Abstract
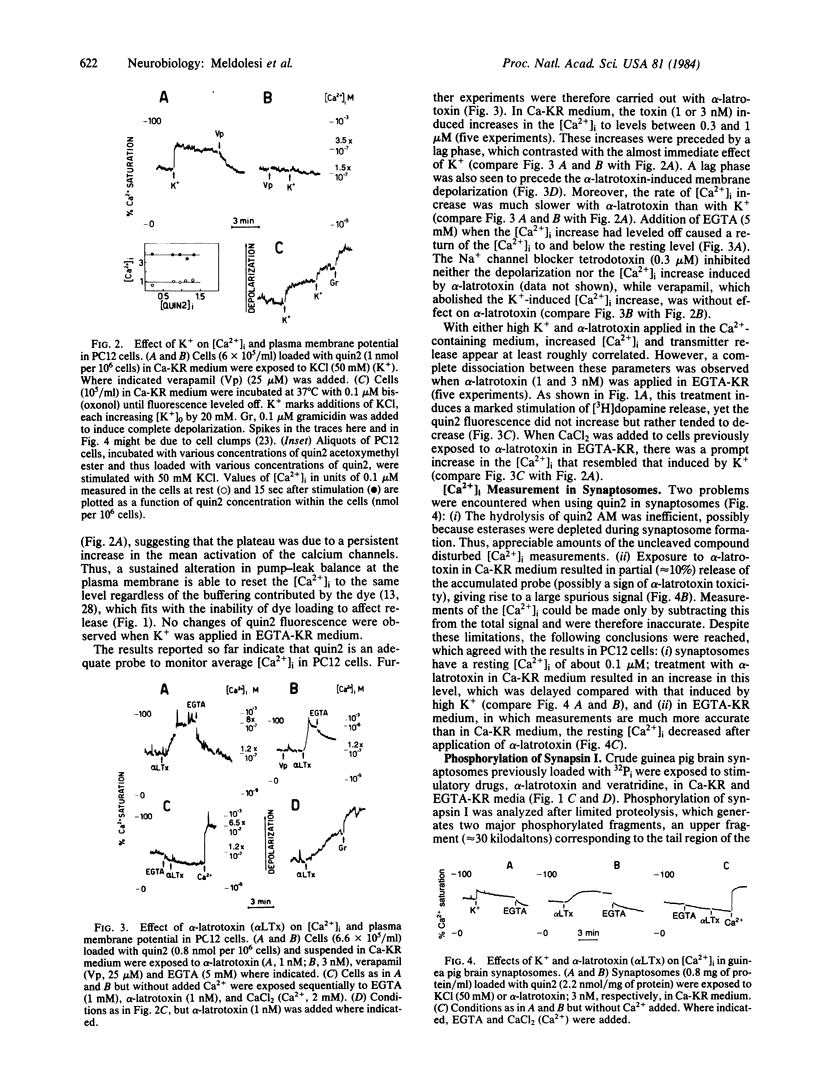
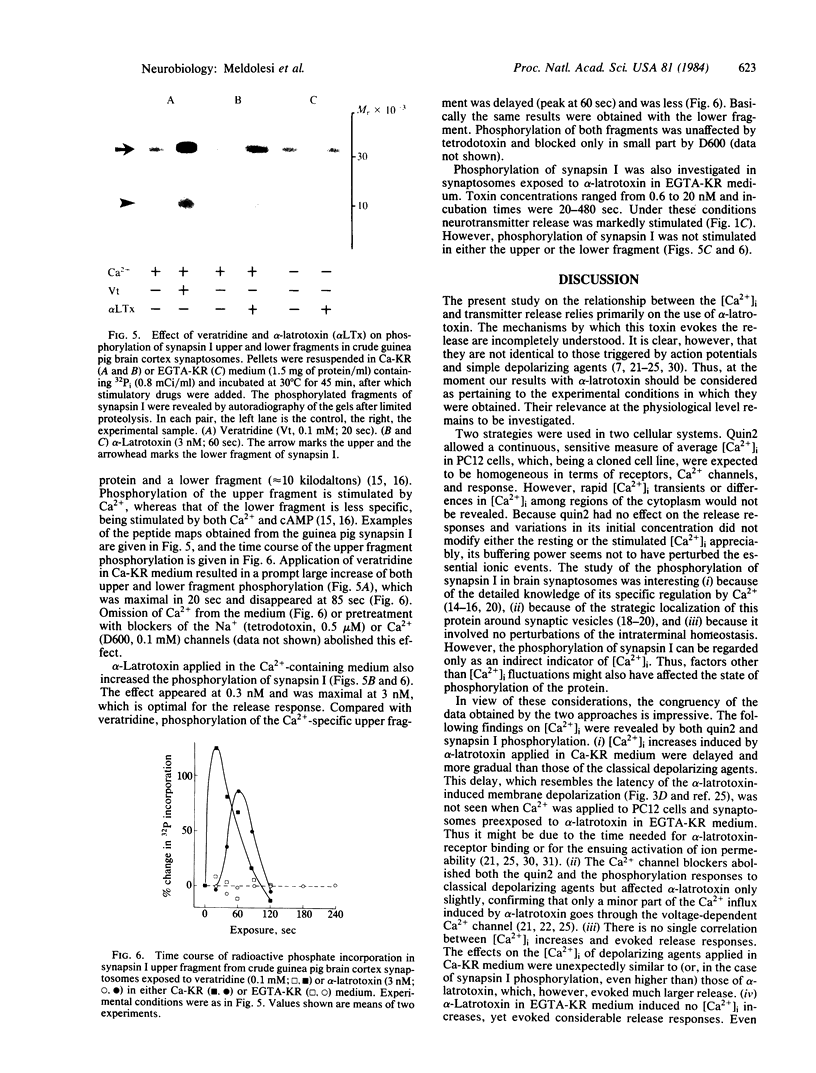
The relationship between the free cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration, [Ca2+]i, and neurotransmitter release was investigated in guinea pig brain synaptosomes and the neurosecretory cell line PC12. Release was induced by alpha-latrotoxin, which acts in both Ca2+ -containing and Ca2+ -free incubation media, or by the classical depolarizing agents high K+ and veratridine, which require extracellular Ca2+. Two complementary approaches were used to reveal changes of [Ca2+]i: (i) direct measurement by a fluorescent Ca2+ indicator (quin2) and (ii) study of the Ca2+ -dependent phosphorylation of a protein, synapsin I, located at the cytoplasmic surface of synaptic vesicles. Depolarizing agents, when applied in Ca2+ -containing medium, induced the [Ca2+]i to increase promptly 3- to 6-fold, drastically increased synapsin I phosphorylation, and caused stimulation of transmitter release. With alpha-latrotoxin, the [Ca2+]i increase was delayed and occurred at a slower rate, the increase of synapsin I phosphorylation was less drastic, and the release response was much more pronounced. In Ca2+ -free medium, depolarizing agents released no transmitter and had no effect on [Ca2+]i or synapsin I phosphorylation, whereas with alpha-latrotoxin these processes were dissociated: considerable stimulation of the release without apparent change of [Ca2+]i and synapsin I phosphorylation. We conclude that the relationship between average [Ca2+]i and transmitter release is not straightforward and, in particular, that the release evoked by alpha-latrotoxin in Ca2+ -free medium is mediated by a factor(s) other than bulk redistribution of Ca2+ from intracellular stores.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustine G. J., Levitan H. Presynaptic effect of Erythrosin B at the frog neuromuscular junction: ion and photon sensitivity. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:65–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba A., Fisherman J. S., Cooper J. R. Action of sulfhydryl reagents on cholinergic mechanisms in synaptosomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jun 15;28(12):1879–1883. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90639-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birks R. I., Cohen M. W. The influence of internal sodium on the behaviour of motor nerve endings. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jul 9;170(1021):401–421. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P. Vesicle hypothesis of the release of quanta of acetylcholine. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):396–441. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Harris S. M., Jr, Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Synapsin I (Protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. II. Its specific association with synaptic vesicles demonstrated by immunocytochemistry in agarose-embedded synaptosomes. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1355–1373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasso A., Alemà S., Rufini S., Senni M. I. Black widow spider toxin-induced calcium fluxes and transmitter release in a neurosecretory cell line. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):774–776. doi: 10.1038/283774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., DeGennaro L. J., Greengard P. Differential phosphorylation of multiple sites in purified protein I by cyclic AMP-dependent and calcium-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1482–1488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Multiple phosphorylation sites in protein I and their differential regulation by cyclic AMP and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Spontaneous and evoked activity of motor nerve endings in calcium Ringer. