Abstract
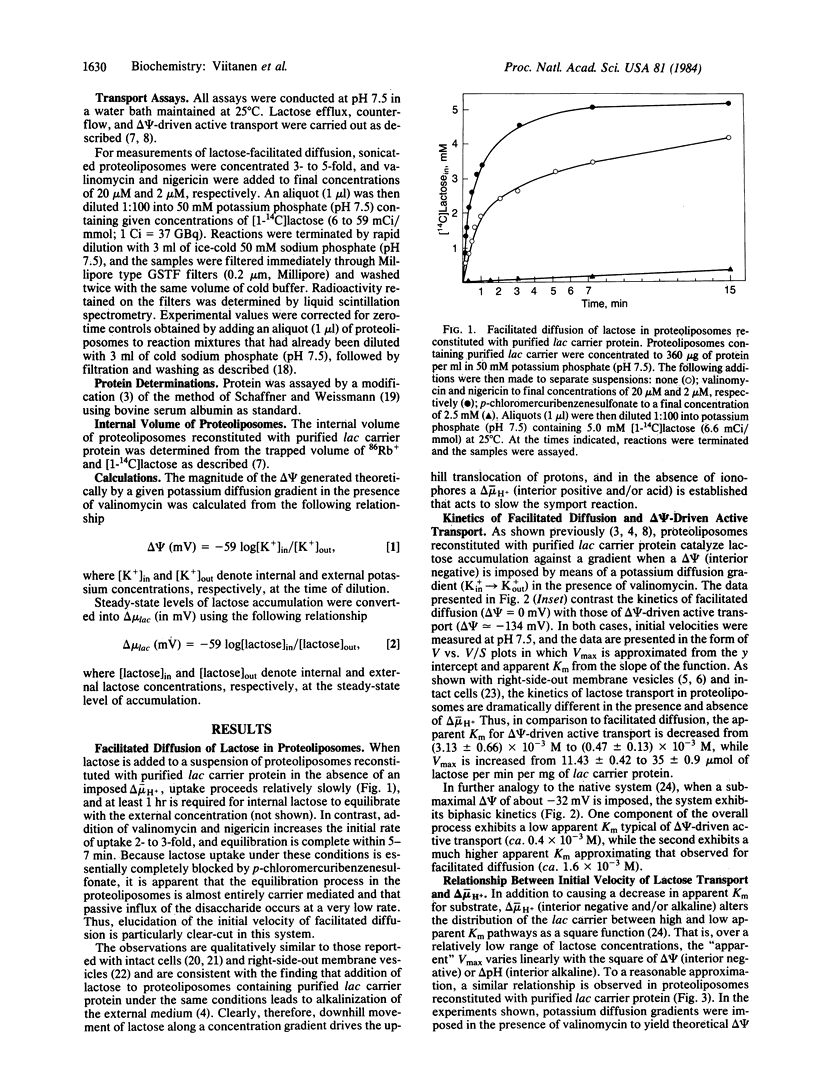
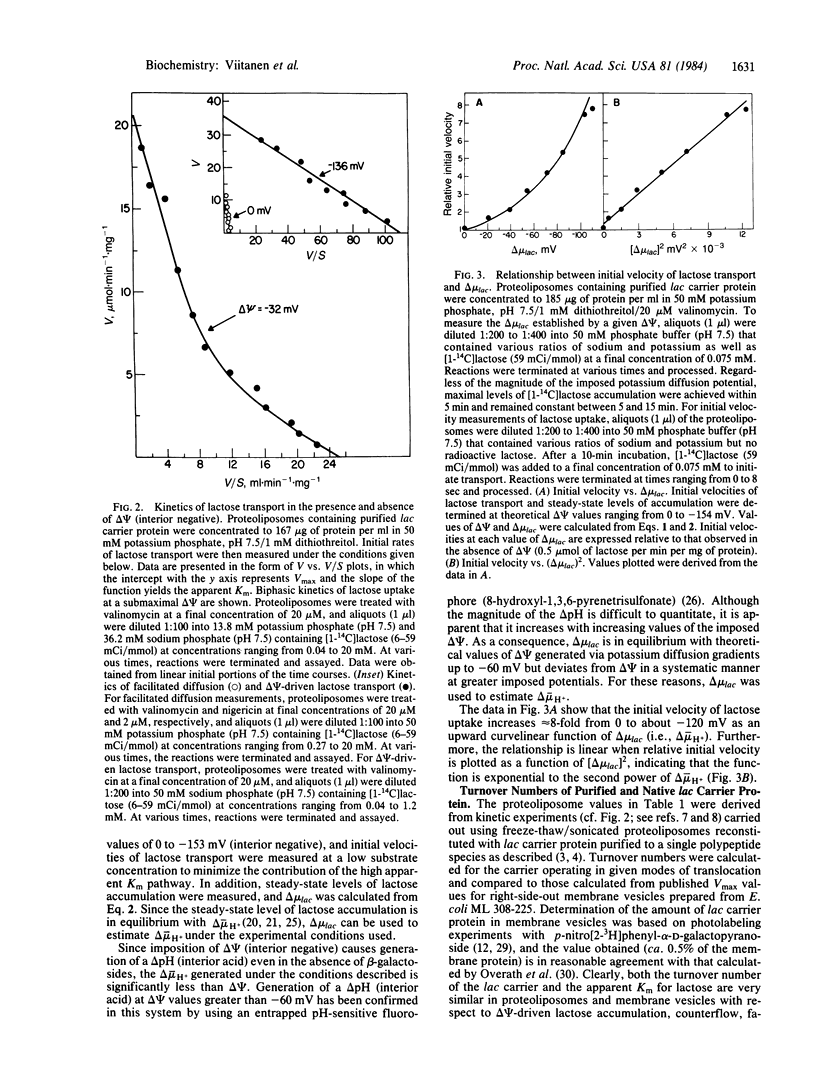
Proteoliposomes reconstituted with lac carrier protein purified from the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli catalyze each of the translocation reactions typical of the beta-galactoside transport system (i.e., active transport, counterflow, facilitated influx and efflux) with turnover numbers and apparent Km values comparable to those observed in right-side-out membrane vesicles. Furthermore, detailed kinetic studies show that the reconstituted system exhibits properties analogous to those observed in membrane vesicles. Imposition of a membrane potential (delta psi, interior negative) causes a marked decrease in apparent Km (by a factor of 7 to 10) with a smaller increase in Vmax (approximately equal to 3-fold). At submaximal values of delta psi, the reconstituted carrier exhibits biphasic kinetics, with one component manifesting the kinetic parameters of active transport and the other exhibiting the characteristics of facilitated diffusion. Finally, at low lactose concentrations, the initial velocity of influx varies linearly with the square of the proton electro-chemical gradient. The results provide quantitative support for the contention that a single polypeptide species, the product of the lac y gene, is responsible for each of the transport reactions typical of the beta-galactoside transport system.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth I. R., Mitchell W. J., Hamilton W. A. Quantitative analysis of proton-linked transport systems. The lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):687–696. doi: 10.1042/bj1820687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchel D. E., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B. Sequence of the lactose permease gene. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):541–545. doi: 10.1038/283541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Tahara S. M., Patel L., Goldkorn T., Kaback H. R. Preparation, characterization, and properties of monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6894–6898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement N. R., Gould J. M. Pyranine (8-hydroxy-1,3,6-pyrenetrisulfonate) as a probe of internal aqueous hydrogen ion concentration in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1534–1538. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Boublik M., Kaback H. R. Structure of the lac carrier protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Garcia M. L., Newman M. J., Patel L., Kaback H. R. Lactose-proton symport by purified lac carrier protein. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5634–5638. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. L., Patel L., Padan E., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles: evidence for the involvement of histidine residue(s) in the response of the lac carrier to the proton electrochemical gradient. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5800–5805. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. L., Viitanen P., Foster D. L., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose translocation in proteoliposomes reconstituted with lac carrier protein purified from Escherichia coli. 1. Effect of pH and imposed membrane potential on efflux, exchange, and counterflow. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2524–2531. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazi A., Shechter E. Lactose transport in Escherichia coli cells. Dependence of kinetic parameters on the transmembrane electrical potential difference. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 22;644(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldkorn T., Rimon G., Kaback H. R. Topology of the lac carrier protein in the membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3322–3326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldkorn T., Rimon G., Kempner E. S., Kaback H. R. Functional molecular weight of the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli as studied by radiation inactivation analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1021–1025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge R., Boos W. Maltose and lactose transport in Escherichia coli. Examples of two different types of concentrative transport systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):443–478. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S. An ecf mutation in Escherichia coli pleiotropically affecting energy coupling in active transport but not generation or maintenance of membrane potential. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8582–8588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. The lac carrier protein in Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1983;76(2):95–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02000610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:698–709. