Abstract
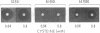
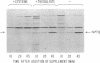
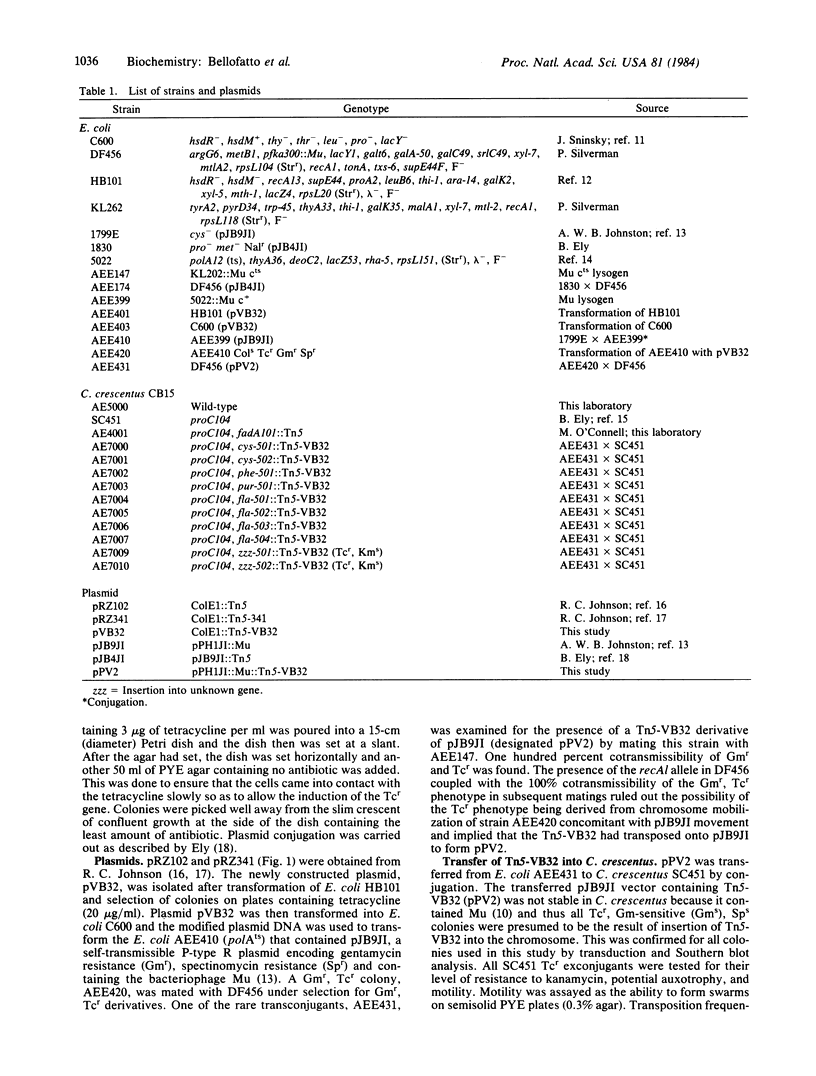
A promoter probe, Tn5-VB32, was constructed and placed in a P group R plasmid containing bacteriophage Mu sequences, allowing transfer of the transposon to bacteria such as Caulobacter, Rhizobium, and Agrobacterium without retention of the plasmid. The probe carries an altered Tn5 transposon that allows detection of chromosomal promoter regions by virtue of acquired kanamycin resistance. A fragment of DNA containing the neomycin phosphotransferase II (NPT II) gene from Tn5, lacking its promoter region but retaining its translation initiation signal, was inserted into a Tn5 derivative that lacked the entire NPT II gene and a large portion of the IS50L sequence while retaining its ability to transpose. This Tn5 derivative also contained the intact tetracycline resistance-encoding region of the transposon Tn10. Transposition of the Tn5-VB32 promoter probe into the Caulobacter crescentus chromosome generated auxotrophic and motility mutants and Southern blot analysis of DNA from these mutants showed Tn5-VB32 sequences in random-sized chromosomal restriction fragments. Transcriptional regulation by exogenous cysteine of NPT II gene expression was demonstrated in a cysteine auxotroph generated by Tn5-VB32 insertional inactivation. NPT II synthesis, measured by agar plate assays of kanamycin resistance and by immunoprecipitation of the NPT II protein, was repressed in the presence of cysteine and derepressed in its absence. Several fla- mutants were also isolated by Tn5-VB32 mutagenesis and shown to confer kanamycin resistance. Insertions within temporally regulated genes, such as those involved in flagellar biosynthesis and chemotaxis functions, can now be used directly to monitor transcriptional regulation from Caulobacter promoter sequences.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agabian N., Evinger M., Parker G. Generation of asymmetry during development. Segregation of type-specific proteins in Caulobacter. J Cell Biol. 1979 Apr;81(1):123–136. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerswald E. A., Ludwig G., Schaller H. Structural analysis of Tn5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):107–113. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. T., Croft R. H., Ferber D. M., Gerardot C. J., Schoenlein P. V., Ely B. Genetic mapping with Tn5-derived auxotrophs of Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):888–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.888-898.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand K. P., Postle K., Wray L. V., Jr, Reznikoff W. S. Overlapping divergent promoters control expression of Tn10 tetracycline resistance. Gene. 1983 Aug;23(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M., Clerget M., Galas D. J. The transposition frequency of IS1-flanked transposons is a function of their size. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 15;154(2):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras I., Shapiro L., Henry S. Membrane phospholipid composition of Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1130–1136. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1130-1136.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Croft R. H. Transposon mutagenesis in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):620–625. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.620-625.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B. Transfer of drug resistance factors to the dimorphic bacterium Caulobacter crescentus. Genetics. 1979 Mar;91(3):371–380. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. R., Agabian N. The nucleotide sequence of the Mr = 28,500 flagellin gene of Caulobacter crescentus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7395–7401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Reznikoff W. S. DNA sequences at the ends of transposon Tn5 required for transposition. Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):280–282. doi: 10.1038/304280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Chan R. K., Tye B. K., Botstein D. Mutagenesis by insertion of a drug-resistance element carrying an inverted repetition. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):561–575. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y. Fusions of flagellar operons to lactose genes on a mu lac bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):16–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.16-26.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M. Mutations in the temperate phage P22 and lysogeny in Salmonella. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):22–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhausen M., Agabian N. Caulobacter flagellin mRNA segregates asymmetrically at cell division. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):630–632. doi: 10.1038/302630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhausen M., Gill P. R., Parker G., Agabian N. Cloning of developmentally regulated flagellin genes from Caulobacter crescentus via immunoprecipitation of polyribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6847–6851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Kinross J. Conditional lethality of recA and recB derivatives of a strain of Escherichia coli K-12 with a temperature-sensitive deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase I. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):971–978. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.971-978.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A. Role of transcription in the temporal control of development in Caulobacter crescentus (stalk-rifampin-RNA synthesis-DNA synthesis-motility). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Chen L. S., Newton A. Isolation and expression of cloned hook protein gene from Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4863–4867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purucker M., Bryan R., Amemiya K., Ely B., Shapiro L. Isolation of a Caulobacter gene cluster specifying flagellum production by using nonmotile Tn5 insertion mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6797–6801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L., Mansour J., Shaw P., Henry S. Synthesis of specific membrane proteins is a function of DNA replication an phospholipid synthesis in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 5;159(2):303–322. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Gomes S. L., Sweeney K., Ely B., Shapiro L. Methylation involved in chemotaxis is regulated during Caulobacter differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5261–5265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]