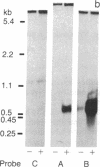
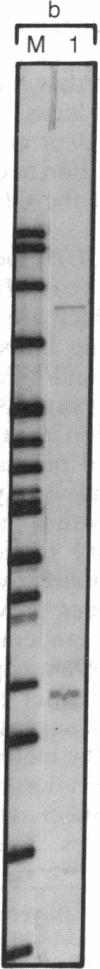
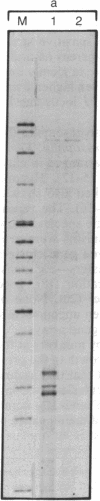
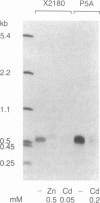
Abstract
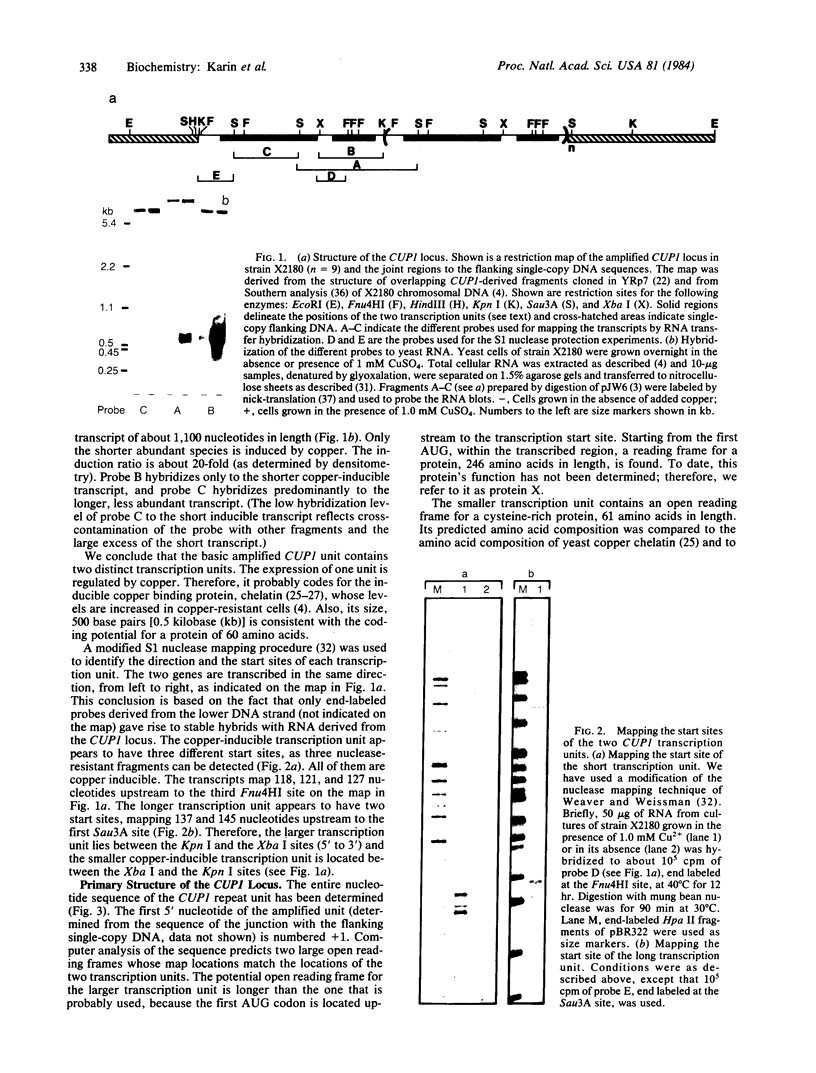
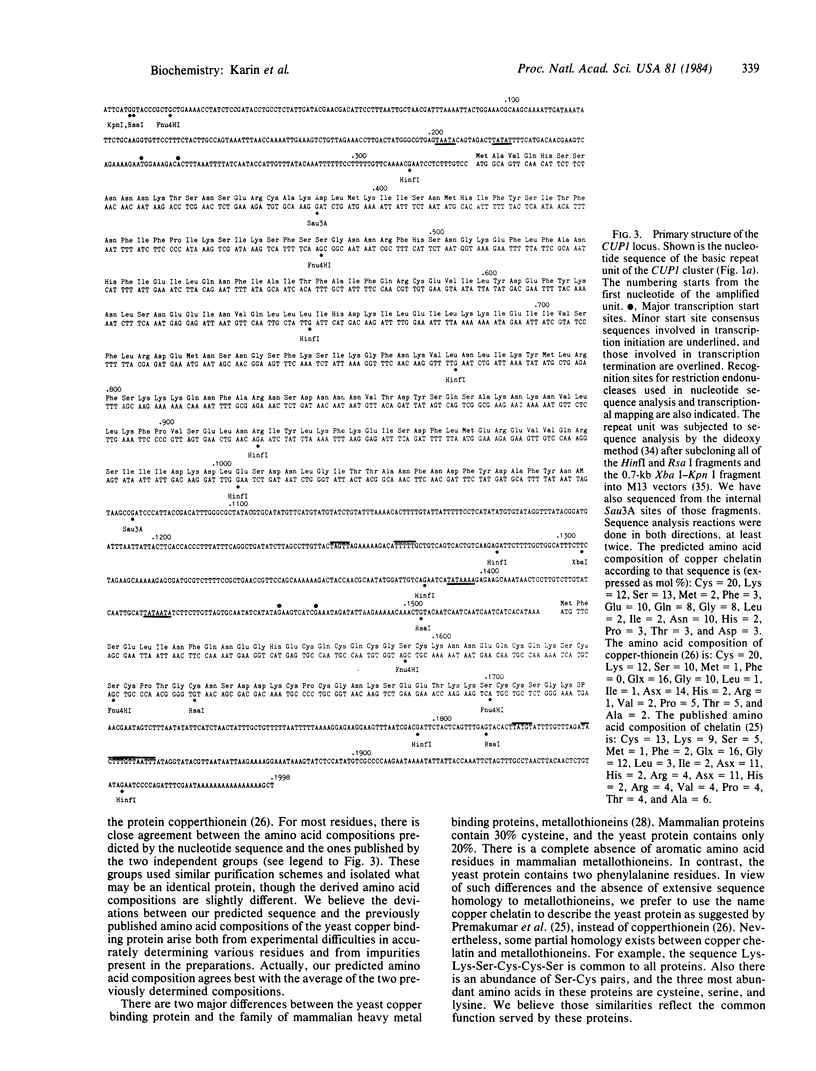
Copper resistance in yeast is controlled by the CUP1 locus. The level of resistance is proportional to the copy number of this locus, which can be found in up to 15 tandemly iterated copies. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms controlling the amplification and expression of the CUP1, locus, we determined its full nucleotide sequence. We have also identified and mapped two transcription units within the basic amplification unit of CUP1 in laboratory yeast strains. One of those transcription units is inducible by copper and encodes a low molecular weight copper binding protein--copper chelatin. The increased production of chelatin, due to both gene amplification and induction of transcription, leads to increased resistance of yeast cells to copper ions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRENES-POMALES A., LINDEGREN G., LINDEGREN C. C. Gene control of coppersensitivity in Saccharomyces. Nature. 1955 Oct 29;176(4487):841–842. doi: 10.1038/176841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach L. R., Palmiter R. D. Amplification of the metallothionein-I gene in cadmium-resistant mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., DeGennaro L. J., Gelfand D. H., Bishop R. J., Valenzuela P., Rutter W. J. Ribosomal RNA genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Physical map of the repeating unit and location of the regions coding for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S, and 25 S ribosomal RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8118–8125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buongiorno-Nardelli M., Amaldi F., Lava-Sanchez P. A. Amplification as a rectification mechanism for the redundant rRNA genes. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 2;238(83):134–137. doi: 10.1038/newbio238134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G. The organization of genetic units in chromosomes. J Cell Sci. 1967 Mar;2(1):1–7. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Brown D. D. Adjacent repeating units of Xenopus laevis 5S DNA can be heterogeneous in length. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):477–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90199-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn R. H., Lowry J. C., Kedes L. H. Histone genes of the sea urchin (S. purpuratus) cloned in E coli: order, polarity, and strandedness of the five histone-coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):147–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer J. H., Farrelly F. W., Barnitz J. T., Rownd R. H. Construction and restriction endonuclease mapping of hybrid plasmids containing Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 16;151(3):229–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00268786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. J., Krieg P., Harvey R. P., Hewish D. A., Wells J. R. Histone genes are clustered with a 15-kilobase repeat in the chicken genome. Nature. 