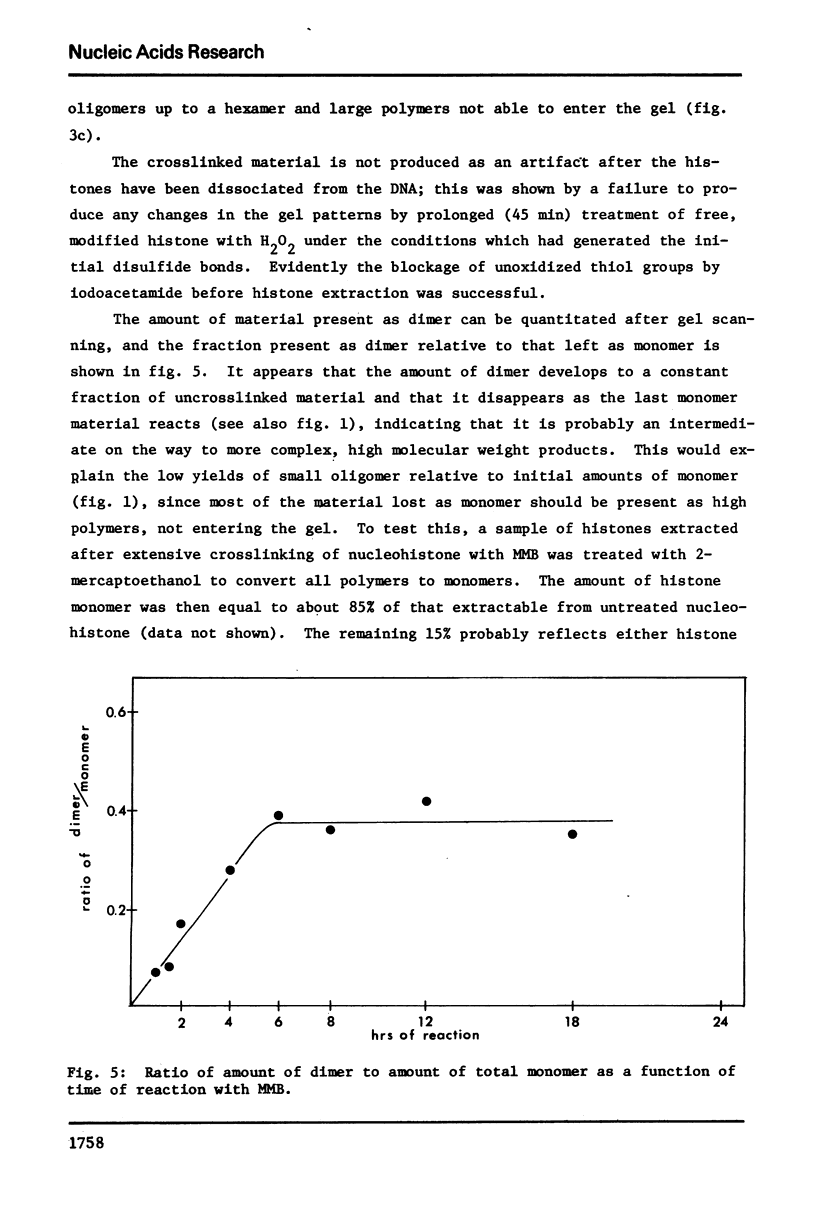
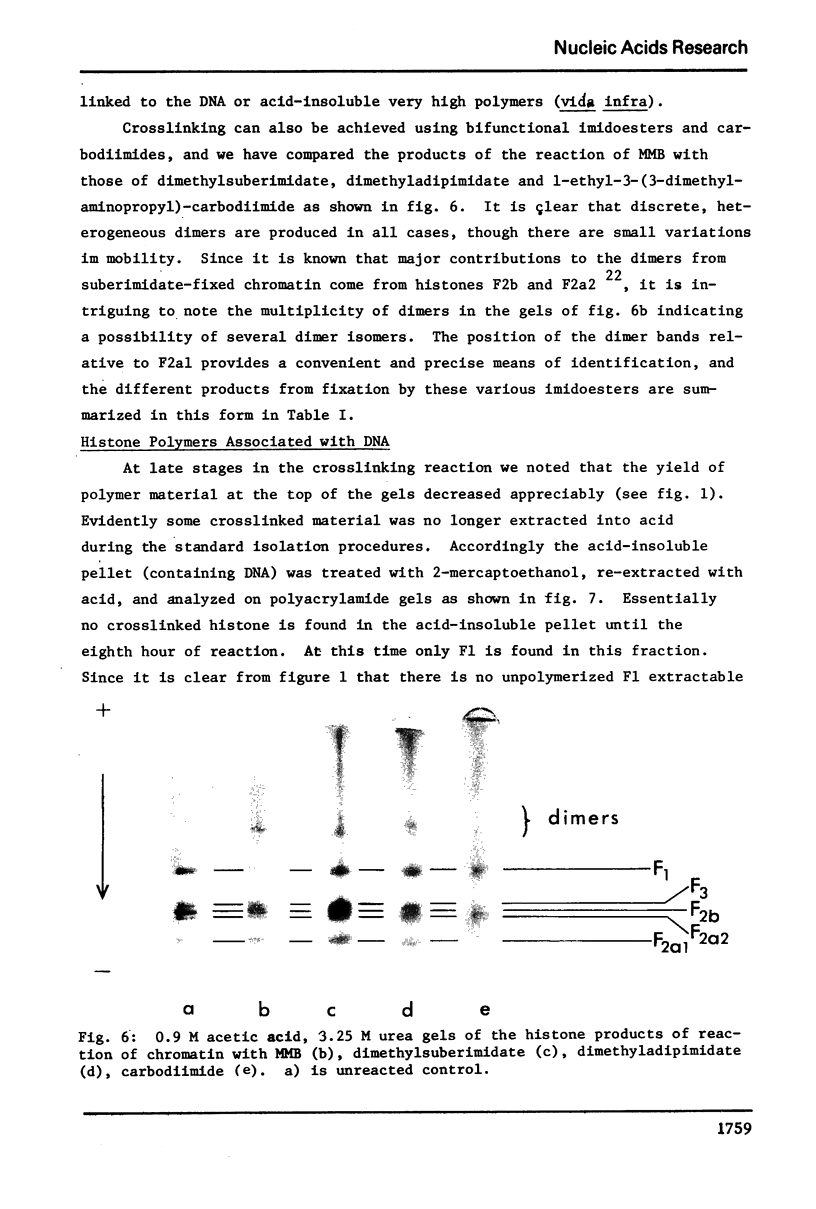
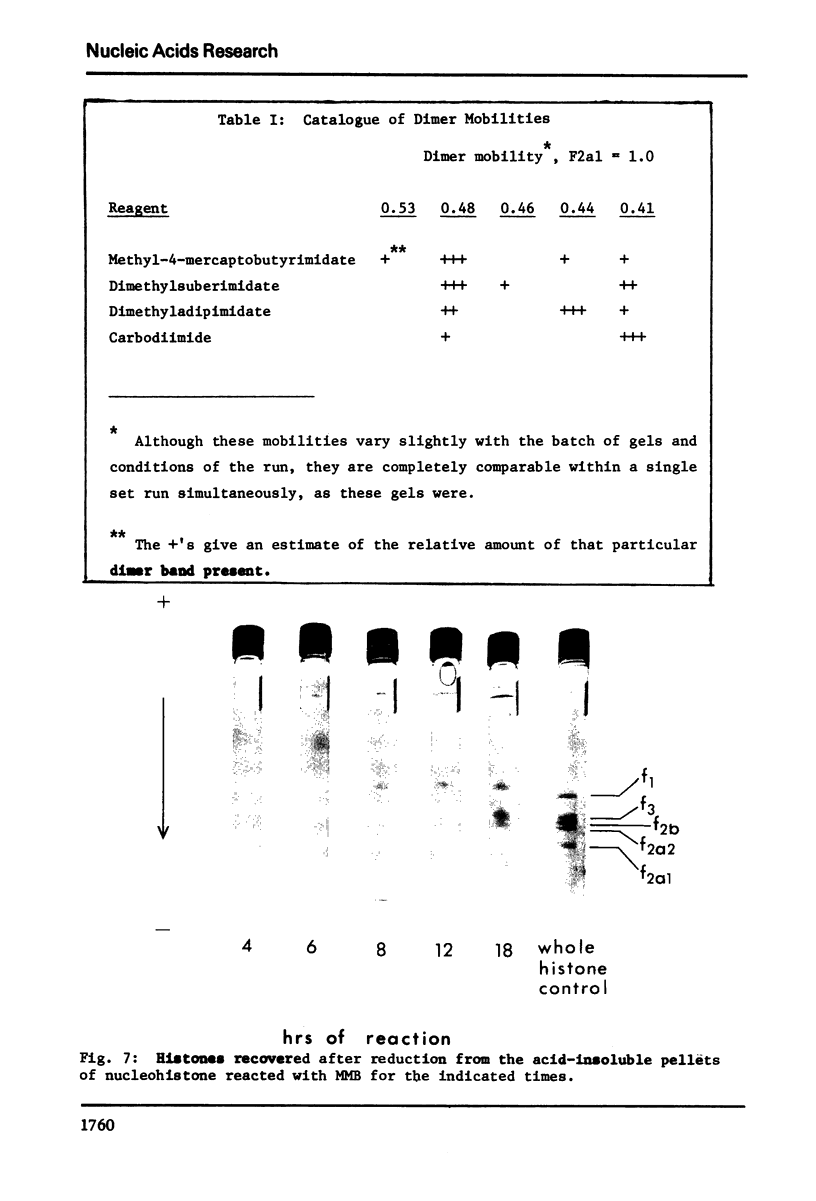
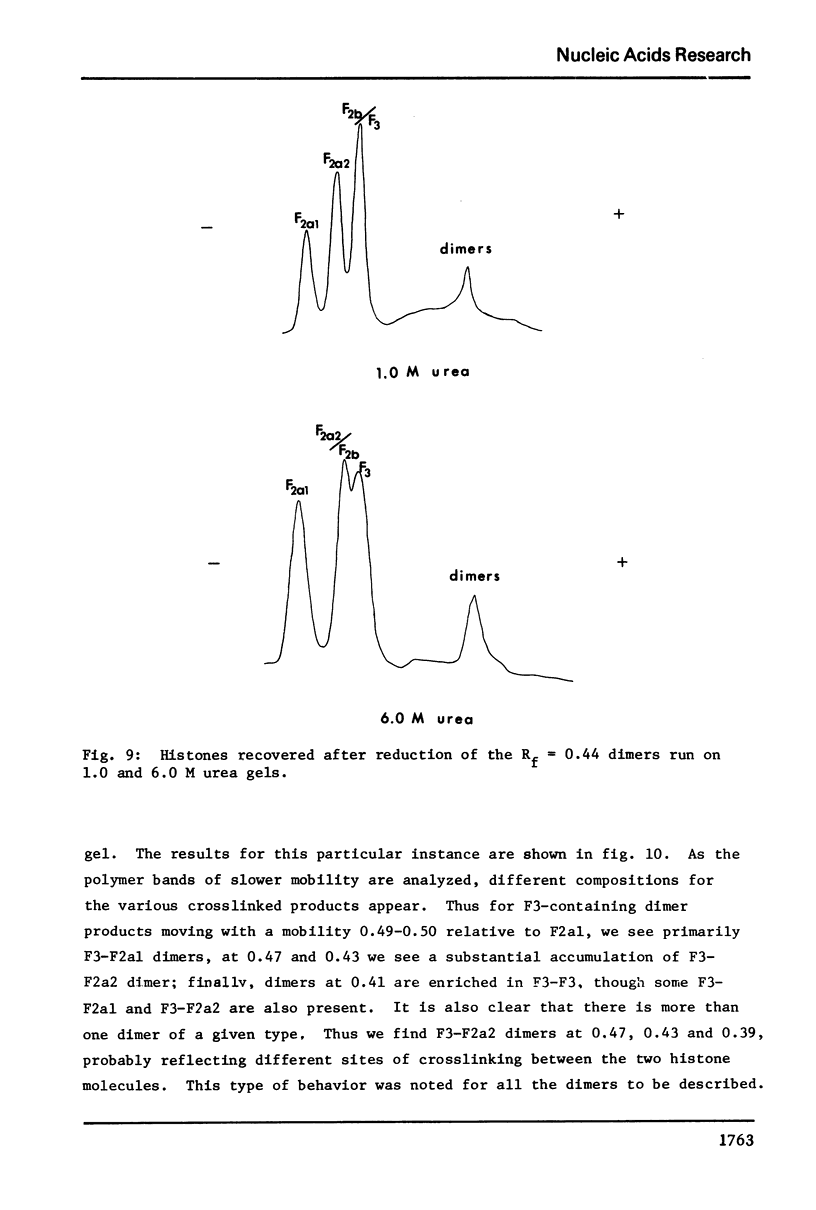
The primary sequence organization of histones upon the DNA molecule in chromatin has been analyzed by extension of the nucleoprotein at very low ionic strength and crosslinking with a reversible crosslinking reagent, methyl-4-mercaptobutyrimidate. Histones extracted after limited reaction were fractionated into different classes and the composition of the oligomers analyzed after reduction of the crosslinked material. We have found that the following dimers occur at a high frequency: (F3-F2b), (F3-F2a2), and (F2b-F2a2), whereas (F2b-F2al), (F3-F2al) and (F3-F3) occur with a lower frequency. F1 appears to polymerize rapidly to largely homogeneous polymers of high molecular weight. These results are analyzed in terms of several models proposed for chromatin structure.
Full text
PDF





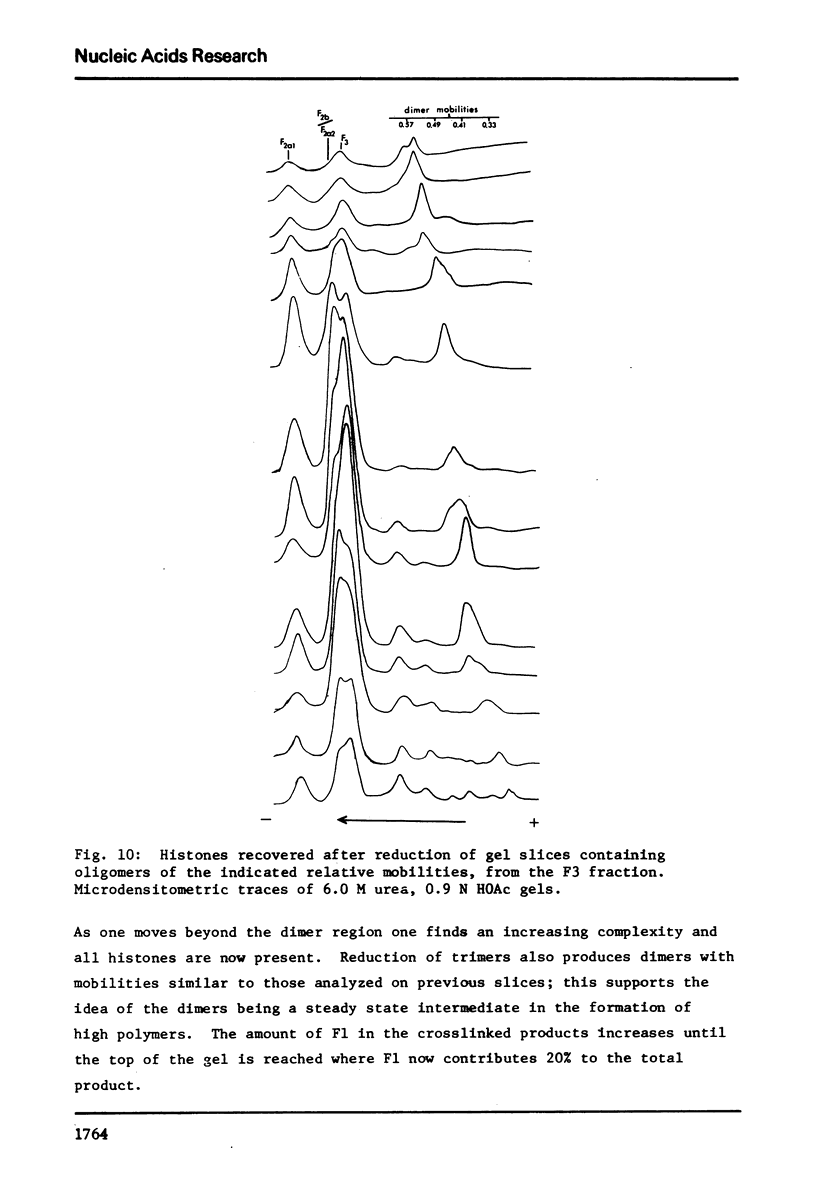
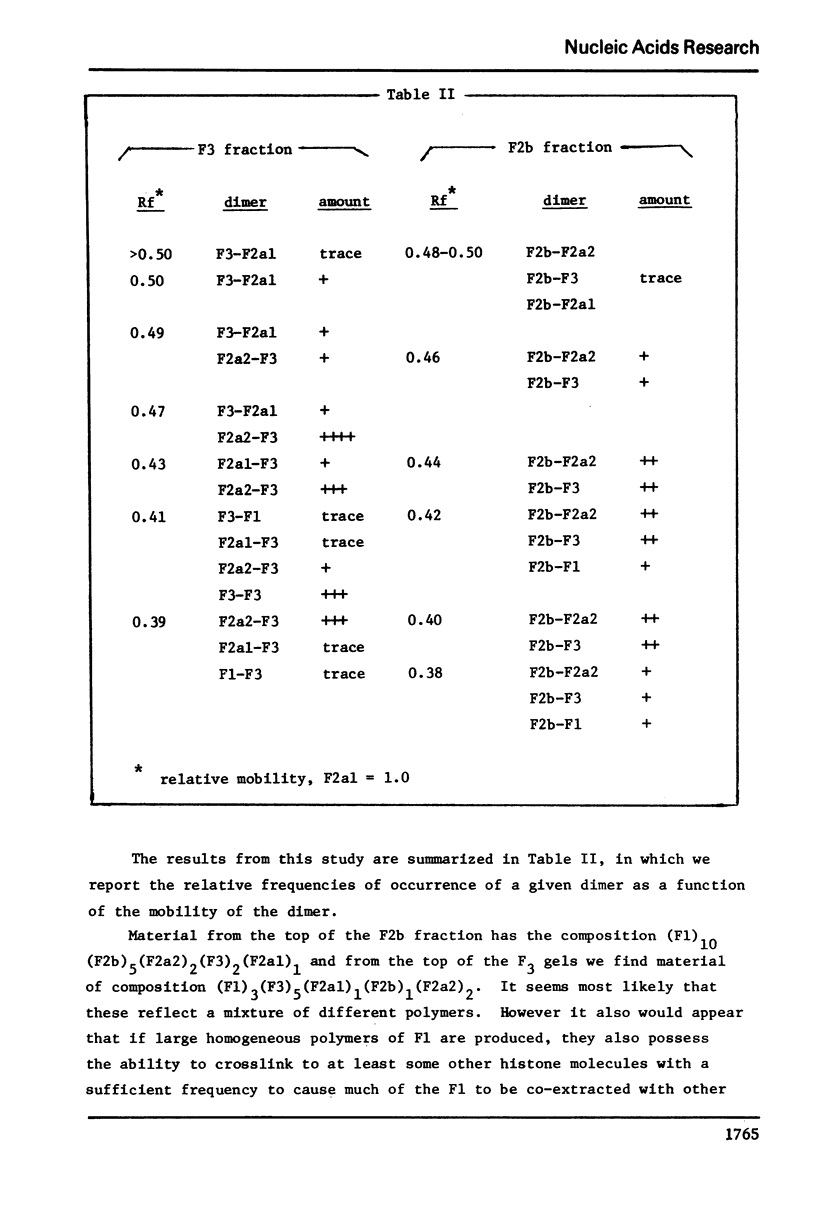
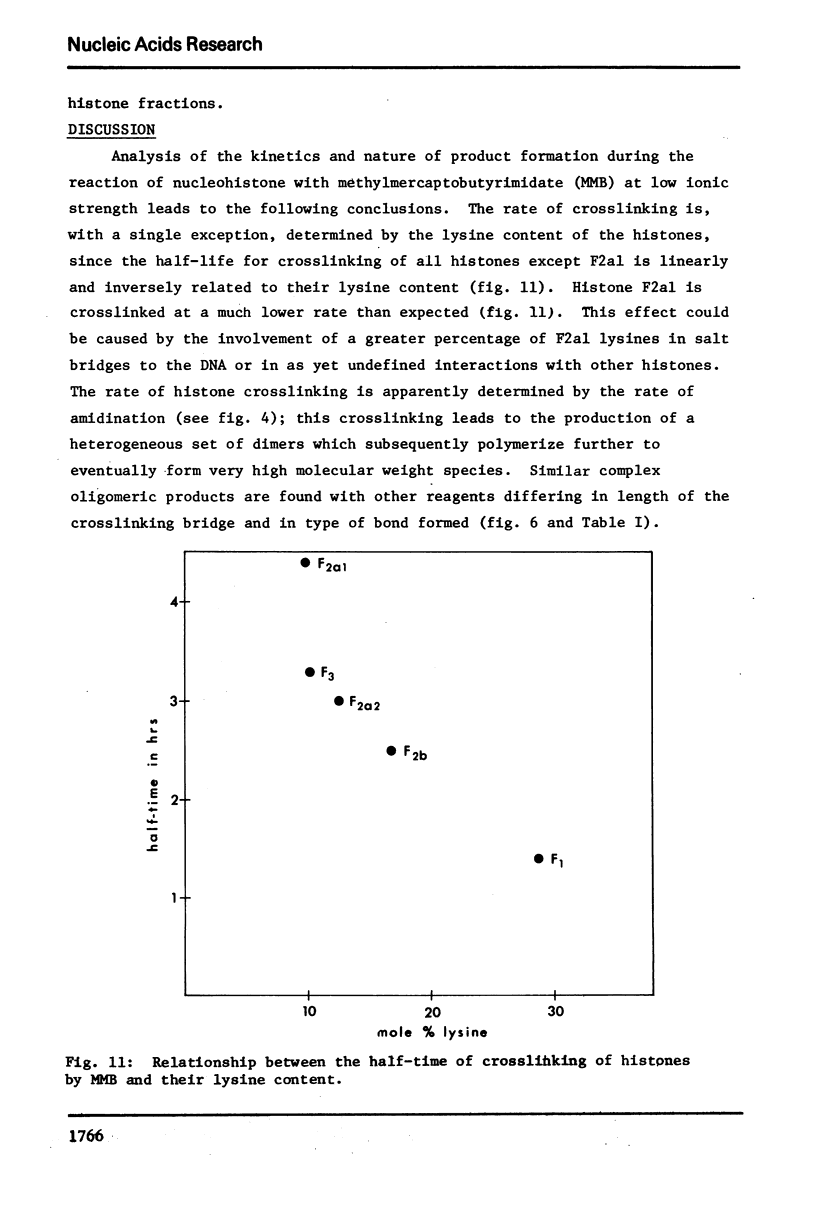




