Abstract
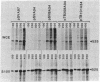
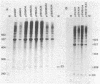
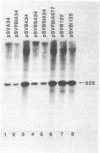
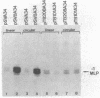
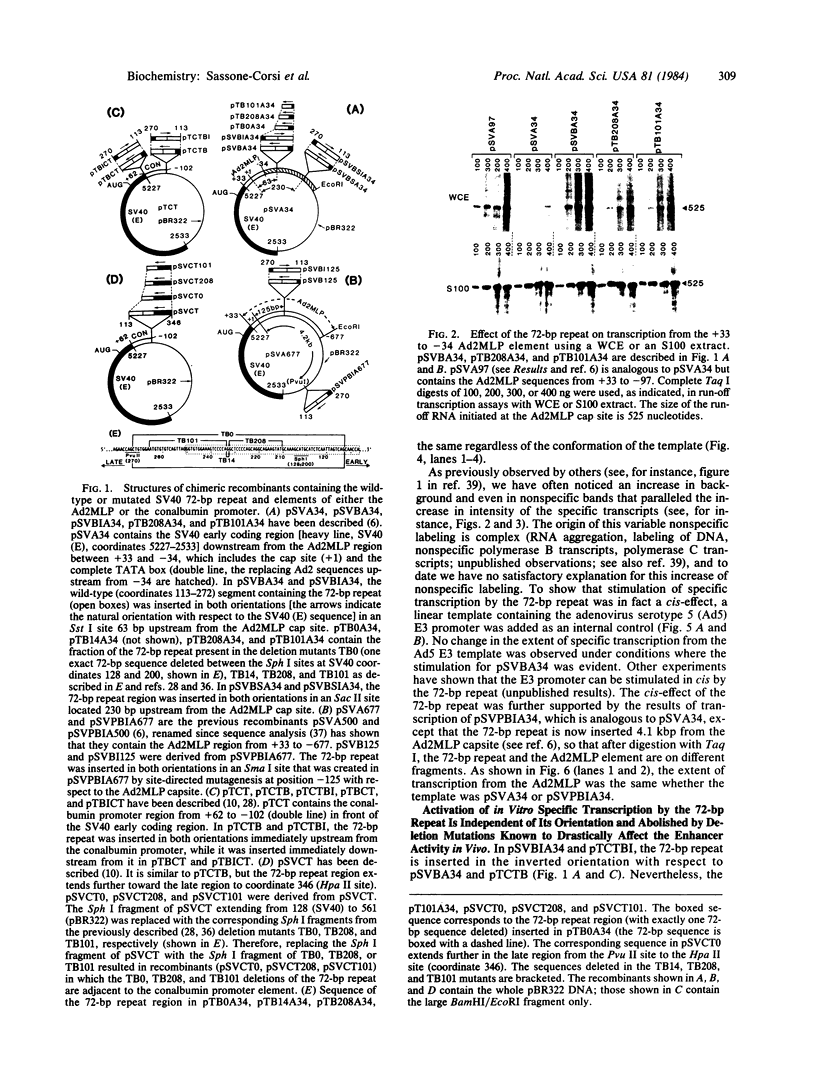
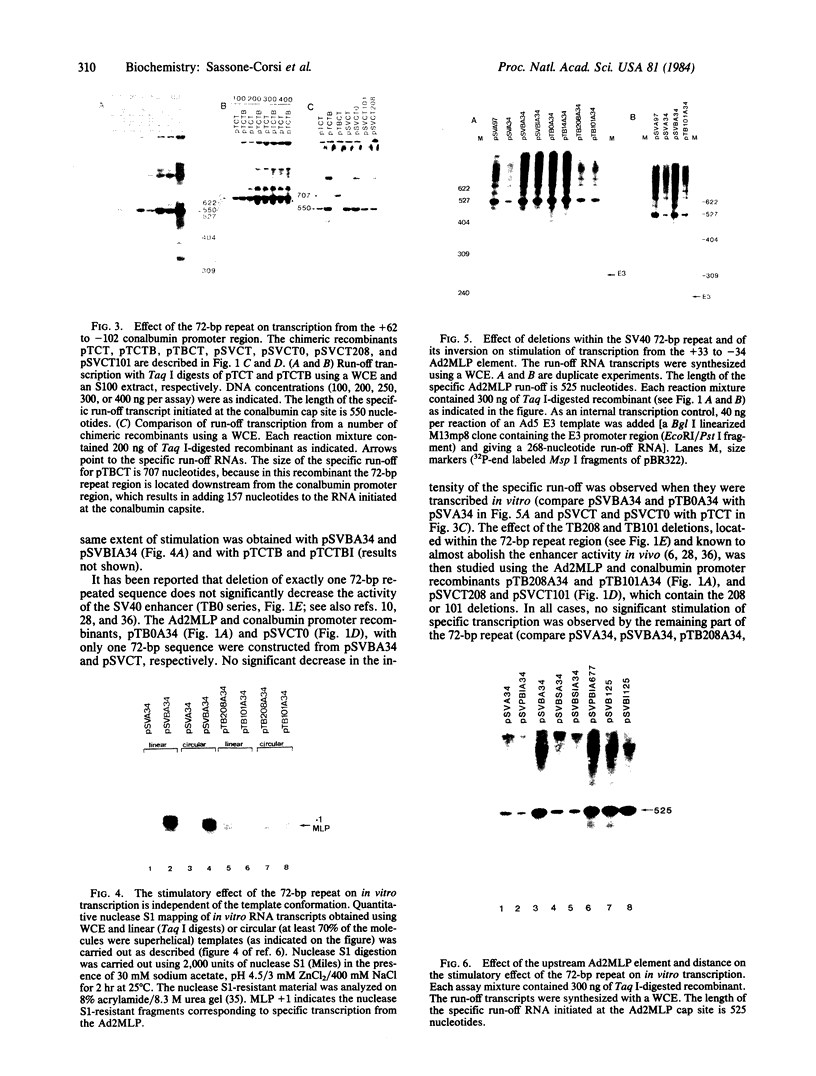
Insertion of the simian virus 40 enhancer upstream from the +33 to -34 adenovirus major late promoter element or the +62 to -102 conalbumin promoter region causes a 10-fold stimulation of specific transcription using a whole cell extract but not an S100 extract. Many of the in vivo effects of the enhancer were mimicked in vitro. This stimulation occurred only in cis, with either orientation of the 72-base-pair repeat, and was markedly decreased by deletions known to diminish the enhancer activity in vivo. However, in vitro, the 72-base-pair repeat did not stimulate at a distance or in the presence of a strong upstream promoter element.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss M. A. Enhancer elements in immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):281–282. doi: 10.1038/303281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Baty D., Chambon P. The repeated GC-rich motifs upstream from the TATA box are important elements of the SV40 early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2447–2464. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Simian virus 40 early- and late-region promoter functions are enhanced by the 72-base-pair repeat inserted at distant locations and inverted orientations. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):991–999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Transcription in vivo from SV40 early promoter deletion mutants without repression by large T antigen. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):127–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingeras T. R., Sciaky D., Gelinas R. E., Bing-Dong J., Yen C. E., Kelly M. M., Bullock P. A., Parsons B. L., O'Neill K. E., Roberts R. J. Nucleotide sequences from the adenovirus-2 genome. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13475–13491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Delimitation of far upstream sequences required for maximal in vitro transcription of an H2A histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notake M., Kurosaki T., Yamamoto T., Handa H., Mishina M., Numa S. Sequence requirement for transcription in vitro of the human corticotropin/beta-lipotropin precursor gene. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;133(3):599–605. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Tjian R. SV40 T antigen binding site mutations that affect autoregulation. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1227–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Promotion of specific in vitro transcription by excised "TATA" box sequences inserted in a foreign nucleotide environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3941–3958. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions: nucleotide sequence requirements for initiation by RNA polymerase II and III. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:25–46. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. Protein contacts for promoter location in eukaryotes. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):755–755. doi: 10.1038/303755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Suzuki Y. Faithful transcription initiation of fibroin gene in a homologous cell-free system reveals an enhancing effect of 5' flanking sequence far upstream. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90371-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Transcription from the SV40 early-early and late-early overlapping promoters in the absence of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1605–1611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M. Enhancing elements for activation of eukaryotic promoters. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):17–18. doi: 10.1038/297017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Olson L., Banerji J., Schaffner W. Analysis of the transcriptional enhancer effect. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):911–919. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]