Abstract
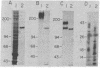
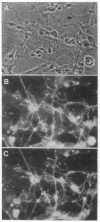
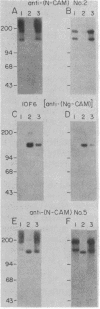
Previous studies in this laboratory have led to the identification of the neural cell adhesion molecule, N-CAM, a homophilic ligand that mediates adhesion between neurons as well as between neurons and striated muscle precursors. By means of a similar immunological approach but with different assays, we have now identified a cell adhesion molecule on neurons (Ng-CAM) that mediates the heterotypic adhesion between neuronal membranes and glial cells. In this paper, we compare certain aspects of the structure and function of Ng-CAM and embryonic N-CAM from the chicken. Ng-CAM was localized by specific antibodies on neurons but not on glia, and double-staining methods showed that individual neurons contained both Ng-CAM and N-CAM. Embryonic Ng-CAM migrates primarily as a single component of Mr 135,000; its apparent Mr shifted to 127,000 after neuraminidase treatment. In contrast, the embryonic form of N-CAM migrates on NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels in the apparent Mr range of 200,000-250,000; after neuraminidase treatment, N-CAM migrates as two components of Mr 170,000 and Mr 140,000. Although both Ng-CAM and N-CAM have calcium-independent binding mechanisms, immunologically based cell adhesion assays suggested that they have different specificities in mediating cell adhesion. Whereas 0.25 micrograms of Ng-CAM partially neutralized the ability of 0.5 mg of polyspecific antineural Fab' fragments to inhibit the heterotypic binding of neuronal membrane vesicles to glial cells and larger amounts of Ng-CAM completely neutralized this inhibition, 20 micrograms of N-CAM had no neutralization activity in this assay. Reciprocally, 0.25 micrograms of N-CAM partially neutralized the ability of 0.5 mg of the same Fab' fragments to inhibit the direct homotypic aggregation of neuronal cells, but 20 micrograms of Ng-CAM had no detectable activity. Although peptide maps of the two cell adhesion molecules differed considerably and despite the differences in binding specificity of these molecules, two independently derived monoclonal antibodies were found to crossreact with both Ng-CAM and N-CAM. Therefore, these different neuronal cell adhesion molecules with distinct binding specificities share at least one antigenic determinant, raising the possibility that they arose from a common evolutionary precursor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brackenbury R., Thiery J. P., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. I. An immunological assay for molecules involved in cell-cell binding. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6835–6840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Hoffman S., Rutishauser U., Hemperly J. J., Edelman G. M. Molecular topography of the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM: surface orientation and location of sialic acid-rich and binding regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3116–3120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules. Science. 1983 Feb 4;219(4584):450–457. doi: 10.1126/science.6823544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Chuong C. M. Embryonic to adult conversion of neural cell adhesion molecules in normal and staggerer mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):7036–7040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.7036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Gallin W. J., Delouvée A., Cunningham B. A., Thiery J. P. Early epochal maps of two different cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin W. J., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Characterization of L-CAM, a major cell adhesion molecule from embryonic liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1038–1042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. Kinetics of homophilic binding by embryonic and adult forms of the neural cell adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5762–5766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Sorkin B. C., White P. C., Brackenbury R., Mailhammer R., Rutishauser U., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Chemical characterization of a neural cell adhesion molecule purified from embryonic brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7720–7729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J Comp Neurol. 1972 May;145(1):61–83. doi: 10.1002/cne.901450105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P., Sidman R. L. Weaver mutant mouse cerebellum: defective neuronal migration secondary to abnormality of Bergmann glia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):240–244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Synaptic specificity in the cerebellar cortex: study of anomalous circuits induced by single gene mutations in mice. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:333–346. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Brackenbury R., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Differences in the carbohydrate structures of neural cell-adhesion molecules from adult and embryonic chicken brains. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11064–11069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. Binding properties of a cell adhesion molecule from neural tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):685–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo C., Changeux J. P. Bergmann fibers and granular cell migration in the cerebellum of homozygous weaver mutant mouse. Brain Res. 1974 Sep 13;77(3):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90636-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Duband J. L., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in early chicken embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6737–6741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S. S., Somjen G. G. Neuron-glia interactions. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1979 Feb;17(1):1–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]