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axel R., Melchior W., Jr, Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. Specific sites of interaction between histones and DNA in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4101–4105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley J., Chalkley R. An approach to the structure of native nucleohistone. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):468–474. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Pollard H. B. The presence of F3-F2a1 dimers and F1 oligomers in chromatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):282–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Cary P. D., Chapman G. E., Crane-Robinson C., Danby S. E., Rattle H. W., Boublik M., Palau J., Aviles F. J. Studies on the role and mode of operation of the very-lysine-rich histone H1 (F1) in eukaryote chromatin. The conformation of histone H1. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Apr 1;52(3):605–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Hewish D. R., Mobbs J. Mammalian chromatin substructure studies with the calcium-magnesium endonuclease and two-dimensional polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):67–72. doi: 10.1042/bj1430067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalkley R. Histone propinquity using imidoesters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 19;64(2):587–594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalkley R., Hunter C. Histone-histone propinquity by aldehyde fixation of chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1304–1308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Anna J. A., Jr, Isenberg I. A histone cross-complexing pattern. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 19;13(24):4992–4997. doi: 10.1021/bi00721a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Chromatin structure: deduced from a minichromosome. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1202–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. E., Walker I. O. A model for chromatin sub-structure incorporating symmetry considerations of histone oligomers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Mar;2(3):405–421. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.3.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. E., Walker I. O. Covalent cross-linking of histones in chromatin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80477-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. I. Isolation of a histone IIb1-IIb2 complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 15;54(4):1588–1594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Thomas J. O. Chromatin structure; oligomers of the histones. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):865–868. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson H. G., McCarthy B. J. Histone-histone associations within chromatin. Cross-linking studies using tetranitromethane. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 11;14(5):1073–1078. doi: 10.1021/bi00676a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Internal structure of the chromatin subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1573–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Spheroid chromatin units (v bodies). Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins D. E., Wright E. B. Glutaraldehyde fixation of isolated eucaryotic nuclei. Evidence for histone-histone proximity. J Cell Biol. 1973 Nov;59(2 Pt 1):304–317. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.2.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D., Sommer K. R., Panyim S., Spiker S., Chalkley R. A modified procedure for fractionating histones. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(2):349–353. doi: 10.1042/bj1290349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Bilek D., Chalkley R. An electrophoretic comparison of vertebrate histones. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4206–4215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. The molecular weights of vertebrate histones exploiting a modified sodium dodecyl sulfate electrophoretic method. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7557–7560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Sommer K. R., Chalkley R. Oxidation of the cysteine-containing histone F3. Detection of an evolutionary mutation in a conservative histone. Biochemistry. 1971 Oct 12;10(21):3911–3917. doi: 10.1021/bi00797a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon J. F., Wilkins M. H., Richards B. M. Super-helical model for nucleohistone. Nature. 1967 Jul 29;215(5100):508–509. doi: 10.1038/215508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roark D. E., Geoghegan T. E., Keller G. H. A two-subunit histone complex from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 24;59(2):542–547. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Moudrianakis E. N. The F3-F2a1 complex as a unit in the self-assembly of nucleoproteins. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1718–1726. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Van Holde K. E. The effect of trypsin on nuclease-resistant chromatin fragments. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):152–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior M. B., Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Chromatin fragments resembling v bodies. Science. 1975 Jan 17;187(4172):173–175. doi: 10.1126/science.1111096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Holde K. E., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Shaw B. R. A model for particulate structure in chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1579–1586. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lente F., Jackson J. F., Weintraub H. Identification of specific crosslinked histones after treatment of chromatin with formaldehyde. Cell. 1975 May;5(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. B., Olins D. E. Histone stoichiometry in chicken erythrocyte nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 7;63(3):642–650. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80432-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bruggen E. F., Arnberg A. C., van Holde K. E., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Shaw B. R. Electron microscopy of chromatin subunit particles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1365–1370. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]