Abstract
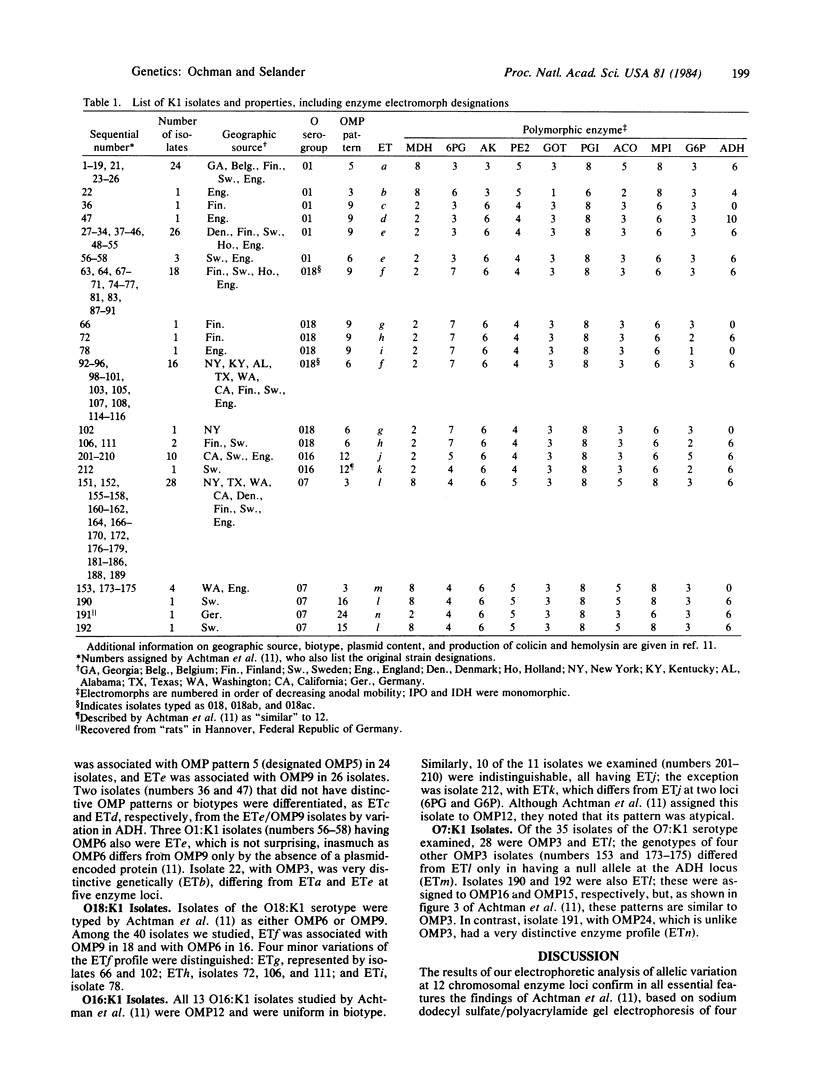
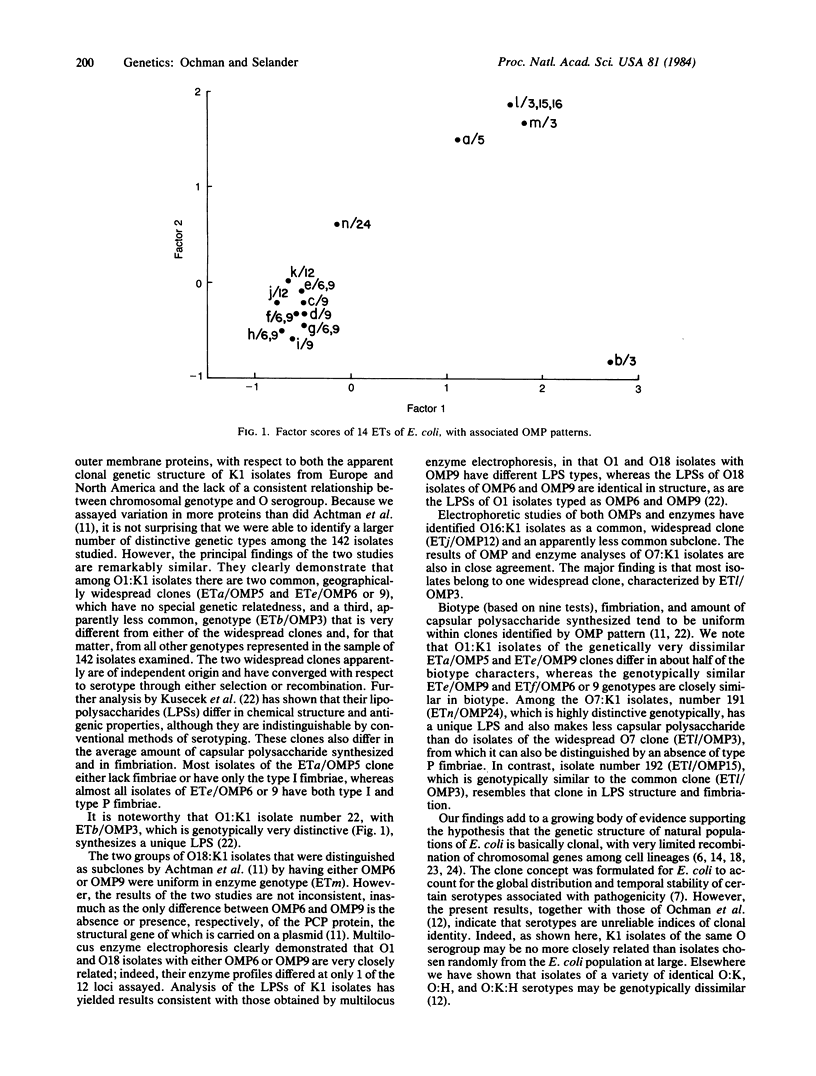
Genotypes of 142 K1 isolates of four O serogroups of Escherichia coli from human hosts in Europe and the United States were characterized by an electrophoretic analysis of allozymic variation in 12 chromosomally encoded enzymes. The genetic structure of natural populations revealed by this analysis is closely similar to that indicated in earlier studies by Achtman and colleagues of the electrophoretic migration pattern for four outer membrane proteins and the chemical structure of the cell-wall lipopolysaccharides. The combined evidence demonstrates that most of the K1 isolates belong to a small number of geographically widespread clones. The distribution of O serogroups among the isolates does not consistently correspond to the clonal structure; O1:K1 isolates represent at least two distantly related, geographically widespread clones, one of which is genetically similar to a clone of the O18:K1 serotype. These findings for K1 isolates add to a growing body of evidence supporting the hypothesis that the genetic structure of natural populations of E. coli is basically clonal, with very limited recombination of chromosomal genes. Clonal structure has important implications for the study of the determinants of pathogenicity and disease specificity in E. coli.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettelheim K. A., Ismail N., Shinebaum R., Shooter R. A., Moorhouse E., Farrell W. The distribution of serotypes of Escherichia coli in cow-pats and other animal material compared with serotypes of E. coli isolated from human sources. J Hyg (Lond) 1976 Jun;76(3):403–406. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400055327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettelheim K. A. The sources of "OH" serotypes of Escherichia coli. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Feb;80(1):83–113. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Skerman F. J., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence divergence among strains of Escherichia coli and closely related organisms. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):953–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.953-965.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Levin B. R., Lidin-Janson G., Whittam T. S., Svanborg Edén C., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and relationships among strains of Escherichia coli in the intestine and those causing urinary tract infections. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:203–227. doi: 10.1159/000318331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Levin B. R., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and temporal variation in the E. coli population of a human host. Genetics. 1981 Jul;98(3):467–490. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykhuizen D. E., Hartl D. L. Functional effects of PGI allozymes in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1983 Sep;105(1):1–18. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykhuizen D., Hartl D. L. Selective neutrality of 6PGD allozymes in E. coli and the effects of genetic background. Genetics. 1980 Dec;96(4):801–817. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl D. L., Dykhuizen D. E. Potential for selection among nearly neutral allozymes of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6344–6348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann K., Jann B. The K antigens of Escherichia coli. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:53–79. doi: 10.1159/000407421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkman R., Crawford I. P. Clustered third-base substitutions among wild strains of Escherichia coli. Science. 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):378–380. doi: 10.1126/science.6346486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Whittam T. S., Caugant D. A., Selander R. K. Enzyme polymorphism and genetic population structure in Escherichia coli and Shigella. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2715–2726. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Evans D. J., Jr, Sack R. B., Sack D. A., Wadström T. Special Escherichia coli serotypes among enterotoxigenic strains from diarrhoea in adults and children. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1976 Jun 1;162(2):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF02121318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Serology of Escherichia coli fimbriae. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:80–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Mercer A., Kusećek B., Pohl A., Achtman M. Induction of bacteremia in newborn rats by Escherichia coli K1 is correlated with only certain O (lipopolysaccharide) antigen types. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):599–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.599-608.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarff L. D., McCracken G. H., Schiffer M. S., Glode M. P., Robbins J. B., Orskov I., Orskov F. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli K1 in healthy and diseased newborns. Lancet. 1975 May 17;1(7916):1099–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Levin B. R. Genetic diversity and structure in Escherichia coli populations. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6999623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. P., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Schneerson R. Comparative analysis of plasmids and some metabolic characteristics of Escherichia coli K1 from diseased and healthy individuals. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):200–206. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.200-206.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Ochman H., Selander R. K. Geographic components of linkage disequilibrium in natural populations of Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Evol. 1983 Dec;1(1):67–83. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Ochman H., Selander R. K. Multilocus genetic structure in natural populations of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


