Abstract
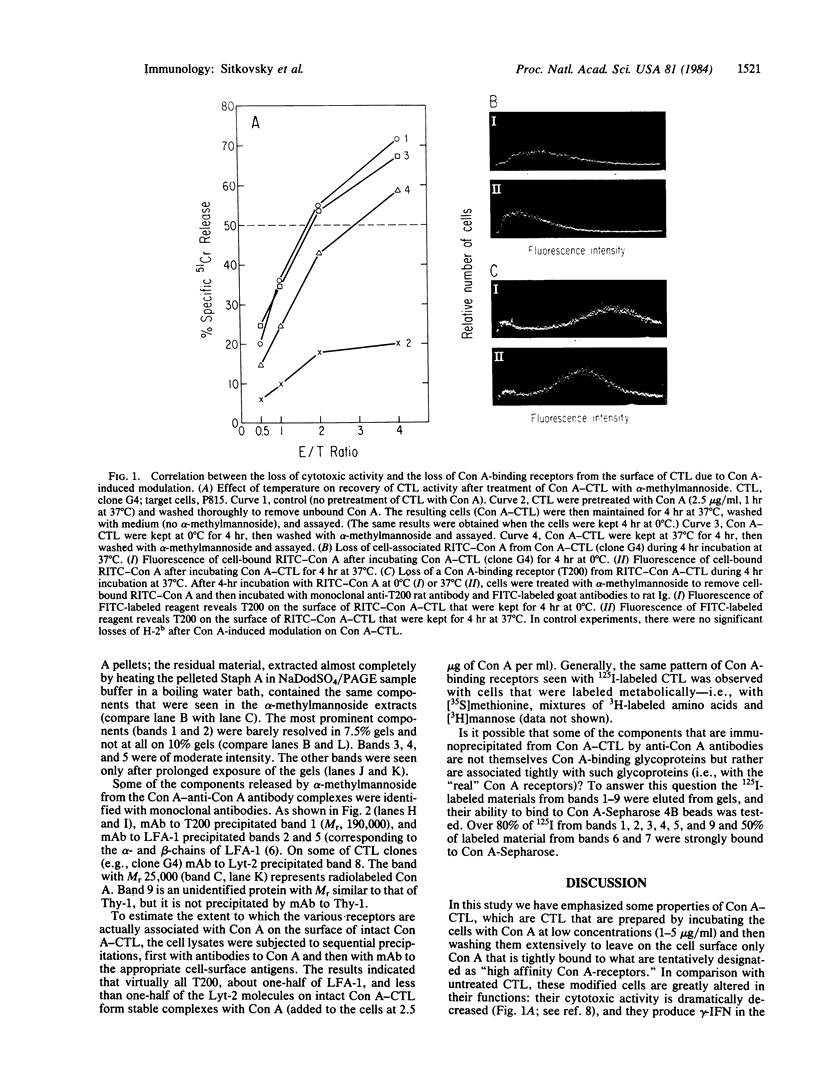
A small set of concanavalin A (Con A)-binding glycoproteins was isolated from the surface membrane of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and partly identified using monoclonal antibodies. The binding of Con A by these glycoproteins on the CTL surface results in the secretion of gamma-interferon and in blocking the effector functions of the cells-namely, antigen-specific and lectin-dependent cytotoxicity. The Con A is evidently bound tightly to some surface structures ("Con A-receptors") that are required for the activation and cytotoxic activity of CTL. To isolate and identify these receptors, antibodies to Con A were used. After Con A was allowed to bind to radiolabeled cloned CTL (labeled with 125I or [35S]methionine or 3H-labeled amino acids), the cells were washed thoroughly, lysed in detergents and anti-Con A antibodies were added to bind to the Con A-receptor complexes. The resulting aggregates were adsorbed with protein A-bearing Staphylococci and the receptors were then specifically released from the pelleted bacteria by alpha-methyl-D-mannoside and analyzed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions. Eight to nine labeled components were seen by autoradiography and with the aid of monoclonal antibodies to known T-cell surface molecules, four were identified as T200, lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA)-1, alpha- and beta-chains, and (on some clones) Lyt-2. Other components with Mr congruent to 160,000, 120,000, 46,000, 42,000, and 23,000 have not been identified. The procedures described here may have general application in the studies of the functional properties of other cell surface molecules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan M. J. The major histocompatibility complex determines susceptibility to cytotoxic T cells directed against minor histocompatibility antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1349–1364. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G. Reversible induction of natural killer cell activity in cloned murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):155–158. doi: 10.1038/305155a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis E., Chang T. W., Eisen H. N. Cyclical changes in susceptibility of a myeloma tumor (LPC-1) to immune destruction. III. Periodic production of a cell surface glycoprotein and changes in reactivity with cytotoxic T cells and anti-H-2d sera. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2245–2250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon D., Martz E., Reynolds T., Kürzinger K., Springer T. A. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1): a surface antigen distinct from Lyt-2,3 that participates in T lymphocyte-mediated killing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4535–4539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon D., Martz E., Reynolds T., Kürzinger K., Springer T. A. Monoclonal antibody to a novel lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1): mechanism of blockade of T lymphocyte-mediated killing and effects on other T and B lymphocyte functions. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):590–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely J. M., Fitch F. W. Alloreactive cloned T cell lines. VII. Comparison of the kinetics of IL 2 release stimulated by alloantigen or Con A. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1274–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. Alloreactive cloned T cell lines. I. Interactions between cloned amplifier and cytolytic T cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):876–895. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwell L., Skidmore B., Marrack P., Kappler J. Concanavalin A-inducible, interleukin-2-producing T cell hybridoma. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):893–904. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Fisher R. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte surface receptors for Con A and PHA. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):710–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T., Bevan M. J. Specificity of T-cell cones illustrates altered self hypothesis. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):460–462. doi: 10.1038/294460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. R., Raulet D. H., Pasternack M. S., Bevan M. J. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes produce immune interferon in response to antigen or mitogen. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1198–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Clonotypic structures involved in antigen-specific human T cell function. Relationship to the T3 molecular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):705–719. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama E., Shiku H., Stockert E., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cytotoxic T cells: Lyt phenotype and blocking of killing activity by Lyt antisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Sitkovsky M. V., Eisen H. N. The site of action of N-alpha-tosyl-L-lysyl-chloromethyl-ketone (TLCK) on cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2477–2483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. IgG or IgM monoclonal antibodies reactive with different determinants on the molecular complex bearing Lyt 2 antigen block T cell-mediated cytolysis in the absence of complement. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2665–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman W. E., Talal N., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A., Ledbetter J. A. Surface antigens on mouse natural killer cells: use of monoclonal antibodies to inhibit or to enrich cytotoxic activity. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):982–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity to trinitrophenyl-modified syngeneic lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Aug;4(8):527–533. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara N., Sachs D. H. Mouse alloantibodies capable of blocking cytotoxic T-cell function. I. Relationship between the antigen reactive with blocking antibodies and the Lyt-2 locus. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):432–444. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitkovsky M. V., Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. Inhibition of cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity by concanavalin A. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1372–1376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S. Interspecies spleen-myeloma hybrid producing monoclonal antibodies against mouse lymphocyte surface glycoprotein, T200. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):313–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):701–702. doi: 10.1038/248701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]