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose translocation in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. 1. Effect of pH on efflux, exchange, and counterflow. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3691–3697. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., LeBlanc G., Kaback H. R. Specific labeling of the lac carrier protein in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli by a photoaffinity reagent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6319–6323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Robertson D. E., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose translocation in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. 2. Effect of imposed delata psi, delta pH, and Delta mu H+. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3697–3704. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita K., Patel L., Gennis R. B., Kaback H. R. Reconstitution of active transport in proteoliposomes containing cytochrome o oxidase and lac carrier protein purified from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4889–4893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. J., Foster D. L., Wilson T. H., Kaback H. R. Purification and reconstitution of functional lactose carrier from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11804–11808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Teather R. M., Simoni R. D., Aichele G., Wilhelm U. Lactose carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Transport and binding of 2'-(N-dansyl)aminoethyl beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside and p-nitrophenyl alpha-d-galactopyranoside. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):1–11. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Patel L., Kaback H. R. Effect of diethylpyrocarbonate on lactose/proton symport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6221–6225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Garcia M. L., Kaback H. R. Direct measurement of lactose/proton symport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles: further evidence for the involvement of histidine residue(s). Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5805–5810. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate C. A., Suit J. L. The eup genetic locus of Escherichia coli and its role in H+/solute symport. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12974–12980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The relationship between the electrochemical proton gradient and active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):854–859. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. E., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L., Kaback H. R. Active transport in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli: the electrochemical proton gradient alters the distribution of the lac carrier between two different kinetic states. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5692–5702. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M., Bramhall J., Riede I., Wright J. K., Fürst M., Aichele G., Wilhelm U., Overath P. Lactose carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Structure and expression of plasmids carrying the Y gene of the lac operon. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):223–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viitanen P., Garcia M. L., Foster D. L., Kaczorowski G. J., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose translocation in proteoliposomes reconstituted with lac carrier protein purified from Escherichia coli. 2. Deuterium solvent isotope effects. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2531–2536. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarejo M. Evidence for two lac Y gene derived protein products in the E. coli membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):16–23. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80239-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarejo M., Ping C. Localization of the lactose permease protein(s) in the E. coli envelope. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 14;82(3):935–942. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. K., Schwarz H., Straub E., Overath P., Bieseler B., Beyreuther K. Lactose carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Reconstitution of galactoside binding and countertransport. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jun;124(3):545–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells and its relation to active transport of lactose. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):669–673. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