1979 May 10;279(5709):132–136. doi: 10.1038/279132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel S., Welch J. W. Tandem gene amplification mediates copper resistance in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5342–5346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover D. M., Hogness D. S. A novel arrangement of the 18S and 28S sequences in a repeating unit of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne D C, Mortimer R K. Chromosome Mapping in Saccharomyces: Centromere-Linked Genes. Genetics. 1960 Aug;45(8):1085–1110. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.8.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidecker G., Messing J., Gronenborn B. A versatile primer for DNA sequencing in the M13mp2 cloning system. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Cathala G., Nguyen-Huu M. C. Expression and regulation of a human metallothionein gene carried on an autonomously replicating shuttle vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4040–4044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning R. F., Samols D. R., Gage L. P. The genes for 18S, 5.8S and 28S ribosomal RNA of Bombyx mori are organized into tandem repeats of uniform length. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):153–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premakumar R., Winge D. R., Wiley R. D., Rajagopalan K. V. Copper-chelatin: isolation from various eucaryotic sources. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Sep;170(1):278–288. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinz R., Weser U. Cuprodoxin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jun 15;54(2):224–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Buck L. B., Axel R. A structure for amplified DNA. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Gross K., Telford J., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of psammechinus miliaris: II. The arrangement of the five histone-coding and spacer sequences. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D. Unequal mitotic sister chromatid exchange and disproportionate replication as mechanisms regulating ribosomal RNA gene redundancy. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:491–500. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch J. W., Fogel S., Cathala G., Karin M. Industrial yeasts display tandem gene iteration at the CUP1 region. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1353–1361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Brown D. D., Reeder R. H. The molecular basis for length heterogeneity in ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 25;105(4):461–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. The structural organization of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):193–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weser U., Hartmann H. J., Fretzdorff A., Strobel G. J. Homologous copper(I)-(thiolate)2-chromophores in yeast copper thionein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 23;493(2):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Yanofsky C. Yeast gene TRP5: structure, function, regulation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1491–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamb T. J., Petes T. D. Analysis of the junction between ribosomal RNA genes and single-copy chromosomal sequences in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]