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):689–706. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. Calcium-dependence of catecholamine release from bovine adrenal medullary cells after exposure to intense electric fields. J Membr Biol. 1982;68(2):107–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01872259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Kesteven N. T. Evoked transient intracellular free Ca2+ changes and secretion in isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 May 23;218(1211):177–199. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarization-induced phosphorylation of specific proteins, mediated by calcium ion influx, in rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2764–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J. Studies on alpha-latrotoxin receptors in rat brain synaptosomes: correlation between toxin binding and stimulation of transmitter release. J Neurochem. 1982 Jun;38(6):1559–1569. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb06633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Calcium transients recorded with arsenazo III in the presynaptic terminal of the squid giant synapse. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 May 22;212(1187):197–211. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Rugolo M., Scott I. G., Meldolesi J. alpha-latrotoxin of black widow spider venom depolarizes the plasma membrane, induces massive calcium influx, and stimulates transmitter release in guinea pig brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7924–7928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Arslan P., Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J. Anti-immunoglobulin, cytoplasmic free calcium, and capping in B lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):335–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Lew D. P., Wollheim C. B., Tsien R. Y. Is cytosolic ionized calcium regulating neutrophil activation? Science. 1983 Sep 30;221(4618):1413–1415. doi: 10.1126/science.6310757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quastel D. M., Hackett J. T., Cooke J. D. Calcium: is it required for transmitter secretion? Science. 1971 Jun 4;172(3987):1034–1036. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3987.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L. F., Kelly R. B. A molecular description of nerve terminal function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:871–926. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. T-cell mitogens cause early changes in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ and membrane potential in lymphocytes. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):68–71. doi: 10.1038/295068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng M. C., Siekevitz P. The binding interaction between alpha-latrotoxin from black widow spider venom and a dog cerebral cortex synaptosomal membrane preparation. J Neurochem. 1979 Jul;33(1):263–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P., Berzins K., Cohen R. S., Blomberg F., Grab D. J., Siekevitz P. Subcellular distribution in cerebral cortex of two proteins phosphorylated by a cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):308–319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade P. D., Fritz L. C., Siekevitz P. The effect of diamide on transmitter release and on synaptic vesicle population at vertebrate synapses. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 30;225(2):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90842-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe O., Meldolesi J. The effects of alpha-latrotoxin of black widow spider venom on synaptosome ultrastructure. A morphometric analysis correlating its effects on transmitter release. J Neurocytol. 1983 Jun;12(3):517–531. doi: 10.1007/BF01159388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



