Abstract
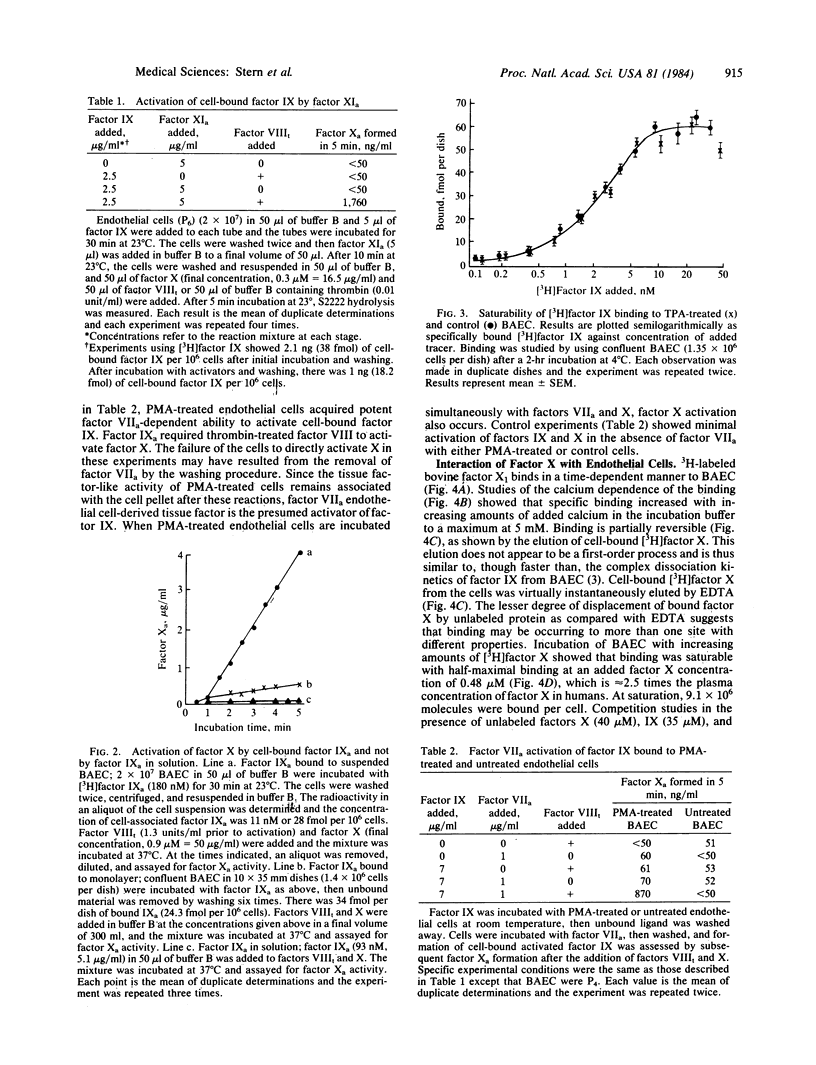
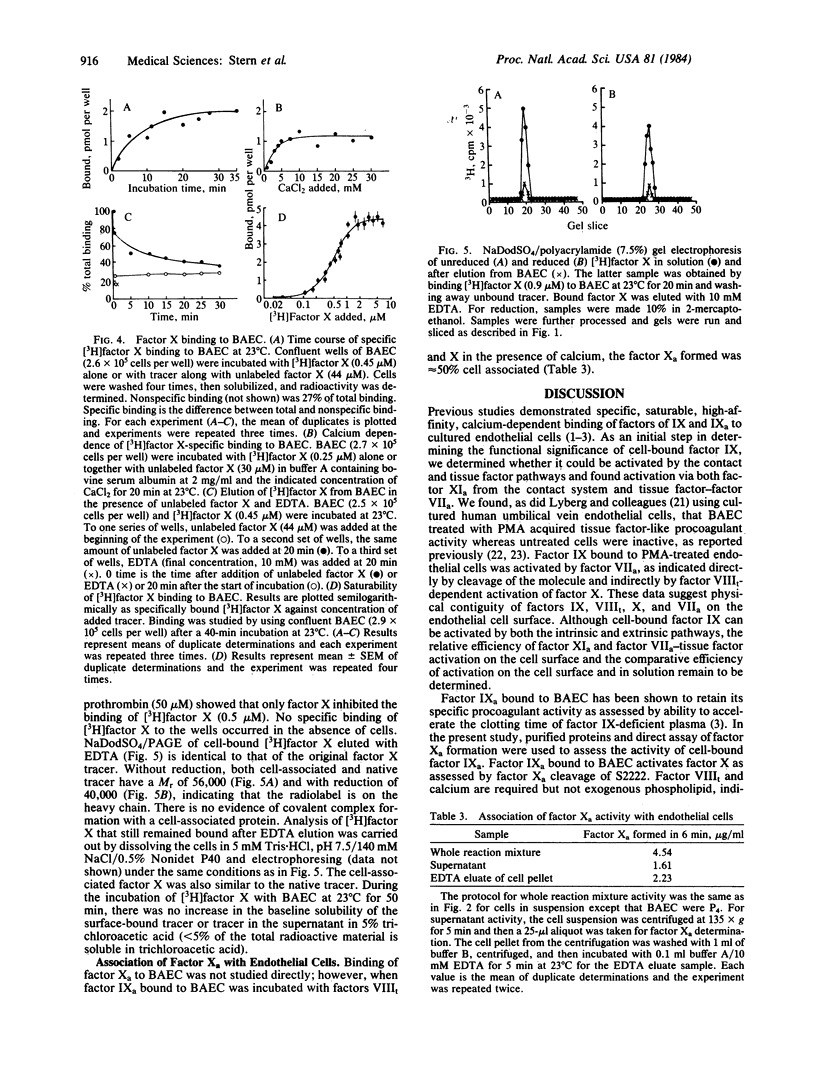
Previous studies have shown that factor IX and its activated form, factor IXa, bind to cultured vascular endothelial cells and that cell-bound factor IXa retains its procoagulant activity. The present studies provide evidence that factor IX bound to cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells can be activated. Factor IX activation was assessed by finding cleavage of the factor IX molecule on NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and by the generation of procoagulant activity as assessed by thrombin-treated factor VIII-dependent generation of factor Xa activity. Cell-bound factor IX (0.8 micrograms per 4 X 10(8) cells per ml) could be activated by factor XIa (5 micrograms/ml) or by factor VIIa (0.1 micrograms/ml) without exogenous tissue factor when endothelial cells were treated with phorbol ester and acquired tissue factor-like procoagulant activity. Regardless of how factor IX was activated, the cell-bound factor IXa required thrombin-treated factor VIII and calcium, but not exogenous phospholipid, to activate factor X. In further experiments, factor X bound to endothelial cells specifically and reversibly with a dependence on calcium and with a lower affinity (half-maximal at 480 nM) than factor IX. At saturation, 9.1 X 10(6) factor X molecules were bound per cell. After activation of factor X by factor IXa, approximately 50% of the factor Xa formed could be eluted from the cells by 10 mM EDTA, suggesting that the factor Xa was cell associated. These observations indicate that endothelial cells can bind and promote the activation of factors IX and X in the absence of platelets or exogenous phospholipid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aurell L., Friberger P., Karlsson G., Claeson G. A new sensitive and highly specific chromogenic peptide substrate for factor Xa. Thromb Res. 1977 Nov;11(5):595–609. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach R., Nemerson Y., Konigsberg W. Purification and characterization of bovine tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8324–8331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K. Basic mechanisms in blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:799–829. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J., Stackrow A. B. Human thrombins. Production, evaluation, and properties of alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3587–3598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. Bovine factor X 1 (Stuart factor). Mechanism of activation by protein from Russell's viper venom. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4892–4899. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. Bovine factors X 1 and X 2 (Stuart factor). Isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4882–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Thompson A. R., Legaz M. E., Meyer R. G., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor). Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4938–4945. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Schwartz S. M. Binding of coagulation factors IX and X to the endothelial cell surface. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):723–731. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90365-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor VII. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 4;14(22):4928–4934. doi: 10.1021/bi00693a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W. Activation of bovine factor VII (proconvertin) by factor XIIa (activated Hageman factor). Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4189–4194. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Hermodson M. A., Davie E. W. Factor X activating enzyme from Russell's viper venom: isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4901–4906. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist P. A., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W. Activation of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor) by factor XIa (activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent) and a protease from Russell's viper venom. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1902–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyberg T., Galdal K. S., Evensen S. A., Prydz H. Cellular cooperation in endothelial cell thromboplastin synthesis. Br J Haematol. 1983 Jan;53(1):85–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb01989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard J. R., Dreyer B. E., Stemerman M. B., Pitlick F. A. Tissue-factor coagulant activity of cultured human endothelial and smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts. Blood. 1977 Sep;50(3):387–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Clyne L. P. An assay for coagulation factor VII using factor VII-depleted bovine plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Feb;83(2):301–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J., Johnson A. J., Karpatkin M. H., Puszkin S. Methods for the production of clinically effective intermediate- and high-purity factor-VIII concentrates. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jul;21(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg S. A., Nemerson Y., Zur M. Kinetics of the activation of bovine coagulation factor X by components of the extrinsic pathway. Kinetic behavior of two-chain factor VII in the presence and absence of tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Drillings M., Nossel H. L., Hurlet-Jensen A., LaGamma K. S., Owen J. Binding of factors IX and IXa to cultured vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4119–4123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dieijen G., Tans G., Rosing J., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipid and factor VIIIa in the activation of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3433–3442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


